Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lesson 8 Mon 12 June 2017
Hochgeladen von
api-350901417Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lesson 8 Mon 12 June 2017
Hochgeladen von
api-350901417Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lesson Plan
Date: Class/Group: Time: P3 & 4
12 June 2017 HASS History - Year 9 (3/11) Room: 115
Subject: The making of the modern world.
Topic: Depth study 2: Investigating World War I (19141918).
Lesson content: Weapons of WW1
Curriculum links: Specific Objectives/Learning Goals:
The causes of World War I and the Students will:
reasons that men enlisted to fight in the Research and understand the weapons used
war (ACDSEH021).
in WW1.
General Capabilities: Analyse the impact this had on technology
Literacy change.
ICT
Critical and creative thinking
Ethical Understanding
Cross-curriculum priorities:
Skills Student Diversity:
Questioning and Researching Each class of Year 9s (3 & 11) have students with
Analysing learning and/or behavioral difficulties. The implication
Evaluating of this is that more attention and scaffolding is required
Communicating and Reflecting for these students. The teacher must be careful not to
pay too much attention to the detriment of the other
students.
Prior Learning: Resources/Materials required:
Students have spent the previous 6 BYOD laptops
weeks of Term 2 learning about My Laptop and wireless mouse
World War 1 and have completed 2 Internet via WiFi
Summative Assessments (CATs).
Teacher resources:
Youtube video
Web quest worksheet
Student resources:
www.firstworldwar.com
Page | 1 Mark Thomas 18608112
Lesson Steps
Time: Procedure Comment
Pre- Turn on projector
lesson Plug in laptop
Arrange desks as needed
Lay out resources as needed
5 mins Welcome and Roll Wait until there is quiet
Discuss learning objectives Remind students of the
Class rules. Emphasise
that no one has the right to
5 mins Hook Video Technology of WWI 3 mins stop you from learning.
https://youtu.be/k7v3cq1ZJjM
40 Activity Jigsaw web quest students to work in 6 groups
mins using the web quest worksheet. Each group is to complete one
weapon only then send and expert to learn from another group
Refer steps below
5 mins Kahoot quiz to reinforce the learning.
Evaluation of Student Learning:
1. Were the students engaged during the lesson?
2. Were the objectives met? If not, why not?
3. Were they able to successfully create their own Excel spreadsheet?
4. Was there sufficient scaffolding leading up to the lesson, i.e. were the students in the ZPD?
5. What was the feedback from the students? Did they enjoy it - was it fun?
Self-Evaluation/Reflection:
1. How did the overall lesson seem to go?
2. Did I stay on time?
3. What was the feedback from the students? Did they enjoy it - was it fun?
4. Did any students struggle to meet the objectives?
5. What would I do differently next time?
Page | 2 Mark Thomas 18608112
Jigsaw Activity
https://www.jigsaw.org/#steps
STEP ONE
Divide students into 5- or 6-person jigsaw groups.
The groups should be diverse in terms of gender, ethnicity, race,
and ability.
STEP TWO
Appoint one student from each group as the leader.
Initially, this person should be the most mature student in the
group.
STEP THREE
Divide the days lesson into 5-6 segments.
STEP FOUR
Assign each student to learn one segment.
Make sure students have direct access only to their own segment.
STEP FIVE
Give students time to read over their segment at least twice and
become familiar with it.
There is no need for them to memorize it.
STEP SIX
Form temporary expert groups by having one student from each
jigsaw group join other students assigned to the same segment.
Page | 3 Mark Thomas 18608112
Give students in these expert groups time to discuss the main
points of their segment and to rehearse the presentations they will
make to their jigsaw group.
STEP SEVEN
Bring the students back into their jigsaw groups.
STEP EIGHT
Ask each student to present her or his segment to the group.
Encourage others in the group to ask questions for clarification.
STEP NINE
Float from group to group, observing the process.
If any group is having trouble (e.g., a member is dominating or
disruptive), make an appropriate intervention. Eventually, it's best
for the group leader to handle this task. Leaders can be trained by
whispering an instruction on how to intervene, until the leader gets
the hang of it.
STEP TEN
At the end of the session, give a quiz on the material.
Students quickly come to realize that these sessions are not just fun
and games but really count.
Page | 4 Mark Thomas 18608112
NAME:______________________________ DATE:_____________ PERIOD:______
The Weapons of World
War I
Identify and investigate: machine guns, trench mortars, grenades, flamethrowers,
poison gas, tanks, planes
WORLD WAR I: A UNIQUE WAR
World War I was unique in that it was a combination of new 20th Century
technology and old 19th Century tactics.
It was the last of the old and the first of the new as far as the type of war it was.
There were soldiers riding horses with swords, as well as tanks, planes, poison gas,
flamethrowers, and machine guns.
Inevitably, this clash of old school tactics and new weaponry led to massive
casualties.
WHAT LED TO THESE NEW INNOVATIONS IN WEAPONRY?
1. THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION:
New technologies came about, and nations now had the resources and ability to
produce large numbers of weapons.
2. FRUSTRATION OF TRENCH WARFARE:
The Central Powers and the Allied Powers were locked in a stalemate that dragged
on for a long time; this forced both sides to come up with new ways to gain
advantages and to kill the enemy.
www.firstworldwar.com
Page | 5 Mark Thomas 18608112
GROUP 1: MACHINE GUNS
(click on Weaponry, then Machine Guns on the list)
How many operators did a machine gun require in WWI?
______ to _______ operators. (scroll down to Machine Gun in
1914 to answer all questions)
How many rounds could a machine gun fire per minute?
_______ to _______ rounds.
In battle, one machine gun was the equivalent to how many rifles?
___________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
What would happen often that made machine guns inoperative?
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
Page | 6 Mark Thomas 18608112
GROUP 2: TRENCH MORTARS
(click on Weaponry, then Trench Mortars on the list)
Was the trench mortar a brand new weapon or an old weapon
that was found to be useful in WWI?
________________________________________________________________
Describe how the trench mortar works: (scroll to The Mortar: A Definition)
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
What were the 3 main advantages of the mortar? (scroll to Its Advantages Over Artillery)
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
Page | 7 Mark Thomas 18608112
GROUP 3: GRENADES
(click on Weaponry, then Grenades on the list)
The grenade was not a new weapon in WWI, but one that was developed a great
deal at the time. What century was the grenade first used?
_______________________________
Grenades could be thrown or launched from a rifle. What were the two ways that
grenades could detonate (explode)? (scroll down to Two Forms of Detonation)
_____________________________ or ______________________________
What was the greatest grenade battle in WWI and how long did it last? (scroll down
to Greatest Grenade Battle of the War)
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
Page | 8 Mark Thomas 18608112
GROUP 4: FLAMETHROWERS
(click on Weaponry, then Flamethrowers on the list)
The flamethrower was a weapon first used by the Germans
in WWI that terrorized their enemies. In what century were
the earliest flamethrowers? ________________________
What is the basic idea of a flamethrower?
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
The operators of flamethrowers led dangerous lives that were often cut short. Why is
this? Give three reasons. (look near one of the pictures)
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
Page | 9 Mark Thomas 18608112
GROUP 5: POISON GAS
(click on Weaponry, then Poison Gas on the list)
Before WWI, the use of poison gas attack was considered uncivilized. What was
the main reason for the use of poison gas in WWI?
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
What battle saw the first use of poison gas by the Germans? When they saw the
yellow-green cloud drifting towards them, what did the French think it was? (scroll
down to Introduction of Poison Gas)
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
Chlorine gas, mustard gas, and phosgene were the three main types of poison gas
used. What act of nature made the use of poison gas just as deadly to the one
delivering it as to the one it was being used against? (scroll to British Setback at Loos)
________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
Page | 10 Mark Thomas 18608112
GROUP 6: TANKS
(click on Weaponry, then Tanks on the list)
The original design of the tank can be traced back to which
century? ________________
In 1899, Frederick Simms designed what he called the motor
war car. What were its three main attributes (features)? (Scroll down to Evolution of the
Tank)
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
What were the attributes that Colonel Swinton insisted that the tank MUST have to
be effective? (scroll down to The Birth of the Landship - or Tank)
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
Page | 11 Mark Thomas 18608112
GROUP 7: PLANES
(click on War In The Air)
Aircraft at first were deemed of little use in combat. What were
they first used for? (click on Introduction)
__________________________________________________________
Fighter planes were mainly used in a defensive role in the Great War. Bombers
carried out the offense. What were the aims of strategic bombing? (click on Bombers)
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
_______________
An ace is a pilot credited with more than five shoot-downs. Who was the top
fighter pilot ace in WWI? What was his nickname? How many shoot-downs was he
credited with? (click on the Top Air Aces)
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________
Page | 12 Mark Thomas 18608112
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cep Lessonplan 450 2Dokument8 SeitenCep Lessonplan 450 2api-549589434Noch keine Bewertungen
- Student Teaching Wwi Invention Lesson PlanDokument5 SeitenStudent Teaching Wwi Invention Lesson Planapi-658998541Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 11 Fri 16 June 2017Dokument2 SeitenLesson 11 Fri 16 June 2017api-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan sp-22Dokument6 SeitenLesson Plan sp-22api-651485779Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 12 Mon 19 June 2017Dokument2 SeitenLesson 12 Mon 19 June 2017api-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2Dokument5 SeitenLesson 2api-438782828Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan2Dokument5 SeitenLesson Plan2api-288469220Noch keine Bewertungen
- IT Project:: Endorsement Subject Class Unit Lesson ResourcesDokument7 SeitenIT Project:: Endorsement Subject Class Unit Lesson Resourcesapi-252933406Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ecur325-Assignment5-Bock LessonDokument7 SeitenEcur325-Assignment5-Bock Lessonapi-400653289Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cagle Learning ExpereinceDokument20 SeitenCagle Learning Expereinceapi-549118486Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 10 Thurs 15 June 2017Dokument2 SeitenLesson 10 Thurs 15 June 2017api-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan 5 Mon 6 June 2017Dokument2 SeitenLesson Plan 5 Mon 6 June 2017api-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Daffin Lesson PlanDokument6 SeitenDaffin Lesson Planapi-532818888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edu-321 Lesson Plan 1Dokument4 SeitenEdu-321 Lesson Plan 1api-658998541Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 9 Tues 13 June 2017Dokument2 SeitenLesson 9 Tues 13 June 2017api-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- FPD IctDokument7 SeitenFPD Ictapi-279449568Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wwi Technology LessonDokument3 SeitenWwi Technology Lessonapi-341952960Noch keine Bewertungen
- Microteach 4Dokument5 SeitenMicroteach 4api-333574925Noch keine Bewertungen
- LP 1 Industry Growth 1Dokument2 SeitenLP 1 Industry Growth 1api-272540117Noch keine Bewertungen
- Victoria de Leon Lesson Plan 2 With StrategyDokument5 SeitenVictoria de Leon Lesson Plan 2 With Strategyapi-552950576Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Plan 8th Grade CH 11Dokument7 SeitenUnit Plan 8th Grade CH 11api-311857507Noch keine Bewertungen
- Web 2Dokument3 SeitenWeb 2api-656325889Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Plan For PortfolioDokument18 SeitenUnit Plan For Portfolioapi-273331065Noch keine Bewertungen
- ww2 LessonDokument4 Seitenww2 Lessonapi-365479423Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Guide: Unit/Chapter Objective/Generalization/Big Idea: LESSON OBJECTIVE: 3-Part Learning ObjectiveDokument3 SeitenLesson Plan Guide: Unit/Chapter Objective/Generalization/Big Idea: LESSON OBJECTIVE: 3-Part Learning Objectiveapi-458619511Noch keine Bewertungen
- PortfolioexceptlessonsDokument4 SeitenPortfolioexceptlessonsapi-201570723Noch keine Bewertungen
- EDUC 2220 Lesson PlanDokument5 SeitenEDUC 2220 Lesson PlannathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEP Lesson Plan Form: Lesson Idea/Topic and Rational/RelevanceDokument6 SeitenCEP Lesson Plan Form: Lesson Idea/Topic and Rational/Relevanceapi-512186934Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lessonplanday 4Dokument3 SeitenLessonplanday 4api-315425483Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Grade 90 Minutes Lesson) ?: Secondary Lesson Plan TemplateDokument4 Seiten9 Grade 90 Minutes Lesson) ?: Secondary Lesson Plan TemplateRyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lessonplanday 2 VietnamDokument3 SeitenLessonplanday 2 Vietnamapi-315425483Noch keine Bewertungen
- Student Teaching Lesson 2 9th WDokument4 SeitenStudent Teaching Lesson 2 9th Wapi-658998541Noch keine Bewertungen
- Events of WwiDokument3 SeitenEvents of Wwiapi-356387598Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 13Dokument2 SeitenLesson 13api-238735118Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Unit Plan Template 1Dokument5 SeitenDigital Unit Plan Template 1api-388375861Noch keine Bewertungen
- Session Guide - Learning Difficulties - Group 2 Come With Me in The World of Learners With Difficulties I. GreetingsDokument5 SeitenSession Guide - Learning Difficulties - Group 2 Come With Me in The World of Learners With Difficulties I. GreetingsCharie Enrile-JaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- World War I Lesson PlanDokument2 SeitenWorld War I Lesson PlanErisa HanelliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Cl.7th AugustDokument9 SeitenLesson Plan Cl.7th AugustGaurav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flint Lesson Plan 4Dokument4 SeitenFlint Lesson Plan 4api-282214741Noch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Beyond The Basic Prductivity Tools Lesson Idea TemplateDokument2 Seiten04 Beyond The Basic Prductivity Tools Lesson Idea Templateapi-478236222Noch keine Bewertungen
- Local Media8641172567169889860Dokument6 SeitenLocal Media8641172567169889860ABUBAKAR SALMONoch keine Bewertungen
- 7K LessonDokument4 Seiten7K Lesson4tdrhvy4ccNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBL Class-Viii AugustDokument3 SeitenCBL Class-Viii AugustGaurav ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan 2 Hass Year 9Dokument5 SeitenLesson Plan 2 Hass Year 9api-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson-4-Tics 3Dokument3 SeitenLesson-4-Tics 3api-335109262Noch keine Bewertungen
- Athens Lesson 11Dokument3 SeitenAthens Lesson 11api-697852119Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science InquiryDokument8 SeitenScience Inquiryapi-409093587Noch keine Bewertungen
- Df-Ficha Pedagógica-6th-Reg-Project 5Dokument8 SeitenDf-Ficha Pedagógica-6th-Reg-Project 5Katflores FloresrualesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan For Implementing NETS - S-Template I: (More Directed Learning Activities)Dokument8 SeitenLesson Plan For Implementing NETS - S-Template I: (More Directed Learning Activities)Kevin FosterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan 4Dokument6 SeitenLesson Plan 4api-296156561Noch keine Bewertungen
- LP 2 Captains of IndustryDokument3 SeitenLP 2 Captains of Industryapi-272540117Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stage 1-Desired Results - You May Use Student Friendly LanguageDokument2 SeitenStage 1-Desired Results - You May Use Student Friendly Languageapi-396407573Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan 4 Hass Year 9Dokument4 SeitenLesson Plan 4 Hass Year 9api-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Uoi Work Plan-Htww-Wk 5Dokument7 SeitenUoi Work Plan-Htww-Wk 5toobahaseebzafarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forces Causing Movement CompletelessonDokument28 SeitenForces Causing Movement Completelessonapi-616056306Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kortas Unit PlanDokument7 SeitenKortas Unit Planapi-272488373Noch keine Bewertungen
- Learning SegmentDokument23 SeitenLearning Segmentapi-510714748Noch keine Bewertungen
- FlippedlessonplanDokument3 SeitenFlippedlessonplanapi-355722927Noch keine Bewertungen
- LP (Introductions) (Menna Youssef)Dokument3 SeitenLP (Introductions) (Menna Youssef)MennaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment 2 Welcome To and Acknowledgement of Country FinalDokument7 SeitenAssessment 2 Welcome To and Acknowledgement of Country Finalapi-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Station 5 - HeadstonesDokument1 SeiteStation 5 - Headstonesapi-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment 2 - Learning Program Final Mark Thomas 18608112Dokument47 SeitenAssessment 2 - Learning Program Final Mark Thomas 18608112api-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Film Is Set in CondahDokument4 SeitenThe Film Is Set in Condahapi-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Station 3 - How Do Belgium Students Feel About ww1Dokument1 SeiteStation 3 - How Do Belgium Students Feel About ww1api-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Billy Sing EssayDokument2 SeitenBilly Sing Essayapi-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 10 Thurs 15 June 2017Dokument2 SeitenLesson 10 Thurs 15 June 2017api-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Scams Brochure Marking SheetDokument1 SeiteScams Brochure Marking Sheetapi-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Propaganda Posters of World War OneDokument31 SeitenPropaganda Posters of World War Oneapi-350901417100% (1)
- Lesson 7 Fri 15 June 2017Dokument8 SeitenLesson 7 Fri 15 June 2017api-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Probsolution NytlnDokument1 SeiteProbsolution Nytlnapi-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sweatshops PPT After LanceDokument10 SeitenSweatshops PPT After Lanceapi-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 9 Tues 13 June 2017Dokument2 SeitenLesson 9 Tues 13 June 2017api-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Christmas Truce WorksheetDokument2 SeitenChristmas Truce Worksheetapi-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Weapons of ww1 Web QuestDokument4 SeitenWeapons of ww1 Web Questapi-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan 5 Mon 6 June 2017Dokument2 SeitenLesson Plan 5 Mon 6 June 2017api-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan 4 Hass Year 9Dokument4 SeitenLesson Plan 4 Hass Year 9api-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mosharaf HossainDokument2 SeitenMosharaf HossainRuhul RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wwii TictactoeDokument2 SeitenWwii Tictactoeapi-557780348Noch keine Bewertungen
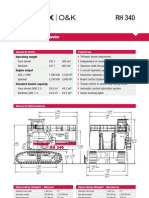
- Hydraulic Mining ExcavatorDokument8 SeitenHydraulic Mining Excavatorasditia_07100% (1)
- A Review of Service Quality ModelsDokument8 SeitenA Review of Service Quality ModelsJimmiJini100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry 1Dokument265 SeitenOrganic Chemistry 1Israk Mustakim IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top Activist Stories - 5 - A Review of Financial Activism by Geneva PartnersDokument8 SeitenTop Activist Stories - 5 - A Review of Financial Activism by Geneva PartnersBassignotNoch keine Bewertungen
- SecuritizationDokument46 SeitenSecuritizationHitesh MoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Study Between Online and Offilne Learning With Reference of Tutedude E-LearningDokument61 SeitenComparative Study Between Online and Offilne Learning With Reference of Tutedude E-LearningDeeksha Saxena0% (2)
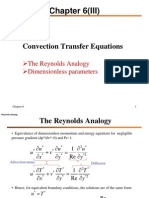
- Convection Transfer EquationsDokument9 SeitenConvection Transfer EquationsA.N.M. Mominul Islam MukutNoch keine Bewertungen
- IcarosDesktop ManualDokument151 SeitenIcarosDesktop ManualAsztal TavoliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Minute Pediatric ConsultDokument5 Seiten5 Minute Pediatric Consultajescool0% (4)
- Focus Edition From GC: Phosphate Bonded Investments For C&B TechniquesDokument35 SeitenFocus Edition From GC: Phosphate Bonded Investments For C&B TechniquesAlexis De Jesus FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZygalDokument22 SeitenZygalShubham KandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seabank Statement 20220726Dokument4 SeitenSeabank Statement 20220726Alesa WahabappNoch keine Bewertungen
- Odisha State Museum-1Dokument26 SeitenOdisha State Museum-1ajitkpatnaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThorpeDokument267 SeitenThorpezaeem73Noch keine Bewertungen
- Contoh Discussion Text Tentang HomeworkDokument8 SeitenContoh Discussion Text Tentang Homeworkg3p35rs6100% (1)
- Curriculum Guide Ay 2021-2022: Dr. Gloria Lacson Foundation Colleges, IncDokument9 SeitenCurriculum Guide Ay 2021-2022: Dr. Gloria Lacson Foundation Colleges, IncJean Marie Itang GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 9 Quiz 4Dokument3 SeitenMath 9 Quiz 4Lin SisombounNoch keine Bewertungen
- Native VLAN and Default VLANDokument6 SeitenNative VLAN and Default VLANAaliyah WinkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Union Test Prep Nclex Study GuideDokument115 SeitenUnion Test Prep Nclex Study GuideBradburn Nursing100% (2)
- Retail Banking Black BookDokument95 SeitenRetail Banking Black Bookomprakash shindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Switching Simulation in GNS3 - GNS3Dokument3 SeitenSwitching Simulation in GNS3 - GNS3Jerry Fourier KemeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument6 SeitenChapter 1Grandmaster MeowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kapinga Kamwalye Conservancy ReleaseDokument5 SeitenKapinga Kamwalye Conservancy ReleaseRob ParkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- NIQS BESMM 4 BillDokument85 SeitenNIQS BESMM 4 BillAliNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Find Fatty Material of Different Soap SamplesDokument17 SeitenTo Find Fatty Material of Different Soap SamplesRohan Singh0% (2)
- Google Tools: Reggie Luther Tracsoft, Inc. 706-568-4133Dokument23 SeitenGoogle Tools: Reggie Luther Tracsoft, Inc. 706-568-4133nbaghrechaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dreaded Attack - Voyages Community Map Rules v1Dokument2 SeitenDreaded Attack - Voyages Community Map Rules v1jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bandhan Neft Rtgs FormDokument2 SeitenBandhan Neft Rtgs FormMohit Goyal50% (4)