Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Nets For Administrators 2002
Hochgeladen von
Maria MashorOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Nets For Administrators 2002
Hochgeladen von
Maria MashorCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ISTE NATIONAL EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGY STANDARDS (NETS)
Effective Leadership for Technology in Schools AND PERFORMANCE INDICATORS FOR ADMINISTRATORS
(Developed by the TSSA Collaborative and adopted by ISTE NETS)
INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY FOR TECHNOLOGY IN EDUCATION I. LEADERSHIP AND VISIONEducational leaders inspire a shared vision IV. SUPPORT, MANAGEMENT, AND OPERATIONSEducational
ffectively using technology across all functions of campus-level leaders including principals and Role definition and job descriptions administrator who masters the tools and processes
E a school system is, in itself, significant systemic
reform. There is a wealth of evidence showing that
facilitating change in schools, and especially maintaining
assistant principals.
The NETSA embraces that vision and extends it to
additional administrative job roles. These standards are
Individual and system accountability
Accreditation of schools and of administrator
preparation programs
that allow creative and dynamic management of
available information.
During the process of developing the TSSA, the writing
for comprehensive integration of technology and foster an
environment and culture conducive to the realization of that vision.
Educational leaders:
A. facilitate the shared development by all stakeholders of a vision for
technology use and widely communicate that vision.
leaders ensure the integration of technology to support
productive systems for learning and administration.
Educational leaders:
A. develop, implement, and monitor policies and guidelines to
ensure compatibility of technologies.
that change, depends heavily on capable leadership. It is indicators of effective leadership for technology in team members, the NETS Leadership Team, and members
imperative, therefore, that we focus on leadership for B. maintain an inclusive and cohesive process to develop, implement, B. implement and use integrated technology-based management
schools. They define neither the minimum nor maximum Certification (credentialing) of administrators of the collaborating organizations identified a number
technology in schools if we are to optimize its benefits in and monitor a dynamic, long-range, and systemic technology plan and operations systems.
level of knowledge and skills required of a leader, and Self-assessment and goal setting of areas in which these leadership guidelines could be to achieve the vision. C. allocate financial and human resources to ensure complete and
learning, teaching, and school operations. are neither a comprehensive list nor a guaranteed recipe enhanced. The initial TSSA phase of this effort does not C. foster and nurture a culture of responsible risk-taking and advocate sustained implementation of the technology plan.
The International Society for Technology in Education for effective technology leadership. Rather, these Design of technology tools for school administrators address the specifics of some administrative positions. policies promoting continuous innovation with technology. D. integrate strategic plans, technology plans, and other
(ISTE) and its NETS Leadership Team are pleased to standards are a national consensus among educational The audience for these standards is also varied. School ISTEs NETSA extends the outstanding TSSA work to D. use data in making leadership decisions. improvement plans and policies to align efforts and leverage
announce the National Educational Technology Standards stakeholders of what best indicates effective school two new specific job roles: E. advocate for research-based effective practices in use of technology. resources.
boards, administrators, human resources staff,
for Administrators (NETSA) Project. The NETSA follows leadership for comprehensive and appropriate use of F. advocate, on the state and national levels, for policies, programs, E. implement procedures to drive continuous improvements of
professional development staff, higher education the district technology director or coordinator, and technology systems and to support technology replacement
on the success of the NETS for Students (NETSS) and technology in schools. Although created as a result of a and funding opportunities that support implementation of the
personnel, and state education agencies will make use of district technology plan. cycles.
NETS for Teachers (NETST). A significant beginning to the national consensus building process, these standards this resource. Others include state and federal policy- the building-level technology facilitator.
II. LEARNING AND TEACHINGEducational leaders ensure that V. ASSESSMENT AND EVALUATIONEducational leaders use
NETSA phase of ISTEs NETS Project has already been should not be viewed as constraining nor construed as a makers, industry representatives and service providers, technology to plan and implement comprehensive systems of
These two leadership roles for technology correspond to curricular design, instructional strategies, and learning environments
completed with the release of the Technology Standards rationale to inhibit new development, innovation, or effective assessment and evaluation.
Standards for Administrators for School Administrators (TSSA) document. ISTE
participated in the TSSA Collaborative and had a lead role
progress for schools or for school leadership.
professional organizations, parents, taxpayers, and other
community constituents. This places priority, then, on
the district technology director who facilitates
technology integration systemwide, and the technology
integrate appropriate technologies to maximize learning and teaching.
Educational leaders: Educational leaders:
The TSSA Collaborative and the many professionals who clarity and simplicity of language, free from specific facilitator for a campus who leads and supports teachers A. identify, use, evaluate, and promote appropriate technologies to A. use multiple methods to assess and evaluate appropriate uses
in managing the inclusive, broad-based development enhance and support instruction and standards-based curriculum of technology resources for learning, communication, and
contributed to this effort realize the wide range of roles education jargon. The NETSA document speaks to a and other campus instructional staff members as they
process. As a result, the ISTE NETSA initiative confidently leading to high levels of student achievement. productivity.
administrators play in schools, even when titles are variety of audiences, and it encourages accomplished grow in the appropriate use of technology in teaching,
integrates and builds on the work of the TSSA B. facilitate and support collaborative technology-enriched learning B. use technology to collect and analyze data, interpret results,
similar. School and system size, degree of site-based leaders to stay abreast of current strategies and learning, and instructional management. These two and communicate findings to improve instructional practice
Collaborative. Those who embrace NETST and NETSS will environments conducive to innovation for improved learning.
The National Educational governance, community characteristics, and strengths of accepted principles as technology evolves. additional profiles appear in the full document, National and student learning.
realize a comfortable articulation with both the TSSA and C. provide for learner-centered environments that use technology to
the expanded NETSA. individual administrators are but a few of the An underlying assumption of these standards is that Educational Technology Standards for Administrators. meet the individual and diverse needs of learners. C. assess staff knowledge, skills, and performance in using
Technology Standards for technology and use results to facilitate quality professional
parameters that may cause variations in actual job roles. administrators should be competent users of Additionally, NETSA includes an expanded look at the D. facilitate the use of technologies to support and enhance
Administrators (NETSA) The vision of the TSSA Collaborative is that the TSSA development and to inform personnel decisions.
For this reason, wise consumers of these standards will information and technology tools common to system-wide conditions that must be in place for even
instructional methods that develop higher-level thinking, decision-
document identifies knowledge and skills that constitute making, and problem-solving skills. D. use technology to assess, evaluate, and manage administrative
Project is an ISTE initiative apply this national resource in ways that acknowledge information-age professionals. The effective 21st accomplished leadership to realize the full potential of and operational systems.
the corewhat every P12 administrator needs the local context of school leadership. E. provide for and ensure that faculty and staff take advantage of
that incorporates the regardless of specific job roleand then extends the core century administrator is a hands-on user of technology. technology. Documentation of authentic case studies of quality professional learning opportunities for improved learning VI. SOCIAL, LEGAL, AND ETHICAL ISSUESEducational leaders
The standards and job profiles can be applied in a rich Many of the benefits of technology are lost for the effect these standards are having in real school and teaching with technology. understand the social, legal, and ethical issues related to
Technology Standards for to include the specific needs of administrators in each of technology and model responsible decision-making related to
three job roles: array of situations, such as: administrators who rely on an intermediary to check districts is a part of this project, as is support for III. PRODUCTIVITY AND PROFESSIONAL PRACTICEEducational leaders these issues.
School Administrators their e-mail, manipulate critical data, or handle other assessing administrators progress toward achieving apply technology to enhance their professional practice and to
superintendent and executive cabinet, Administrator preparation and professional increase their own productivity and that of others. Educational leaders:
developed by the TSSA technology tasks for them. While technology empowers these standards. As with other NETS projects, current
development program design Educational leaders: A. ensure equity of access to technology resources that enable
district-level leaders for content-specific or other administrators by the information it can readily produce practitioners significantly influence support features and empower all learners and educators.
Collaborative. and communicate, it exponentially empowers the A. model the routine, intentional, and effective use of technology.
district programs, and Assessment and evaluation that are an important part of NETS for Administrators. B. identify, communicate, model, and enforce social, legal, and
B. employ technology for communication and collaboration among ethical practices to promote responsible use of technology.
colleagues, staff, parents, students, and the larger community.
C. promote and enforce privacy, security, and online safety
C. create and participate in learning communities that stimulate, related to the use of technology.
NETS PROJECT PARTNERS nurture, and support faculty and staff in using technology for
D. promote and enforce environmentally safe and healthy
ISTE NETS Project Partners National Association of Elementary School Principals Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) ISTE CAPT3 Project Partners Association of Educational Service Agencies (AESA) Enterasys Networks, Inc. improved productivity.
practices in the use of technology.
(NAESP) www.pbs.org/teacherline International Society for Technology in Education International Society for Technology in Education D. engage in sustained, job-related professional learning using
American Association of School Librarians (AASL), a Apple, Inc.
www.naesp.org Software & Information Industry Association (SIIA) (ISTE) technology resources. E. participate in the development of policies that clearly enforce
division of the American Library Association (ALA) Edmin.com, Inc. Microsoft Corporation
National Association of Secondary School Principals www.siia.net copyright law and assign ownership of intellectual property
www.ala.org/aasl Consortium for School Networking (CoSN) NCRTEC at North Central Regional Educational E. maintain awareness of emerging technologies and their potential
(NASSP) MC Squared developed with district resources.
American Federation of Teachers (AFT) www.nassp.org NCRTEC at North Central Regional Educational Laboratory (NCREL) uses in education.
Teacher Universe, Inc.
www.aft.org
National Council for Accreditation of Teacher ISTE NETS Co-Sponsors University of Alaska Anchorage
Laboratory (NCREL) Netschools Corporation F. use technology to advance organizational improvement. The materials contained on this panel and on the reverse side of this poster were originally
Association for Supervision and Curriculum Education (NCATE) Apple, Inc. Southern Regional Education Board (SREB) NSBA ITTE Network produced as a project of the Technology Standards for School Administrators Collaborative.
Development (ASCD) www.apple.com Kentucky State Department of Education
www.ncate.org Preparing Tomorrows Teachers to Use Technology (PT3) ISTE WEB SITE: WWW.ISTE.ORG
www.ascd.org
National Education Association (NEA) Intel Corporation TSSA Collaborative Mississippi State Department of Education program of the U.S. Department of Education
The Council of Chief State School Officers (CCSSO) www.nea.org www.intel.com/education/ Chair: James Bosco, Western Michigan University For more information, contact: ISTE grants permission to photocopy this document for educational purposes providing
Principals Executive Program, University of North Teacher Universe, Inc.
www.ccsso.org National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) that appropriate credit is included on the copies. Please use the following credit line:
The NEA Foundation for the Improvement of Education American Association of School Administrators (AASA) Carolina
Council for Exceptional Children (CEC) (NFIE) Classroom of the Future Don Knezek, Project Director Lajeane G. Thomas, Director Reprinted with permission from National Educational Technology Standards for
National Association of Elementary School Principals College of Education, Western Michigan University To order or find out more about NETSA: Administrators, published by the International Society for Technology in Education (ISTE),
www.cec.sped.org www.nfie.org www.cotf.edu NETS for Administrators Project ISTE NETS Project NETS Project, copyright 2002, ISTE, 800.336.5191 (U.S. & Canada) or 541.302.3777 (Intl),
(NAESP)
International Society for Technology in Education National School Boards Associations (NSBA) U.S. Department of Education Toll-Free (U.S. and Canada): 800.336.5191 TSSA Standards Project Louisiana Tech University iste@iste.org, www.iste.org. All rights reserved.
National Association of Secondary School Principals TSSA Contributors
(ISTE) ITTE: Education Technology Programs www.ed.gov/Technology/ International Calls: 541.302.3777 ISTEs NCPT3 E-Mail: lthomas@latech.edu
(NASSP) Copyright 2002,
www.iste.org www.nsba.org/itte Apple, Inc. E-Mail: iste@iste.org University of North Texas Phone: 318.257.3923
National School Boards Association (NSBA) International Society for Technology in Education
Chancery Software, Ltd. E-Mail: dknezek@iste.org ISBN 1-56484-189-8
ISTEs Online Bookstore: www.iste.org/bookstore
Phone: 210.313.7538
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Julia Raymond Lorenz (2000) PDFDokument79 SeitenJulia Raymond Lorenz (2000) PDFDimas DcnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Career Maturity of School ChildrenDokument6 SeitenCareer Maturity of School Childrenizzah011004Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tennessee Self-Concept ScaleDokument9 SeitenTennessee Self-Concept ScaleJosé SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 Achievement MotivationDokument18 Seiten07 Achievement MotivationsivapathasekaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review JurnalDokument61 SeitenReview JurnalRaja Dwika GusriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dev Plan 2022Dokument2 SeitenDev Plan 2022Marison GerantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development Plan SampleDokument2 SeitenDevelopment Plan Samplemargie faustinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEA-SLP 2023 Learners OrientationDokument36 SeitenSEA-SLP 2023 Learners OrientationEd RosiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edad 5320 Iste Standards Analysis Chart 1Dokument3 SeitenEdad 5320 Iste Standards Analysis Chart 1api-627011822Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.tvet (Internasional)Dokument9 Seiten1.tvet (Internasional)Anonymous I8hLvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ipcrf Development PlanDokument1 SeiteIpcrf Development PlanLhea Joy T. Cipriano100% (23)
- 3.1 Learning SpacesDokument2 Seiten3.1 Learning SpacesJosé Pedro TelesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Susan Brooks-Young - Digital-Age Literacy For Teachers - Applying Technology Standards To Everyday Practice PDFDokument133 SeitenSusan Brooks-Young - Digital-Age Literacy For Teachers - Applying Technology Standards To Everyday Practice PDFUla UlalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssessmentDokument26 SeitenAssessmentgreg savageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mentoring Coaching Data of SHsDokument7 SeitenMentoring Coaching Data of SHsJaymar Kevin PadayaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FISD Technology Professional Development: EDLD 5352 Instructional Leadership: The Technology LinkDokument5 SeitenFISD Technology Professional Development: EDLD 5352 Instructional Leadership: The Technology LinkTeam KanzNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELT - Asia Developmental Writing 2013Dokument40 SeitenELT - Asia Developmental Writing 2013Tahir HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prof LRNG To Improv Achiev For All StsDokument1 SeiteProf LRNG To Improv Achiev For All StsgcimorelliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fs1-Episode 11Dokument28 SeitenFs1-Episode 11Abegail Linaga83% (82)
- Diploma in Information Technology Bachelor of Information Technology (HONS)Dokument2 SeitenDiploma in Information Technology Bachelor of Information Technology (HONS)Leanne TehNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEF Effective PD Recommendations PosterDokument1 SeiteEEF Effective PD Recommendations PosterEdwardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technology Integration Organization Flow ChartDokument1 SeiteTechnology Integration Organization Flow Chartcynthialpetty4754Noch keine Bewertungen
- Iso-Research Action Plan and IdpDokument7 SeitenIso-Research Action Plan and IdpAngela RuleteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ipcrf Development PlanDokument1 SeiteIpcrf Development PlanLhea Joy T. Cipriano93% (15)
- ELT Asia Developmental Reading 2013Dokument36 SeitenELT Asia Developmental Reading 2013EndiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Butcherg Assign4Dokument7 SeitenButcherg Assign4api-349780383Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engineer Grades ChartDokument1 SeiteEngineer Grades ChartSapri PamuluNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAC PLAN 2023 2024.newDokument3 SeitenLAC PLAN 2023 2024.newrosemarie lozada78% (9)
- Educational TechnologyDokument19 SeitenEducational TechnologyARS Printing Press100% (2)
- Technology PlanDokument5 SeitenTechnology Planapi-328483487Noch keine Bewertungen
- HPT For CTEDokument5 SeitenHPT For CTEJeremy ReedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 Ippd John CorsinoDokument2 Seiten2015 Ippd John CorsinoRENATO EGANGNoch keine Bewertungen
- School Quality Improvement PlanDokument8 SeitenSchool Quality Improvement PlanNhomeo Arnais AblandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASSURE - MODEL Abad 21Dokument1 SeiteASSURE - MODEL Abad 21PDPPPK1022R Mohamad Amir Syazwan Bin Mohamad ZainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 9 Training Development ProgramDokument9 SeitenGroup 9 Training Development Programariane galenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Management SystemDokument4 SeitenLearning Management SystemBatrishya IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unstructured-Schuster-7430 FinalDokument8 SeitenUnstructured-Schuster-7430 Finalapi-368727465Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ideas What Could We Improve What Worked QuestionsDokument2 SeitenIdeas What Could We Improve What Worked QuestionsJazcel GalsimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ipcrf Development PlanDokument1 SeiteIpcrf Development PlanGretchen Limot Baclay-Menendez100% (4)
- Forecast 5 Future Learning Provocations PosterDokument1 SeiteForecast 5 Future Learning Provocations PosterJouberto HeringerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unstructured Field Experience Log Summer 7500 1 1 2Dokument11 SeitenUnstructured Field Experience Log Summer 7500 1 1 2api-368727465Noch keine Bewertungen
- BPED 253 - Philippine Traditional DancesDokument6 SeitenBPED 253 - Philippine Traditional DancesFernando Bornasal100% (1)
- RPMS Developmental-PlanDokument2 SeitenRPMS Developmental-PlanErnie EstreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lyceum of The Philippines - Davao: Classroom Instruction Delivery Alignment MapDokument2 SeitenLyceum of The Philippines - Davao: Classroom Instruction Delivery Alignment MapKeenly PasionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Etextbook 978 0078137204 Organizational Behavior Key Concepts Skills Best PracticesDokument62 SeitenEtextbook 978 0078137204 Organizational Behavior Key Concepts Skills Best Practicesbeatrice.bump837100% (49)
- School Human Resource Development Plan 2021 2022Dokument1 SeiteSchool Human Resource Development Plan 2021 2022Mylene Dupitas100% (8)
- Lunduyan Sa Kahusayan Cohort 4 Action PlanDokument2 SeitenLunduyan Sa Kahusayan Cohort 4 Action PlanRansel Burgos100% (2)
- NAAC & NBA Brochure 28 APRDokument2 SeitenNAAC & NBA Brochure 28 APReee.kitshodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ipcrf-Development PlanDokument4 SeitenIpcrf-Development Planrachell ann mangosingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Educator and Leader DevelopmentDokument2 SeitenEducator and Leader DevelopmentBajeWuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Education Division of Cebu City: Ict Action Plan For The Year 2017 - 2018Dokument4 SeitenDepartment of Education Division of Cebu City: Ict Action Plan For The Year 2017 - 2018Bert BinonzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Henley Postgraduate BrochureDokument22 SeitenHenley Postgraduate BrochureBryan LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional Acadamic CurriculumDokument53 SeitenFunctional Acadamic Curriculumzubaida sharifNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDUP2122i - ISTE Mind MapDokument1 SeiteEDUP2122i - ISTE Mind MapBrian RichardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skills To Succeed Academy Educators GuideDokument102 SeitenSkills To Succeed Academy Educators GuideDhess Dulay BambaNoch keine Bewertungen
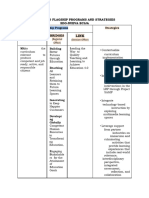
- Enhanced Flagship Programs and Strategies V2.0Dokument4 SeitenEnhanced Flagship Programs and Strategies V2.0EUDOLFO FLORESNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENHANCED-FLAGSHIP-PROGRAMS-AND-STRATEGIES-V2.0Dokument4 SeitenENHANCED-FLAGSHIP-PROGRAMS-AND-STRATEGIES-V2.0EUDOLFO FLORESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pabe IpcrDokument1 SeitePabe IpcrPrincess AnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mib DelhiDokument1 SeiteMib DelhiSatish AddaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 9 - 1ST Quarter - Week 7 Day 1-3Dokument20 SeitenGrade 9 - 1ST Quarter - Week 7 Day 1-3Marjohn ElentorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tingkah Laku KepimpinanDokument9 SeitenTingkah Laku KepimpinanMaria MashorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important Competencies For The Selection of Effective School Leaders: Principals' PerceptionsDokument42 SeitenImportant Competencies For The Selection of Effective School Leaders: Principals' PerceptionsMaria MashorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grady Leading The Technology Powered School cH1 PDFDokument23 SeitenGrady Leading The Technology Powered School cH1 PDFMaria Mashor100% (1)
- (Ncbssh-Tdna) Guide and Tools: Department of EducationDokument48 Seiten(Ncbssh-Tdna) Guide and Tools: Department of EducationMaria MashorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grady Leading The Technology Powered School cH1 PDFDokument23 SeitenGrady Leading The Technology Powered School cH1 PDFMaria Mashor100% (1)
- Tingkah Laku KepimpinanDokument9 SeitenTingkah Laku KepimpinanMaria MashorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frog VLEDokument431 SeitenFrog VLEMaria Mashor100% (1)
- 20-14 Iste Standards-A PDFDokument2 Seiten20-14 Iste Standards-A PDFapi-352786056Noch keine Bewertungen
- Utah Elementary School Principals - Preparation As Technology LeadDokument163 SeitenUtah Elementary School Principals - Preparation As Technology LeadMaria MashorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banoglu PDFDokument23 SeitenBanoglu PDFMaria MashorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grady Leading The Technology Powered School cH1 PDFDokument23 SeitenGrady Leading The Technology Powered School cH1 PDFMaria Mashor100% (1)
- Journal EducationDokument22 SeitenJournal EducationMaria MashorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Kepimpinan PengajaranDokument15 SeitenModel Kepimpinan Pengajarannorafiza85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digital News Report 2017 Web - 0 PDFDokument136 SeitenDigital News Report 2017 Web - 0 PDFPepe ArellanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Promoting Technical Education and Vocational TrainingDokument9 SeitenPromoting Technical Education and Vocational TrainingMaria MashorNoch keine Bewertungen
- UTAUT Model For Understanding The Teacher Perceptions Using Frog VLEDokument6 SeitenUTAUT Model For Understanding The Teacher Perceptions Using Frog VLEMaria MashorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Headmaster Technology Leadership in MalaDokument11 SeitenHeadmaster Technology Leadership in MalaMaria MashorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icriis Vle LibreDokument6 SeitenIcriis Vle LibreMaria MashorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tomasz Witkowski - A Review NLPDokument12 SeitenTomasz Witkowski - A Review NLPMaria MashorNoch keine Bewertungen
- UTAUT Model For Understanding The Teacher Perceptions Using Frog VLEDokument6 SeitenUTAUT Model For Understanding The Teacher Perceptions Using Frog VLEMaria MashorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing The Effects of ICTin EducationDokument217 SeitenAssessing The Effects of ICTin EducationMaria MashorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Farrell 09Dokument10 SeitenFarrell 09Maria MashorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedagogical Agent (Agen Bestari)Dokument16 SeitenPedagogical Agent (Agen Bestari)Maria MashorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pembelajaran Maya Di GermanDokument207 SeitenPembelajaran Maya Di GermanMaria MashorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pembelajaran Maya Di GermanDokument207 SeitenPembelajaran Maya Di GermanMaria MashorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ben1 PDFDokument18 SeitenBen1 PDFMaria MashorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Paper 1 - JPNK Mei 10Dokument6 SeitenMaths Paper 1 - JPNK Mei 10Maria MashorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel International GCSE (9-1) Mathematics A Student Book 1Dokument232 SeitenEdexcel International GCSE (9-1) Mathematics A Student Book 1Ahmed KremedNoch keine Bewertungen
- The History and Current Situation of Modern Art in The Philippines by Alice Guillermo PDFDokument66 SeitenThe History and Current Situation of Modern Art in The Philippines by Alice Guillermo PDFJeniel DasigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edited Class Program Sy 2021 2022 Senior HighDokument11 SeitenEdited Class Program Sy 2021 2022 Senior HighRichard TiempoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Talent Acquisition Pitch Deck PDFDokument22 SeitenTalent Acquisition Pitch Deck PDFTeach For MalaysiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Vacunas Latinoamerica 2005Dokument18 SeitenManual Vacunas Latinoamerica 2005Jorge Alonso Medina BustosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gringo Manual On How To Handle Mexicans by Jose Angel GutierrezDokument159 SeitenGringo Manual On How To Handle Mexicans by Jose Angel GutierrezArte Público Press100% (1)
- Mister SeahorseDokument8 SeitenMister Seahorseapi-337371953Noch keine Bewertungen
- Alea Perkovich Youth ResumeDokument2 SeitenAlea Perkovich Youth Resumeapi-4020857640% (1)
- OFSTED Report 2023Dokument6 SeitenOFSTED Report 2023Kalana WeerasingheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mary Grace R. Simbol Mirasol M. Tabarangao: Bepz Elementary SchoolDokument15 SeitenMary Grace R. Simbol Mirasol M. Tabarangao: Bepz Elementary SchoolHarmin Ilustrado VillamarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecological Systems TheoryDokument2 SeitenEcological Systems TheoryyaqqqqqsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanisms For Effectiveness: A Look Into The Child Friendly School System in Junior High SchoolDokument11 SeitenMechanisms For Effectiveness: A Look Into The Child Friendly School System in Junior High SchoolJennyrose BongabongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lisa Liang Resume 2019 FinalDokument2 SeitenLisa Liang Resume 2019 Finalapi-457206005Noch keine Bewertungen
- 32Dokument34 Seiten32tonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework Should Be Given To Students or NotDokument6 SeitenHomework Should Be Given To Students or Notafetrdwfs100% (1)
- Brigada Eskwela WorkplanDokument4 SeitenBrigada Eskwela WorkplanDjakeMabagos95% (22)
- Study Habit of The Grade 12 StudentsDokument46 SeitenStudy Habit of The Grade 12 StudentsLORENA AMATIAGANoch keine Bewertungen
- Isaac Frank: Teacher Certification Bachelor of Arts, MathematicsDokument3 SeitenIsaac Frank: Teacher Certification Bachelor of Arts, Mathematicsapi-255851513Noch keine Bewertungen
- Editing STATEMENT OF PURPOSE KajolDokument12 SeitenEditing STATEMENT OF PURPOSE KajolPramod Sapkota100% (1)
- Working Process SBOADokument2 SeitenWorking Process SBOAalehanieNoch keine Bewertungen
- April Disbursement-Reports-HcadDokument65 SeitenApril Disbursement-Reports-HcadcutmytaxesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mario V. Mariano JRDokument3 SeitenMario V. Mariano JRJay-ar Mario Valentin MarianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Focus 2 2E Students Book With Answers PDF - SECOND EDITION A2+B TEACHER'S BOOK VOCABULARY - StudocuDokument1 SeiteFocus 2 2E Students Book With Answers PDF - SECOND EDITION A2+B TEACHER'S BOOK VOCABULARY - Studocuxbxdgssmx8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 3 Geometry UnitDokument28 SeitenGrade 3 Geometry Unitapi-296766699Noch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheets' BookletDokument78 SeitenWorksheets' BookletEstyleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vladimir Putin - Personal WebsiteDokument11 SeitenVladimir Putin - Personal WebsiteMack MichaelsNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Southeastern Philippines: Course ObjectivesDokument132 SeitenUniversity of Southeastern Philippines: Course Objectivesfame charity porio100% (1)
- Dsaæh Ek/ Fed F'K (KK CKSMZ: Central Board of Secondary EducationDokument1 SeiteDsaæh Ek/ Fed F'K (KK CKSMZ: Central Board of Secondary EducationDinesh Kumar BeheraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions For The Qualifying Exam For PrincipalsDokument8 SeitenQuestions For The Qualifying Exam For PrincipalsAnnaliza Gabon Panis100% (2)
- Research Instrument On Student Engagement PDFDokument3 SeitenResearch Instrument On Student Engagement PDFJayson DigamonNoch keine Bewertungen