Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pricing and Costing in A Competitive Environment Answers To End of Chapter Exercises
Hochgeladen von
Jay BrockOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pricing and Costing in A Competitive Environment Answers To End of Chapter Exercises
Hochgeladen von
Jay BrockCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
Chapter 2
Pricing and Costing in a Competitive Environment
Answers to End of Chapter Exercises
Q 2.1
Selling price per unit 36 30
Variable cost per unit 21 21
Contribution per unit 15 9
Units 4300 5800
Total contribution 64500 52200
i) A price of 36 leads to the higher contribution.
ii) There is a need to check assumptions; marketing strategy of the company,
A B
Q 2.2
Labour 10 5
Material 5 6
Overhead 5 5
Total cost 20 16
Mark-up (20%) 4 3.2
Selling price 24 19.2
Contribution 5
Contn 10 units 50
The management would need to consider whether it is a sufficiently large contract to
justify this contract. It would be necessary to consider the potential implications of:
i) The reaction of other customers if they find out about this large discount.
ii) The reaction of other competitors if they hear about these large discounts
being provided.
iii) Assumptions on costs
Q 2.3
Direct labour 200
Direct material 100
Overhead 100
400
20% profit margin 80
Quote 480
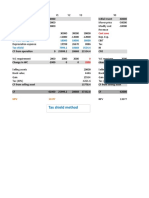
Q 2.4 Selling price 40 38 36 34 32 30 28
Variable cost 20 20 20 20 20 20 20
Contribution 20 18 16 14 12 10 8
Demand 2000 2400 3000 3800 4800 6000 7500
Total contribution 40000 43200 48000 53200 57600 60000 60000
Fixed cost 8000 12000 12000 16000 20000 24000 32000
Profit 32000 31200 36000 37200 37600 36000 28000
The optimum price that will lead to maximum profits is 32
Assumptions on costs at different volumes and the assumed relationship between price
and volume.
2008 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
www.wileyeurope.com/college/bowhill
2
Q 2.5 Revenue 50 x 25,000 = 1,250,000
Total cost 1,000,000
Profit 250,000
a) return on sales is 25%
b) Need to undertake cost reduction studies e.g. value engineering, tear down analysis
2008 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
www.wileyeurope.com/college/bowhill
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CAMELBACK COMMUNICATIONS REVAMPS COSTING SYSTEMDokument23 SeitenCAMELBACK COMMUNICATIONS REVAMPS COSTING SYSTEMVidya Sagar Ch100% (2)
- Solution - Cash Flow Projection - FinalDokument51 SeitenSolution - Cash Flow Projection - Finalanon_355962815100% (1)
- RUNNING HEAD: Accounting Questions 1Dokument6 SeitenRUNNING HEAD: Accounting Questions 1Chirayu ThapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process costing MCQ practice questionsDokument19 SeitenProcess costing MCQ practice questionsYến Nguyễn100% (1)
- Problem 16-27 Joint-Cost Allocation, Sales Value, Physical Measure, and NRV MethodsDokument8 SeitenProblem 16-27 Joint-Cost Allocation, Sales Value, Physical Measure, and NRV MethodsVon Andrei MedinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 14 Simulation Modeling: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Dokument20 SeitenChapter 14 Simulation Modeling: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Jay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 Transportation and Assignment Models: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Dokument30 SeitenChapter 9 Transportation and Assignment Models: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Jay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control in Divisionalized Organizations Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesDokument6 SeitenControl in Divisionalized Organizations Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesJay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joint Product & By-Product ExamplesDokument15 SeitenJoint Product & By-Product ExamplesMuhammad azeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q36 Hayfield - Incl FXDokument4 SeitenQ36 Hayfield - Incl FXZamm FNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Estate Development.Dokument8 SeitenReal Estate Development.Christopher KipsangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decision MakingDokument5 SeitenDecision Makingconstruction omanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measuring and Improving Internal Business Processes Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesDokument7 SeitenMeasuring and Improving Internal Business Processes Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesJay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Accounting Level 3/series 3 2008 (Code 3016)Dokument18 SeitenCost Accounting Level 3/series 3 2008 (Code 3016)Hein Linn Kyaw100% (3)
- Option A Option B Location A Location B Million MillionDokument6 SeitenOption A Option B Location A Location B Million MillionAkshita ChordiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feasibility Study On Recycled Plastic Sand Bricks Production For Persimmon PLCDokument10 SeitenFeasibility Study On Recycled Plastic Sand Bricks Production For Persimmon PLCAndy VicenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- SINGH007 Ans Homework Lec 14 To 21Dokument47 SeitenSINGH007 Ans Homework Lec 14 To 21Lau Chun GuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Merrion Products Ltd teaching case focuses on decision making with scarce resourcesDokument3 SeitenMerrion Products Ltd teaching case focuses on decision making with scarce resourcesHiba N IkhmyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revisionary Test Paper - Final - Syllabus 2012 - Dec2013: Group - IV Paper 17 - Strategic Performance Management Section - ADokument71 SeitenRevisionary Test Paper - Final - Syllabus 2012 - Dec2013: Group - IV Paper 17 - Strategic Performance Management Section - ANagendra KrishnamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- C B FC 20% A: Debt RatioDokument4 SeitenC B FC 20% A: Debt Ratiojohn condesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment7 - CostAcc - Re Do Exercise - VanessaDokument5 SeitenAssignment7 - CostAcc - Re Do Exercise - VanessaVanessa vnssNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer-Key-Chapter-5-BC DeJesusDokument15 SeitenAnswer-Key-Chapter-5-BC DeJesusMerel Rose FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Accounting 1Dokument4 SeitenManagement Accounting 1Tax TrainingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Budget Model Projects Segment Contribution of $166,750Dokument11 SeitenMarketing Budget Model Projects Segment Contribution of $166,750Violen AmeliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculate profit using absorption and marginal costingDokument4 SeitenCalculate profit using absorption and marginal costingLucia XIIINoch keine Bewertungen
- CH # 8 (By Product)Dokument10 SeitenCH # 8 (By Product)Rooh Ullah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cases On Activity Based Costing SystemDokument6 SeitenCases On Activity Based Costing SystemEnusah PeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Budgetary Control Systems Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesDokument3 SeitenBudgetary Control Systems Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesJay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Further Decision-Making Problems Answers To End of Chapter ExercisesDokument6 SeitenFurther Decision-Making Problems Answers To End of Chapter ExercisesJay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensitivity and Breakeven Analysis: Lecture No. 29 Professor C. S. Park Fundamentals of Engineering EconomicsDokument26 SeitenSensitivity and Breakeven Analysis: Lecture No. 29 Professor C. S. Park Fundamentals of Engineering EconomicsFeni Ayu LestariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard costing analysis and variance calculationDokument16 SeitenStandard costing analysis and variance calculationGurveer SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installment Sales and Long Term Construction ContractDokument13 SeitenInstallment Sales and Long Term Construction ContractPaupauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joint CostingDokument5 SeitenJoint CostingDuddella Arun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breakeven Quiz 1 With SolutionDokument2 SeitenBreakeven Quiz 1 With Solutionfarsi786Noch keine Bewertungen
- GUIDE TO DISCOUNTED CASH FLOW ANALYSIS AND PROJECT EVALUATIONDokument6 SeitenGUIDE TO DISCOUNTED CASH FLOW ANALYSIS AND PROJECT EVALUATIONDorianne BorgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12Dokument7 SeitenChapter 12Ednel GubacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 and 5 Multiple Choice Answers and SolutionsDokument10 SeitenChapter 1 and 5 Multiple Choice Answers and SolutionsPamela Keith VargasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Costing and Manufacturing Methods Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesDokument5 SeitenStandard Costing and Manufacturing Methods Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesJay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost and Management Accounting Exam Questions Cover Production CostingDokument9 SeitenCost and Management Accounting Exam Questions Cover Production CostingFungai MajuriraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Mix Decision: IllustrationDokument2 SeitenProduct Mix Decision: IllustrationMeghan Kaye LiwenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absorption and Marginal Costing TemplateDokument13 SeitenAbsorption and Marginal Costing TemplateGeorge PNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACCT 404 Management Accounting: Solutions To Examples: Relevant Information and Analysis For Decision MakingDokument17 SeitenACCT 404 Management Accounting: Solutions To Examples: Relevant Information and Analysis For Decision MakingVanessa Boakye DankwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPA review exam solutions for management advisory servicesDokument6 SeitenCPA review exam solutions for management advisory servicesMark Anthony Casupang100% (1)
- Total Peso Sales Required 120,000 / (.25-0.1) 800,000 Less Prior Sales 400,000Dokument2 SeitenTotal Peso Sales Required 120,000 / (.25-0.1) 800,000 Less Prior Sales 400,000kmarisseeNoch keine Bewertungen
- FMA Exam Paper JULY 2018 PAPER 1 Solution and Marking GuideDokument18 SeitenFMA Exam Paper JULY 2018 PAPER 1 Solution and Marking GuideFidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DocxDokument5 SeitenDocxainun nisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bab 8 Costing by Product and Joint ProductDokument5 SeitenBab 8 Costing by Product and Joint ProductAntonius Sugi Suhartono100% (1)
- Joint and by Product ExercisesDokument2 SeitenJoint and by Product ExercisesAnsherina AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LVC Session - 3 (Illustrations)Dokument6 SeitenLVC Session - 3 (Illustrations)Srinivasan NarasimmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cañas Alexia V Pa1Dokument4 SeitenCañas Alexia V Pa1Joshua BangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bab 8 by ProductDokument5 SeitenBab 8 by ProductSilvani Margaretha SimangunsongNoch keine Bewertungen
- PM Exercise Solutions Session 1-6 CH 2-10Dokument47 SeitenPM Exercise Solutions Session 1-6 CH 2-10sxywangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Costing Series 2-2009Q6Dokument2 SeitenCosting Series 2-2009Q6May CcmNoch keine Bewertungen
- F2.1 Management Accounting - Answ J2022Dokument20 SeitenF2.1 Management Accounting - Answ J2022NKURUNZIZA FrancoisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latihan BEP - Nicolast CarlosDokument1 SeiteLatihan BEP - Nicolast CarlosNicholas CarlosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate in Management Accounting Level 3/series 3-2009Dokument15 SeitenCertificate in Management Accounting Level 3/series 3-2009Hein Linn Kyaw100% (2)
- Flexible BudgetsDokument23 SeitenFlexible BudgetsAyushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of CostsDokument4 SeitenApplication of CostsApril Jean TubisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 8 MCQ and Variance AnswersDokument8 SeitenSession 8 MCQ and Variance AnswersGhulam NabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jawaban Relevant CostDokument18 SeitenJawaban Relevant CostReviandi RamadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Markets and Economics: Energy Costs, Trading, EmissionsVon EverandPower Markets and Economics: Energy Costs, Trading, EmissionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual: (Updated Through November 11, 2013)Dokument55 SeitenSolution Manual: (Updated Through November 11, 2013)Jay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual Chapter 9 - Government Accounting: Fund-Based Financial StatementsDokument25 SeitenSolution Manual Chapter 9 - Government Accounting: Fund-Based Financial StatementsJay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aa2e Hal SM Ch09Dokument19 SeitenAa2e Hal SM Ch09Jay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The Consolidation Process: Learning Objectives - Coverage by QuestionDokument21 SeitenIntroduction To The Consolidation Process: Learning Objectives - Coverage by QuestionJay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 15 Markov Analysis: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Dokument18 SeitenChapter 15 Markov Analysis: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Jay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 13 Waiting Lines and Queuing Theory Models: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Dokument34 SeitenChapter 13 Waiting Lines and Queuing Theory Models: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Jay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual: (Updated Through November 11, 2013)Dokument23 SeitenSolution Manual: (Updated Through November 11, 2013)Jay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11 Network Models: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Dokument32 SeitenChapter 11 Network Models: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Jay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12 Project Management: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Dokument36 SeitenChapter 12 Project Management: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Jay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 16 Statistical Quality Control: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Dokument20 SeitenChapter 16 Statistical Quality Control: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Jay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Regression Models: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Dokument27 SeitenChapter 4 Regression Models: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Jay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument12 SeitenChapter 1Dennisse M. Vázquez-Casiano IsraelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Inventory Control Models: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Dokument27 SeitenChapter 6 Inventory Control Models: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Jay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Probability Concepts and Applications: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Dokument34 SeitenChapter 2 Probability Concepts and Applications: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Jay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting and Strategic Analysis Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesDokument6 SeitenAccounting and Strategic Analysis Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesJay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Forecasting: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Dokument27 SeitenChapter 5 Forecasting: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Jay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategy and Control System Design Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesDokument5 SeitenStrategy and Control System Design Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesJay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH23 PDFDokument5 SeitenCH23 PDFJay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measuring and Improving Internal Business Processes Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesDokument7 SeitenMeasuring and Improving Internal Business Processes Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesJay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Appraisal of The Organization Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesDokument5 SeitenInternal Appraisal of The Organization Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesJay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Political: Strategic Analysis - The External Environment Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesDokument6 SeitenPolitical: Strategic Analysis - The External Environment Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesJay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measuring Shareholder Value Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesDokument5 SeitenMeasuring Shareholder Value Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesJay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Budgetary Control, Performance Management and Alternative Approaches To Control Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesDokument2 SeitenBudgetary Control, Performance Management and Alternative Approaches To Control Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesJay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluating Strategies and Writing The Business Plan Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesDokument4 SeitenEvaluating Strategies and Writing The Business Plan Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesJay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identifying Suitable Strategic Options Answer To End of Chapter Exercises Siegmund LTDDokument7 SeitenIdentifying Suitable Strategic Options Answer To End of Chapter Exercises Siegmund LTDJay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Social Responsibility: Objectives, Strategy and Influences Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesDokument3 SeitenCorporate Social Responsibility: Objectives, Strategy and Influences Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesJay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Costing and Control Using Accounting Rules Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesDokument4 SeitenStandard Costing and Control Using Accounting Rules Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesJay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Funding The Business Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesDokument2 SeitenFunding The Business Answer To End of Chapter ExercisesJay BrockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcript of Warren Buffett Interview With FCICDokument23 SeitenTranscript of Warren Buffett Interview With FCICSantangel's ReviewNoch keine Bewertungen
- What's All The Furor Over Executive CompensationDokument10 SeitenWhat's All The Furor Over Executive CompensationMaryKnoll UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2 FIN460Dokument28 SeitenAssignment 2 FIN460tazrian nekeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepaid Utility Service Offers Benefits but Also Raises ConcernsDokument13 SeitenPrepaid Utility Service Offers Benefits but Also Raises ConcernsJuliet LalonneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case HimontDokument24 SeitenCase Himontssaurabh88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing MixDokument84 SeitenMarketing MixVijay GaneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- How monetary policy impacts Pakistan's economic growthDokument10 SeitenHow monetary policy impacts Pakistan's economic growthSamsam RaufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frishling (2002) A Discrete QuestionDokument2 SeitenFrishling (2002) A Discrete QuestiontartakNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cost of Capital, Corporation Finance & The Theory of InvestmentDokument16 SeitenThe Cost of Capital, Corporation Finance & The Theory of Investmentlinda zyongweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Exam 1 Practice - SolutionDokument6 SeitenMidterm Exam 1 Practice - SolutionbobtanlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIMA p1 March 2011 Post Exam GuideDokument18 SeitenCIMA p1 March 2011 Post Exam GuidearkadiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer buying behaviors and product types comparisonDokument12 SeitenConsumer buying behaviors and product types comparisonJoana Felicia L.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Writing Task 1Dokument19 SeitenWriting Task 1Trian NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engro CorDokument28 SeitenEngro CorAbNoch keine Bewertungen
- f5 Short Notes MHADokument25 Seitenf5 Short Notes MHAKlaus MIKENoch keine Bewertungen
- Gashub - 2018Dokument23 SeitenGashub - 2018Ricky PrasetyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- COVER - April 2014Dokument116 SeitenCOVER - April 2014Anna StroudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cooper Industries ADokument16 SeitenCooper Industries AEshesh GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Egypt Auto IndustryDokument13 SeitenEgypt Auto IndustryYadvendra SahaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- COST ACCOUNTING 1-6 FinalDokument22 SeitenCOST ACCOUNTING 1-6 FinalChristian Blanza Lleva0% (1)
- Present Value of AnnuitiesDokument2 SeitenPresent Value of AnnuitiesJai Prakash100% (1)
- Quotation MarksDokument3 SeitenQuotation MarksSujith GladwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mining Valuation: Three Steps Beyond A Static DCF Model: FeatureDokument4 SeitenMining Valuation: Three Steps Beyond A Static DCF Model: Feature2fercepolNoch keine Bewertungen
- AFAR FPB With AnswerDokument20 SeitenAFAR FPB With AnswerJana Trina LibatiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 Capital Budgeting Models NPV IRR PIDokument18 SeitenChapter 8 Capital Budgeting Models NPV IRR PIAdmire MamvuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- FT Weekend USA - April 2-3-2022Dokument48 SeitenFT Weekend USA - April 2-3-2022Nguyễn Xuân TăngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delhi VAT Act 2004: Key Definitions AdvisoryDokument3 SeitenDelhi VAT Act 2004: Key Definitions AdvisoryDheerajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimize capital structure and maximize ROEDokument13 SeitenOptimize capital structure and maximize ROESneha Dwivedi100% (1)
- SdasdasDokument297 SeitenSdasdasbisnis clubNoch keine Bewertungen
- MARGINAL COSTING ExamplesDokument10 SeitenMARGINAL COSTING ExamplesLaljo VargheseNoch keine Bewertungen