Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
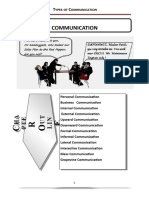
Types of Communication
Hochgeladen von
NicoleCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Types of Communication
Hochgeladen von
NicoleCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
BUSINESS COMMUNICATION
LESSON 3:
TYPES OF COMMUNICATION
Contents
Communication Network
An organization is a composite of many individuals working
Methods of Communication Verbal and nonverbal together, towards its growth. They are constantly interacting
Channels of communication formal and informal with each other and with people outside the company. The
Dimensions of communication upward, downward, horizontal and communication network in an organization is of two types:
diagonal 1. Internal
2. External
We have by now gathered some knowledge on what communi-
Internal Communication
cation is, how is it important in business and key stages of
communication as well. Today we shall learn the different Formal Communication
methods of communication, channels and dimensions of Interaction between members of the same organizations called
communication. internal communication. It could be both formal and informal.
Large organizations with hundreds of people working find it
Introduction very difficult to have direct interaction with each and everyone.
When Anil entered in his office on a Monday morning, he
They adopt a number of strategies, e.g., newsletters, annual
found that somebody had tempered with his personal com-
reports to communicate the essential message. In such large
puter and that it was plugged on. He called up his personal
setups, it is neither possible nor necessary to transmit all
secretary and enquired as to who could have done that. After a
information to every member.
while she reported that two marketing executive came on
Some of the merits of formal communication network are
Saturday evening to seek some information and since he was
discussed below:
not there, they used his computer for that. Sandeep was very
angry and wanted to stop this practice. He called those execu- 1. Satisfy the information needs of the -organization - Formal
tives and and warned them. He issued a memo to this effect channels of communication are designed to cater to the
and distributed it in the office. informational needs of the organization, i.e., when and
where, what kind of information is required and who is to
Here Anil used speech (words spoken), writing (memo) , body
provide it. Thus the formal communication channels are
language (his expression when he talked to the marketing
needed for the very reason of activating information flow in
executives and paralanguage (stern tone of voice) to make his
the organiza-tion.
people aware of his sentiments.
2. Integrates the organization - Formal communication
Both formal (i.e. memo) and informal channels (discussion
channels work as linking wires in a big sized organization,
among employees) contributed to spread the news.
and thus integrate its functioning.
Note the dimensions of communication even in the small
3. Coordination and control- By providing required
office environment. Anil Enquires from his secretary , warns the
information at right time to right places, the formal
executives and issues a memo - all are downward communica-
communication networks greatly facilitates coordination and
tion. Secretary reports, executives reply to Sandeep all are
control in the organization.
upward communication. Secretary enquires about who came in
the bosss room horizontal communication. 4. Sorts the information for high-level executives - Formal
communication channels facilitate the flow of selective
Now we will see the various forms of communication and
information to the top executives. Otherwise they will be
different channels and directions through which communica-
finding themselves in the midst of all relevant and irrelevant
tion may pass.
information.
Methods of Communication 5. Restricts unwanted flow of information - When a person is
One of the ways of communicating is by words whether by supposed to formally communicate some information to
way of speech or by way of writing. Another is by using the some authority, that itself has a restrictive implication that he
expressions other than words , like gestures , body language, need not disseminate this information anywhere else.
etc. A third mode of communication is circumstantial commu-
6. Reliability and accuracy of information - When information
nication, that is the people communicating make no deliberate
moves through formal channel, it has to have some basis to
effort, the message is conveyed by the way the things are . For
substantiate it. It is any time more reliable and accurate than
example : the elaborate dcor of ones office room conveys that
the informally obtained information.
he is holding a high position in the organization. We will divide
our discussion into two categories. However, the formal communication network entails some
limitations also:
Copy Right: Rai University
14 11.234
1. Time consuming and expensive - Since formal Patterns of Grapevine Communication
BUSINESS COMMUNICATION
communication channels involve lot many levels, The grapevine is active in almost every organization. Lets take a
information takes time to travel across. More-over, paper look at how communication travels along the informal
work, involvement of executives time, and other facilities network-the well-known grape-vine. There appear to be four
required for the communication network make it an patterns to this form of communication.
expensive proposi-tion. The single strand is the way in which most people view the
2. It increases the workload of the line supervisor - Since most grapevine. In this, person A tells something to person B, he
of the reporting goes from down to up, generally line tells that to person C, he tells that to another person down
supervisor is the person who has to devote a good deal of the line to Y and so on. This chain is least accurate in passing
time because in forwarding information, under formal the information.
channels. This leaves him with little time to perform other In the gossip chain, one person seeks out and tells everyone
organizational functions properly. the information that he has obtained. This chain is often
3. Information may get distorted - There are dangers of used when information of an interesting but non-job
messages being lost, filtered or distorted as they pass related nature is being conveyed.
through many points. In the probability chain, individuals are indifferent about
4. Creates gaps between top executives and lower subordinates whom they offer information to; they tell people at random,
- Formal communication channels reduce the need of contact and those people in turn tell others at random. This chain is
between the top executive and the subordinates at the lowest often used when the information is mildly interesting but
level. Many a times they do not even recognize each other. insignificant.
This adversely affects superior subordi-nate relationship. In the cluster chain, person A conveys the information to a
Whatever these limitations are, the need for a formal network few selected individuals; some of those individuals then
of communica-tion cannot be done away with. An organization inform a few selected others. Research evidence shows that
has to have a formal commu-nication structure. Of course one the cluster is the most popular pattern that grapevine
can strive to make it more economic and efficient by not being communications take. That is, a few people are active
too rigid and too elaborate. communica-tors on the grapevine. As a rule, only about 10
per cent of the people in an organization act as liaisons who
Informal Communication
pass on information to more than one other person. Which
Informal communication network is not a deliberately formed
individuals are active on the grapevine often depends on the
network. It arises to meet needs that arent satisfied by formal
message. A message that sparks the interest of an employee
communication. Employees form friendships, and cliques
may stimulate him to tell someone else. However, another
develop, they talk in gatherings, the persons working at same
message thats perceived to be of lesser interest may never be
place may talk just like that, and likewise. These in turn allow
transmitted further.
employees to fill. in communication gaps within the formal
channels. Following are some of the sources of informal Grapevine show admirable disregard for rank or authority and
communication: may link organization members in any combination of
directions- horizontal, vertical, and diagonal. As Kieth Devis
1. Grapevine _. channel mostly associated with gossip and
puts it, the grapevine flows around water coolers, down
rumors
hallways, through lunchrooms, and wherever people get
2. Social gatherings - organizational gatherings give a chance to together in groups.
people of various ranks to meet and talk
Merits of informal Communication
3. Management by walking around - where a manager
The informal communication has the following advantages:
informally walks through the work area and casually talk to
employees 1. Satisfies social needs of members - Man being a social
creature needs to have social interaction. Informal
4. Secretaries/administrative assistants - It is very common that
communication satisfies this need very well. Also, it provides
the secre-taries or administrative assistants of the top bosses
the workers an outlet to freely express their fears, views and
pass and receive much information informally.
thoughts.
Since grapevine is the most widespread and commonly used
2. Better human relations - Informal communication is a very
informal commu-nication network, we would discuss it in detail.
good way to promote good human relations in the
The grapevine exists outside the formal channels and is used by
organization.
people to transmit casual, personal, and social interchanges at
work. It is an expression of their natural motivation to com- 3. Speed - The informal communication (specially grapevine) is
muni-cate. It consists of rumors, gossip, and truthful a very speedy network to spread the information. Managers
information. Its speed is very fast as compared formal communi- may use the grapevine to distribute information through
cation. For instance, a study conducted by Keith Davis revealed planned leaks or judiciously placed just between you and
that wife of a plant supervisor has a baby at 11.00 p.m. and a me remarks.
plant survey the next day at 2.00 p.m. showed that 46% of the 4. It works as a linking chain - It links even those people who
management personnel knew of it through the grapevine. do not fall in the official chain of command.
Copy Right: Rai University
11.234 15
5. It serves to fill the possible gaps in the formal While communicating at the internal level, an individual can, on
BUSINESS COMMUNICATION
communication. a few occasions, be slightly relaxed. The same would not hold
true if he is communicating at the external level. Much is at
Limitations of Informal Communication
stake at the time of external communication as individuals are
The limitations of informal communication are as follows:
representatives of the companies, they need to protect the
1. Not authentic - Informal communication is not authentic. image of the organization and create a positive impression that
Different per-sons may distort the message because of has long-lasting impact.
different interpretations.
2. Responsibility cannot be fixed - Informal communication is
Dimensions of Communication
Within an organization, communication may flow downward,
oral in nature and it is very difficult to fix the responsibility
upward, horizontally, or diagonally. Following discussion
of the communicator for the message transmitted. It may
pertains to these dimensions of communication networks:
lead to generation of rumors in the organiza-tion.
3. Not dependable - Informal channels may not always be Downward Communication
active therefore is not dependable. Downward communication occurs when-ever messages flow
from top of the organization through various levels to the
4. It may lead to the leakage of confidential information.
bottom of the organization. There may be several types of
5. Incomplete information - Grapevine information is generally downward commu-nications, namely-:
incomplete.
1. Job procedures/instructions- directions about what to do or
Note that despite all these limitations, the informal communi- how to do the things. For example, when you restock the
cation system permits employees to satisfy their need for social shelves, put the new merchan-dise behind the old stock is
interaction, and works parallel to the formal network. It can be an instruction.
used positively to improve an organizations performance by
2. Job rationale- Explanation of purpose of doing a task in a
creating alternative, and frequently faster and more efficient
certain way. For example, we rotate the stock like that so that
channels of communication. The mangers can do this if they
the customers wont wind up with stale merchandise is a
pay due attention to informal communication networks.
statement explaining the purpose of the instruction given in
External Communication the above example.
Communication is an ongoing process. It does not only take 3. Policies and practices - Information about rules, regulations,
place with people within the organization but with people policies, and practices to be followed. For example, II dont
outside the organization as well. If a company has to survive in try to argue with the unhappy customers. If you cant handle
the competitive environment, it has to adopt the latter form of them, call the manager is an instruction about the practice
communication also. The image of the company is contingent followed in the organization.
upon the relationship that it maintains with people outside.
4. Feedback/motivation - Telling the subordinates about their
External communication can take on a number of forms.
performance and. motivating them, like- life you keep up the
1. Advertising good work, you will be assistant manager by the end of the
2. Media interaction year.
3. Public relations Thus when we say downward communication, we mean that
4. Presentations communication is flowing from upper rung of the ladder of
the organization to the lower one, no matter what form it takes.
5. Negotiations
This communication helps the subordinates to know what is
6. Mails expected of them and brings in greater job satisfaction and
7. Telegrams improves morale of the employees.
8. Letters The main problem with the downward communication is that
External communication could again be oral or written. The when the information passes through various hierarchical
first three forms of communication mentioned above, viz. channels, there are chances that it gets distorted by the time it
advertising, media interaction, and public relations, fall mainly reaches to the targeted person. Since the person giving the
within the domain of corporate communications. Establishing message has different level of understanding than that of the
good relations, negotiating or conducting a deal, interacting receiver, it may also happen that the way receiver interprets the
with clients, issuing tenders, soliciting proposals, sending letters message is not what the sender wants to convey. Very often, in
are all part of external communication. this is a different task as practice, the recipient not having the ability to understand the
interaction takes place and varies between a host of people communication may hinder communication. The message may
belonging to different disciplines, with different personalities also be insufficient or unclear. An example would be a commu-
and different expectations. As communication proceeds with nication quoting the location of a meeting without any
external customers, almost all skills needed for adept communi- instruction on how to find that location. The message could be
cation have to be brought to the fore to avoid any too big to be fully understood in the time available. An
embarrassment or lapse in performance. example would be a manager attempting to explain too much
of a complex task at a time. The result may be confusion, or, at
worst, exasperation.
Copy Right: Rai University
16 11.234
When the message passes through many channels, it may get The main problem is the difference in approach and vision of
BUSINESS COMMUNICATION
delayed. At times the message may get lost in between. different functionaries, who look the things from their own
However, these problems do not undermine the importance of angles.
downward communication. If the efforts are made to make
direct and clear communica-tions, these may be overcome.
Upward Communication - Messages flowing from subordi-
nates to superiors are termed as upward communication. Some
of the examples are given below: Department Department
We will have the job done by tomorrow - is a reply to an A B
equity from the boss. The problem with the machine is
continuing. It stops working after every hour and has to be
restarted. -subordinate informing unsolved work problem to Diagonal or crosswise Communication - Diagonal commu-
the superior. nication cuts across functions and levels in an organization.
When a supervisor in the credit department communicates
Upward communication is important because It helps the top
directly with a regional marketing manager, whos not only in a
management in knowing about the attitudes, behaviour,
different department but also at a higher level in the organiza-
opinions, activities and feelings of the workers on the job. On
tion,- theyre engaged in diagonal communication.
the basis of such knowledge and information, the management
may improve its behaviour, introduce motivational plans and Given the potential for problems, why would individuals resort
improve its controlling function. Subordinates get an outlet for to diagonal communication? The answer again is efficiency and
their grievances, suggestions, and opinions, etc. They may feel speed. In some situations, bypassing vertical and horizontal
that they are contributing towards the goals of the organiza- channels expedites action and prevents others from being used
tion. Despite the importance of upward communication, merely as conduits between senders and receivers. Also, the
employees find it difficult to participate in it. Being frank with increased use of electronic mail systems in organizations has
superiors can be risky, especially when the news is not what the made diagonal communication much easier. A major problem
boss wants to hear. Busy superiors may also be too occupied to with this form of communication is that it departs from the
pay attention to employees. Most of the responsibility for normal chain of command. To minimize communication gaps,
improving upward communication rests with managers. They most diagonal communications also encompass a vertical
can begin the process by announcing their willingness to hear communication to superiors or subordinates who may have
from, subordinates. The management may use an open door been bypassed.
policy, grievance procedures, periodic inter-views, group Communication is required at every level from every direction
meetings and the suggestions book, etc. depending upon the situational need. Formal network channels
facilitate the flow of information in every direction-downward,
upward, horizontal, and diagonal. Although communication
along every dimension entails its own merits and problems, we
Upward Downward cannot do without any of them.
Communication Communication The Strengths and weaknesses of each communication method
are not just a factor of the media elements they can employ, but
also the broad categories that they fall into. There are four
independent dimensions that help considerably in categorizing
the methods:
Horizontal and Lateral Communication - This is a commu- Recorded v live
nication between persons of same hierarchical level. The main Passive v interactive
object of this type of communication is to coordinate the
Local v remote
efforts of different but related activities. The most obvious type
of horizontal communication goes on between members of Push v pull
the same division of an organization; office workers in the
same department, co-workers on a construction project, For
example accounts department calls mainte-nance to get a
machine repaired, hospital admission call intensive care to
reserve a bed and so on.
Horizontal communication helps in coordinating the activities
of different departments at the same level. The departmental
heads may sit together and thrash out problems/wastage of
time, money, labor and-materials.
Copy Right: Rai University
11.234 17
BUSINESS COMMUNICATION
Recorded Live
Recorded communication is prepared in advance of its Live communication is delivered as it happens, in real-time.
delivery. Examples are audio tapes and CDs; videotapes; CD- Examples are live radio and TV broadcasts; one-to-ones;
ROMs; letters, memos and reports; manuals; printed meetings; phone calls and video conferencing calls.
materials; faxes; e-mails; intranet pages and some radio and The advantage of live communication is that it is immediate.
TV broadcasts.
The advantages of recorded communication are that it delivers
a consistent message each time; the message can be a
considered one and the recipient can access the communication
at a time that suits them.
Passive Interactive
Passive communication is one-way. The receiver is not able to Interactive communication is two-way. Each party in the
respond directly to the communication. Examples are audio process is able to send and receive communication. Ex-
tapes and CDs; videotapes; manuals; printed materials; faxes; amples are CD-ROMs (assuming they do not contain purely
radio and TV broadcasts. linear material); letters, memos and e-mails (to the extent
that they are exchanged); the intranet (to the extent that
The advantages of passive communication are that it requires
interactive facilities are provided); one-to-ones; meetings;
less effort from the recipient and that, because there are no
phone calls and videoconferencing calls.The advantages of
opportunities for interaction, it is quicker.
interactive communication are the opportunities it provides
for feedback; the greater degree of confidence it provides that
the message has been understood; the recipient can to some
extent control the pace of the communication and the
message can be tailored to better meet the recipients needs.
Local Remote
Local communication is stand-alone and off-line. It occurs Remote communication is delivered at a distance. It is
where you are, even though it might have been originated at a networked, on-line, transmitted. Examples are e-mails; the
distance. Examples are audio tape and CDs; videotapes; CD- intranet; radio and TV broadcasts; phone calls and
ROMs; letters, memos and reports; manuals; printed videoconferencing calls. The process by which faxes are
materials; one-to-ones and meetings. Faxes are local even transmitted is also remote.
though the process by which they are transmitted is not.The
advantages of local communication are that no sacrifice has to The advantages of remote communication are that there is
be made to quality because of bandwidth limitations and that no delay in getting the message to the recipient, wherever
there are fewer restrictions on where the media can be used or they are and that communication can take place over large
the communication can take place. distances. An advantage of remote, recorded media, such as
intranet pages, is that they can be easily updated centrally.
Push Push communications are sent to specific recipients. Pull Pull communications are made available to be accessed
Examples are letters, memos and reports; faxes and e-mails; at the recipients discretion. Examples are audio tapes and
one-to-ones; meetings; phone calls and videoconferencing CDs; videotapes; CD-ROMs; manuals; printed materials; the
calls.The advantage of push communication is the greater intranet; radio and TV broadcasts.The advantages of pull
certainty that it provides that a message will reach its target communication are that it is less stressful for the recipient
within an appropriate timeframe. and that very large quantities of information can be made
available at any one time.
Communication methods compared
IT IS NOW POSSIBLE to look at the applicability of each method by identifying where it sits against each of the four dimensions
and the media elements it is capable of employing.
Copy Right: Rai University
18 11.234
BUSINESS COMMUNICATION
Characteristics by dimension Characteristics by dimension Characteristics by dimension
Audio Recorded, so consistent, considered, Through the spoken word can be When the message can be conveyed
tape/CD accessible when suits user specific, convey tone of voice using sound alone; when interaction
Passive, so requires less effort from Through non-verbal sounds can create is not required; when recipients have
recipient, quicker emotional response, realism access to players; when no other
medium is suitable, e.g. when
Local, so potential for high quality,
travelling
portable
Typical applications: education and
Pull, so less stressful, good for large
training on the move
quantities of info
Video- Recorded, so consistent, considered, Through the spoken word can be When the message requires high
tape accessible when suits user specific, convey tone of voice quality moving images; when you
Passive, so requires less effort from Through moving images can be direct need to create a memorable impres-
recipient, quicker and memorable, attract attention, sion; when interaction is not
show motion, including body required; when the size of the
Local, so potential for high quality,
language audience makes it cost-effective; when
portable
recipients have access to players
Pull, so less stressful, good for large Through non-verbal sounds can create
emotional response, realism Typical applications: corporate
quantities of info
communications
CD-Rrom Recorded, so consistent, considered, Through the written word can be When the message requires a wide
accessible when suits user specific, self-paced Through the range of media types; when interac-
Interactive, so opportunities for spoken word can be specific, convey tion is required; when the message
feedback, can check message has been tone of voice Through still images can needs to be tailored to the recipient;
understood, recipient can control be direct and memorable, self- when the size of the audience makes
pace, message can be tailored pacedThrough moving images can be it cost-effective; when recipients have
direct and memorable, attract access to players
Local, so potential for high quality,
attention, show motion, including Typical applications: training and
portable
body languageThrough non-verbal point-of-sale programmes
Pull, so less stressful, good for large sounds can create emotional response,
quantities of info realism
Letters / Recorded, so consistent, considered, Through the written word can be When the message can be conveyed
memos / accessible when suits user specific, self-paced using text and still images; when it is
reports Interactive, so opportunities for Through still images can be direct and important that you know the
feedback, can check message has been memorable, self-paced recipient will see the message; when
understood, recipient can control the message needs to be tailored to
pace, message can be tailored the recipient; when e-mail is not
available, when portability is needed
Local, so potential for high quality,
or when hard copy is essential
portable
Typical applications: everyday
Push, so message will reach target on
business communications where no
time
on-line alternative
Manuals Recorded, so consistent, considered, Through the written word can be When the message can be conveyed
accessible when suits user specific, self-paced using text and still images; when an
Passive, so requires less effort from Through still images can be direct and intranet is not available, portability is
recipient, quicker memorable, self-paced needed or hard copy is essential
Local, so potential for high quality, Typical applications: reference, where
portable no on-line alternative
Pull, so less stressful, good for large
quantities of info
Copy Right: Rai University
11.234 19
BUSINESS COMMUNICATION
Characteristics by dimension Characteristics by dimension Characteristics by dimension
Printed Recorded, so consistent, considered, Through the written word can be When the message can be conveyed
materials accessible when suits user specific, self-paced using text and still images; when
Passive, so requires less effort from Through still images can be direct and quality is important; when the size
recipient, quicker memorable, self-paced of the audience makes it cost-
effective; when an intranet is not
Local, so potential for high quality,
available, portability is needed or
portable
hard copy is essential
Pull, so less stressful, good for large
Typical applications: corporate
quantities of info
communications, marketing materials
Fax Recorded, so consistent, considered, Through the written word can be When the message can be conveyed
accessible when suits user specific, self-paced Through still using text and still images; when it is
Passive, so requires less effort from images can be direct and memorable, important that you know the
recipient, quicker self-paced recipient will see the message; when
the recipient is at a distance; when e-
Push, so message will reach target on
mail is not available; when the
time
recipient has a fax machine;
Typical applications: business
messages if no on-line alternative
E-mail Through the written word can be
Recorded, so consistent, considered, specific, self-paced When the message can be conveyed
accessible when suits user using text alone; when it is impor-
Interactive, so opportunities for tant that you know the recipient will
feedback, can check message has been see the message; when the recipient is
understood, recipient can control at a distance; when the message
pace, message can be tailored needs to be tailored to the recipient;
when both parties have e-mail access
Remote, so no delays, regardless of
distance Typical applications: everyday
business communications
Push, so message will reach target on
time
Intranet Recorded, so consistent, considered, Through the written word can be When the message can be conveyed
accessible when suits user specific, self-paced using sound alone; when the
Interactive, so opportunities for Through still images can be direct and recipient is at a distance; (if live)
feedback, can check message has been memorable, self-paced when communication needs to be
understood, recipient can control immediate; when the recipient has a
pace, message can be tailored radio receiver
Remote, so no delays, regardless of Typical applications: none
distance
Pull, so less stressful, good for large
quantities of info
Radio Passive, so requires less effort from Through the spoken word can be When the message can be conveyed
recipient, quicker specific, convey tone of voice using text and still images; when an
Remote, so no delays, regardless of Through non-verbal sounds can create intranet is not available, portability is
distance emotional response, realism needed or hard copy is essential
Pull, so less stressful, good for large Typical applications: reference, where
quantities of info no on-line alternative
Copy Right: Rai University
20 11.234
BUSINESS COMMUNICATION
Characteristics by dimension Characteristics by dimension Characteristics by dimension
TV Passive, so requires less effort from Through the spoken word can be When the message requires high
recipient, quicker Remote, so no delays, specific, convey tone of voice quality moving images; when the
regardless of distancePull, so less Through moving images can be direct recipient is at a distance; (if live)
stressful, good for large quantities of and memorable, attract attention, when communication needs to be
info show motion, including body immediate; when the recipient has a
languageThrough non-verbal sounds TV receiver Typical applications:
can create emotional response, corporate communications using
realism satellite
One to Live, so immediate Through the spoken word can be When the message requires the
Ones Interactive, so opportunities for specific, convey tone of voice parties to see each other; when
feedback, can check message has been Through moving images (in this case interaction is required; when commu-
understood, recipient can control normal sight) can be direct and nication needs to be immediate;
pace, message can be tailored memorable, attract attention, show when the message needs to be
motion, including body language tailored to the recipient
Local, so can take place anywhere
Typical applications: interviews,
Push, so message will reach target on
everyday business communications
time
Meetings Live, so immediate Through the spoken word can be When the message requires the
Interactive, so opportunities for specific, convey tone of voice parties to see each other; when
feedback, can check message has been Through moving images (in this case interaction is required; when commu-
understood, recipient can control normal sight) can be direct and nication needs to be immediate;
pace, message can be tailored memorable, attract attention, show when the message needs to be
motion, including body language tailored to the recipient
Local, so can take place anywhere
Typical applications: presentations,
Push, so message will reach target on
seminars, reviews, briefing sessions,
time
group decision-making
Phone Live, so immediate Through the spoken word can be When the message can be conveyed
Interactive, so opportunities for specific, convey tone of voice using sound alone; when interaction
feedback, can check message has been is required; when communication
understood, recipient can control needs to be immediate; when the
pace, message can be tailored recipient is at a distance; when the
message needs to be tailored to the
Remote, so no delays, regardless of
recipient; when both parties have
distance
access to a phone
Push, so message will reach target on
Typical applications: everyday
time
business communications
Video Live, so immediate Through the spoken word can be When the message requires the
confer- Interactive, so opportunities for specific, convey tone of voice parties to see each other; when
encing feedback, can check message has been Through moving images can be direct interaction is required; when commu-
understood, recipient can control and memorable, attract attention, nication needs to be immediate;
pace, message can be tailored show motion, including body when the recipient is at a distance;
language when the message needs to be
Remote, so no delays, regardless of
tailored to the recipient; when both
distance
parties have access to video
Push, so message will reach target on conferencing facilities
time
Typical applications: important
meetings held at a distance
Copy Right: Rai University
11.234 21
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Communication: Yl:office AdministrationDokument15 SeitenCommunication: Yl:office AdministrationAngel LawsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communicating: Lesson 6Dokument17 SeitenCommunicating: Lesson 6Jackielyn AbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMMUNICATION IN ORGANIZATION PPT FinalDokument34 SeitenCOMMUNICATION IN ORGANIZATION PPT FinalVa Nes SaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rebyuwer Siguro Sa Orgbev Chapter 12Dokument4 SeitenRebyuwer Siguro Sa Orgbev Chapter 12Jerico DungcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 7 Communication in The WorkplaceDokument14 SeitenModule 7 Communication in The WorkplaceHazel TanongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 7 & 8 Latest (Lengkap 15.2.2023)Dokument20 SeitenTopic 7 & 8 Latest (Lengkap 15.2.2023)NURIN ZHARIF SYAHINDAH BINTI ABDULLAHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bus 1Dokument31 SeitenBus 1NNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perception and Communication in Businesss Organization: COMMUNICATION Is A Technique Involving TheDokument3 SeitenPerception and Communication in Businesss Organization: COMMUNICATION Is A Technique Involving TheEethan ENoch keine Bewertungen
- The Communication ProcessDokument2 SeitenThe Communication ProcessBea CiriloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication (Connecting in A Digital World) : Text Book Lesikar's BusinessDokument48 SeitenCommunication (Connecting in A Digital World) : Text Book Lesikar's BusinessIsmail EmonNoch keine Bewertungen
- HUMAN BEHAVIOR IN ORGANIZATIONDokument12 SeitenHUMAN BEHAVIOR IN ORGANIZATIONCrystal ValeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Forms of Business Communicati ONDokument8 SeitenDifferent Forms of Business Communicati ONAngelica MinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMI CH 3 A and BDokument11 SeitenBMI CH 3 A and Bs.casama.gabrieldeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 4Dokument10 SeitenCH 4rozina seidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument41 SeitenUnit 1Raksa MaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Types of Communication 21august 2013 As Was PrintDokument8 Seiten04 Types of Communication 21august 2013 As Was PrintVANNoch keine Bewertungen
- BBA 1 Communication SkillsDokument12 SeitenBBA 1 Communication SkillsSatyam SenNoch keine Bewertungen
- BA 213 - Chapter 6Dokument18 SeitenBA 213 - Chapter 6dororoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication SkillsDokument7 SeitenCommunication SkillsHitesh SemwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Four PDFDokument31 SeitenChapter Four PDFRamadan DestaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6Dokument3 SeitenChapter 6Christian Paul Samog-oy67% (6)
- Chapter 6 CommunicatingDokument24 SeitenChapter 6 CommunicatingRahel Yemane Embaye Tewelde50% (2)
- What Is CommunicationDokument16 SeitenWhat Is CommunicationNoel BactonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 - Communications - Information TechnologyDokument4 Seiten07 - Communications - Information TechnologyLee Ann Peñano CabanlitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 6 COMMUNICATION.Dokument5 SeitenModule 6 COMMUNICATION.Winnie ToribioNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENG 1 WPC - Effective Communication2Dokument36 SeitenENG 1 WPC - Effective Communication2Frances Faye RamoresNoch keine Bewertungen
- BUS COM. - Chapter - 1Dokument48 SeitenBUS COM. - Chapter - 1Rubayet HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Communication As A Crucial Tool in Organizational ManagementDokument5 SeitenAssessment of Communication As A Crucial Tool in Organizational ManagementKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication: Module - 1Dokument22 SeitenCommunication: Module - 1Saloni AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environment: Interpersonal CommunicationDokument6 SeitenEnvironment: Interpersonal CommunicationAnn SerratoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leading (Part 2) : Definition of CommunicationDokument14 SeitenLeading (Part 2) : Definition of CommunicationJoana MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sahid - Managing Communication LDokument12 SeitenSahid - Managing Communication LTabsamsung UnguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership and MngmentDokument32 SeitenLeadership and MngmentGeorgez Joy C. FetizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types and Methods of CommunicationDokument19 SeitenTypes and Methods of Communicationkhushbu guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Types of MotivesDokument1 Seite3 Types of MotivesAT4-11 HUMSS 2 CEDRICK ILAONoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 BC-MGT 269Dokument30 SeitenChapter 1 BC-MGT 269Anonymous lGWT2FK7ko0% (1)
- Types of CommuDokument2 SeitenTypes of CommuFATIMA AYRAA SALIHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Media and Information LiteracyDokument4 SeitenMedia and Information LiteracyHazel TarregaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - Organizational Communication and PowerDokument15 SeitenChapter 5 - Organizational Communication and PowerSteffany RoqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- MNGT 121 Chapter 11 Communication 1Dokument4 SeitenMNGT 121 Chapter 11 Communication 1Ali-al Anzar LanguidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Communication AssignmentDokument19 SeitenBusiness Communication AssignmentashairwaysNoch keine Bewertungen
- BC Lecture Notes DCSDokument63 SeitenBC Lecture Notes DCSBipul KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nature and Scope of CommunicationDokument20 SeitenNature and Scope of Communicationvickey_singh200897383% (6)
- (SUMMARY) Perilaku Keorganisasian (Chapter 11) PDFDokument7 Seiten(SUMMARY) Perilaku Keorganisasian (Chapter 11) PDFtaqi taqaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Communication Assignment No: 1Dokument4 SeitenBusiness Communication Assignment No: 1Naina ImtiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purposive CommunicationDokument7 SeitenPurposive CommunicationGUILLERMO GENESISNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMC (MMS Sem 1)Dokument61 SeitenEMC (MMS Sem 1)Aravind ShekharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Itp - PPT 20231222 193319 0000Dokument12 SeitenItp - PPT 20231222 193319 0000khu.pNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effective Communication For Safety: by Estonido, RicoDokument62 SeitenEffective Communication For Safety: by Estonido, RicoLouis MontecilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAS For Organization and Management (Grade 11)Dokument7 SeitenLAS For Organization and Management (Grade 11)rosellerNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOPIC 1 For StudentsDokument11 SeitenTOPIC 1 For StudentsLoredana BandalacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business CommunicationDokument21 SeitenBusiness CommunicationAbhie GhailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Business CommunicationDokument3 SeitenUnderstanding Business Communicationhanikajason0708Noch keine Bewertungen
- Channels of Communication: Presented ByDokument18 SeitenChannels of Communication: Presented BySachin SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of CommunicationDokument9 SeitenTypes of CommunicationJanie Mae Tupal LorejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meaning of Communication: Process of Transmission: First, Something Is Classification On The Basis On Medium EmployedDokument3 SeitenMeaning of Communication: Process of Transmission: First, Something Is Classification On The Basis On Medium EmployedDonali Gem Manalang PableoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Communication in The WorkplaceDokument17 SeitenChapter 1 - Communication in The WorkplaceMahmudul HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q&A Communication & Interpersonal SkillsDokument55 SeitenQ&A Communication & Interpersonal Skillsselvakumar.uNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of Endorser Types in Political Endorsement AdvertisingDokument25 SeitenEffects of Endorser Types in Political Endorsement AdvertisingNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- PersuasiuneaDokument10 SeitenPersuasiuneaNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capitolul 1 - PersuasiuneaDokument10 SeitenCapitolul 1 - PersuasiuneaNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- American ExperienceDokument1 SeiteAmerican ExperienceNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tipuri de Startegii de PersuasiuneDokument3 SeitenTipuri de Startegii de PersuasiuneNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tipuri de Startegii de PersuasiuneDokument3 SeitenTipuri de Startegii de PersuasiuneNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- PersuasiuneaDokument10 SeitenPersuasiuneaNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principii de Organizare A Mesajelor Corporatiste: Communication For Success, Flat WorldDokument4 SeitenPrincipii de Organizare A Mesajelor Corporatiste: Communication For Success, Flat WorldNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporation in American Society Denny May 2008Dokument35 SeitenCorporation in American Society Denny May 2008jamilkhannNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 C'S' and 4 S'S: 10 11.234 © Copy Right: Rai UniversityDokument2 Seiten7 C'S' and 4 S'S: 10 11.234 © Copy Right: Rai UniversityNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- (P14) Madukar, BC. InterviewsDokument22 Seiten(P14) Madukar, BC. InterviewsIoana Iuly MateiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types & Methods of CommunicationDokument6 SeitenTypes & Methods of CommunicationNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- (P14) Madukar, BC. InterviewsDokument22 Seiten(P14) Madukar, BC. InterviewsIoana Iuly MateiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 10: Listening Skills: 1. Prejudice Against The Speaker - at Times We Have ConflictDokument6 SeitenLesson 10: Listening Skills: 1. Prejudice Against The Speaker - at Times We Have ConflictNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spencer, Where Is Public Affairs Going PDFDokument4 SeitenSpencer, Where Is Public Affairs Going PDFNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post, Managing Public AffairsDokument16 SeitenPost, Managing Public AffairsNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objectives of Business CommunicationDokument4 SeitenObjectives of Business CommunicationNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extras: Listening ProcessDokument9 SeitenExtras: Listening ProcessNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- StakeholdersDokument2 SeitenStakeholdersNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spencer, Where Is Public Affairs GoingDokument4 SeitenSpencer, Where Is Public Affairs GoingNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Handbook of Public AffairsDokument598 SeitenThe Handbook of Public AffairsNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caldwell, The Public Affairs FunctionDokument4 SeitenCaldwell, The Public Affairs FunctionNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allen, Public Affairs-New Wave of ResearchDokument9 SeitenAllen, Public Affairs-New Wave of ResearchNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass MediaDokument9 SeitenMass MediaNicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 2Dokument32 SeitenPresentation 2NicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deh-X6650bt Deh-X4650bt Operating Manual (Eng-Por-Esp)Dokument72 SeitenDeh-X6650bt Deh-X4650bt Operating Manual (Eng-Por-Esp)lgszlgsz0% (1)
- 18Csc203J:Computer Organization and ArchitectureDokument56 Seiten18Csc203J:Computer Organization and ArchitectureSENTHIL RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technics SL p999Dokument58 SeitenTechnics SL p999garberer1100% (1)
- Cde 126 BTDokument70 SeitenCde 126 BTFelisha TrujilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2004 07 PDFDokument84 Seiten2004 07 PDFGeorge Acosta100% (1)
- Axm p90rs Deq p01Dokument41 SeitenAxm p90rs Deq p01khairul izwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiat Scudo RadioDokument22 SeitenFiat Scudo RadioAnonymous iYKTkmhpZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cdrom Drive OffsetsDokument74 SeitenCdrom Drive OffsetsJuerrt5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Compaq Presario P5000Dokument95 SeitenCompaq Presario P5000Anonymous rp7BuFyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary and Secondary MemoryDokument44 SeitenPrimary and Secondary Memoryshahabuddin khan100% (2)
- Pioneer DEH-200MP Owners Manual English RussianDokument47 SeitenPioneer DEH-200MP Owners Manual English RussianDonald HeyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aiwa CSD fd77 Manual de Usuario Páginas 9 12Dokument4 SeitenAiwa CSD fd77 Manual de Usuario Páginas 9 12Mr. Gonza M.Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4K Ultra HD Blu-Ray - SONYDokument44 Seiten4K Ultra HD Blu-Ray - SONYAlfonso CalderonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schema Technics RAK CH219WHDokument2 SeitenSchema Technics RAK CH219WHJosif LombauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Radio Pionner 1650Dokument200 SeitenManual Radio Pionner 1650jamaya82Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ict GenerationDokument55 SeitenIct GenerationGODFREY MULOKOZINoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Manual Acer TravelMate 540 Series PDFDokument127 SeitenService Manual Acer TravelMate 540 Series PDFmohzgo100% (1)
- Blu-Ray Disc (Seminar Report)Dokument15 SeitenBlu-Ray Disc (Seminar Report)api-26629623100% (1)
- CatalogDokument115 SeitenCatalogJorge Luis SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Holographic Memory: October 2015Dokument23 SeitenHolographic Memory: October 2015tobilobaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Information Reference Line 069 Belt-Drive CD Player: Art For The EarDokument3 SeitenProduct Information Reference Line 069 Belt-Drive CD Player: Art For The EarAdrian HesseNoch keine Bewertungen
- NewOctavia Accessories ENG PDFDokument15 SeitenNewOctavia Accessories ENG PDFTajma Dziho100% (1)
- DEH-3730MP DEH-3700MP: Operation ManualDokument84 SeitenDEH-3730MP DEH-3700MP: Operation ManualNori AbdennourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Input-output-And Storage DevicesDokument20 SeitenInput-output-And Storage DevicesDinesh Acharya100% (2)
- Computer BasicsDokument409 SeitenComputer Basicsmukesh_kumar_470% (1)
- Yes No: Siemens Manual CD - 7ML19985KG01, Rev. 1.6Dokument2 SeitenYes No: Siemens Manual CD - 7ML19985KG01, Rev. 1.6mohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- BP Sample 4 A Record LabelDokument16 SeitenBP Sample 4 A Record Labelhanire40100% (1)
- DVD Conversion: Video Tapes (VHS, VHS-C, Hi-8, Mini DV)Dokument2 SeitenDVD Conversion: Video Tapes (VHS, VHS-C, Hi-8, Mini DV)Trigos NetshopNoch keine Bewertungen