Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
TEV Ammonia Sporlan
Hochgeladen von
Drew CruzCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
TEV Ammonia Sporlan
Hochgeladen von
Drew CruzCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CATALOG Page 3
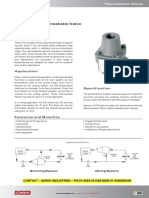
Thermostatic Expansion Valves
The same features and design principles found in thermostatic nozzle. If the discharge tube is not removed from the valve, the
expansion valves for Refrigerants 12, 22, 134a, and 502 are combination of the discharge tube and distributor nozzle may
also incorporated in Sporlan thermostatic expansion valves for create an excessive pressure drop resulting in a substantial loss
Ammonia. They have proven their value and acceptance in the of TEV capacity. Refer to page 8 for further information on
Industry for over 65 years. ammonia distributors.
Refrigerant 717 (Ammonia) Applications The nominal 75 and 100 ton Type A valves do not employ a
Thermostatic expansion valves for ammonia applications discharge tube since their valve outlets are designed to serve as
require special design considerations due to the erosive effects a secondary orifice to reduce pressure drop across the valve
of ammonia vapor. For this type of application, Sporlan has port.
developed the Types D and A thermostatic expansion valves.
Like other components of ammonia systems, the Types D and Thermostatic Charges for Ammonia Valves
A valves are made from steel and steel alloys. The materials Thermostatic charges C, Z, and L are available for the Type D
used in the manufacture of these valves are listed on pages 4 thermostatic expansion valve. The Type L thermostatic charge
and 5. is the only charge available for the Type A valve.
With ammonia systems, the formation of flash vapor at the The Types C and Z thermostatic charges provide operating
expansion valve port causes valve seat erosion or wire draw- advantages for systems that cycle in response to a suction
ing to occur. This effect is further aggravated by high velocity pressure switch or thermostat. These charges are also recom-
ammonia mixed with dirt or scale passing through the port of mended for systems using a small capacity compressor. The
the expansion valve. Fortunately, seat erosion can be mini- table below lists the recommended temperature range for each
mized and valve life extended if the following steps are taken: charge.
1. Maintain vapor-free liquid at the TEV inlet at all times.
THERMOSTATIC EVAPORATOR
2. Maintain clean ammonia through effective filtration. CHARGE TEMPERATURE F
C 40 to 0
3. Reduce the velocity of the ammonia through the TEV Z 0 to -20
port by reducing the pressure drop across the port.
For applications at evaporator temperature below -20F, consult
Sporlan Valve Company, Washington, Missouri 63090.
Step 1 can be accomplished through proper system design.
Liquid line vapor is prevented by adequately sizing liquid lines
and providing sufficient subcooling. Cold storage plants often have large centralized ammonia sys-
tems consisting of many evaporators connected to one or more
Step 2 can be assured with the use of a Sporlan Catch-All large compressors. This makes for fairly stable suction pres-
Filter-Drier. This filter-drier is an effective scale trap when sures. The Sporlan type L charge responds more quickly to
used on ammonia systems. For further information on the use changes in bulb temperature allowing for a quicker pull-down
of the Catch-All Filter-Drier with ammonia systems, refer to of the conditioned space temperature. Therefore, for large
Bulletin 40-10 and page 15 of this bulletin. ammonia systems consisting of multiple evaporators, the Type
L charge is recommended.
Step 3 can be accomplished with the use of a removable dis-
charge tube or the nozzle of a refrigerant distributor. These
components reduce the velocity and pressure drop at the
expansion valve port by introducing a restriction or added
pressure drop in the valve outlet passage.
The removable discharge tube is threaded into the outlet of the
Type D valves, and the nominal 20, 30, and 50 ton Type A
valves. The discharge tube is the principle difference between
ammonia TEVs and TEVs used with other refrigerants.
Discharge tube sizes are listed in the Type D and A valve spec-
ifications on pages 4 and 5.
The discharge tube in the outlet passage must be removed when
the TEV is combined with a Sporlan ammonia distributor and
Page 4 CATALOG
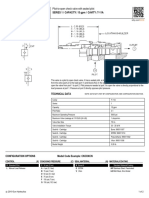
Type D FPT Flange Connections
The Sporlan Type D valve is an externally adjustable valve listed below. Refer to Sporlan Bulletin 20-10 for additional
with a gray cast iron body. It is available with either FPT or application information on this subject.
socket weld flange connections. The thermostatic element is
replaceable, and all internal parts are serviceable. An optional Note: The discharge tube must be
XD-074 (1/2 FPT) external inlet strainer may be ordered with removed when a refrigerant dis-
this valve. The nominal 1 and 2 ton Type D valves are identi- tributor is applied to the valve.
cal, with the exception of their discharge tubes, as are the nom- Outlet Connections
inal 10 and 15 ton valves. One of these valves can be D flange
converted to the other by exchanging the discharge tubes.
Distributors
1130, 1132, 1133, 1180 (aluminum)
Refrigerant distributors that will mate directly to this valve are 1182 (aluminum)
SPECIFICATIONS ELEMENT SIZE NO. 23, GASKET JOINT
TYPE Charges Available
Net Weight Lbs.
Bold figures are standard and will be
Weight Lbs.
Thermostatic
Refrigeration
Tube Orifice
furnished unless otherwise specified.
CAPACITY
Discharge
NOMINAL
Shipping
Tons of
Inches
Port Flange Ring
External Size
Length Ft.
Size OD X ID
Internal
Std. Tubing
Equalizer Inches CONNECTIONS Inches Inches
Equalizer
1/8" FPT FPT
INLET OUTLET
DA-1 DAE-1 1 1/16 1/32
5
DA-2 DAE-2 2 1/16 1/16
DA-5 DAE-5 5 7/64 5/64 C-Z-L 10 1/4, 3/8, or 1/2 1.12 x 0.75 8 9
DA-10 DAE-10 10 3/16 7/64 15
DA-15 DAE-15 15 3/16 5/32
2.75
BULB SIZES Inches
REFRIGERANT
CHARGES
717 Ammonia
2.31 Discharge Tube C-Z-L 0.75 x 4.00
Compact combination of XD
1.38 Strainer MA5A3 Solenoid
Valve DA Thermostatic
Expansion Valve & 1130
Steel Distributor
Inlet Strainer
Screen
4.06 Assembly
1/16 Port
P/N 3777-000
7/64 & 3/16
Port
P/N 3777-001
Types XD Strainer
DA Thermostatic
3.25
Expansion Valve &
1132 Steel Distributor
5.06
MATERIALS & DETAILS OF CONSTRUCTION
VALVE PIN TYPE of INLET
BODY SEAT PIN PUSHROD(S) CONNECTIONS
TYPE CARRIER JOINTS STRAINER
Stainless Removable
Gray Iron Tungsten Stainless Stainless Pipe Flange,
D Casting Steel or
Steel Alloy Carbide Steel Steel Gasket Socket Weld Strainer
Screen
CATALOG Page 5
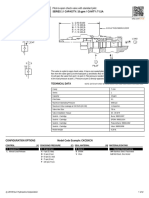
Type A FPT Flange Connections
The Sporlan Type A valve is an externally adjustable valve other by exchanging their discharge tubes. The nominal 75 and
with a gray cast iron body and either FPT or socket weld 100 ton Type A valves do not employ a discharge tube, nor are
flange connections. The ther- their outlets tapped to receive one.
mostatic element is replace-
able. An optional 8004 (1/2 Refrigerant distributors that will mate directly to this valve are
FPT) or 8006 (3/4 FPT) listed below. Refer to Sporlan Bulletin 20-10 for additional
strainer may be ordered with application information on this subject. Note: The discharge
this valve. tube must be removed from the nominal 20, 30, and 50 ton
Type A valves when a refrigerant distributor is applied.
The nominal 20 and 30 ton
Type A valves are identical Outlet Connections
A flange
with the exception of their dis-
charge tubes. One of these Distributors
valves can be converted to the 1138, 1185 (aluminum)
SPECIFICATIONS ELEMENT SIZE NO. 12, GASKET JOINT
Charges Available
TYPE
Net Weight Lbs.
Bold figures are standard and will be
Weight Lbs.
Thermostatic
Refrigeration
Tube Orifice
furnished unless otherwise specified.
Discharge
CAPACITY
NOMINAL
Shipping
Port Flange Ring
Tons of
Inches
Length Ft.
Std. Tubing
External Size Size OD x ID
Internal CONNECTIONS Inches
Equalizer Inches Inches
Equalizer FPT
1/8" FPT
INLET OUTLET
AA-20 AAE-20 20 5/16 1/8
AA-30 AAE-30 30 5/16 5/32 10 1/2, 3/4, or 1
L
AA-50 AAE-50 50 3/8 3/16 1.75 x 1.25 10 11
Only 15
AA-75 AAE-75 75 3/8
3/4 or 1
AA-100 AAE-100 100 7/16
3.62 BULB SIZES Inches
REFRIGERANT
CHARGE
717 Ammonia
2.38 L - Only 0.88 OD x 6.00
5.00
Inlet Strainer
Screen
Assembly
P/N 1471-000 8004 Strainer AA
Thermostatic Expansion
Valve & 1185 Aluminum
5.38 Distributor
7.25
MATERIALS & DETAILS OF CONSTRUCTION
VALVE PIN TYPE of INLET
BODY SEAT PIN PUSHROD(S) CONNECTIONS
TYPE CARRIER JOINTS STRAINER
20 & 30 Ton: Removable
Gray Iron Stainless Tungsten Carbide Stainless Stainless Pipe Flange,
A Casting Steel 50, 75, & 100 Ton: Steel Steel Gasket Socket Weld Strainer
Screen
Stainless Steel
Page 6 CATALOG
Thermostatic Expansion Valve Capacities Tons of Refrigeration
These ratings are based on vapor free 86F liquid refrigerant entering the TEV, a maximum opening superheat of 7F, and a
standard factory air test setting.
AC and AL THERMOSTATIC CHARGES
EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE F
VALVE NOMINAL PORT DISCHARGE 40 20 5
TYPE CAPACITY SIZE TUBE SIZE PRESSURE DROP ACROSS VALVE psi
80 100 120 140 100 120 140 160 100 120 140 160
D 1 1/16 1/32 1.08 1.21 1.32 1.43 1.02 1.12 1.21 1.29 0.85 0.93 1.00 1.07
D 2 1/16 1/16 2.16 2.41 2.64 2.86 2.05 2.24 2.42 2.59 1.69 1.85 2.00 2.14
D 5 7/64 5/64 5.40 6.03 6.61 7.14 5.12 5.61 6.05 6.47 4.23 4.63 5.00 5.35
D 10 3/16 7/64 10.8 12.1 13.2 14.3 10.2 11.2 12.1 12.9 8.45 9.26 10.0 10.7
D 15 3/16 5/32 16.2 18.1 19.8 21.4 15.4 16.8 18.2 19.4 12.7 13.9 15.0 16.0
A 20 5/16 1 /8 19.3 21.6 23.6 25.5 18.8 20.6 22.2 23.7 16.9 18.5 20.0 21.4
A 30 5/16 5/32 28.9 32.3 35.4 38.2 28.1 30.8 33.3 35.6 25.4 27.8 30.0 32.1
A 50 3/8 3/16 48.2 53.9 59.0 63.7 46.9 51.4 55.5 59.3 42.3 46.3 50.0 53.5
A 75 3/8 72.3 80.8 88.5 95.6 70.4 77.1 83.3 89.0 63.4 69.4 75.0 80.2
A 100 7/16 96.4 108 118 127 93.8 103 111 119 84.5 92.6 100 107
AZ and AL THERMOSTATIC CHARGES
EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE F
VALVE NOMINAL PORT DISCHARGE -10 -20
TYPE CAPACITY SIZE TUBE SIZE PRESSURE DROP ACROSS VALVE psi
120 140 160 180 120 140 160 180
D 1 1/16 1/32 0.61 0.66 0.71 0.75 0.52 0.56 0.60 0.63
D 2 1/16 1/16 1.06 1.14 1.22 1.29 0.89 0.96 1.03 1.09
D 5 7/64 5/64 2.48 2.68 2.87 3.04 2.09 2.26 2.42 2.56
D 10 3/16 7/64 5.24 5.66 6.05 6.42 4.42 4.78 5.11 5.42
D 15 3/16 5/32 7.27 7.85 8.39 8.90 6.13 6.62 7.08 7.51
A 20 5/16 1/8 15.9 17.2 18.4 19.5 13.6 14.7 15.8 16.7
A 30 5/16 5/32 23.9 25.8 27.6 29.3 20.5 22.1 23.6 25.1
A 50 3/8 3/16 39.9 43.1 46.0 48.8 34.1 36.9 39.4 41.8
A 75 3/8 59.8 64.6 69.1 73.2 51.2 55.3 59.1 62.7
A 100 7/16 79.7 86.1 92.1 97.7 68.2 73.7 78.8 83.6
LIQUID TEMPERATURE ENTERING TEV F
EXAMPLE: Actual capacity of nominal 10 ton valve at -10F evapo-
REFRIGERANT 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 86 90 100 rator, 160 psi pressure drop and 60F liquid temperature = 6.05
CORRECTION FACTOR, CF LIQUID TEMPERATURE tons x 1.08 = 6.53 tons.
717 1.27 1.24 1.20 1.17 1.14 1.11 1.08 1.05 1.02 1.00 0.99 0.96
These factors include corrections for liquid refrigerant density and net refrigerating effect and are based on an average evaporator tem-
perature of 0F. However, they may be used for any evaporator temperature from -20F to 40F since the variation in the actual factors
across this range is insignificant.
CATALOG Page 7
Selection Procedure
The following procedure should be used when selecting a mine the nominal capacity of the valve from the second col-
Refrigerant 717 Ammonia TEV: umn of the table. On multiple evaporator systems, select each
valve on the basis of individual evaporator capacity.
1. Determine the pressure drop across the valve.
Subtract the evaporating pressure from the condensing pressure. 4. Determine if an external equalizer is required.
The condensing pressure used in this calculation should be the The amount of pressure drop between the valve outlet and bulb
minimum operating condensing pressure of the system. From location will determine if an external equalizer is required. The
this value, subtract all other pressure losses to obtain the net recommendations given in Table 1 are suitable for most field
pressure drop across the valve. Be sure to consider all of the fol- installed systems. Use an externally equalized valve when pres-
lowing possible sources of pressure drop: (1) friction losses sure drop between the valve outlet and bulb location exceeds
through refrigeration lines including the evaporator and con- values shown in Table 2. An externally equalized valve must be
denser; (2) pressure drop across liquid line accessories such as a used on evaporators, which employ a refrigerant distributor.
solenoid valve and filter-drier; and (3) static pressure loss (gain)
Table 2
due to the vertical lift (drop) of the liquid line, see Table 1.
EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE F
Table 1
REFRIGERANT 40 20 0 -20
VERTICAL LIFT FEET PRESSURE DROP psi
REFRIGERANT 20 40 60 80 100 717 Ammonia 3 2 1. 5 1.0
STATIC PRESSURE LOSS psi
717 Ammonia 5 10 15 20 25 When the thermostatic expansion valve is equipped with an
external equalizer, it must be connected. Do not cap off the
It is not necessary to subtract the pressure drop across the equalizer connection, as it will prevent the valve from operat-
refrigerant distributor when determining the pressure drop ing properly.
across a Sporlan Type D or Type A valve with a nominal rat-
ing of 50 tons or less. These valves employ a discharge tube in 5. Select the Sporlan Selective Thermostatic Charge
the valve outlet passageway, and it should be removed when a Select the charge according to the design evaporator tempera-
distributor is connected to the valve. Sporlan distributors are ture and the valve application. The subject of R-717 thermo-
normally selected to provide a 40 psi pressure drop at design static charges is discussed on page 3. Refer to Bulletin 10-9 for
load conditions for ammonia applications. Removing the dis- a complete discussion of Sporlan Selective Thermostatic
charge tube from the valve will compensate for this pressure Charges.
drop. Refer to Bulletin 20-10 for further information on refrig-
erant distributors. Selection Example:
Refrigerant 717
2. Determine the liquid temperature of the Application: Refrigeration, single evaporator system
refrigerant entering the valve.
Design evaporator temperature 5F
The R-717 Ammonia TEV rating tables on page 6 are based on
Design condenser temperature 90F
a liquid temperature of 86F. For other liquid temperatures,
Refrigerant liquid temperature 80F
apply the correction factor given in the table.
Design evaporator capacity 5 tons
a. Design
E evaporating
EMP Available pressure drop across TEV
OR T
temperature
Condensing pressure (psig) 166
RAT 0
EVA
P O 2 SS V b. Available pressure drop Evaporator pressure (psig) -19
P A CRO 0
RO 16 147
S U RE D 40 1.07
S 1
120 1.0 0 2.14 Liquid line and accessories loss (psi) -7
0.9 3 2 . 0 0 5.35 CAPA Distributor and tubes loss (psi) 0
. 8 5 5 . 0 0 10.7 EVAPO CITY (tons) 140
1 RATING
4.6 3 10 . 0 Conde
ns TEMP
Temp. ing
9.26
(F) 0 5 10
Refrigerant liquid correction factor 1.02
80 3
90 2 .1 5.2 7 The DAE-5 has a valve capacity of: 5.00 x 1.02 = 5.10 tons at
The valve capacity should equal .8 5.0 .2 5F evaporator temperature, 140 psi pressure drop, and 80F
100 6.9
or slightly exceed the tonnage 2.5 4 liquid temperature.
.7 6.6
rating of the system.
Thermostatic charge, see page 3: C
3. Select valve from the rating tables.
Select a valve based on the design evaporating temperature Selection: DAE-5-C
and the available pressure drop across the valve. If possible, An externally equalized valve must be used on evaporators
the valve rating should equal or slightly exceed the design rat- employing a refrigerant distributor due to the pressure drop cre-
ing of the system. Be sure to apply the appropriate liquid tem- ated by the distributor. Pressure drop due to the distributor is not
used in the calculation to determine pressure drop across the TEV
perature correction factor to the valve ratings shown in the since the valves discharge tube will be removed. Refer to step 1 of
tables. Once the desired valve rating has been located, deter- the selection procedure.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Dae 15 Y764Dokument4 SeitenDae 15 Y764Gerber GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRE-120Dokument4 SeitenDRE-120Gesiel SoaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fpe 1 2 Válvula TermostáticaDokument6 SeitenFpe 1 2 Válvula TermostáticamarbbanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commercial Heavy Duty Water Heater With Surface Mount ThermostatsDokument4 SeitenCommercial Heavy Duty Water Heater With Surface Mount Thermostatsfirefightermanta31Noch keine Bewertungen
- ALLWEILER - Volute Casing Centrifugal Pumps of Inline DesignDokument16 SeitenALLWEILER - Volute Casing Centrifugal Pumps of Inline DesignHamza AbdelhamidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ficha Tecnica Trampa Termostatica Archive A PDFDokument2 SeitenFicha Tecnica Trampa Termostatica Archive A PDFAlexis PradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- L & M Series Ultra-Capacity Float & Thermostatic Steam Trap: Description How To OrderDokument2 SeitenL & M Series Ultra-Capacity Float & Thermostatic Steam Trap: Description How To OrderJozsef MagyariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volute Casing Centrifugal Pumps of Block Design Series NB: VM 528 GB/2012.06 - Ident No. 795 261Dokument20 SeitenVolute Casing Centrifugal Pumps of Block Design Series NB: VM 528 GB/2012.06 - Ident No. 795 261safwan azizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Heat Exchangers: Shell & Tube Marine CondensersDokument16 SeitenAdvanced Heat Exchangers: Shell & Tube Marine CondensersMarco CambeiroaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Three-Way Thermostatic Valve: SelectionDokument2 SeitenThree-Way Thermostatic Valve: SelectionRoshaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid. State.: Commercial ElectricDokument4 SeitenSolid. State.: Commercial ElectricImtiyaz KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Level Gauges & Level Transmitters: FeaturesDokument3 SeitenMagnetic Level Gauges & Level Transmitters: Featuressunshine dreamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flash Recovery Vessels-Technical InformationDokument2 SeitenFlash Recovery Vessels-Technical InformationdzungNoch keine Bewertungen
- DMBF Full en Metric LetterDokument4 SeitenDMBF Full en Metric LetterRonaldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blue Box Zeta2002 Manual4Dokument14 SeitenBlue Box Zeta2002 Manual4Carlos MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- System - Rated - Plus - W - Sub - 150 Water Hammer PPPDokument2 SeitenSystem - Rated - Plus - W - Sub - 150 Water Hammer PPPJeffry GabilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eco-Mix: Alternate Temperature Thermostatic Mixing ValvesDokument2 SeitenEco-Mix: Alternate Temperature Thermostatic Mixing ValveskcloiobkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Costing 040419Dokument24 SeitenReference Costing 040419Bency ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet E Thermostatic Valve 0612 Rev8Dokument10 SeitenDatasheet E Thermostatic Valve 0612 Rev8Mohamed AhteewishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Of Fire In: A.K. Mukhopadhyay and P.P. SinghDokument13 SeitenOf Fire In: A.K. Mukhopadhyay and P.P. SinghImmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet AMOT 6BDokument6 SeitenDatasheet AMOT 6BMohamed AhteewishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manejadora - Cba25uh - 018 Al 060 - Lennox - Ficha Tecnica - I LennoxDokument16 SeitenManejadora - Cba25uh - 018 Al 060 - Lennox - Ficha Tecnica - I LennoxWalter BernalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manejadora - Cba25uh - 018 Al 060 - Lennox - Ficha Tecnica - I LennoxDokument16 SeitenManejadora - Cba25uh - 018 Al 060 - Lennox - Ficha Tecnica - I LennoxWalter BernalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screw Pumps Series SPF: Application Shaft SealingDokument16 SeitenScrew Pumps Series SPF: Application Shaft Sealingmsh16000Noch keine Bewertungen
- fb4cnf 04pd PDFDokument16 Seitenfb4cnf 04pd PDFgabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fan Coil Unit - Small Profile - Unilux-2PipeDokument4 SeitenFan Coil Unit - Small Profile - Unilux-2PipePamela De MeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dfu Ti D148 01 BRDokument2 SeitenDfu Ti D148 01 BRNoo SokiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Pilot-To-Open Check Valve With Sealed Pilot: Series 1 / Capacity: 15 GPM / Cavity: T-11ADokument2 SeitenModel Pilot-To-Open Check Valve With Sealed Pilot: Series 1 / Capacity: 15 GPM / Cavity: T-11AVignesh PandiyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Pilot-To-Open Check Valve With Standard Pilot: Series 1 / Capacity: 15 GPM / Cavity: T-11ADokument2 SeitenModel Pilot-To-Open Check Valve With Standard Pilot: Series 1 / Capacity: 15 GPM / Cavity: T-11AAnurag JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sta-D: Balancing Valves JuneDokument4 SeitenSta-D: Balancing Valves JuneAdel MercadejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Pilot-To-Open Check Valve With Standard Pilot: Series 1 / Capacity: 15 GPM / Cavity: T-11ADokument2 SeitenModel Pilot-To-Open Check Valve With Standard Pilot: Series 1 / Capacity: 15 GPM / Cavity: T-11AErasmo LimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- V5329A TWDokument4 SeitenV5329A TWS M NaveedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDokument4 SeitenRefrigeration and Air ConditioningJasminkoCvitešićNoch keine Bewertungen
- CKEB_full_en_metric_letterDokument2 SeitenCKEB_full_en_metric_letterRafalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 160 RT1003 1009Dokument12 Seiten160 RT1003 1009Procurement PardisanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Condensador DZ11SDokument16 SeitenCondensador DZ11SIsrael ArceoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normally Closed Solenoid Valves PDFDokument55 SeitenNormally Closed Solenoid Valves PDFrahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Float & Thermostatic Steam Traps: For Efficient Condensate Drainage of Industrial Process and HVAC EquipmentDokument12 SeitenFloat & Thermostatic Steam Traps: For Efficient Condensate Drainage of Industrial Process and HVAC Equipmentmember1000Noch keine Bewertungen
- LOGIC CARTRIDGE LODCXDN - Full - en - Us - LetterDokument2 SeitenLOGIC CARTRIDGE LODCXDN - Full - en - Us - LetterHassan KhattabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Millennium: Air Cooled Screw Liquid ChillersDokument64 SeitenMillennium: Air Cooled Screw Liquid ChillersJulian Andres VillarrealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Condenser ManualDokument48 SeitenCondenser ManualVishal Kumar Laddha100% (1)
- Air Valves For Industry Since 1949: Namur Direct Mount Pneumatic Actuator ValvesDokument4 SeitenAir Valves For Industry Since 1949: Namur Direct Mount Pneumatic Actuator ValvesCalidad - TGINoch keine Bewertungen
- Precision Plumbing Products: "Specify With Confidence - Install With Pride"Dokument2 SeitenPrecision Plumbing Products: "Specify With Confidence - Install With Pride"Janavi RajaganapathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulators For Heating and Air Conditioning Systems: ApplicationsDokument18 SeitenCirculators For Heating and Air Conditioning Systems: Applicationsresistance-bandsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam control and condensate drainage for heat exchangersDokument6 SeitenSteam control and condensate drainage for heat exchangerssushant_jhawerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inst. ManualDokument8 SeitenInst. ManualHamoud Al khayatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24032017010149derval Cast Steel Gate Valve - VS01 (ASME 150)Dokument4 Seiten24032017010149derval Cast Steel Gate Valve - VS01 (ASME 150)abdo elmokademNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eclipse F: Thermostatic Radiator ValvesDokument8 SeitenEclipse F: Thermostatic Radiator Valvessandra1833Noch keine Bewertungen
- Model B: Thermostatic Control ValvesDokument13 SeitenModel B: Thermostatic Control ValvesRei_budNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ficha Tecnica Amstrong.1Dokument2 SeitenFicha Tecnica Amstrong.1ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Alfacond Range: Plate CondensersDokument2 SeitenAlfacond Range: Plate Condensersandres mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model B: Thermostatic Control ValvesDokument13 SeitenModel B: Thermostatic Control ValvesMohamed AhteewishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Engineering For Design of Liquid (326-452)Dokument127 SeitenModern Engineering For Design of Liquid (326-452)Misha's Kitchen And OtherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dat vd11-vd12-vd13 eDokument2 SeitenDat vd11-vd12-vd13 eEnrique Alonso Tasson RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flanged Linear Valve Pn6/16: FeaturesDokument4 SeitenFlanged Linear Valve Pn6/16: FeaturesCrisTimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valvula Honeywel V5329a1Dokument4 SeitenValvula Honeywel V5329a1DAVIDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Free Flow Nose To Side Check Valve With Bypass OrificeDokument2 SeitenModel Free Flow Nose To Side Check Valve With Bypass OrificeRenjithSivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vapour AbsorptinDokument12 SeitenVapour AbsorptinDhruv BajpaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaporator Coil Installation Instructions 96654002 ADPDokument4 SeitenEvaporator Coil Installation Instructions 96654002 ADPgeoffffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkyl Halide and Aryl HalideDokument43 SeitenAlkyl Halide and Aryl HalideShivanshi0950% (2)
- Erosion Tecnalia 2016 06Dokument17 SeitenErosion Tecnalia 2016 06FernanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry-College 3Dokument10 SeitenChemistry-College 3Subhabrata MabhaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPC F1 IS Unit 2 Water - TeacherEdDokument29 SeitenSPC F1 IS Unit 2 Water - TeacherEdFor BackupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibacterial Surfaces For Biomedical DevicesDokument15 SeitenAntibacterial Surfaces For Biomedical DevicesClever Ricardo ChinagliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ - Question-Paper-11 PDFDokument16 SeitenMCQ - Question-Paper-11 PDFMuhammad TauseefNoch keine Bewertungen
- EP0070932B1Dokument5 SeitenEP0070932B1bayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jess 106Dokument16 SeitenJess 106Tej Krishan SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coway water purifiers product collectionDokument10 SeitenCoway water purifiers product collectionSyida NaufalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 1 Biology F4Dokument12 SeitenTest 1 Biology F4Nurfatin JamaludinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Lecture Planner - Prayas 2022 - Complete Lecture Planner - Early Dropper Batch JEE - Chemistry PlannerDokument2 SeitenChemistry Lecture Planner - Prayas 2022 - Complete Lecture Planner - Early Dropper Batch JEE - Chemistry PlannerPradeep Yadav100% (1)
- Pop-up and Starter Fertilizers for Corn: Rates, Placement and Nutrient RemovalDokument5 SeitenPop-up and Starter Fertilizers for Corn: Rates, Placement and Nutrient RemovaluserNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Unit 1&2) PDFDokument41 Seiten(Unit 1&2) PDFJaiPrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- My first experience student teaching chemistry at Manila Science High SchoolDokument2 SeitenMy first experience student teaching chemistry at Manila Science High SchoolIta Adri SupriatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sodium Carbonate Production from Trona OreDokument17 SeitenSodium Carbonate Production from Trona OreVaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- OPSS 369 Nov08Dokument7 SeitenOPSS 369 Nov08Muhammad UmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bass String Diameters and TensionsDokument6 SeitenBass String Diameters and Tensionsbonruiz100% (1)
- AAMA Vs Qualicoat 2018Dokument12 SeitenAAMA Vs Qualicoat 2018viet nguyen cao0% (1)
- Fishing in Drilling OperationsDokument19 SeitenFishing in Drilling Operationsmts1234100% (1)
- ST TLE Agri. Crop Production 7 NO. 1Dokument3 SeitenST TLE Agri. Crop Production 7 NO. 1Vince Zoi Galvan100% (1)
- Potabilización de AguaDokument9 SeitenPotabilización de AguaSHEILA GINIVA BUSTOS YAIMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Aditya Dixit2223bag16gt002 Module 2 Org..Dokument18 SeitenAditya Dixit2223bag16gt002 Module 2 Org..DADADADGGGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Based Thermosetting Resins For FuturDokument34 SeitenBio Based Thermosetting Resins For Futursatish kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Data Sheet: Pt. Musim MasDokument6 SeitenSafety Data Sheet: Pt. Musim MasAydilover AydinousNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Set Up a New Aquarium in 7 Easy StepsDokument40 SeitenHow to Set Up a New Aquarium in 7 Easy StepsAndrew HardcastleNoch keine Bewertungen
- UPSEE Full-Paper 2006Dokument40 SeitenUPSEE Full-Paper 2006AditiBhatnagar1100% (1)
- Method Statement For Installation of Water Recticulation SystemDokument18 SeitenMethod Statement For Installation of Water Recticulation SystemRabi'atul Adawiyah Ismail100% (2)
- ACUSOL™ 820 Rheology Modifier/Stabilizer: Description ApplicationsDokument9 SeitenACUSOL™ 820 Rheology Modifier/Stabilizer: Description Applicationsbob bobkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyanide-Free Gold Ore Dressing Agent PDFDokument13 SeitenCyanide-Free Gold Ore Dressing Agent PDFAldemar Arciniegas100% (1)
- Lecture Notes Air Pollution TechnologiesDokument27 SeitenLecture Notes Air Pollution TechnologiesMedo HamedNoch keine Bewertungen