Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Toxic - Gas - Measurement PDF
Hochgeladen von
Touhid IslamOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Toxic - Gas - Measurement PDF
Hochgeladen von
Touhid IslamCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Date August 27, 2001
Toxic gas measurement: No AN20010827
Application Note Ceiling, TWA and STEL By Lars Boettern
Preface Carbon monoxide (CO) is a good ex- Time Weighted Average (TWA):
ample of a chronically toxic gas. Car-
Many toxic substances are commonly bon monoxide bonds to the hemoglo- TWA values are calculated by taking
encountered in industry. The presence bin molecules in red blood cells. Red the sum of exposure during a workday
of toxic substances may be due to blood cells contaminated with CO are to a particular toxic contaminant in
materials being stored or used, the unable to transport Oxygen. Although terms of parts-per-million-hours and
work being performed, or may be gen- very high concentrations of carbon dividing by an eight-hour period.
erated by natural processes. Exposure monoxide may be acutely toxic, and
to toxic substances can produce dis- lead to immediate respiratory arrest or
ease, bodily injury, or death in unpro- death, it is the long term physiological
tected workers. effects due to chronic exposure at
It is important to determine the lower levels that take the greatest toll
amounts of any toxic materials poten- on affected workers. This is the situa-
tially present in the workplace. The tion with regards to smokers, parking
amounts of toxic materials potentially garage attendants, or others chroni-
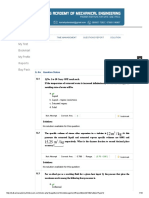
cally exposed to carbon monoxide in Due to the fact that the TWA calcula-
present will determine the procedures tion involves the division of the sum
and personal protective equipment, the workplace. Exposure levels are
frequently too low to produce imme- of exposure by 8 hours, the TWA
which must be used. The safest course value varies with the length of the ex-
of action is to eliminate or perma- diate symptoms, but small repeated
exposures systematically reduce the posure as shown in the chart below.
nently control hazards through engi-
neering, workplace controls, ventila- bloods capacity to carry oxygen, . Exposure Avg. Con-
This partial impairment of the blood TWA
tion, or other safety procedures. Un- Time centration
protected workers may not be exposed supply may lead over time to serious 4 Hours 100 PPM 50 PPM
to levels of toxic contaminants, which physiological consequences. 8 Hours 100 PPM 100 PPM
exceed Permissible Exposure Limit Prudent monitoring programs must 12 Hours 100 PPM 150 PPM
(PEL) concentrations. Ongoing take both short and long-term expo-
monitoring is necessary to insure that sures risks into account, so there are Short Term Exposure Limits
exposure levels have not changed in a three independent exposure measure- (STEL)
way that requires the use of different ments and alarm types built into the
or more rigorous procedures or design of all Biosystems toxic gas de- Toxic substances may have short-term
equipment. tectors. exposure limits, which are higher than
the eight hour TWA. The STEL is the
Airborne toxic substances are typi- maximum average concentration to
cally classified on the basis of their Ceiling level
which an unprotected worker may be
ability to produce physiological ef- exposed in any fifteen-minute interval
OSHA has assigned some, but not all,
fects on exposed workers. Toxic sub- during the day.
toxic substances with a ceiling level.
stances tend to produce symptoms in
This is the highest concentration of a
two time frames.
toxic substance to which an unpro-
Higher levels of exposure tend to pro- tected worker should ever be exposed,
duce immediate and acute physiologi- even for a very short time. Never enter
cal responses, while lower levels of an environment even momentarily
exposure over long periods of time when concentrations of toxic sub-
may not produce physical symptoms stances exceed the ceiling level.
for years.
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a good ex- Any fifteen-minute periods in which
ample of an acutely toxic substance, the average STEL concentration ex-
which is immediately lethal at rela- ceeds the permissible level must be
tively low concentrations. Exposure to separated from each other by at least
a 1,000 PPM (parts per million) con- one hour. A maximum of four of these
centration of H2S in air produces periods is allowed per eight-hour shift.
rapid paralysis of the respiratory sys-
tem, cardiac arrest, and death within
minutes.
Page 1 of 1
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Toxic Gas MeasurementDokument1 SeiteToxic Gas MeasurementLeo ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Process SafetyDokument37 SeitenChemical Process Safetyharish14586Noch keine Bewertungen
- ELA909 Lecture1 IntroductionandFundamentalsDokument68 SeitenELA909 Lecture1 IntroductionandFundamentalsXavier MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Property Standard Method For DeterminationDokument5 SeitenProperty Standard Method For DeterminationvannesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Toxic EffectsDokument4 SeitenTypes of Toxic Effectsmsaqibraza93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrogen Sulfide - Health Effects, Detection and Exposure PreventionDokument16 SeitenHydrogen Sulfide - Health Effects, Detection and Exposure PreventionsorinakesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assess and Apply Basic Principles of ChemistryDokument30 SeitenAssess and Apply Basic Principles of ChemistryyousefNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.3 Workplace Environment Measurement: OSHS Rule 1071 - General ProvisionsDokument8 Seiten2.3 Workplace Environment Measurement: OSHS Rule 1071 - General ProvisionsMarianne BallesterosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Threshold Limit Values For Chemical Substances: Adopted by ACGIH With Intended ChangesDokument18 SeitenThreshold Limit Values For Chemical Substances: Adopted by ACGIH With Intended ChangesrosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- New TLV Exposure Limit - Measuring Hydrogen Sulfide From Cole-Parmer IndiaDokument4 SeitenNew TLV Exposure Limit - Measuring Hydrogen Sulfide From Cole-Parmer Indiaromerov24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ozone Solutions MSDS OzoneDokument4 SeitenOzone Solutions MSDS OzoneHasnanurfajriahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glossary of MSDS TermsDokument13 SeitenGlossary of MSDS TermsNguyen Duc Dung100% (1)
- L DNu MD 5 OK3Dokument2 SeitenL DNu MD 5 OK3Wen InsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental, Health, and Safety OverviewDokument11 SeitenEnvironmental, Health, and Safety OverviewBradSiefkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industry AbbreviationsDokument39 SeitenIndustry Abbreviationsrafik1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Key Concepts in Gas Detection: A Guide To Understanding Todays's Gas Detection TechnologyDokument6 SeitenKey Concepts in Gas Detection: A Guide To Understanding Todays's Gas Detection TechnologyRobVajkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental and Safety Aspects in Process IndustriesDokument6 SeitenEnvironmental and Safety Aspects in Process Industriesyadavsuyash007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Significance of Threshold Limit ValuesDokument30 SeitenSignificance of Threshold Limit ValuesZankhana Dave100% (5)
- Epichlorohydrin Handling and Safety ManualDokument6 SeitenEpichlorohydrin Handling and Safety Manualubaid_nedianNoch keine Bewertungen
- UK Operations Guidelines For Drilling Operations: Subject: H2S (Hydrogen Sulphide) ProceduresDokument13 SeitenUK Operations Guidelines For Drilling Operations: Subject: H2S (Hydrogen Sulphide) ProceduresMostafa ElghifaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haz ChemDokument5 SeitenHaz ChemguhadebasisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 60 - Sensor TriggerDokument9 Seiten60 - Sensor TriggerP SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 5 Oh StandardsDokument31 SeitenTopic 5 Oh StandardsAqill 01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To IHDokument100 SeitenIntro To IHHazem TawfikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hazardous Materials: Toxic Substances Hazardous SubstancesDokument8 SeitenHazardous Materials: Toxic Substances Hazardous Substancesdineshv74Noch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Engineeringin Process Plantsmodule2Dokument20 SeitenSafety Engineeringin Process Plantsmodule2yurirostovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health and Safety HazardsDokument4 SeitenHealth and Safety HazardsAbdullah IshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Acute Inhalation Toxicity": Adopted: 12 May 1981Dokument14 Seiten"Acute Inhalation Toxicity": Adopted: 12 May 1981Intan NoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 04 805 Safety Engineering in Process Plants - Module2Dokument43 SeitenCH 04 805 Safety Engineering in Process Plants - Module2JEFY JEAN ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Effluent Gas MonitoringDokument10 SeitenEffluent Gas Monitoringwcms00Noch keine Bewertungen
- Material Safety Data Sheet: 1. Chemical Product and Company Identification (Rev. 9-04)Dokument8 SeitenMaterial Safety Data Sheet: 1. Chemical Product and Company Identification (Rev. 9-04)Arcangelo Di TanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day 2 Occupational Health HazardsDokument62 SeitenDay 2 Occupational Health Hazardsmike cams100% (2)
- Unit 2CDokument4 SeitenUnit 2CNella NellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MsdsDokument7 SeitenMsdsFebriansyah AnandyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4 Occupational Health StandardDokument41 SeitenLecture 4 Occupational Health Standardsiti zubaidahNoch keine Bewertungen
- ToxicologyDokument31 SeitenToxicologyHeart Hacker HarryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advancements in The Study of H2S Toxicology. IIDokument13 SeitenAdvancements in The Study of H2S Toxicology. IIMurthy FSAINoch keine Bewertungen
- Xenon Lan The Us CompleteDokument5 SeitenXenon Lan The Us CompleteAC_REGISTERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anesthetic GasDokument3 SeitenAnesthetic GasJuan PáezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 3 ToxicologyDokument20 Seiten2 3 ToxicologyNanmathi Balachandran 10G 21Noch keine Bewertungen
- 54 Strating NeedleTrapDokument11 Seiten54 Strating NeedleTrapP SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benzene (MSDS)Dokument8 SeitenBenzene (MSDS)Hikaru Graeme Enoki-JolliffeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bai Tap Chuong 3Dokument10 SeitenBai Tap Chuong 3Quynh NhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isoflurane MsdsDokument4 SeitenIsoflurane Msdsrangga_rspNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atmosphric PollutionDokument10 SeitenAtmosphric Pollutionعلي الاسديNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pak Waluyo - Standards-and-LimitsDokument37 SeitenPak Waluyo - Standards-and-LimitsNdra NugrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Republic of Turkey Ministry of Labour and Social Security Occupational Health and Safety CenterDokument55 SeitenRepublic of Turkey Ministry of Labour and Social Security Occupational Health and Safety CenterKim Lien TrinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC07 Chemical Safety IDokument108 SeitenMC07 Chemical Safety ISeayoung LEENoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen: Liquid Oxygen Can Cause Severe Skin and EyeDokument6 SeitenOxygen: Liquid Oxygen Can Cause Severe Skin and EyeSHERIEFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toxicity PDFDokument41 SeitenToxicity PDFFazlinda Ziadi0% (1)
- Threshold Limit Value - Wikipedia PDFDokument17 SeitenThreshold Limit Value - Wikipedia PDFManojkumar0% (1)
- Occupational Lead Poisoning - American Family PhysicianDokument15 SeitenOccupational Lead Poisoning - American Family Physicianyasser ChemssoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module IIIDokument104 SeitenModule IIIibuddhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Engineering: Applied Science & Computing 2008Dokument46 SeitenSafety Engineering: Applied Science & Computing 2008falkirk10bNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sewer Pipe Inspecting CleaningDokument6 SeitenSewer Pipe Inspecting CleaningShah MuzzamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Data Sheet For OzoneDokument3 SeitenSafety Data Sheet For OzoneJKP Gradska čistoća BeogradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eto SterilizationDokument9 SeitenEto SterilizationEjaj SumitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hazard of Toxicity H2SDokument29 SeitenHazard of Toxicity H2SBerbik MukorobinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 3Dokument95 SeitenLec 3Vivek Kumar M LNoch keine Bewertungen
- DM Plan Belkuchi - English PDFDokument261 SeitenDM Plan Belkuchi - English PDFTouhid IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bertelsen2001 Article FutureUSMotorVehicleEmissionStDokument8 SeitenBertelsen2001 Article FutureUSMotorVehicleEmissionStTouhid IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Degree Completion Checklist-Summary College of Graduate Studies, The University of ToledoDokument1 SeiteDegree Completion Checklist-Summary College of Graduate Studies, The University of ToledoTouhid IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- FuMaTech FumasepmembranesDokument4 SeitenFuMaTech FumasepmembranesTouhid IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Khanna's Objective Questions in Petroleum EngineeringDokument396 SeitenKhanna's Objective Questions in Petroleum EngineeringTouhid Islam92% (13)
- 10.isca RJCS 2015 106Dokument5 Seiten10.isca RJCS 2015 106Touhid IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Email ProfessorsDokument12 SeitenHow To Email ProfessorsTouhid IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vapor Liquid EquilibriumDokument39 SeitenVapor Liquid EquilibriumTouhid IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Industrial Training at Eastern Refinery LimitedDokument109 SeitenReport On Industrial Training at Eastern Refinery LimitedTouhid Islam67% (3)
- Inter-Phase Mass TransferDokument12 SeitenInter-Phase Mass TransferTouhid IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tubular Bowl CentrifugeDokument22 SeitenTubular Bowl CentrifugeTouhid Islam100% (1)
- Crude Tower Simulation Using Aspen HYSYSDokument32 SeitenCrude Tower Simulation Using Aspen HYSYSTouhid Islam100% (2)
- Spectrophotometric Determination of Protein ConcentrationDokument16 SeitenSpectrophotometric Determination of Protein ConcentrationTouhid IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Durability Studies On Concrete With Fly Ash & GGBS: A.H.L.Swaroop, K.Venkateswararao, Prof P KodandaramaraoDokument5 SeitenDurability Studies On Concrete With Fly Ash & GGBS: A.H.L.Swaroop, K.Venkateswararao, Prof P Kodandaramaraoபுருஷோத்தமன் சரவணன்Noch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer To Fluids With Phase ChangeDokument9 SeitenHeat Transfer To Fluids With Phase Changepraveen4ubvsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heavy Metal - Metalsorb eDokument4 SeitenHeavy Metal - Metalsorb ehclpmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 1Dokument295 SeitenPaper 1Shreyas TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- MetalCoat 470 480 Brochure enDokument9 SeitenMetalCoat 470 480 Brochure endanceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Practice QuestionsDokument6 SeitenGas Practice QuestionsJames DellavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project 4 Ethylene OxideDokument12 SeitenProject 4 Ethylene OxideNhan Nguyen Van100% (4)
- En 10263-1Dokument30 SeitenEn 10263-1Mogos PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Accredited List of Accredited EIA Consultant Organizations (As On March 05, 2015) Organizations - 170Dokument135 SeitenList of Accredited List of Accredited EIA Consultant Organizations (As On March 05, 2015) Organizations - 170santhoshneo02@gmail.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaowool Board Low Temperature PDFDokument2 SeitenKaowool Board Low Temperature PDFmaxibarrios72Noch keine Bewertungen
- Zhang 2022Dokument10 SeitenZhang 2022Statistics LearningNoch keine Bewertungen
- Component in Making Fiber Board As Substitute For HardiflexDokument9 SeitenComponent in Making Fiber Board As Substitute For Hardiflexxiniac_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Transformers: Erection, Commissioning, Operation and Maintenance Manual FORDokument229 SeitenTransformers: Erection, Commissioning, Operation and Maintenance Manual FORJyoti Prakash Prusty100% (1)
- OctaveDokument2 SeitenOctaveDavid CovatzinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method For Ultra High Purity Gold - Gold Refining ForumDokument11 SeitenMethod For Ultra High Purity Gold - Gold Refining Forummladen lakic100% (1)
- TDS OF H-408 Silicone Adjuvant For AgricultureDokument2 SeitenTDS OF H-408 Silicone Adjuvant For AgricultureAda FuNoch keine Bewertungen
- USP Monographs - Miconazole NitrateDokument2 SeitenUSP Monographs - Miconazole NitrateMukarram MudjahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dyestone Blue MX SDS SA-0186-01Dokument5 SeitenDyestone Blue MX SDS SA-0186-01gede aris prayoga mahardikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading Focus Grade 7Dokument38 SeitenReading Focus Grade 7Khristie Lyn AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dissolution GelatinDokument14 SeitenDissolution Gelatinايناس ماجدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sodium Metabisulphite RPTDokument51 SeitenSodium Metabisulphite RPTGodolias WoldemariamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nitrogen, Total, TNT, 0 To 25.0, Persulfate Digestion Method 10071Dokument9 SeitenNitrogen, Total, TNT, 0 To 25.0, Persulfate Digestion Method 10071Dwiyana YogasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stoichiometry: Calculations With Chemical Formulas and EquationsDokument47 SeitenStoichiometry: Calculations With Chemical Formulas and EquationsAngelo Miguel GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis EnvironmentDokument66 SeitenThesis EnvironmentSorathNoch keine Bewertungen
- GATE-2018 - Mechanical Engineering Online Test Series ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICSDokument10 SeitenGATE-2018 - Mechanical Engineering Online Test Series ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICSDebashis NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brochures WSM2-Y PDFDokument16 SeitenBrochures WSM2-Y PDFkunkzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hot Work PermitDokument2 SeitenHot Work PermitRex UrbiztondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HDPE CatalogDokument56 SeitenHDPE CatalogSalwa AlsamnehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bateria Data PDFDokument2 SeitenBateria Data PDFJulian GuascalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carnauba-Super-Micropowder 2442 P 5: ApplicationDokument1 SeiteCarnauba-Super-Micropowder 2442 P 5: Application333cubi333Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Age of Agile: How Smart Companies Are Transforming the Way Work Gets DoneVon EverandThe Age of Agile: How Smart Companies Are Transforming the Way Work Gets DoneBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (5)
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelVon EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Electrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tVon EverandElectrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (27)
- Design Thinking and Innovation Metrics: Powerful Tools to Manage Creativity, OKRs, Product, and Business SuccessVon EverandDesign Thinking and Innovation Metrics: Powerful Tools to Manage Creativity, OKRs, Product, and Business SuccessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laws of UX: Using Psychology to Design Better Products & ServicesVon EverandLaws of UX: Using Psychology to Design Better Products & ServicesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (9)
- The Design Thinking Playbook: Mindful Digital Transformation of Teams, Products, Services, Businesses and EcosystemsVon EverandThe Design Thinking Playbook: Mindful Digital Transformation of Teams, Products, Services, Businesses and EcosystemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureVon EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- CATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part I : Getting Started and Sketcher WorkbenchVon EverandCATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part I : Getting Started and Sketcher WorkbenchBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (10)
- Designing for Behavior Change: Applying Psychology and Behavioral Economics 2nd EditionVon EverandDesigning for Behavior Change: Applying Psychology and Behavioral Economics 2nd EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- 507 Mechanical Movements: Mechanisms and DevicesVon Everand507 Mechanical Movements: Mechanisms and DevicesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (28)
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsVon EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)
- The Maker's Field Guide: The Art & Science of Making Anything ImaginableVon EverandThe Maker's Field Guide: The Art & Science of Making Anything ImaginableNoch keine Bewertungen
- Articulating Design Decisions: Communicate with Stakeholders, Keep Your Sanity, and Deliver the Best User ExperienceVon EverandArticulating Design Decisions: Communicate with Stakeholders, Keep Your Sanity, and Deliver the Best User ExperienceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (19)
- UX: Simple and Effective Methods for Designing UX Great Products Using UX Programming TheoriesVon EverandUX: Simple and Effective Methods for Designing UX Great Products Using UX Programming TheoriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design for How People Think: Using Brain Science to Build Better ProductsVon EverandDesign for How People Think: Using Brain Science to Build Better ProductsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (8)
- Arowana: The Complete Owner’s Guide for the Most Expensive Fish in the World - Arowana Fish Tank, Types, Care, Food, Habitat, Breeding, Mythology – Includes Silver, Platinum, Red, Jardini, Black, Golden, GreenVon EverandArowana: The Complete Owner’s Guide for the Most Expensive Fish in the World - Arowana Fish Tank, Types, Care, Food, Habitat, Breeding, Mythology – Includes Silver, Platinum, Red, Jardini, Black, Golden, GreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Big Book of Pet Names ~ More than 10,000 Pet Names! The Most Complete Guide to Pet Names & MeaningsVon EverandThe Big Book of Pet Names ~ More than 10,000 Pet Names! The Most Complete Guide to Pet Names & MeaningsNoch keine Bewertungen