Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Potential Energy Surface PES
Hochgeladen von
Fadjar Mulya0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
13 Ansichten1 Seitepotential energy surface definition
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenpotential energy surface definition
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
13 Ansichten1 SeitePotential Energy Surface PES
Hochgeladen von
Fadjar Mulyapotential energy surface definition
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
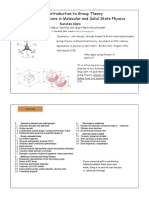
Potential energy surface
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A potential energy surface (PES) describes the energy of a system, especially a collection of
atoms, in terms of certain parameters, normally the positions of the atoms. The surface might define
the energy as a function of one or more coordinates; if there is only one coordinate, the surface is
called a potential energy curve or energy profile. An example is the Morse potential.
It is helpful to use the analogy of a landscape: for a system with two degrees of freedom (e.g. two
bond lengths), the value of the energy (analogy: the height of the land) is a function of two bond
lengths (analogy: the coordinates of the position on the ground).[1]
PES for water molecule: Shows the energy minimum corresponding to optimized molecular structure for water-
O-H bond length of 0.0958nm and H-O-H bond angle of 104.5
The PES concept finds application in fields such as chemistry and physics, especially in the
theoretical sub-branches of these subjects. It can be used to theoretically explore properties of
structures composed of atoms, for example, finding the minimum energy shape of a molecule or
computing the rates of a chemical reaction.
Read more : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Potential_energy_surface
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Tetrachloroaluminate Ion On Graphene Quantum Dots: Towards The Design of Cathode For Aluminum-Ion BatteryDokument10 SeitenTetrachloroaluminate Ion On Graphene Quantum Dots: Towards The Design of Cathode For Aluminum-Ion BatteryFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Size-Dependent Bandgap Modulation of Zno Nanowires by Tensile StrainDokument5 SeitenSize-Dependent Bandgap Modulation of Zno Nanowires by Tensile StrainFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physica E: Low-Dimensional Systems and Nanostructures: SciencedirectDokument7 SeitenPhysica E: Low-Dimensional Systems and Nanostructures: SciencedirectFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Surface Science: Full Length ArticleDokument8 SeitenApplied Surface Science: Full Length ArticleFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Si Si Bond Morethan3angstromDokument17 SeitenSi Si Bond Morethan3angstromFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Niaz 2016Dokument11 SeitenNiaz 2016Fadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- From Periodic DFT Calculations To Classical Molecular Dynamics SimulationsDokument4 SeitenFrom Periodic DFT Calculations To Classical Molecular Dynamics SimulationsFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of SN Nanowire Encapsulated Carbon Nanotube For Li-Ion Battery Anode by DFT CalculationsDokument3 SeitenEvaluation of SN Nanowire Encapsulated Carbon Nanotube For Li-Ion Battery Anode by DFT CalculationsFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supawadee Namuangruk: EducationDokument2 SeitenSupawadee Namuangruk: EducationFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Papers Structure of The Novel Ternary Hydrides Li TT D (TT Si and Ge)Dokument6 SeitenResearch Papers Structure of The Novel Ternary Hydrides Li TT D (TT Si and Ge)Fadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accurate Single-Particle Determination of The Band Gap in Silicon NanowiresDokument4 SeitenAccurate Single-Particle Determination of The Band Gap in Silicon NanowiresFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18 Small-Angle Scattering Y.amemiyaDokument60 Seiten18 Small-Angle Scattering Y.amemiyaFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Donation Application FormDokument2 SeitenBlood Donation Application FormFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stefanoski 2013Dokument3 SeitenStefanoski 2013Fadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kim 2019Dokument23 SeitenKim 2019Fadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chen 2019Dokument6 SeitenChen 2019Fadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- First-Principles Study of Li Ion Diffusion in LifepoDokument5 SeitenFirst-Principles Study of Li Ion Diffusion in LifepoFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Li Ti NanoporousDokument9 SeitenLi Ti NanoporousFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- First-Principles Study of Li Ion Diffusion in LifepoDokument5 SeitenFirst-Principles Study of Li Ion Diffusion in LifepoFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Man Thir Am 2015Dokument23 SeitenMan Thir Am 2015Fadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chen 2019Dokument6 SeitenChen 2019Fadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Energy: Stefan AdamsDokument6 SeitenApplied Energy: Stefan AdamsFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch09Dokument36 Seitench09Dilay SerttanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Energy: Stefan AdamsDokument6 SeitenApplied Energy: Stefan AdamsFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Li 2017 Nanoporous PolimerDokument9 SeitenLi 2017 Nanoporous PolimerFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 201707HK Conference ProgramDokument43 Seiten201707HK Conference ProgramFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10.1007/s00894 017 3521 7 PDFDokument9 Seiten10.1007/s00894 017 3521 7 PDFFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis, Characterization and DFT Study of 4,4 - Oxydianiline Imines As Precursors of Tetrahalo-1,3-Oxazepine-1,5-DioneDokument6 SeitenSynthesis, Characterization and DFT Study of 4,4 - Oxydianiline Imines As Precursors of Tetrahalo-1,3-Oxazepine-1,5-DioneFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fritz Haber Institute PDFDokument31 SeitenFritz Haber Institute PDFFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Tribute To Jan Erik AlmlOF PAPERDokument11 SeitenA Tribute To Jan Erik AlmlOF PAPERFadjar MulyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)