Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Maintenance Planning and Scheduling
Hochgeladen von
SyedNadeemAhmedCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Maintenance Planning and Scheduling
Hochgeladen von
SyedNadeemAhmedCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Maintenance Planning and Scheduling
Course Overview:
Maintenance planning and scheduling using structured and systematic approaches are critical for every
successful plant. Maintenance planning and scheduling are the fastest and most effective investments
that an organization can make to improve plant productivity and equipment availability.
This course is designed to build competency in maintenance planning and scheduling. The techniques
that participants will learn in this course will allow for effective planning and scheduling of maintenance
resources.
The course covers all the fundamentals and advanced methods and applications that a suitably qualified
professional would use in carrying out fully functional plant maintenance. In summary, the course
provides a step-by-step practical guide to best practices of maintenance planning and scheduling that
will essentially reduce maintenance costs and deliver maximum business benefits.
Course Duration
3 days
Course Objectives
Optimal selection/ planning for work orders of preventive maintenance, predictive
maintenance, run to failure maintenance and maintenance by redundancy/ re-design
Effective use of condition monitoring technologies (i.e. vibration, acoustic emission, infrared
thermography and wear debris) for maintenance work orders
Integration of reliability centered maintenance with maintenance planning and scheduling
Management of maintenance backlog
Demonstration of Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) and radically
novel Enterprise Resource Planning Software
Who Should Attend
This highly interactive training course will benefit anyone responsible for maintenance, who wishes to
build competency in maintenance planning and scheduling to improve plant performance. This includes:
Maintenance Engineer/ Planner/ Schedulers/ Supervisors/ Managers
Plant Engineer/ Manager
Operation Engineer/ Manager
Material and Storeroom Engineer/ Manager
Production Engineer/ Manager
Mechanical Engineer/ Manager
Course Agenda
Day One
Maintenance Planning and Scheduling: The Key Elements of Maintenance
Session 1
Ensuring that your Maintenance Planning Contributes to the Companys Profit to Achieve Business
Outcomes
Introduction
Maintenance: Definitions, the Main Concepts and the Seven Basic Questions
Planning and Scheduling Maintenance: Introduction
Planning and Scheduling Maintenance: Who Are the Main People? A Planner, a Maintenance
Supervisor, a Craftsman, Storeroom Personnel, an Operations Superintendent and an Operator
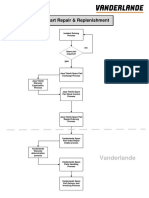
Flow Chart of Maintenance Planning & Scheduling
Developing High Quality Maintenance Work Orders
Work Orders: Top Ten Essential Estimations
Work Orders: Industrial Case Studies
Maintenance Planning Principles
Maintenance Scheduling Principles
Why Week is Enough for Maintenance Schedule?
Session 2
Converting Maintenance Strategy into Smart Tactics to Ensure an Optimal Approach to Maintenance
Build Systematic Maintenance Tactics for Your Organization:
Preventive Maintenance
Predictive Maintenance
Run to Failure Maintenance
Proactive Maintenance
Maintenance by Redundancy
Opportunity Maintenance
Opportunistic Maintenance
Corrective Maintenance
Session 3
Selecting Maintenance Types for Work Orders that Increases Reliability of Assets
Maintenance Strategy: Seven Stages Process
Asset Functions: Primary and Secondary
Asset Failures: Potential and Functional
The Instantaneous Hazard (Failure) Rates: Traditional View, Bathtub, Slow Aging, Best New,
Random Failure and Worst New
Relationship Between the Failure Rate Pattern and Maintenance Type Selection for Work Orders
Planning of Job Frequencies for Work Orders for Predictive Maintenance Using the P-F Interval,
the Net P-F Interval and Multiple P-F Interval
Estimation of the Optimum Maintenance Interval for Work Orders for Predictive and Preventive
Maintenance
Asset Operating Context
The Operating Context: Industrial Case Studies
Failure Modes
Hidden and Evident Failures
Analyzing Failure Effects
Analyzing Failure Consequences for Maintenance Type Selection for Work Orders:
Hidden Consequences
Safety and Environmental Consequences
Operational Consequences
Non-Operational Consequences
Determining Equipment Criticality for Work Orders
The Main Rules for Selecting Maintenance Types for Work Orders:
Predictive Maintenance Selection
Preventive Maintenance Selection
Failure Finding Maintenance Selection
Maintenance by Re-Design/ Redundancy Selection
Breakdown Maintenance Selection
Determining When to Prevent Failure and When to Allow Failure to Occur; Replace, Maintain or
Refurbish: Optimally Planning Your Next Maintenance Action
Logic Diagram for Maintenance Type Selection for Work Orders
Integration of Maintenance with Maintenance Planning
Integration of Maintenance with Maintenance Planning: Industrial Case Studies
Day Two
Session 1
Effectively Planning Asset Overhauls:
Time Between Asset Overhauls
Service Limit Overhauls
New Limit Overhauls
Session 2
Planning Predictive Maintenance Using Condition Based Maintenance (CBM) Technologies
Innovative CBM Approaches to Maximize Equipment Availability
How to Plan Vibration CBM for Work Orders
How to Plan Acoustic Emission CBM for Work Orders
How to Plan Wear Debris CBM for Work Orders
How to Plan Infrared Thermography CBM for Work Orders
New International Standard for Planning
Condition Based Maintenance for Work Orders Condition Based Maintenance: Nine Industrial
Case Studies, Including Four Video Case Studies
Session 3
Improving Advanced Planning and Scheduling in your Management Process. Maintenance Software and
the Main Planning/ Scheduling Techniques
Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS):
Asset Records
Asset Control
Plant and Equipment Information
Work Order Issue and Control
Estimation of Maintenance Key Performance Indicators
Inventory/ Stores Management
Planning Predictive/ Preventive Maintenance
Managing Condition Monitoring Outputs
Advanced Maintenance Planning Software:
Equipment Selection
Failure/ Fault Consequence Classification
Priority of Maintenance Tasks
Frequency for Predictive/ Preventive Maintenance
Optimum Combination of Maintenance Tasks
Corrective Maintenance
Management of FMEA and FMECA
Maintenance Tasks: Reports and Graphical Presentation
Work Breakdown Structures: The Main Principles
Gantt Chart: The Main Principles
Management of Maintenance Backlog
Day Three
Session 1
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP). Maximizing ERP as a Tool to Reduce Costs and Improve Productivity,
Quality and Control
New Generation Enterprise Resource Planning Software
ERP: The Future Trends
Maintenance Control via Audit
Time Planning for Maintenance
Session 2
Planning Maintenance via Root Cause Analysis and Failure Assessment to Essentially Cut Unnecessary
Maintenance Costs
Principles of Root Cause Analysis of Failures for the Proactive Maintenance; an Approach of Six
Root Causes
The Generic Eight Disciplines Problem Solving Technique for Root Cause Analysis Planning
Root Causes of Assets Failures: Description
Planning Industrial Root Cause Analysis for Assets: 17 Industrial Case Studies
Planning Failure Assessment for Maintenance: 9 Classical Steps
Planning Failure Assessment for Maintenance: Industrial Case Studies
Session 3
The People Matter: Developing Sustainable Planning by your Team to Meet Future Needs of
Maintenance
Implementation of the Planned Maintenance: Teamwork and Facilitator
Human Errors in Planned Maintenance
Reduction of Human Errors in Planned Maintenance
Planned Maintenance: Application and Achievements; Measuring Effectiveness of the Planning
and Scheduling Process
Review: Learning Outcomes
Closing Comments
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Preventive Maintenance Part IDokument20 SeitenPreventive Maintenance Part Ismodi20Noch keine Bewertungen
- TPM For BoilerDokument5 SeitenTPM For BoilerHuynh Thi Minh TrangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To MaintenanceDokument38 SeitenIntroduction To MaintenancemarianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Spare Part ManagementDokument32 Seiten6 Spare Part Managementdumbresanjay3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Preventive and Predictive Maintenance StrategiesDokument3 SeitenPreventive and Predictive Maintenance StrategiesSyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preventive Maintenance Part IDokument21 SeitenPreventive Maintenance Part IKABADDI RISINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- AV ME SOP 02 Criticality AnalysisDokument4 SeitenAV ME SOP 02 Criticality AnalysisjfejfeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO-14001 in Indian Petrochemicals CaseDokument6 SeitenISO-14001 in Indian Petrochemicals Caseapi-3701058Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maintenance Planning PrincipleDokument7 SeitenMaintenance Planning PrincipleReza Fitra KasturiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reaching Peak OM Performance in Power GenerationDokument16 SeitenReaching Peak OM Performance in Power GenerationbobeisyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintenance Planning and Scheduling1Dokument31 SeitenMaintenance Planning and Scheduling1Shahid Mehmud100% (3)
- Maintenance PlanningDokument27 SeitenMaintenance Planningnelson_ferns100% (3)
- Maintenance Management 3Dokument16 SeitenMaintenance Management 3SHAHABAZINoch keine Bewertungen
- Operation Department Procedure PDFDokument39 SeitenOperation Department Procedure PDFRajeevAgrawal100% (1)
- Cwa 15740Dokument19 SeitenCwa 15740Marco Antonio Bolivar AneivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PG Procedure - GMRDokument18 SeitenPG Procedure - GMRK NiteshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintenance PracticesDokument10 SeitenMaintenance Practicesarman_joon2003100% (1)
- Asset Maintenance ManagementDokument28 SeitenAsset Maintenance ManagementMayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Maintenance - A ComparisonDokument18 SeitenTypes of Maintenance - A ComparisonEusebio NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintenance Job PrioritisationDokument4 SeitenMaintenance Job PrioritisationSamuel ndopuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintenance SparePartsDokument79 SeitenMaintenance SparePartsCarlos SouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fmea PDFDokument36 SeitenFmea PDFalsoraya00100% (1)
- Journal of Quality in Maintenance EngineeringDokument20 SeitenJournal of Quality in Maintenance EngineeringJose100% (1)
- Mapcon CMMS Feature ChartDokument6 SeitenMapcon CMMS Feature ChartStar RangerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Management: Professor Lucia Miree American University in BulgariaDokument75 SeitenPerformance Management: Professor Lucia Miree American University in BulgariaNilesh RavindranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Description Description Cause Code Failure Class Failure CodeDokument389 SeitenDescription Description Cause Code Failure Class Failure CodeharshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spare Parts ProcedureDokument3 SeitenSpare Parts Proceduresurya agung100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Maintenance PlanningDokument3 SeitenFundamentals of Maintenance PlanningYousef AsmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implementing Total Productive Maintenance in Electronics IndustryDokument24 SeitenImplementing Total Productive Maintenance in Electronics IndustryUmang SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 22400 2 2014Dokument15 SeitenIso 22400 2 2014zhide wangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exactspace: Power Plant AnalyticsDokument24 SeitenExactspace: Power Plant AnalyticsK Senthil Ram KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMMS Technical Object and Preventative Maintenance FormDokument7 SeitenCMMS Technical Object and Preventative Maintenance Formken1962Noch keine Bewertungen
- 05DTPS - Best Practices For Energy Efficiency - Reliance - InfrastructureDokument14 Seiten05DTPS - Best Practices For Energy Efficiency - Reliance - InfrastructurentpckanihaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ogn Ops Perf 002Dokument12 SeitenOgn Ops Perf 002VIBHAVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Best PracticesDokument56 SeitenPlant Best PracticesHelien Parra RiverosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reliability Centred Maintenance Shivajichoudhury DownloadDokument4 SeitenReliability Centred Maintenance Shivajichoudhury DownloadNantha KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reliability Engineer: Organizational RelationshipsDokument6 SeitenReliability Engineer: Organizational RelationshipsJosé David Cruz MahechaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Red Flags SurveyDokument6 SeitenRed Flags Surveyhmp90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Why Quality Is Important and How It Applies in Diverse Business and Social Environments, Volume IDokument29 SeitenWhy Quality Is Important and How It Applies in Diverse Business and Social Environments, Volume IBusiness Expert PressNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ith FGD in The Name of God: Iata Operational Safety Audit (Iosa) (Iosa)Dokument26 SeitenIth FGD in The Name of God: Iata Operational Safety Audit (Iosa) (Iosa)SHAHABAZINoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintenance ManagementDokument7 SeitenMaintenance ManagementNadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Milk RunDokument161 SeitenMilk RunHoussem MoujahedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using Reliability Data To Improve Power Plant PerformanceDokument166 SeitenUsing Reliability Data To Improve Power Plant PerformanceDwiko RiyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction of MaintenanceDokument35 SeitenIntroduction of Maintenanceekhwan82100% (1)
- FMEA Wind Turbine GeneratorDokument10 SeitenFMEA Wind Turbine Generatorscorpionking888Noch keine Bewertungen
- CMMS Selection GuideDokument6 SeitenCMMS Selection GuidehamadaabdelgawadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equipment Criticality AnalysisDokument20 SeitenEquipment Criticality AnalysisArmandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- India Casestudy2 Thermal Power PlantDokument13 SeitenIndia Casestudy2 Thermal Power PlantVinodh GbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ogn Ops Mech 031Dokument21 SeitenOgn Ops Mech 031VIBHAV100% (1)
- Maintenance Planning SystemsDokument55 SeitenMaintenance Planning SystemsGyogi MitsutaNoch keine Bewertungen
- X70 Corrective MaintenanceDokument12 SeitenX70 Corrective Maintenancelems9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maintenance Optimization: A Critical Aspect of The Equipment Reliability ProgramDokument28 SeitenMaintenance Optimization: A Critical Aspect of The Equipment Reliability ProgramJose Carlos Sierra CiudadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spares Parts Management Ii - 200809Dokument9 SeitenSpares Parts Management Ii - 200809Dipanshu SinglaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inventory Management PowerPoint PresentationDokument30 SeitenInventory Management PowerPoint PresentationHisaan KamranNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMM09 Cerrejon 1a. Maintenance StrategyDokument6 SeitenAMM09 Cerrejon 1a. Maintenance StrategyDavid VelandiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintenance ManagementDokument27 SeitenMaintenance ManagementFurqan Shabbir100% (1)
- Maintenance Planning, Techniques & Cost Control: Snehal PandyaDokument18 SeitenMaintenance Planning, Techniques & Cost Control: Snehal PandyaSnehal PandyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Aero-Engine Reliability and Maintenance Cost Optimization RP-AV-02Dokument1 SeiteAdvanced Aero-Engine Reliability and Maintenance Cost Optimization RP-AV-02Reliable Plant Solutions SDN BHDNoch keine Bewertungen
- OMRP - KL and Abu DhabiDokument4 SeitenOMRP - KL and Abu DhabiSyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Aircraft Reliability and Maintenance Cost Optimization RP-AV-02Dokument1 SeiteAdvanced Aircraft Reliability and Maintenance Cost Optimization RP-AV-02SyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Equipment RCA For Process, Petrocchemical and Power Plants RP-REL-03Dokument1 SeiteProcess Equipment RCA For Process, Petrocchemical and Power Plants RP-REL-03SyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essentials of Plant Maintenance & Reliability Program For Engineers and Tech Prof - APAC Industry.Dokument2 SeitenEssentials of Plant Maintenance & Reliability Program For Engineers and Tech Prof - APAC Industry.SyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Programme - MIMA3 17-19oct. 23Dokument12 SeitenProgramme - MIMA3 17-19oct. 23SyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Turbine Performance, Operational, Reliability Improvement and Maint Cost Reduction in Process & Power Generation Plants PDFDokument1 SeiteGas Turbine Performance, Operational, Reliability Improvement and Maint Cost Reduction in Process & Power Generation Plants PDFSyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiler Inspection Study GuideDokument30 SeitenBoiler Inspection Study GuideSyedNadeemAhmed100% (2)
- PUB Performance of Generating Plant 2010 WECDokument123 SeitenPUB Performance of Generating Plant 2010 WECSyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aircraft Lease SampleDokument6 SeitenAircraft Lease SampleSyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inbi Gtbi 2018Dokument5 SeitenInbi Gtbi 2018SyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shutdown and Turnaround Course OutlineDokument4 SeitenShutdown and Turnaround Course OutlineSyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Aircraft Reliability Dec KL NadeemDokument4 SeitenAdvanced Aircraft Reliability Dec KL NadeemSyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pump GuidelinesDokument205 SeitenPump GuidelinesSyedNadeemAhmed100% (1)
- Aircraft Reliability Improvement & Maintenance Management In-House Training ProposalDokument8 SeitenAircraft Reliability Improvement & Maintenance Management In-House Training ProposalSyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- PumpsDokument79 SeitenPumpsSyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Six SigmaDokument5 SeitenWhat Is Six SigmaBimith AkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dyrobes BrochureDokument2 SeitenDyrobes BrochureSyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintenance Planning and SchedulingDokument74 SeitenMaintenance Planning and Schedulingapi-3732848100% (16)
- Pump GuidelinesDokument205 SeitenPump GuidelinesSyedNadeemAhmed100% (1)
- ARMD DescriptionDokument21 SeitenARMD DescriptionSyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCM In-House Training CourseDokument4 SeitenRCM In-House Training CourseSyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotate 2011 IIRME PDFDokument6 SeitenRotate 2011 IIRME PDFSyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Maintenance Cost Reduction Nov KL NadeemDokument5 SeitenPlant Maintenance Cost Reduction Nov KL NadeemSyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arim Jan SG LindaDokument4 SeitenArim Jan SG LindaSyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ram RCM Spof Mar KL LindaDokument4 SeitenRam RCM Spof Mar KL LindaSyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arim Jan SG LindaDokument4 SeitenArim Jan SG LindaSyedNadeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Supply Chain Management A Balanced Approach 4th Edition Wisner Solutions ManualDokument36 SeitenPrinciples of Supply Chain Management A Balanced Approach 4th Edition Wisner Solutions Manualoutlying.pedantry.85yc100% (28)
- SecurityFund PPT 1.1Dokument13 SeitenSecurityFund PPT 1.1Fmunoz MunozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Play ClawDokument2 SeitenPlay ClawFrenda SeivelunNoch keine Bewertungen
- 300u Specs Diodo 300 Amps. 25 Dolares RadiosurtidoraDokument6 Seiten300u Specs Diodo 300 Amps. 25 Dolares RadiosurtidorarepelindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of Specification 1st QDokument5 SeitenTable of Specification 1st QVIRGILIO JR FABINoch keine Bewertungen
- Honda IzyDokument16 SeitenHonda IzyTerry FordNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesser Known Homoeopathic Medicines of Alopecia Areata.20200718115446Dokument9 SeitenLesser Known Homoeopathic Medicines of Alopecia Areata.20200718115446BruntNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement and Scaling Techniques1Dokument42 SeitenMeasurement and Scaling Techniques1Ankush ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Truss-Design 18mDokument6 SeitenTruss-Design 18mARSENoch keine Bewertungen
- Brahms Symphony No 4Dokument2 SeitenBrahms Symphony No 4KlausNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caradol sc48 08Dokument2 SeitenCaradol sc48 08GİZEM DEMİRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sales Forecast Template DownloadDokument9 SeitenSales Forecast Template DownloadAshokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fire Prevention Plan Template - FINAL 5-30-08Dokument5 SeitenFire Prevention Plan Template - FINAL 5-30-08Peter GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect2 - 1151 - Grillage AnalysisDokument31 SeitenLect2 - 1151 - Grillage AnalysisCheong100% (1)
- Song LyricsDokument13 SeitenSong LyricsCyh RusNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 PBDokument7 Seiten1 PBIndah Purnama TaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural Cataclysms and Global ProblemsDokument622 SeitenNatural Cataclysms and Global ProblemsphphdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project ProposalDokument4 SeitenProject Proposaljiaclaire2998100% (1)
- Rights of Parents in IslamDokument11 SeitenRights of Parents in Islamstoneage989100% (2)
- John Wren-Lewis - NDEDokument7 SeitenJohn Wren-Lewis - NDEpointandspaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guncha Arora: Professional Profile Career HistoryDokument1 SeiteGuncha Arora: Professional Profile Career HistoryNitin MahawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bench-Scale Decomposition of Aluminum Chloride Hexahydrate To Produce Poly (Aluminum Chloride)Dokument5 SeitenBench-Scale Decomposition of Aluminum Chloride Hexahydrate To Produce Poly (Aluminum Chloride)varadjoshi41Noch keine Bewertungen
- Music 9 Q3 Mod4 Musical Elements of Given Romantic Period PiecesDokument19 SeitenMusic 9 Q3 Mod4 Musical Elements of Given Romantic Period PiecesFinn Daniel Omayao100% (1)
- Roles and Responsibilities of An InstructorDokument4 SeitenRoles and Responsibilities of An InstructorMohanlal SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summative Reflection CommDokument5 SeitenSummative Reflection Commapi-546460750Noch keine Bewertungen
- Prognostic Factors and Management of Patients With Choanal AtresiaDokument7 SeitenPrognostic Factors and Management of Patients With Choanal Atresiafarah maulida martaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nescom Test For AM (Electrical) ImpDokument5 SeitenNescom Test For AM (Electrical) Impشاہد یونسNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adaptive Leadership: Leadership: Theory and PracticeDokument14 SeitenAdaptive Leadership: Leadership: Theory and PracticeJose Daniel Quintero100% (1)
- ইসলাম ও আধুনিকতা – মুফতি মুহম্মদ তকী উসমানীDokument118 Seitenইসলাম ও আধুনিকতা – মুফতি মুহম্মদ তকী উসমানীMd SallauddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reaction Paper FinalDokument5 SeitenReaction Paper FinalJelo RoxasNoch keine Bewertungen