Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Sasasdsa
Hochgeladen von
jeff2010pax0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
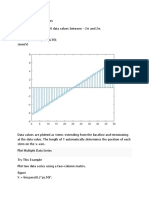
12 Ansichten2 SeitenVárias coisas que não sei explicar no moento.
Originaltitel
sasasdsa
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenVárias coisas que não sei explicar no moento.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
12 Ansichten2 SeitenSasasdsa
Hochgeladen von
jeff2010paxVárias coisas que não sei explicar no moento.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
cv::Mat padded; //expand input image to optimal size
int m = cv::getOptimalDFTSize(I.rows);
int n = cv::getOptimalDFTSize(I.cols); // on the border add zero values
cv::copyMakeBorder(I, padded, 0, m - I.rows, 0, n - I.cols,
cv::BORDER_CONSTANT, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat planes[] = { cv::Mat_<float>(padded), cv::Mat::zeros(padded.size(),
CV_32F) };
cv::Mat complexI;
cv::merge(planes, 2, complexI); // Add to the expanded another plane
with zeros
cv::dft(complexI, complexI); // this way the result may fit in the
source matrix
// compute the
magnitude and switch to logarithmic scale
// => log(1 +
sqrt(Re(DFT(I))^2 + Im(DFT(I))^2))
cv::split(complexI, planes); // planes[0] = Re(DFT(I),
planes[1] = Im(DFT(I))
cv::magnitude(planes[0], planes[1], planes[0]);// planes[0] = magnitude
cv::Mat magI = planes[0];
magI += cv::Scalar::all(1); // switch to logarithmic scale
cv::log(magI, magI);
// crop the spectrum, if it has an odd number of rows or columns
magI = magI(cv::Rect(0, 0, magI.cols & -2, magI.rows & -2));
// rearrange the quadrants of Fourier image so that the origin is at the
image center
int cx = magI.cols / 2;
int cy = magI.rows / 2;
cv::Mat q0(magI, cv::Rect(0, 0, cx, cy)); // Top-Left - Create a ROI per
quadrant
cv::Mat q1(magI, cv::Rect(cx, 0, cx, cy)); // Top-Right
cv::Mat q2(magI, cv::Rect(0, cy, cx, cy)); // Bottom-Left
cv::Mat q3(magI, cv::Rect(cx, cy, cx, cy)); // Bottom-Right
cv::Mat tmp; // swap quadrants (Top-Left with
Bottom-Right)
q0.copyTo(tmp);
q3.copyTo(q0);
tmp.copyTo(q3);
q1.copyTo(tmp); // swap quadrant (Top-Right with Bottom-
Left)
q2.copyTo(q1);
tmp.copyTo(q2);
cv::normalize(magI, magI, 0, 1, CV_MINMAX); // Transform the matrix with
float values into a
//
viewable image form (float between values 0 and 1).
cv::Mat bgr_planes[3]; ///
Separate the image in 3 places ( B, G and R )
/// Compute the histograms:
cv::calcHist(&bgr_planes[0], 1, 0, cv::Mat(), b_hist, 1, &histSize,
&histRange, uniform, accumulate);
cv::calcHist(&bgr_planes[1], 1, 0, cv::Mat(), g_hist, 1, &histSize,
&histRange, uniform, accumulate);
cv::calcHist(&bgr_planes[2], 1, 0, cv::Mat(), r_hist, 1, &histSize,
&histRange, uniform, accumulate);
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Mgre NotesDokument319 SeitenMgre NotesHan JuliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book The Algebra of Coplanar VectorDokument384 SeitenBook The Algebra of Coplanar VectorCr CharleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Periodic Test in Math Grade 8Dokument3 SeitenFirst Periodic Test in Math Grade 8Gerson Acosta86% (44)
- Binomial TheoremDokument13 SeitenBinomial Theoremvipul daveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full PDFDokument2.311 SeitenFull PDFJennifer Reyna Guillén100% (1)
- Radical Equations 2Dokument4 SeitenRadical Equations 2api-304977850Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2606 Maths Paper With Solution EveningDokument10 Seiten2606 Maths Paper With Solution EveningAkshaan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gra de 11 Functions WorksheetDokument4 SeitenGra de 11 Functions WorksheetLincoln Munashe KaparadzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANPDokument10 SeitenANPRoumaissa Gueddouche100% (1)
- CS 5104 NP-Completeness notesDokument9 SeitenCS 5104 NP-Completeness notesCuong TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ss 2Dokument5 SeitenSs 2Raja AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam ProblemsDokument5 SeitenExam ProblemsVan DungctNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matrix Chain Multiplication - DP OptimizationDokument19 SeitenMatrix Chain Multiplication - DP OptimizationArslan Ahmed DanishNoch keine Bewertungen
- From: Powered by ©Dokument12 SeitenFrom: Powered by ©mech_lalit2k77856Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ch6 - Linear ProgrammingDokument22 SeitenCh6 - Linear Programminghehehehehe_Noch keine Bewertungen
- PDE SolutionsDokument4 SeitenPDE SolutionsSamer AL SalhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec8 PDFDokument42 SeitenLec8 PDFbipin bamNoch keine Bewertungen
- MA 109 College Algebra Chapter 1 PDFDokument20 SeitenMA 109 College Algebra Chapter 1 PDFr22_22Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7.1 09 - Real Numbers Solved Questions PDFDokument8 Seiten7.1 09 - Real Numbers Solved Questions PDFloveriarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet01dated05072021 PDFDokument1 SeiteWorksheet01dated05072021 PDFPushpendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to find the last installment in a loan repayment series with decreasing installmentsDokument13 SeitenHow to find the last installment in a loan repayment series with decreasing installmentsKshama GiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- L1 Examples - Introduction To First Order Differential EquationsDokument6 SeitenL1 Examples - Introduction To First Order Differential EquationsCarlo EdolmoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 11U Mid Term My Exam FinalDokument10 SeitenGrade 11U Mid Term My Exam FinalAshley OffmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus Format PG MathsDokument26 SeitenSyllabus Format PG MathsTotal FunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mth302a FCHDokument2 SeitenMth302a FCHDhruvil SanganiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus 2 A Simplified Text in Integral CalculusDokument150 SeitenCalculus 2 A Simplified Text in Integral CalculusRic NapusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mycbseguide: Cbse Class 10 Mathematics Sample Paper - 01 (MCQ Based)Dokument13 SeitenMycbseguide: Cbse Class 10 Mathematics Sample Paper - 01 (MCQ Based)rajitha GouraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assign5sol EE650Dokument3 SeitenAssign5sol EE650Pradeep KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 5 - SolutionDokument5 SeitenWorksheet 5 - SolutionalyNoch keine Bewertungen
- G 1 1 P - C M (3 0 S) : Final Practice ExamDokument32 SeitenG 1 1 P - C M (3 0 S) : Final Practice ExamIan Jeff DimaunahanNoch keine Bewertungen