Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Power Tools Tutorial
Hochgeladen von
choopoOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Power Tools Tutorial
Hochgeladen von
choopoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Trelis Power Tools GUI Tutorial
Trelis Power Tools GUI Tutorial
Overview
In this tutorial you learn how to use Trelis Power Tools to decompose and cleanup a geometry so that it
can be properly meshed. The following features will be covered:
Importing Geometry
Analyzing Geometry
Geometry Power Tools
Webcutting
Imprint/Merge
Mesh Power Tools
Meshing
Each step is described in detail in the following sections. For this tutorial you will need to have a basic
understanding of the Trelis GUI functionality, including how to select entities, maneuver in the graphics
window, operate the Command Panel, and use toolbars. If you have not already done so, we
recommend completing the Getting Started with Trelis Tutorial first.
NOTE: Many of the steps in this tutorial include operations on specific entities that are identified by ID.
When the solid modeling kernel is updated in Trelis the ID space may change. As such, you may not be
able to rely on the IDs specified in this tutorial. Please look at the associated graphics to determine
which entity/ID is being referred to.
Step 1: Import the Geometry
Begin by opening a new session of Trelis. To complete this tutorial, you will need to download the ACIS
file that contains the geometry definition.
To Import the Geometry
1. Download geometry file knuckle.sat
Note: You will need to access this file from the Trelis web site under Support/Documentation.
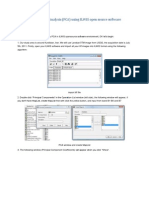
2. Select Import from the File menu.
The following dialog box will appear. Open the file by clicking on the name and selecting Open. If you do
not see the file, make sure that you are in the right directory, and that the file type is set to ACIS.
Revised May 28, 2013 1|P a g e
Trelis Power Tools GUI Tutorial
3. Leave all of the import settings on their default settings and click Finish.
Your graphics window will appear as follows
Revised May 28, 2013 2|P a g e
Trelis Power Tools GUI Tutorial
Use the mouse to rotate the image to get a better perspective.
Step 2: Analyze the Geometry
The Power Tools panel is located on the left side of the Trelis window. Tools for Geometry Diagnostics
and Meshability can be found in the Power Tools panel.
Many geometries that are imported from other solid modeling software contain inconsistencies or small
gaps that can cause meshing to fail. These problems are the result of differences in tolerances, file
transfer loss, or inherent limitations in the parent system. In other instances, the geometry has no
Revised May 28, 2013 3|P a g e
Trelis Power Tools GUI Tutorial
inconsistencies, but may be unsuitable for meshing because of topology such as small angles, overlap, or
features smaller than the desired meshing size.
Many of these problems can be fixed using the tools on the Power Tools menu. These include Split
Surface, Heal, Tweak, Remove, Merge, Composite, Collapse Angle, Collapse Curve, and Collapse Surface.
Some of these tools will be demonstrated in this tutorial.
To start, we need to analyze the geometry to see what is preventing the geometry from being meshable.
We will then go through the proper steps to decompose and cleanup the geometry so it will mesh.
To Analyze the Geometry
1. Click on the Diagnose Geometry tab from the Power Tools
panel.
2. Enter all in the Volume ID(s) field.
3. Enter 1 in the Shortest Edge Length field.
4. Click Analyze.
After the Analyze Button is pushed, a display area will appear as
shown above. There are four suspected problems with this
geometry: Close Loops, Blend Surfaces, Curves with Small Angles,
and Badly Defined Geometry. The numbers in parentheses indicate
the number of occurrences of this problem in the model. Clicking
the arrow by each label will display the entities by ID with this
problem. Clicking on the arrow by each entity will cause that entity's children or parents to be listed
(depending on the entity and the type of geometry test). See documentation on Geometry Repair for
more information about the display window.
Clicking on the name of an entity will highlight that entity in the graphics window.
Select Vertex 45 under Curves with Small Angles
Observe that this vertex is highlighted in the graphics window.
Right click and select Zoom To from the list of options
Revised May 28, 2013 4|P a g e
Trelis Power Tools GUI Tutorial
The graphics window should look like this:
Right Click on Vertex 45 and select Reset Zoom from the list of options
The image should now be reset to the previous graphics state.
You can experiment with some of the other options in the top half of the right click menu. They are:
Fly-in - Animated zoom feature
Locate - Labels entity
Draw - Draw this entity by itself
Draw with Neighbors - Draw this entity with all adjacent curves and surfaces
Clear Highlights - Clear all highlighted entities
The Reset Graphics button can be found in the menu of buttons at the bottom of the Diagnose
Geometry tab- Refreshes graphics screen; Pressing the reset graphics button on the menu may also
reset the graphics window.
Step 3: Healing the Geometry
The first step to improving any geometry is to look for badly defined
geometry and to fix it using the Autoheal tool in Trelis. It is always a good
idea to run the Autoheal on imported geometry. In this example, the Power
Tools has located some badly defined curves. This step will show you how to
fix these curves.
To Heal the Geometry
1. With the Diagnose Geometry tab still open, Click the Heal button in
the lower left of the panel. (Alternatively, you can manually
Revised May 28, 2013 5|P a g e
Trelis Power Tools GUI Tutorial
highlight all Badly Defined Curves, right click, and select Heal Owning Body from the list of
options).
Note: The Diagnose Geometry Tool does not execute any geometry clean-up commands directly, but
directs you to the place on the Command Panel where this function can be executed.
2. Now on the Command Panel, verify that 1 is in the Volume ID(s) field.
3. Select Autoheal.
4. Click Apply.
The output window on the Trelis GUI should appear with the following message. You may have to scroll
to see the whole thing. The percentages before and after healing are 97% to 100%. Healing has been
successful.
Run the geometry analysis test again to guarantee that all bad geometry has been removed.
Revised May 28, 2013 6|P a g e
Trelis Power Tools GUI Tutorial
Step 4: Removing Small Surfaces
Some surfaces are too small for analysis and should be removed from the model. In this example,
Surface 15 and Surface 17 fall into that category, assuming that the distance between curves on these
surfaces is smaller than the desired final mesh size.
To Remove Small Surfaces
1. Click on the Diagnose Geometry tab from the Power Tools panel.
2. Enter all in the Volume ID(s) field and enter 1 in the Shortest Edge Length field
3. Click Analyze.
4. Expand the Closed Loops from the Entity ID menu.
Surface 15 and 17 will appear and they both will need to be
removed.
5. Click on Surface 17 and then click the Remove Button
from the Real menu. (Alternatively, you can also right
click and select Remove). The Command Panel will
appear with the Remove settings open. The Surface ID
should also appear in the input field.
6. Verify that the Extend and Remove Individually boxes
are checked.
7. Click Apply.
Repeat steps 1-7 for Surface 15.
Step 5: Web Cutting
Web cutting is this process of dividing volumes into sweepable regions
by cutting with a plane.
Since the model has holes through it, sweeping is not possible from a
single source and target. However, we can make the volume meshable
by dividing the model into sweepable regions using a series of webcuts.
To make the first Webcut
1. On the Command Panel, click on Geometry and then Volume.
2. Click on the Webcut action button.
3. Select Plane Normal To Curve (vertex) from the drop-down
menu.
4. Enter 1 in the Volume ID(s) field. This can also be done using the
Pick Widget function.
5. Enter 59 in the Curve ID field. This can also be done using the
Revised May 28, 2013 7|P a g e
Trelis Power Tools GUI Tutorial
Pick Widget function.
6. Select Fraction from the Method menu.
7. Enter 1 in the Value field.
8. Click Preview and then Apply.
To make the second Webcut
1. With the Webcut window still open, enter 1 in the Volume ID(s) field. This can also be done
using the Pick Widget function.
2. Enter 59 in the Curve ID field. This can also be done using the Pick Widget function.
3. Select Fraction from the Method menu.
4. Enter 0 in the Value field.
5. Click Apply.
To make the third, and final, Webcut
1. With the Webcut window still open, enter 4 in
the Volume ID(s) field. This can also be done
using the Pick Widget function.
2. Enter 31 in the Curve ID field. This can also be
done using the Pick Widget function.
3. Select Fraction from the Method menu.
4. Enter 1 in the Value field.
5. Click Apply.
Revised May 28, 2013 8|P a g e
Trelis Power Tools GUI Tutorial
The final webcut model should look like this:
Step 6: Imprint/Merge
Imprinting is the process of projecting curves from one surface onto an overlapping surface. Merging is
the process of taking two overlapping surfaces and merging them into one surface shared by two
volumes, creating non-manifold geometry. Both imprinting and merging are necessary to make adjacent
volumes have identical meshes at their intersection. Imprinting and merging is almost always necessary
after webcutting.
To Imprint and Merge
1. On the Command Panel, click on Geometry and then Volume.
2. Click on the Imprint Merge action button.
3. Select Imprint/Merge from the drop-down menu.
4. Enter all in the Volume ID(s) field.
5. Click Apply.
Step 7: Mesh Power Tools
The Mesh Power Tool provides an easy and graphical way to determine if
volumes are meshable. This tool will employ the AutoScheme feature in Trelis to
select and assign schemes to meshable volumes. If a volume is not currently
meshable, it will be flagged and highlighted. Use the Mesh Power Tool to
determine if the volume is currently meshable and to apply schemes to the
remaining volumes.
To check Meshability
1. Click on Diagnose Meshability from the Power Tools panel.
2. Enter all in the Volume ID(s) field.
Revised May 28, 2013 9|P a g e
Trelis Power Tools GUI Tutorial
3. Click Analyze.
Note: All volumes that are meshable are highlighted in
green, and all volumes that are not meshable are
highlighted in red.
All of the schemes have now been set with a sweeping
algorithm. The model is ready to be meshed. All volumes
should appear green in the graphics window.
Toggle the Reset Graphics button (located at the bottom right corner of the Power Tools panel) to
return volumes to their original colors.
Step 8: Meshing the Model
Now that you have used the Mesh Power Tools to apply schemes to the
remaining volumes. The Geometry is ready to be meshed.
To Mesh the Geometry
1. On the Command Panel, click on Mesh and then Volume.
2. Click on the Mesh action button.
3. Enter all in the Select Entities to Mesh field.
Note: There is no need to press the Apply Scheme button since the
scheme has already been set in the Meshing Tools.
4. Click Mesh.
Revised May 28, 2013 10 | P a g e
Trelis Power Tools GUI Tutorial
Congratulations! You have just completed the Power Tools Tutorial.
Revised May 28, 2013 11 | P a g e
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Solidworks NotesDokument98 SeitenSolidworks Notesmadmaxx42100% (2)
- Sample Questions Ap Calculus Ab and BC Exams PDFDokument45 SeitenSample Questions Ap Calculus Ab and BC Exams PDFIshaan UtkarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- MasterCAM 3D Model CreationDokument20 SeitenMasterCAM 3D Model CreationmartfilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural EfficiencyDokument5 SeitenStructural EfficiencychoopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arihant Maths Sample PaperDokument192 SeitenArihant Maths Sample PaperYash Saini100% (5)
- VXmodel Tutorial - Scan-to-CAD 2Dokument15 SeitenVXmodel Tutorial - Scan-to-CAD 2shahnawaz875Noch keine Bewertungen
- SolidWorks 2015 Learn by doing-Part 3 (DimXpert and Rendering)Von EverandSolidWorks 2015 Learn by doing-Part 3 (DimXpert and Rendering)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (5)
- Autodesk Inventor Intermediate Level - EnglishDokument211 SeitenAutodesk Inventor Intermediate Level - EnglishGiLang MaulanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FreeStyle Shaper and OptimizerDokument234 SeitenFreeStyle Shaper and OptimizerPrathameshNalawdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solidworks 2018 Learn by Doing - Part 3: DimXpert and RenderingVon EverandSolidworks 2018 Learn by Doing - Part 3: DimXpert and RenderingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding nth Roots and Radical ExpressionsDokument82 SeitenUnderstanding nth Roots and Radical ExpressionsKeppy AricangoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importing 3d Model Into MastercamDokument20 SeitenImporting 3d Model Into MastercamMarsono Bejo SuwitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pillar Gridding in PETRELDokument14 SeitenPillar Gridding in PETRELHenry Reynolds DarcyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essay Writing GuideDokument25 SeitenEssay Writing GuideChe HindsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fault Modeling: Important Icons Used in The Process StepsDokument13 SeitenFault Modeling: Important Icons Used in The Process StepsIng. José Marín100% (1)
- AMI Mesh Editing TutorialDokument29 SeitenAMI Mesh Editing TutorialWoong KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Petrel Software Work Flow Part 2Dokument32 SeitenPetrel Software Work Flow Part 2Jaime AlfonsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- OMS435 OmniStudio Student Take Home Guide v1.0Dokument44 SeitenOMS435 OmniStudio Student Take Home Guide v1.0Vojta DlapalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project - Function Family AlbumDokument3 SeitenProject - Function Family AlbumMegan Golding50% (6)
- QSCad Trial Version TutorialDokument23 SeitenQSCad Trial Version TutorialHerman Mwakoi0% (1)
- Create 3D Surfaces From InterpretationsDokument12 SeitenCreate 3D Surfaces From InterpretationsMuhammad Bilal100% (1)
- Exercise 1 - Running & Post-Processing An ExampleDokument26 SeitenExercise 1 - Running & Post-Processing An ExampleCarlos L. OyuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolidWorks 2016 Learn by doing 2016 - Part 3Von EverandSolidWorks 2016 Learn by doing 2016 - Part 3Bewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- Powermill Full 2015-0Dokument457 SeitenPowermill Full 2015-0wladwolf94% (16)
- To Rough Using Adaptive ClearingDokument4 SeitenTo Rough Using Adaptive ClearingMiguel Angel Munguia FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNC Milling Tutorial - 2D Machining of Sample PartDokument26 SeitenCNC Milling Tutorial - 2D Machining of Sample PartFilipe Alberto De MagalhãesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partmaker Tech Note 041999: Automatic Z-Depth Extraction: File Dialog Box Choose Z - Demo - DXF As Shown BelowDokument8 SeitenPartmaker Tech Note 041999: Automatic Z-Depth Extraction: File Dialog Box Choose Z - Demo - DXF As Shown Below123anthonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pro E MechanicaDokument7 SeitenPro E Mechanicajagg_studNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pro Engineer Basic Pro MechanicaDokument7 SeitenPro Engineer Basic Pro MechanicaMatheus StefaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Import and Repair CAD for FEA AnalysisDokument7 SeitenImport and Repair CAD for FEA AnalysismuhannedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise - Enumeration AreasDokument10 SeitenExercise - Enumeration AreasdepitlupikasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shapes On CNC Machines. Here We Study Mastercam For CNC Milling MachinesDokument11 SeitenShapes On CNC Machines. Here We Study Mastercam For CNC Milling MachinesMarius CucuietNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grading From A Building Footprint To A SurfaceDokument4 SeitenGrading From A Building Footprint To A SurfaceAugusto Riascos R.Noch keine Bewertungen
- CIM and Automation Lab ManualDokument39 SeitenCIM and Automation Lab ManualHareesha N G67% (3)
- Introduction 9.04Dokument93 SeitenIntroduction 9.04Wilfredo Nieves OsoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autodesk Inventor Assembly OptimizationDokument8 SeitenAutodesk Inventor Assembly Optimizationjack-bcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catia Tutorial 5: Generative Part Structural AnalysisDokument65 SeitenCatia Tutorial 5: Generative Part Structural AnalysismatmeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AltairTutorial Topography UpdatedDokument20 SeitenAltairTutorial Topography UpdatedKevin Andrés Garzón MijaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- On The Ribbon, Click CAM Tab 2D Milling Panel FaceDokument9 SeitenOn The Ribbon, Click CAM Tab 2D Milling Panel FaceGokilaDevi ChandrakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slide2 Tutorials - Quick Start TutorialDokument24 SeitenSlide2 Tutorials - Quick Start Tutorialyaseen90azizNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Using The TetraMesh Process ManagerDokument9 Seiten4 Using The TetraMesh Process ManagerDhileeban NagarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turning TutorialDokument15 SeitenTurning TutorialMiguelAlejandroObregónOlivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE415 NX TURNING CAM TUTORIALDokument20 SeitenECE415 NX TURNING CAM TUTORIALRobert CollinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part C. Tutorial Part 1 - Creating, Analyzing and Designing The Basic ModelDokument5 SeitenPart C. Tutorial Part 1 - Creating, Analyzing and Designing The Basic ModelyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 AlignmentsDokument4 Seiten03 AlignmentsJayson J. PagalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08 Turning TutorialDokument45 Seiten08 Turning TutorialrodrigodelacalperezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mesh-Intro 19.2 WS5.4 CFD Workshop Instructions Auto Ext Aero Poly PDFDokument42 SeitenMesh-Intro 19.2 WS5.4 CFD Workshop Instructions Auto Ext Aero Poly PDFlufabaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inspection Tutorial Sheet Metal PartDokument16 SeitenInspection Tutorial Sheet Metal PartPaulo Roberto SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06Altair HyperView 10.0学习资料02Dokument21 Seiten06Altair HyperView 10.0学习资料02王钦文Noch keine Bewertungen
- FASTBLANK For ProE Instructions PDFDokument11 SeitenFASTBLANK For ProE Instructions PDFNhan LeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Settlement of Circular Footing On SandDokument26 SeitenSettlement of Circular Footing On SandninoronaldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2: Assembly and Solidworks MotionDokument10 SeitenTutorial 2: Assembly and Solidworks Motionkiran_wakchaureNoch keine Bewertungen
- HM-2015: Auto-Midsurfacing With Advanced Extraction OptionsDokument6 SeitenHM-2015: Auto-Midsurfacing With Advanced Extraction OptionsmuhannedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No.01: FEA Bending in CATIADokument8 SeitenExperiment No.01: FEA Bending in CATIATrived DoijodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial IL Orthophoto DEM NeogeoDokument16 SeitenTutorial IL Orthophoto DEM NeogeoQoudar RamdhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alignments Tutorials: Creating, Editing, and Offsetting AlignmentsDokument3 SeitenAlignments Tutorials: Creating, Editing, and Offsetting AlignmentsJerel Aaron FojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- May 03Dokument12 SeitenMay 03Cecil VictorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter1 DemonstrationDokument10 SeitenChapter1 DemonstrationSantiago UrgilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter1 Demonstration PDFDokument9 SeitenChapter1 Demonstration PDFJohny SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 5Dokument12 SeitenLab 5Musa aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Input Data Editing: 3.1 Creating Reservoir BoundaryDokument7 SeitenInput Data Editing: 3.1 Creating Reservoir BoundaryjihadspiritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unsupervised Classfication Using ER MapperDokument9 SeitenUnsupervised Classfication Using ER MapperavisenicNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Introduction To The Creo Parametric Basic Modeling ProcessDokument37 Seiten01 Introduction To The Creo Parametric Basic Modeling ProcessЛазар РадојичићNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAE 477/577 - Spring 2016 CAD Applications: CategoryDokument22 SeitenMAE 477/577 - Spring 2016 CAD Applications: CategoryZurina MANoch keine Bewertungen
- EdgeCAM Lesson2Dokument23 SeitenEdgeCAM Lesson2aralvoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Manual: Finite Element Model of 2016 Xenith X2E (Safety Equipment Institute Model X2E) Version 1.0 For LS-DYNADokument41 SeitenUser Manual: Finite Element Model of 2016 Xenith X2E (Safety Equipment Institute Model X2E) Version 1.0 For LS-DYNAchoopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRII Fact Sheet Cotton Research and Development Corporation PDFDokument2 SeitenBRII Fact Sheet Cotton Research and Development Corporation PDFchoopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Riley2013 Foot Kinematics and Loading of Professional Athletes in AmericanDokument7 SeitenRiley2013 Foot Kinematics and Loading of Professional Athletes in AmericanchoopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biofabrication and Tissue Engineering: Insight SeriesDokument13 SeitenBiofabrication and Tissue Engineering: Insight SerieschoopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual 2016 Schutt Air XP Pro Helmet Model v1.0Dokument30 SeitenManual 2016 Schutt Air XP Pro Helmet Model v1.0choopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time 4 ResearchpresentationslidesDokument66 SeitenTime 4 ResearchpresentationslideschoopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Manual: Finite Element Models of Helmet Assessment Tools Version 1.0 For LS-DYNADokument35 SeitenUser Manual: Finite Element Models of Helmet Assessment Tools Version 1.0 For LS-DYNAchoopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual 2016 Riddell Revolution Classic Helmet Model v1.0Dokument32 SeitenManual 2016 Riddell Revolution Classic Helmet Model v1.0choopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book For ResearchersDokument16 SeitenBook For Researcherslaugh47Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manual 2017 Vicis Zero1 Helmet Model v1.0-1Dokument34 SeitenManual 2017 Vicis Zero1 Helmet Model v1.0-1choopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TranscriptDokument2 SeitenTranscriptchoopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcript 2Dokument2 SeitenTranscript 2choopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nature Waiting For Motivational Fairy PDFDokument1 SeiteNature Waiting For Motivational Fairy PDFnirajkulkarni09Noch keine Bewertungen
- SAC AUS18 Agenda v29 PDFDokument2 SeitenSAC AUS18 Agenda v29 PDFchoopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAC AUS18 Agenda v29 PDFDokument2 SeitenSAC AUS18 Agenda v29 PDFchoopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wearable ExoDokument1 SeiteWearable ExochoopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbo Change Your Writing Today - NatureDokument2 SeitenTurbo Change Your Writing Today - NatureDaniel LujánNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled 1Dokument1 SeiteUntitled 1choopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assembly64 PDFDokument357 SeitenAssembly64 PDFAnonymous qHRe6oNoch keine Bewertungen
- NMNBDokument3 SeitenNMNBchoopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RubbishDokument1 SeiteRubbishchoopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Australian Engineering Education Facts - Update October 2018Dokument2 SeitenAustralian Engineering Education Facts - Update October 2018choopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SsDokument1 SeiteSschoopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RubbishDokument1 SeiteRubbishchoopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Share-LinkDokument1 SeiteShare-LinkchoopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dakota White, Kyle Perry CEA A-Day P.MDokument6 SeitenDakota White, Kyle Perry CEA A-Day P.MchoopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LICENSEDokument2 SeitenLICENSEchoopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jim 2018 0001Dokument5 SeitenJim 2018 0001choopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Precalculus A Right Triangle Approach 5th Edition Beecher Solutions ManualDokument36 SeitenPrecalculus A Right Triangle Approach 5th Edition Beecher Solutions Manuallawerslowbackplpy100% (30)
- Rules of Differentiation: 1. Constant Function RuleDokument18 SeitenRules of Differentiation: 1. Constant Function RuleZhiYar NamiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Project-2Dokument5 SeitenMaths Project-2PLAY LYRICSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xii New Syllabus 2023 24-1Dokument27 SeitenXii New Syllabus 2023 24-1HP PCXNoch keine Bewertungen
- C++ in One Day - The Ultimate Beginners Guide To C++ With 7 Awesome ProjectsDokument112 SeitenC++ in One Day - The Ultimate Beginners Guide To C++ With 7 Awesome ProjectsKen KenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector Space Interpretation of Random VariablesDokument6 SeitenVector Space Interpretation of Random VariablesSiva Kumar GaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use E-Papers, Save Trees: Above Line Hide When Print OutDokument101 SeitenUse E-Papers, Save Trees: Above Line Hide When Print OutPRUTHVI100% (2)
- Transfer Function Lecture NotesDokument217 SeitenTransfer Function Lecture Notesprasanna43275% (4)
- AIR Basic Calculus Q3 W3 - Module 7 CorrectedDokument13 SeitenAIR Basic Calculus Q3 W3 - Module 7 CorrectedLove EpiphanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- GCSEPaper 2 HSet Aedxe QPDokument16 SeitenGCSEPaper 2 HSet Aedxe QPdamindaNoch keine Bewertungen
- QM Sem IDokument123 SeitenQM Sem Isanai_0204Noch keine Bewertungen
- Math-IIIDokument2 SeitenMath-IIIAnil Marsani100% (1)
- Math CadDokument480 SeitenMath Cadrebelion1310Noch keine Bewertungen
- UM2039 User Manual: World Smallest Time-of-Flight Ranging and Gesture Detection Sensor Application Programming InterfaceDokument26 SeitenUM2039 User Manual: World Smallest Time-of-Flight Ranging and Gesture Detection Sensor Application Programming InterfacepepenitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimization Methods2Dokument10 SeitenOptimization Methods2s200849298Noch keine Bewertungen
- KEY CONCEPTS OF RATIONAL FUNCTIONSDokument10 SeitenKEY CONCEPTS OF RATIONAL FUNCTIONSRobert John Basia BernalNoch keine Bewertungen
- AITT Class Test I Batch 34 QuestionsDokument5 SeitenAITT Class Test I Batch 34 QuestionsDevashish BhartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robot Unit Lesson PlanDokument8 SeitenRobot Unit Lesson Planapi-385924845Noch keine Bewertungen
- Report of Square GearDokument9 SeitenReport of Square GearsrajaprojectsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Word - Unit 4.lesson 7.more Linear ModelingDokument4 SeitenMicrosoft Word - Unit 4.lesson 7.more Linear Modelingbob evansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approximations in Physics PDFDokument5 SeitenApproximations in Physics PDFMina TawadrosNoch keine Bewertungen
- WINCAPS III Arm View GuideDokument37 SeitenWINCAPS III Arm View GuideBrian LaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HaskellDokument290 SeitenHaskellazmodeuz47Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Cal 11 Mod7Dokument33 SeitenBasic Cal 11 Mod7Banana QNoch keine Bewertungen
- One - Way Table of SpecificationDokument1 SeiteOne - Way Table of SpecificationElisha Marie AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen