Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
The PUERPERIUM
Hochgeladen von
springdingOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The PUERPERIUM
Hochgeladen von
springdingCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
THE PUERPERIUM o Multipara Uterus contracts more vigorously
o Primipara Uterus contracts tonically
- r/t release of Oxytocin & relieved by Analgesics
PUERPERIUM
- delivery of the Placenta lasting until 6 weeks after delivery. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Physiologic changes during pregnancy return to pre-pregnancy state. CHANGES IN THE LOWER REPRODUCTIVE TRACT
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
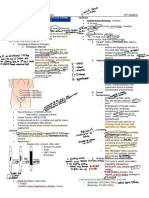
CHANGES IN THE REPRODUCTIVE TRACT - Lower Uterine Segment contracts & retracts
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- - Cervix contracts & the Cervical Opening narrows.
- External Os remain wider with bilateral depressions r/t lacerations
Involution of the Uterus during delivery Fish Mouth Appearance
- Uterus contracts tonically, reducing its size - Vaginal Canal forms a smooth-walled passage, decreasing in size;
o Fundus is slightly below the umbilicus Rugae reappear at 3rd week.
o Myometrial Blood Vessel compression Hemostasis - Hymen gets torn, forming the Myrtiform Caruncles
(prevents Post-Partum Hemorrhage)
- 10th-12th Post-Partum Day = Uterus descends into the Pelvic Cavity & Perineal Care
becomes impalpable abdominally. - Water & Mild Soap from ANTERIOR to POSTERIOR.
- 6 weeks = Non-Pregnant size - Ice Packs applied to the Episiotomy Wound to reduce swelling &
- from 1000 grams to 70 grams discomfort; Analgesics may help
- r/o Hematoma/Cellulitis if perineal pain is severe/persistent.
Involution of the Placental Site - Stool Softeners for 4th Degree Lacerations
- Placental Vessels undergo Thrombosis & Hyalinization
o Extruded with the slough of the necrotic Placental Site, ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
which is gradually exfoliated & extruded out. CHANGES IN THE URINARY TRACT
o Complete extrusion may last up to 6 weeks ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Infiltration with Granulocytes & Mononuclear Cells extending into
the Endometrium & Superficial Myometrium - Increased Urinary Bladder capacity & is insensitive to Intravesical
- 7th Day = regeneration of Endometrial Glands & Stroma (from Fluid Pressure Overdistention, Incomplete Emptying, & Increased
Placental Site Margin & Decidua Basalis) Residual Urine
o Aggravated by exposure to paralyzing effects of Regional
Endometrial Regeneration Block Anesthesia & trauma during delivery Hyperemia
- 2-3 Days Post-Partum = remaining Decidua is split into 2 layers. & Edema
o Superficial Layer = necrotic & is sloughed in the Lochia - Diuresis during the 1st week as compensation of excess ECF
o Basal Layer = remains viable; source f new endometrium - Dilated Collecting Duct System returns to normal size by 6 weeks.
- Full restoration of the entire endometrium at 3rd week Post-Partum - Patients are encouraged to void within a few hours after delivery.
Imaging Findings ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- UTZ = Uterus retroverted & the cavity empty in early Puerperium. CHANGES IN THE BREAST & LACTATION
o Fluid & Debris in the Cavity (Mid-Puerperium) ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
o Day 56 = empty Cavity appearing as a thin white line
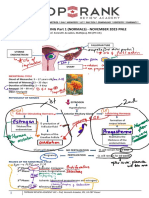
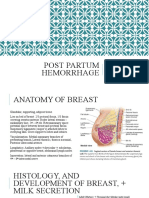
- Positive correlation between Parity & Uterine Diameter (larger - complex Humoral & Neural Mechanisms involving several hormones
Uterus in the Multiparous group) prepare the Breast for Lactation.
- Route of Delivery = Uterus larger at 1-3 months after CS delivery. o Progesterone, Estrogen, HPL, Prolactin, Insulin, & Cortisol
- Regular Breast Feeding = smaller Uteri (3 months Post-Partum) - Growth & Development of Lactiferous Ducts & Alveolar Secretory
Epithelium System.
Fourth Stage of Labor - Prolactin = stimulates unopposed milk lactose formation; levels
- 1st hour after delivery of the Placenta. increase by suckling.
- Time of greatest risk of significant hemorrhage - Oxytocin = pulsatile secretion & stimulates milk expression (Let
- Monitor Vital Signs q15 minutes or more often as necessary. Down Reflex); may also be stimulated by cry of the infant, while
- Palpate Uterus periodically to ensure well contraction. fright/stress inhibits it.
o Massage via Abdominal Wall if relaxation is noted
- Monitor amount of vaginal bleeding by inspection Phases of Milk Secretion
- Uterine Atony = Uterine Relaxation & increased Vaginal Bleeding. - quality varies as time progresses Post-Partum.
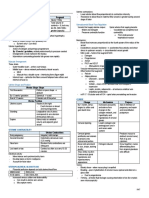
- Colostrum = 1st milk secreted (lasts for 5 days)
Lochia o Thick & yellowish
- Vaginal Discharge from the Uterus during Post-Partum. o High CHON (-Lactalbumin, -Lactoglobulin, & Casein) &
- Erythrocytes, Decidua, Epithelial Cells, & Bacteria Mineral Content; Less CHO
- Lochia Rubra = reddish-brown discharge (3-4 days) o Larger Fat Globules
- Lochia Serosa = paler in color (4-10 days) o Immunoglobulin A = protection against Enteric Pathogens
- Lochia Alba = yellowish white; consists of Leukocytes & reduced fluid - Mature Milk is more watery & contains more Fat & Lactose
content (> 10 days) concentration.
- May persist from 4-8 weeks. o Also rich in Antibodies
- Sudden but transient increased Uterine Bleeding may occur between o Contains all Vitamins except Vitamin K.
7-14 days Post-Partum. o Changes composition to match infants nutritional needs
o Slough of eschar over the site of Placental attachment o Contains Growth Fx promoting cellular growth &
o Self-limited differentiation Organ System Maturation of the NB
o Retained Placental Tissue = if does not subside within a
few hours Local Setting
- Exclusive Breastfeeding for the 1st 6 months
After Pain - Republic Act No. 7600 (Rooming-In & Breastfeeding Act of 1992)
- intermittent, crampy lower abdominal pain Post-Partum o Requires all Private & Government Health Institutions
- duration & intensity increased with parity. adopt Rooming-In & Breastfeeding practices.
o Requires that all well infants delivered vaginally without - Presence of Silver Striae (Stretch Marks)
complications shall be given to their mothers to hold & - Diastasis Recti = marked separation of the Rectus Muscles.
caress immediately after birth & through the assistance of o Midline Abdominal Wall formed only by Peritoneum,
a hospital staff, initiate Breastfeeding in the Delivery attenuated Fascia, SC Fat, & Skin
Room (Latching-On). o Self-limited; exercise may improve the condition
o Infants should be roomed0in with their mothers 30
minutes to 1 hour after delivery to promote & facilitate ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
breastfeeding. OTHER ISSUES
o Mothers shall be given their babies to hold & caress after ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
waking up from Anesthesia in CS Deliveries (roomed-in
within 3-4 hours after birth) PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
- Very early Skin-to-Skin Contact enhanced breastfeeding during early - Early Ambulation is encouraged
Post-Partum Period. o Done gradually r/t dizziness
o Only for uncomplicated Vaginal Delivery
Benefit to the Woman o Associated with less Bladder Cx & incidence of
- Oxytocin released during Milk Let-Down increases contractions & Thromboembolic Disease
lessens maternal blood loss.
o Together with Prolactin, it promotes feeling of WEIGHT LOSS
attachment & relaxation - after delivery with Uterine evacuation & Blood Loss, women
- Breastfeeding is associated with decreased incidence of Ovarian & generally lose 5-6 kg.
Breast Cancer & promotes birth spacing by delaying the return of the - Diuresis = 2-3 kg
Ovulatory Cycle. - Failure to lose weight in 6 months predicts future Obesity.
o Attenuates unfavorable metabolic risk factor changes by
reducing LDL & Fasting Insulin levels POST-NATAL CARE
o May result in Bone Demineralization r/t maternal transfer - enables identification of complications & provide the mother with
of Ca2+ to the Breast Milk even with supplementation. information on how to take care of herself & the baby.
o Remineralization occurs following weaning. - Post-Natal Check Up within 2 days after delivery.
o Mothers are encouraged to drink milk during lactation.
- 2500 Calories = recommended daily caloric requirement for lactating EARLY DISCHARGE
women during the 1st 6 months. - no evidence associating early discharge with adverse outcome.
- No impact in Breastfeeding.
Breast Fever - Done 6-72 hours after delivery
- 37.8C to 39C; accompanies Breast Engorgement during the 1st 24
hours after start of lactation
o Support Breast with a Binder/Brassier
o Apply Ice Bag
o Analgesics
- will not last longer than 16 hours; exclude other causes of fever
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
RETURN OF OVULATION & MENSTRUATION
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- women who do not Breastfeed experience Ovulation as early as 4
weeks after delivery (Mean Period of 10 weeks)
o Menstruation by the 12th week after delivery (average 7
weeks)
- Lactating mothers may delay their Ovulation for 6-10 months.
o r/t persistently elevated Serum Prolactin level, making
Ovaries unresponsive to FSH Stimulation
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CHANGES IN THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Plasma Volume is diminished approximately 1 Liter r/t Blood Loss.
o Increases the same amount by 3rd day Post-Partum r/t ECF
Shift into the Vascular Space.
o 1 week Post-Partum = Blood Volume returns nearly to
Non-Pregnant levels.
- Cardiac Output remains elevated for 2 days Post-Partum but
gradually decreases until reaching normal by the 2nd week.
- Blood Coagulation Fx remain elevated.
o Greatest level of Coagulability during the 1st 48 hours
o Fibrinogen levels remain elevated during 1st week &
progressively declines.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CHANGES IN THE ABDOMINAL WALL
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Abdominal Wall remains soft & flaccid but eventually returns to Pre-
Pregant state.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chang Can DunkDokument110 SeitenChang Can DunkHayden HansenNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Numerology of NamesDokument4 SeitenThe Numerology of Namesspringding100% (1)
- 03 - Glory To GodDokument1 Seite03 - Glory To GodspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Postpartum Period and ComplicationsDokument63 SeitenPostpartum Period and ComplicationsSharmaineAnnePoliciosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDokument22 SeitenMaternal and Child Health NursingRam Van MunsterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Puerperium SeminarDokument79 SeitenPuerperium SeminarMariam Abdul Rashid100% (2)
- Let The Saints Be JoyfulDokument1 SeiteLet The Saints Be JoyfulspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master Class 6 How Not To Lose in ChessDokument81 SeitenMaster Class 6 How Not To Lose in ChessLouie Jay L Bahian100% (2)
- Labor and DeliveryDokument6 SeitenLabor and Deliveryjenryl91% (11)
- GlaucomaDokument5 SeitenGlaucomaspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cervicogenic Headache1Dokument41 SeitenCervicogenic Headache1Jeetendra Soni100% (1)
- Puerperium (Trans)Dokument7 SeitenPuerperium (Trans)Charlie65129Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stages of LaborDokument19 SeitenStages of LaborDumlao JellyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body Mechanics ChecklistDokument7 SeitenBody Mechanics ChecklistPrincess ZantuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2023 PSC Terminal ReportDokument3 Seiten2023 PSC Terminal ReportBobby LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rules of AdjectiveDokument7 SeitenRules of Adjectivemaricelbello368Noch keine Bewertungen
- Regaining Bladder Control: For Incontinence on Exertion or Following Pelvic SurgeryVon EverandRegaining Bladder Control: For Incontinence on Exertion or Following Pelvic SurgeryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of Normal Pueperium and Its ManagementDokument13 SeitenPhysiology of Normal Pueperium and Its ManagementSandhya s100% (3)
- Ob Refresher Part 1 Normals Nov 2023 Pnle For Davao BabiesDokument12 SeitenOb Refresher Part 1 Normals Nov 2023 Pnle For Davao BabiesKristine QuindozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bubblehe PDFDokument3 SeitenBubblehe PDFHenny Kim100% (1)
- Puerperium: Striae GravidarumDokument5 SeitenPuerperium: Striae GravidarumClareen JuanicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Labor and Delivery ProcessDokument13 Seiten1 Labor and Delivery ProcessBardiaga JmayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ob FinalDokument5 SeitenOb Finalsofiapanlilio32Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 4 - Maternal PhysiologyDokument9 SeitenCH 4 - Maternal PhysiologyRandom CommenterNoch keine Bewertungen
- LACERATION - Large Laceration Can Be VAGINAL Laceration - Easier To Locate andDokument2 SeitenLACERATION - Large Laceration Can Be VAGINAL Laceration - Easier To Locate andرجمه ديوانNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 6 - MCN MaternalDokument5 SeitenModule 6 - MCN MaternalChristine DuqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal and Child NursingDokument7 SeitenMaternal and Child NursingErjen Alexandria SiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- If We Certain That There Is No Second Baby, Administer The A Uterotonic DrugDokument3 SeitenIf We Certain That There Is No Second Baby, Administer The A Uterotonic DrugValerie Gonzaga-CarandangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Care of Mother, Child, & Adolescent Lec: PartographDokument6 SeitenCare of Mother, Child, & Adolescent Lec: PartographBardiaga JmayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map Module 5Dokument2 SeitenConcept Map Module 5Ruthangela GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.. PuerperiumDokument83 Seiten8.. PuerperiumDegefaw BikoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ca 1: Obstetric Nursing: Female ReproductiveDokument7 SeitenCa 1: Obstetric Nursing: Female ReproductiveannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive System Topic 1 Normal ObDokument68 SeitenReproductive System Topic 1 Normal ObNur-Sallah AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forceps Delivery (Management) & Puerperium (Postpartum) Stage PDFDokument5 SeitenForceps Delivery (Management) & Puerperium (Postpartum) Stage PDFTandingco, Olivia Mari H.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Post Partum HemorrhageDokument9 SeitenPost Partum HemorrhageghsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Labor Onset TheoriesDokument4 SeitenLabor Onset TheoriesMaverick KimhokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM204 Page 361-471Dokument43 SeitenNCM204 Page 361-471Charlie AbagonNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 107 MidtermDokument34 SeitenNCM 107 MidtermChiaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osce - D&CDokument2 SeitenOsce - D&Cmkct111Noch keine Bewertungen
- 50cm 1.7 20g/day Doubled BW Tripled BW BL +50% Increase Delayed Eruption 1.3 1Dokument5 Seiten50cm 1.7 20g/day Doubled BW Tripled BW BL +50% Increase Delayed Eruption 1.3 1Gisselle PauloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy PuerperiumDokument27 SeitenPhy PuerperiumDevuchandana RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Maternal Health NursingdsdsDokument21 SeitenNotes Maternal Health NursingdsdsL Rean Carmelle MAGALLONESNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 HoDokument1 Seite1 HoGelsam DerramasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Postpartum: Postpartal Period / PuerperiumDokument17 SeitenPostpartum: Postpartal Period / PuerperiumVero SteelNoch keine Bewertungen
- WHCC CheatNotesDokument2 SeitenWHCC CheatNotesMia FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Female Reproductive System ResearchDokument21 SeitenOverview of Female Reproductive System ResearchOmar Ali AyoubkhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- POSTPARTUMDokument2 SeitenPOSTPARTUMJam PasionNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2G-Ballesteros Jan VincentDokument5 Seiten2G-Ballesteros Jan VincentJan Vincent BallesterosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer in ObstetricsDokument16 SeitenReviewer in ObstetricsRizalyn Padua ReyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colostomy Care and IrrigationDokument6 SeitenColostomy Care and IrrigationTheSweetpea501Noch keine Bewertungen
- Intrapartal - Theories of LaborDokument21 SeitenIntrapartal - Theories of LaborJan Oliver YaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH. 12 Study GuideDokument10 SeitenCH. 12 Study GuidePaige Nicole GauthreauxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2 Sex and FertDokument17 SeitenWeek 2 Sex and FertAbmil Ching TinggalongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Puerperium and AnalgesiaDokument12 SeitenPuerperium and AnalgesiaKim RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- (OBa) 1.6 Matrnal Adaptations To Pregnncy (Marinas) - PacisDokument10 Seiten(OBa) 1.6 Matrnal Adaptations To Pregnncy (Marinas) - PacisClyde Yuchengco Cu-unjiengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ob HandoutsDokument22 SeitenOb HandoutsKatriel Geryne ViloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normal PuerperiumDokument23 SeitenNormal Puerperiumnaga maniNoch keine Bewertungen
- NOTES 1st Sem P FDokument6 SeitenNOTES 1st Sem P FReaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON-PLAN-ON-PHYSIOLogical Changes During PregnancyDokument22 SeitenLESSON-PLAN-ON-PHYSIOLogical Changes During PregnancyV.srivaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetrics TempDokument34 SeitenObstetrics TempRichard GreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4physiologyofpuerperium 180930161559Dokument54 Seiten4physiologyofpuerperium 180930161559annu panchalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Postpartum Car1Dokument11 SeitenPostpartum Car1Claire Alvarez OngchuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy & Physiology of The Female Reproductive System: I. External Reproductive OrgansDokument41 SeitenAnatomy & Physiology of The Female Reproductive System: I. External Reproductive OrgansKarla May Manalastas BorromeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive System-ReviewerDokument6 SeitenReproductive System-ReviewerAdrian Faiz VillenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology and Management of Normal PuerperiumDokument132 SeitenPhysiology and Management of Normal PuerperiumAmuNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 107 - SL - Mat - 1Dokument100 SeitenNCM 107 - SL - Mat - 1marilexdomagsangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Observations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itVon EverandObservations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Man’s Guide to Bladder Problems & Urinary IncontinenceVon EverandA Man’s Guide to Bladder Problems & Urinary IncontinenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Observations on Abortion: An account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes, and the method of preventing itVon EverandObservations on Abortion: An account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes, and the method of preventing itNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wound ManagementDokument19 SeitenWound ManagementspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPM16TH Intrapartum and Immediate Postpartum CareDokument25 SeitenCPM16TH Intrapartum and Immediate Postpartum CarespringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine CPG On The Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Adults-2015 Update - Part 2 PDFDokument140 SeitenPhilippine CPG On The Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Adults-2015 Update - Part 2 PDFspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glycogen Metabolism Index CardDokument3 SeitenGlycogen Metabolism Index CardspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 - Memorial AcclamationDokument1 Seite07 - Memorial AcclamationspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09 - Doxology (For Thy)Dokument1 Seite09 - Doxology (For Thy)springdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treatment For 250 Important Medical ConditionsDokument5 SeitenTreatment For 250 Important Medical ConditionsspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Take Our Bread Intro: C-Am-C-Am-Dm-G7 Chorus: ChorusDokument1 SeiteTake Our Bread Intro: C-Am-C-Am-Dm-G7 Chorus: ChorusspringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESSC Tini and MetroDokument2 SeitenESSC Tini and MetrospringdingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Result of Entry Test For Admission To Bacholar Program 2010 Pre-MedicalDokument24 SeitenResult of Entry Test For Admission To Bacholar Program 2010 Pre-MedicalMuhammad IrfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Date:28 Sept 2015 (Monday) Reporting Time: 0900 HRS: SNO Regno Fullname Father'S Name DOBDokument15 SeitenDate:28 Sept 2015 (Monday) Reporting Time: 0900 HRS: SNO Regno Fullname Father'S Name DOBChitransh SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- House Aths Program 2013Dokument4 SeitenHouse Aths Program 2013Edwin ChaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar Harga Produk Kame: Per Feb 2019 NO Kode Produk Kemasan Harga JualDokument1 SeiteDaftar Harga Produk Kame: Per Feb 2019 NO Kode Produk Kemasan Harga JualAdi SukmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TV ChannelsDokument2 SeitenTV ChannelsSubramaniam SundaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Riccardo Belletti - Resume - Aprile 2023Dokument1 SeiteRiccardo Belletti - Resume - Aprile 2023Riccardo BellettiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dorset Term Dates 2016-2017Dokument1 SeiteDorset Term Dates 2016-2017LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MLB Report CardDokument58 SeitenMLB Report CardAustin DeneanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Webtv ListDokument201 SeitenWebtv ListAnonymous UMeUHTNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 - Timing Chain - InstallationDokument7 Seiten10 - Timing Chain - Installation08088338Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Groovy Kind of LoveDokument2 SeitenA Groovy Kind of LovesppiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organizational List Draft 2019Dokument16 SeitenOrganizational List Draft 2019catherine renanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Super ACE Brochure PDFDokument8 SeitenSuper ACE Brochure PDFAdriawan AnnesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vdocuments - MX - Mahindra Scorpio Parts Manual Pik Up 25 CrdeDokument166 SeitenVdocuments - MX - Mahindra Scorpio Parts Manual Pik Up 25 CrdeFILE SERVERNoch keine Bewertungen
- B 8 A 00Dokument3 SeitenB 8 A 00Stuart RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rear Wheel Bearing and Hub Replacement PDFDokument3 SeitenRear Wheel Bearing and Hub Replacement PDFY. VásquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gabarito 01Dokument2 SeitenGabarito 01eleno ribeiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nocturne 82992 PDFDokument6 SeitenNocturne 82992 PDFBenny RiefkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revised Circular Group-B Trials-5&6Dokument4 SeitenRevised Circular Group-B Trials-5&6BILU SADANoch keine Bewertungen
- September 2011 IssueDokument21 SeitenSeptember 2011 IssueTimO'Riley100% (1)
- PT Ortho Assignment Poliomyelitis: Target Organ: Spinal Cord (Ant - Horn Motor Cells) & Brainstem (BulbarDokument3 SeitenPT Ortho Assignment Poliomyelitis: Target Organ: Spinal Cord (Ant - Horn Motor Cells) & Brainstem (BulbarLakshita PrajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- READMEDokument4 SeitenREADMEElias DelgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2008 10 02 BDokument10 Seiten2008 10 02 BSouthern Maryland OnlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examen Final Semana 8 INGLES 1 1 INTENTODokument13 SeitenExamen Final Semana 8 INGLES 1 1 INTENTOClaudia100% (1)