Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
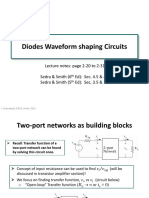
The Piecewise Linear Model
Hochgeladen von
hks4900Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The Piecewise Linear Model
Hochgeladen von
hks4900Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
8/29/2005 The Piecewise Linear Model.
doc 1/3
The Piece-Wise
Linear Model
Q: The CVD model approximates the forward biased junction
diode voltage as vD = 0. 7 V regardless of the junction diode
current. This of course is a good approximation, but in reality,
the junction diode voltage increases (logarithmically) with
increasing diode current. Isnt there a more accurate model?
A: Yes! Consider the Piece-Wise Linear (PWL) model.
+
+ iDi
v i
Replace: with: D
+
iD vD VD 0
rd
iD
PWL 1
model rd
junction
diode v
D
VD0
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
8/29/2005 The Piecewise Linear Model.doc 2/3
In other words, replace the junction diode with three devices
an ideal diode, in series with some voltage source (not 0.7 V!)
and a resistor.
To find approximate current and voltage values of a junction
diode circuit, follow these steps:
Step 1 - Replace each junction diode with the three devices of
the PWL model.
Note you now a have an IDEAL diode circuit! There are no
junction diodes in the circuit, and therefore no junction diode
knowledge need be (or should be) used to analyze it.
Step 2 - Analyze the IDEAL diode circuit. Determine iDi and vDi
for each IDEAL diode.
IMPORTANT NOTE !!! PLEASE READ THIS
CAREFULLY:
Make sure you analyze the resulting circuit precisely as we did
in section 3.1. You assume the same IDEAL diode modes, you
enforce the same IDEAL diode values, and you check the same
IDEAL diode results, precisely as before. Once we replace the
junction diodes with the CVD model, we have an IDEAL diode
circuitno junction diodes are involved!
Step 3 Determine the approximate values iD and vD of the
junction diode from the ideal diode values iDi and vDi :
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
8/29/2005 The Piecewise Linear Model.doc 3/3
+
+ iDi
v i
iD iDi
D
+
iD VD 0
vD
vD v Di + VD 0 + iDi rd
rd
Note therefore, if the IDEAL diode (note here I said IDEAL
diode) is forward biased (iDi > 0 ), then the approximation of the
junction diode current will likewise be positive ( iD > 0 ), and the
approximation of the junction diode voltage (unlike the ideal
diode voltage of vDi = 0 ) will be:
vD = vDi + VD 0 + iDi rd
= 0.0 + VD 0 + iDi rd
= VD 0 + iDi rd
However, if the IDEAL diode is reversed biased (iDi = 0 ), then
the approximation of the junction diode current will likewise be
zero (iD = 0 ), and the approximation of the junction diode
voltage (unlike the ideal diode voltage of vDi < 0 ) will be:
vD = vDi + VD 0 + iDi rd
= vDi +VD 0 + 0
vD < VD 0
NOTE: Do not check the resulting junction diode
approximations. You do not assume anything about the junction
diode, so there is nothing to check regarding the junction diode
answers.
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesVon EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (7)
- EX.3 Small Signal Analysis of Diode PDFDokument17 SeitenEX.3 Small Signal Analysis of Diode PDFram charanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constant-Gain MultiplierDokument10 SeitenConstant-Gain Multiplierstreamer akoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diod RectifierDokument35 SeitenDiod RectifierRizalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit III Arp FullDokument55 SeitenUnit III Arp FullKATHIRAVAN .NNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polytechnic Physics TRB Reference BooksDokument3 SeitenPolytechnic Physics TRB Reference BooksJagan EashwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 3 MOSFET IDokument37 SeitenLec 3 MOSFET Ikrishna_ScrbidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: Shcherbakov BogdanDokument43 SeitenElectronic Devices and Circuits: Shcherbakov BogdanБогдан Щербаков100% (1)
- CHAP 1 Part 2Dokument36 SeitenCHAP 1 Part 2ksreddy2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Electronics & Telecommunication: Presented By: Valluri Bhavana MSC - Etc, 1 Semester Roll No: Pg19Etc-002Dokument22 SeitenDepartment of Electronics & Telecommunication: Presented By: Valluri Bhavana MSC - Etc, 1 Semester Roll No: Pg19Etc-002BHAVANA VALLURINoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 17 Notes 2Dokument11 SeitenChapter 17 Notes 2Rizwan MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHY2 GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit - 4 15032021082835AMDokument19 SeitenPHY2 GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit - 4 15032021082835AMPiyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BJTDokument6 SeitenBJTengineerluvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electronics-L2Dokument33 SeitenBasic Electronics-L2Sushmitha AcharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristics of FETDokument8 SeitenCharacteristics of FETYogesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhotodetectorsDokument43 SeitenPhotodetectorsvinothrece100% (1)
- Lab Requirements of Ece: Infrastructure Requirement As Per Aicte NormsDokument4 SeitenLab Requirements of Ece: Infrastructure Requirement As Per Aicte NormsecessecNoch keine Bewertungen
- BASIC ELECTRONICS - Notes-M1Dokument18 SeitenBASIC ELECTRONICS - Notes-M1Mr SpamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch03 Special-Purpose Diodes PDFDokument49 SeitenCh03 Special-Purpose Diodes PDFSurafel TekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Viii. Low Frequency Characteristics of Junction Field Effect TransistorsDokument6 SeitenLab Viii. Low Frequency Characteristics of Junction Field Effect Transistorssachinshetty001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Exercise On Full Wave and Half Wave SCR RectifiersDokument5 SeitenLab Exercise On Full Wave and Half Wave SCR RectifiersSaji Sovis100% (1)
- Special Purpose DiodesDokument43 SeitenSpecial Purpose DiodesllovresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diode Valve Effect: Electrical and Electronics LabDokument4 SeitenDiode Valve Effect: Electrical and Electronics LabLare ONoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Source.Dokument12 SeitenPower Source.SaritechNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE 251 - Lecture 02 PDFDokument7 SeitenECE 251 - Lecture 02 PDFwhatthefuNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC DC Analysis BJT Diffrential Amp PDFDokument8 SeitenAC DC Analysis BJT Diffrential Amp PDFtanishk jainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab#1.Voltage FollowerDokument5 SeitenLab#1.Voltage FollowerُIBRAHEEM ALHARBINoch keine Bewertungen
- Operational AmplifiersDokument35 SeitenOperational AmplifierskunwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE Experiment No 5Dokument11 SeitenECE Experiment No 5GeeK GuYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiber Optics NotesDokument12 SeitenFiber Optics NotesMonika HansdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voltage & Current DividerDokument28 SeitenVoltage & Current DividerArsal Javed ButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report - Phase ShifterDokument8 SeitenReport - Phase ShifterAmeer AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE320 Electronic NotesDokument331 SeitenEE320 Electronic NotesAngel Pérez Santiago100% (1)
- L07 DC and AC Load LineDokument21 SeitenL07 DC and AC Load LineDebashish Pal100% (1)
- Lecs 2 After MidtermDokument41 SeitenLecs 2 After MidtermAbdalkader Alibrahim100% (1)
- BJT PresentationDokument24 SeitenBJT PresentationzakireceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Properties of Metals TyDokument5 SeitenElectrical Properties of Metals TyNeelam KapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 6Dokument5 SeitenLab 6par1vej2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Narrowband and Wideband FMDokument18 SeitenNarrowband and Wideband FMIslam CandleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid Sate Electronic Devices (Code: 402401) - AY1516-S2Dokument12 SeitenSolid Sate Electronic Devices (Code: 402401) - AY1516-S2MINH NGUYỄN THẾNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC6712 Optical and Microwave Lab ManualDokument98 SeitenEC6712 Optical and Microwave Lab ManualRajesh Natarajan100% (1)
- Ell100 Lab Report: Single Phase Transformer B-H LoopDokument10 SeitenEll100 Lab Report: Single Phase Transformer B-H LoopDevang MaharNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2b RectifierDokument21 Seiten2b RectifierLove StrikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE6201 Circuit Theory Regulation 2013 Lecture Notes PDFDokument251 SeitenEE6201 Circuit Theory Regulation 2013 Lecture Notes PDFrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No.02 To Observe The Characteristics of A Half Wave RectifierDokument4 SeitenExperiment No.02 To Observe The Characteristics of A Half Wave RectifierWaqas MughalNoch keine Bewertungen
- VLSI Notes 1 PDFDokument305 SeitenVLSI Notes 1 PDFKishore KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biasing Circuits of FETDokument10 SeitenBiasing Circuits of FETMonica GunjalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Junction BreakdownDokument41 SeitenJunction BreakdownKamal Jeet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- DACDokument28 SeitenDACRohith Mohan100% (1)
- 2 Introduction To Semiconductor DiodesDokument50 Seiten2 Introduction To Semiconductor DiodesKurt PalacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 4 Half Wave and Full WaveDokument8 SeitenLab 4 Half Wave and Full WaveRashid Rind Rashid Rind100% (1)
- 6 Intrinsic Semiconductor-1Dokument12 Seiten6 Intrinsic Semiconductor-1api-462620165Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fermi Level and Fermi EnergyDokument36 SeitenFermi Level and Fermi Energygirishkumardarisi254Noch keine Bewertungen
- PUT Experiment EditedDokument9 SeitenPUT Experiment EditedReineirDuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE6201 Circuit Theory Regulation 2013 Lecture Notes PDFDokument257 SeitenEE6201 Circuit Theory Regulation 2013 Lecture Notes PDFVenkatesan Swamy100% (1)
- Different Types of DiodesDokument8 SeitenDifferent Types of DiodesAllelie UgotNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Piecewise Linear ModelDokument4 SeitenThe Piecewise Linear ModeldopesrinathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3. Diodes and Rectification 3.1 Diode ModelsDokument4 SeitenLecture 3. Diodes and Rectification 3.1 Diode ModelsHassan FarssiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diodos PDFDokument30 SeitenDiodos PDFEnrique VelilleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter1 2 3 BioDokument132 SeitenChapter1 2 3 BioYanendra SahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infineon ApplicationBrochure General Lighting Brochure ABR v01 00 enDokument52 SeitenInfineon ApplicationBrochure General Lighting Brochure ABR v01 00 enninapavelNoch keine Bewertungen
- User's Guide MR2003B/D: 2. Quick-Start ChecklistDokument9 SeitenUser's Guide MR2003B/D: 2. Quick-Start ChecklistStefán Þór SigurðssonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eectricity C 10Dokument62 SeitenEectricity C 10Gursharan SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daewoo CM-405F DTH-2930SSFVDokument54 SeitenDaewoo CM-405F DTH-2930SSFVMarco Antonio100% (3)
- E-Z Command InstructionsDokument8 SeitenE-Z Command InstructionsSebas CheeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Powin Enclosures Product Manual Rev B01Dokument51 SeitenPowin Enclosures Product Manual Rev B01melihguneriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legend: Electrical NotesDokument1 SeiteLegend: Electrical NotesArt Anthony Tadeo AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wires and Cables PDFDokument14 SeitenWires and Cables PDFRomel Panis88% (8)
- A New Static Induction Thyristor (Sith) Analytical Model: Jue Wang and Barry W. WilliamsDokument11 SeitenA New Static Induction Thyristor (Sith) Analytical Model: Jue Wang and Barry W. WilliamsAbdulAzizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gek 36378D PDFDokument14 SeitenGek 36378D PDFoso0214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Project Oxhydroelectric Effect Procedure and Apparatus To Extract Electric Energy From WaterDokument11 SeitenProject Oxhydroelectric Effect Procedure and Apparatus To Extract Electric Energy From WaterFrancesco Paolo TuccinardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Miniature Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors: NRSA Series NrsaDokument3 SeitenMiniature Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors: NRSA Series NrsaMinh VuNoch keine Bewertungen
- POSTEF - ZXD3000 RectifierDokument3 SeitenPOSTEF - ZXD3000 RectifierNguyen Vu Hoang ThachNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surface Mount Triac: SOT223 (Plastic)Dokument4 SeitenSurface Mount Triac: SOT223 (Plastic)Mike BrdnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Updated Simulation Model of Active Front End Converter: Project Memo AN 01.12.97Dokument11 SeitenUpdated Simulation Model of Active Front End Converter: Project Memo AN 01.12.97bpchimeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design PerspectiveDokument78 SeitenDigital Integrated Circuits: A Design PerspectiveGayathriRajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rekap Data Fasos Fasum Utilitas r40Dokument142 SeitenRekap Data Fasos Fasum Utilitas r40Vincent EliandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spesifikasi Teknis OPMI Lumera 300 Standard With Integrated Camera - 2Dokument1 SeiteSpesifikasi Teknis OPMI Lumera 300 Standard With Integrated Camera - 2RSUD dr. H. ANDI ABDURRAHMAN NOORNoch keine Bewertungen
- PMMC MeasurementDokument97 SeitenPMMC Measurementkiller raoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turnstile Fractal Patch Antenna ReportDokument61 SeitenTurnstile Fractal Patch Antenna ReportShailesh PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4037 Ev2Dokument75 Seiten4037 Ev2batuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installation: Residential/Light Commercial Generator SetsDokument64 SeitenInstallation: Residential/Light Commercial Generator SetsJackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fisher Fieldvue DVC6200 Digital Valve Controller: FeaturesDokument4 SeitenFisher Fieldvue DVC6200 Digital Valve Controller: FeaturessivaintwitterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ma3704 Aircraft Electrical Devices and Systems TUTORIAL 7 - Transformers 1Dokument2 SeitenMa3704 Aircraft Electrical Devices and Systems TUTORIAL 7 - Transformers 1Shaun Raphael LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zip Light Linear 4 18 SpecificationsDokument3 SeitenZip Light Linear 4 18 SpecificationsbjpwongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vvf41-80 - Skc60 Data SheetDokument16 SeitenVvf41-80 - Skc60 Data SheetLogain SunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fronius Ig PV Inverter: Technical Data SheetDokument2 SeitenFronius Ig PV Inverter: Technical Data Sheetfarani87Noch keine Bewertungen
- 6mb524 Catalogue SheetDokument20 Seiten6mb524 Catalogue SheetSalvador FayssalNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSNL Tta - Je 2016 - Basic Engineering - Test Paper - BSNL Je 2016Dokument21 SeitenBSNL Tta - Je 2016 - Basic Engineering - Test Paper - BSNL Je 2016Sunil PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operational and Maintenance Manual Ips System: Rev.00: Al Mazroui Medical & Chemical SuppliesDokument23 SeitenOperational and Maintenance Manual Ips System: Rev.00: Al Mazroui Medical & Chemical SuppliesanfalapNoch keine Bewertungen