Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
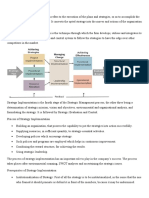
Strategy Implementation-Management Issues1
Hochgeladen von
David Adeabah OsafoCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Strategy Implementation-Management Issues1
Hochgeladen von
David Adeabah OsafoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Strategy Implementation Management Issues
1. Setting of annual objectives
- Establishing annual objectives is a decentralized activity that directly involves all managers in an
organization.
- Active participation in establishing annual objectives can lead to acceptance and commitment.
- Annual objectives are essential for strategy implementation because they
(1) represent the basis for allocating resources;
(2) are a primary mechanism for evaluating managers;
(3) are the major instrument for monitoring progress toward achieving long-term
objectives; and
(4) establish organizational, divisional, and departmental priorities.
- Objectives should be consistent across hierarchical levels and form a network of supportive aims
- Annual objectives should be measurable, consistent, reasonable, challenging, clear,
communicated throughout the organization, characterized by an appropriate time dimension,
and accompanied by commensurate rewards and sanctions
- Annual objectives should be compatible with employees and managers values and should be
supported by clearly stated policies.
2. Developing policies
- Policies facilitate solving recurring problems and guide the implementation of strategy.
- Policies are instruments for strategy implementation.
- Policies set boundaries, constraints, and limits on the kinds of administrative actions that can be
taken to reward and sanction behavior;
- They clarify what can and cannot be done in pursuit of an organizations objective.
- Policies let both employees and managers know what is expected of them, thereby increasing the
likelihood that strategies will be implemented successfully.
- They provide a basis for management control, allow coordination across organizational units, and
reduce the amount of time managers spend making decisions.
- Policies also clarify what work is to be done and by whom.
- They promote delegation of decision making to appropriate managerial levels where various
problems usually arise.
- Simply, policies provide guidance and direct behavior
- Thus, they represent the means for carrying out strategic decisions.
3. Resource allocation
- Four types of resources that can be used to achieve desired objectives: financial resources,
physical resources, human resources, and technological resources.
- Factors that prevents effective and efficient resource allocation are: overprotection of resources,
too great an emphasis on short-run financial criteria, organizational politics, vague strategy
targets, a reluctance to take risks, and a lack of sufficient knowledge.
- The real benefit of resource allocation has to do with the accomplishment of the organizational
objectives
4. Managing conflicts
- Interdependency of objectives and competition for limited resources often leads to conflict.
- Conflict can be defined as a disagreement between two or more parties on one or more issues.
- Conflict may be managed and resolved through avoidance, defusing and confrontation
5. Matching structure with strategy
- Strategy affects the structure of an organization largely because of how objectives and policies
are set; as well as resource allocation.
- Conflict can be defined as a disagreement between two or more parties on one or more issues.
- Conflict may be managed and resolved through avoidance, defusing and confrontation
6. Matching structure with strategy
7. Linking performance and pay to strategy
8. Managing resistance to change
9. Creating a strategy supportive culture
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Strategic ImplementationDokument14 SeitenStrategic Implementationharshit8bp19Noch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management: Strategy ImplementationDokument86 SeitenStrategic Management: Strategy ImplementationBryan Joseph JumawidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic ManagementDokument17 SeitenStrategic ManagementsimhamsidduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument41 SeitenChapter 5AgatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Firm-Level Determinants of Gender Diversity in The Boardrooms - Evidence From Some Emerging MarketsDokument13 SeitenFirm-Level Determinants of Gender Diversity in The Boardrooms - Evidence From Some Emerging MarketsDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Analysis of Internal Environment of a Business OrganisationVon EverandStrategic Analysis of Internal Environment of a Business OrganisationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of CEO 3Dokument7 SeitenRole of CEO 3Prateek Vaishali PahujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management-Full Notes (PGDM)Dokument24 SeitenStrategic Management-Full Notes (PGDM)Tisha TillmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HR Practices in Hotel IndustryDokument80 SeitenHR Practices in Hotel IndustryKiran Barde67% (3)
- The Competitive Advantages of Nations Applying The Diamond Model To ArmeniaDokument19 SeitenThe Competitive Advantages of Nations Applying The Diamond Model To ArmeniaGerardo BermudezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implementing Strategies Management and Operations IssuesDokument28 SeitenImplementing Strategies Management and Operations IssuesBabar Khan100% (1)
- Strategy ImplementationDokument5 SeitenStrategy ImplementationOneof TNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management - 3Dokument12 SeitenStrategic Management - 3Helen FernandesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit I (Strategic Management)Dokument20 SeitenUnit I (Strategic Management)RAMESH KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dawit's AssignmentDokument3 SeitenDawit's Assignmentbilealabebe5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Implementing Strategies: Management and Operations Issues: Key PointsDokument11 SeitenImplementing Strategies: Management and Operations Issues: Key Pointskhurram. khurshidNoch keine Bewertungen
- SM 3Dokument8 SeitenSM 3Amit BadgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bps Final QuestionDokument20 SeitenBps Final Questionbharat khullarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes Topic 1Dokument5 SeitenLecture Notes Topic 1Lawrence PascualNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management - 4Dokument30 SeitenStrategic Management - 4Pallavi.G.P. pallaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 SMDokument10 SeitenUnit 1 SMzenomopia28Noch keine Bewertungen
- SMCGDokument54 SeitenSMCGsreedevd33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bpsa NotesDokument31 SeitenBpsa Noteskrishna_medathatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Policy and Strategy FormulationDokument12 SeitenPolicy and Strategy FormulationRahul BaruahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Strategic Management Unit 1Dokument17 SeitenIntroduction To Strategic Management Unit 1Hujjat UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management Chapter 5Dokument20 SeitenStrategic Management Chapter 5sneha bhongadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management Individual Assignment of Berhe Teklehaymanot Section DDokument11 SeitenStrategic Management Individual Assignment of Berhe Teklehaymanot Section DAwetahegn HagosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6Dokument9 SeitenChapter 6Fisseha KebedeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5 Final Business Research MethodDokument22 SeitenUnit 5 Final Business Research MethodAccurate Health Care CenterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management UNIT-1Dokument32 SeitenStrategic Management UNIT-1manas sotiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management 4 TH ModDokument10 SeitenStrategic Management 4 TH ModShiju ShajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Share STR Mangt ConceptDokument20 SeitenShare STR Mangt ConceptMinhas AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management: SNR Degree College, JiganiDokument50 SeitenStrategic Management: SNR Degree College, Jiganibu butccmNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 1 in Strategic ManagementDokument4 SeitenUNIT 1 in Strategic ManagementCHARISH MAY P. ZAPANTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategy in ManagementDokument8 SeitenStrategy in ManagementtonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - Strategy ImplementationDokument6 SeitenChapter 3 - Strategy Implementationjalaja munirajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Integration of The StudyDokument10 SeitenBusiness Integration of The StudyAB CNoch keine Bewertungen
- StramaDokument25 SeitenStramaRica Mae M. MamangonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Planning Nature and Purpose - Steps Involved inDokument16 SeitenUnit 2 Planning Nature and Purpose - Steps Involved inprasanth689% (18)
- Strategic Management QB AnswersDokument49 SeitenStrategic Management QB AnswerskaranvishweshsharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE - 4 Strategy ImplementationDokument41 SeitenMODULE - 4 Strategy ImplementationRintu RajeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management MelmelDokument38 SeitenStrategic Management MelmelBoRaHaENoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Mangement 4Dokument45 SeitenStrategic Mangement 4kritikachhapolia100% (1)
- Sm-Module 4Dokument7 SeitenSm-Module 4S7photogaphy S7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Business PolicyDokument14 SeitenIntroduction To Business PolicyMazumder SumanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategy Implementation: UNIT-4Dokument19 SeitenStrategy Implementation: UNIT-4VIVEK KUMAR SINGH 13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Planning and ProgrammingDokument28 SeitenPlanning and ProgrammingMark DeguzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategy Implementation: UNIT-4Dokument19 SeitenStrategy Implementation: UNIT-4VIVEK KUMAR SINGH 13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Strategic ManagementDokument90 SeitenIntroduction To Strategic ManagementVivek AdateNoch keine Bewertungen
- HandoutDokument10 SeitenHandoutirisNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Systematic Approach To Organizational DevelopmentDokument2 SeitenA Systematic Approach To Organizational DevelopmentMUHAMMAD KALEEMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual ObjectivesDokument1 SeiteAnnual ObjectivesJanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategy ImplementationDokument6 SeitenStrategy Implementationswatisingla786Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection Paper #2 JEGERDokument8 SeitenReflection Paper #2 JEGERMa. Jamie Lhen Dela FuenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Strategic ManagementDokument7 SeitenModule 1 Strategic ManagementWalidahmad AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- POMDokument5 SeitenPOMfazilhaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Letter C ReportDokument2 SeitenLetter C Reportilove linuxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mba - Iiird Semester Gauhati University Business Policy and Strategic ManagementDokument42 SeitenMba - Iiird Semester Gauhati University Business Policy and Strategic ManagementArjun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PlanningDokument23 SeitenPlanningSeham AlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Implementation, Evaluation and ControllingDokument14 SeitenStrategic Implementation, Evaluation and ControllingtatekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional ImplementationDokument6 SeitenFunctional ImplementationKŕiśhñą ŚińghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter No 1: Introduction To Strategic Management Book Name: Fred.R.DavidDokument14 SeitenChapter No 1: Introduction To Strategic Management Book Name: Fred.R.DavidIbera WazirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 3 7-RevisionDokument38 Seiten1 3 7-RevisionPrashantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Board Diversity and Its Effects On Bank Performance - An International Analysis PDFDokument13 SeitenBoard Diversity and Its Effects On Bank Performance - An International Analysis PDFDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Board Demographic Diversity, Independence, and Corporate Social PerformanceDokument17 SeitenBoard Demographic Diversity, Independence, and Corporate Social PerformanceDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Almeida and Divino (2015)Dokument11 SeitenAlmeida and Divino (2015)David Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CG 01 2015 0007Dokument14 SeitenCG 01 2015 0007David Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agostino, Leonida and Trivieri (2005)Dokument8 SeitenAgostino, Leonida and Trivieri (2005)David Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Does Corporate Governance Structures Promote Shareholders or Stakeholders Value Maximization - Evidence From African BanksDokument20 SeitenDoes Corporate Governance Structures Promote Shareholders or Stakeholders Value Maximization - Evidence From African BanksDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Firm Operation Performance Analysis Using Data Envelopment Analysis and Balanced Scorecard-A Case Study of A Credit Cooperative BankDokument20 SeitenFirm Operation Performance Analysis Using Data Envelopment Analysis and Balanced Scorecard-A Case Study of A Credit Cooperative BankDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Development, International Migrant Remittances and Endogenous Growth in GhanaDokument24 SeitenFinancial Development, International Migrant Remittances and Endogenous Growth in GhanaDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of Bank Branches by Means of Data Envelopment Analysis PDFDokument12 SeitenEvaluation of Bank Branches by Means of Data Envelopment Analysis PDFDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluating The Cost Efficiency of Insurance Companies in GhanaDokument18 SeitenEvaluating The Cost Efficiency of Insurance Companies in GhanaDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Efficiency and Productivity of Banking Sector A Critical Analysis of Literature and Design of Conceptual ModelDokument31 SeitenEfficiency and Productivity of Banking Sector A Critical Analysis of Literature and Design of Conceptual ModelDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost and Profit Efficiency of Conventional and Islamic Banks in GCC CountriesDokument19 SeitenCost and Profit Efficiency of Conventional and Islamic Banks in GCC CountriesDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Benchmarking and Strategic Homogeneity of Indian BanksDokument21 SeitenPerformance Benchmarking and Strategic Homogeneity of Indian BanksDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Female Directors in Bank Boardrooms and Their Influence On Performance and Risk TakingDokument14 SeitenFemale Directors in Bank Boardrooms and Their Influence On Performance and Risk TakingDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- On The Cross-Methodological Validation of Bank Efficiency AssessmentsDokument19 SeitenOn The Cross-Methodological Validation of Bank Efficiency AssessmentsDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- History Lessons DEADokument9 SeitenHistory Lessons DEADavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measuring Efficiency, Effectiveness and Performance of Indian Public Sector BanksDokument27 SeitenMeasuring Efficiency, Effectiveness and Performance of Indian Public Sector BanksDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market Structure, Efficiency and Profitability of Insurance Companies in GhanaDokument23 SeitenMarket Structure, Efficiency and Profitability of Insurance Companies in GhanaDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interpretation of Modelling Results in Data Envelopment AnalysisDokument13 SeitenInterpretation of Modelling Results in Data Envelopment AnalysisDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production Efficiency of Chinese Banks A RevisitDokument19 SeitenProduction Efficiency of Chinese Banks A RevisitDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Predicting Change in Bank Efficiency in Jordan A Data Envelopment AnalysisDokument22 SeitenPredicting Change in Bank Efficiency in Jordan A Data Envelopment AnalysisDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Envelopment Analysis As Nonparametric Least Squares RegressionDokument13 SeitenData Envelopment Analysis As Nonparametric Least Squares RegressionDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Islamic Banks - Efficiency and Its Determinants in PakistanDokument13 SeitenIslamic Banks - Efficiency and Its Determinants in PakistanDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling The Operating Efficiency of Banks A Nonparametric MethodologyDokument16 SeitenModeling The Operating Efficiency of Banks A Nonparametric MethodologyDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Bootstrap Approach To Analyse Productivity Growth in European BankingDokument18 SeitenA Bootstrap Approach To Analyse Productivity Growth in European BankingDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Envelopment Analysis, Operational Research and UncertainityDokument11 SeitenData Envelopment Analysis, Operational Research and UncertainityDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantifying Management's Role in Bank Survival Using DEA - The Case of JamaicaDokument27 SeitenQuantifying Management's Role in Bank Survival Using DEA - The Case of JamaicaDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production Efficiency of Chinese Banks A RevisitDokument19 SeitenProduction Efficiency of Chinese Banks A RevisitDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Profit Efficiency in The European Union Banking Industry - A Directional Technology Distance FunctionDokument18 SeitenProfit Efficiency in The European Union Banking Industry - A Directional Technology Distance FunctionDavid Adeabah OsafoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2 SOSEDokument31 SeitenAssignment 2 SOSEpreetichhikaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sustainable Material Construction FinalllDokument9 SeitenSustainable Material Construction FinallltanujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Report On DominoDokument10 SeitenA Report On DominoTeman MantenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Resource Management PrinciplesDokument61 SeitenHuman Resource Management Principleshayenje rebeccaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Desiree Module Tle 6Dokument23 SeitenDesiree Module Tle 6Desiree NuñezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resource Allocation MethodsDokument3 SeitenResource Allocation MethodsFASIHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Systems Approach To Human Resource ManagementDokument2 SeitenSystems Approach To Human Resource ManagementTitus ClementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analyzing A Company's Resources and Competitive Position Analyzing A Company's Resources and Competitive PositionDokument31 SeitenAnalyzing A Company's Resources and Competitive Position Analyzing A Company's Resources and Competitive PositionDipto KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cadima-2003-Stock Assessment Manual I PDFDokument83 SeitenCadima-2003-Stock Assessment Manual I PDFMaria Ester Chavez GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coceptual Framwork For Housing Development PDFDokument8 SeitenCoceptual Framwork For Housing Development PDFAbubakar MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2023 Sec 1 CH 2 How Can We Sustainably Manage Natural Resources (Student)Dokument32 Seiten2023 Sec 1 CH 2 How Can We Sustainably Manage Natural Resources (Student)Geovy SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vision-Zuidas 100dpiDokument103 SeitenVision-Zuidas 100dpiWindi EmilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Career Planning HRMDokument23 SeitenCareer Planning HRMKritika Singh100% (1)
- Capra (1997 Center For Ecoliteracy 2013a Orr (1992Dokument8 SeitenCapra (1997 Center For Ecoliteracy 2013a Orr (1992Princess GriñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- M1-01 IE103 Technopreneurship 101 (Intro)Dokument26 SeitenM1-01 IE103 Technopreneurship 101 (Intro)Pzynae FlorentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 01Dokument29 SeitenCH 01Xinni XuNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRM Problems, Approaches, and Challenges at GrameenphoneDokument19 SeitenHRM Problems, Approaches, and Challenges at Grameenphonenaimul_bariNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPC EcoDokument22 SeitenPPC Ecokhusi khatun100% (1)
- Low Cost Suatainable Building MaterialDokument45 SeitenLow Cost Suatainable Building MaterialLavanya BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mercial ApplicationsDokument7 SeitenMercial ApplicationsChris TonNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Product-Mix ProblemDokument5 SeitenThe Product-Mix ProblemDhyra ShamsullNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Plan OutlineDokument22 SeitenBusiness Plan OutlineMG MauzarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7230 27959 1 PBDokument5 Seiten7230 27959 1 PBjellie jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Property Rights: Characteristics of Property Rights Property Rights Have Four Main Characteristics. 1. UniversalityDokument4 SeitenProperty Rights: Characteristics of Property Rights Property Rights Have Four Main Characteristics. 1. UniversalityMartin WayneNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Economics Notes ch19 Environment and Sustainable Economic DevelopmentDokument4 Seiten11 Economics Notes ch19 Environment and Sustainable Economic Developmentrohan chaturvediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environment & DevelopmentDokument22 SeitenEnvironment & DevelopmentrashiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Crisis and Sustainable DevelopmentDokument21 SeitenEnvironmental Crisis and Sustainable DevelopmentMatt MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business and Accounting Studies: Grade 10Dokument184 SeitenBusiness and Accounting Studies: Grade 10Ashley GazeNoch keine Bewertungen