Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Sewerage and Drainage Engineering
Hochgeladen von
Renz Pagcaliwagan0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
442 Ansichten3 SeitenWater Resources
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenWater Resources
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
442 Ansichten3 SeitenSewerage and Drainage Engineering
Hochgeladen von
Renz PagcaliwaganWater Resources
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
SEWERAGE AND DRAINAGE ENGINEERINGR A sewer is a pipe or conduit, generally closed, but
normally not flowing full, w/c carries sewage.
Need For a Sewage System
A common sewer serves all abutting properties:
It is the primary duty of any govt to preserve A sanitary sewage carries sanitary sewage and is
health, to improve the standard of living to enhance the designed to exclude storm sewage and infiltration.
mental and physical capabilities, to elevate the socio- Industrial wastes may be carried in sanitary sewers
economic standards of its citizen. depending upon its characteristics. A storm sewer
carries storm sewerage and any other waste w/c may
Health and living standards of the People are be discharge into the streets or onto the ground
connected w/ the ff. surface. A Combined Sewer/Combined System carries
both domestic and storm sewage. While one w/c
a. Availability of potable and palatable water segregates the storm water is called a separate system.
b. The removal, treatment and disposal of all the
waste that are produced House Sewer- pipe conveying waste eater from
c. Improved sanitation of overall envt an individual structure to a common sewer or
other point of disposal.
Important terms Lateral Sewer- a common sewer w/ no tributary
flow except from house sewer.
1. Sewage- liquid waste containing suspended, Submain Sewer- collects flow from one or more
colloidal and dissolved solids. laterals as well as house sewer.
2. Domestic- Sewage liquid waste coming from Main or Trunk sewers- collects flow from
latrines and urinal. several submains as well as house sewers.
3. Sewer- a pipe or conduit w/c carries sewage. Force Main- air pressurized sewer lines w/
4. Sewerage- network of sewers or pipes used for conveys sewage from a pumping station to
the purpose of transporting sewage. another main or to a point of treatment
5. Raw water- untreated waste w/c is in the fresh disposal.
state. Intercepting sewers- intersects otherwise to
6. Sullage- liquid waste flowing from kitchen and separate the dry weather flow from storm-
bathrooms. water flow w/c they may carry.
Relief sewer- sewer w/c has been built to carry
Sewerage refers to the collection, treatment and
a portion of the flow in the system w/
disposal of liquid waste. Sewerage works or sewage
otherwise inadequate capacity.
works include all the physical structures reqd for that
Outfall sewer- sewer w/c carries the collected
collection, treatment and disposal.
waste to a point of treatment or disposal.
Sewage is the liquid waste conveyed by sewer and
SEWAGE PROJECT
may include:
Points of Consideration:
1. Domestic or sanitary sewage- originates in the
1. Population of the city to be served
sanitary convenience of dwellings, commercial
2. Available funds for the purpose
or industrial facilities and institutions.
3. Quality of sewage to be handled
2. Industrial Waste- include the liquid discharge
4. Rainfall in the locality
from industrial processes such as manufacturing
5. Rate of sewage to be expected
and food processing.
6. Source of sewage
3. Storm sewage- flow derived from rainfall
7. Present arrangement of disposal
events and deliberately introduced into sewers
8. Topographical features of the area
intended for its conveyance.
9. Treatment methods
4. Infiltration- w/c enters the sewers from the
10. Trend of town development
ground through leaks.
Project Drawing The DWF depends on:
1. Population
1. Contour plan 2. Type of area
2. Detailed drawing of the project 3. Rate of water Supply
3. Site plan and location 4. Ground Water Infiltration
4. Topographical 5 5
= 1 & = 1
5. Flow diagram
6 6
6. Existing arrangement
7. Nature of sewage
SEWER APPURTENANCE
8. Detailed design
Various accessories on the sewerage system and
9. Outline of specs of construction work
are necessary for the efficient operation of the system.
10. Future population
11. Quality of sewage mode of disposal
IMPOTANT APPURTENANCES
Collection and Conveyance of sewerage
1. Manholes
- Openings of either circular or rectangular in
System of sanitation
shape, constructed on the alignment of a sewer
1. Conservancy system
line to enable a person to enter for inspection,
2. Water carriage system
and flushing.
System of sewage
- Permit inspection, cleaning and maintenance of
1. Separate system of sewage
sewer line and flushed material collected and
2. Combined system
removed from a manhole.
3. Partially Combined or Partially Separate
- Allows joining of sewer, or changing of direction
System
or both. Serves as ventilation of sewers,
facilitate the laying of sewers in convenient
Pattern of Sewerage Layout
length.
1. Perpendicular Pattern- shortest path
Location
2. Interceptor Pattern - Backflow
- All junction of two or more sewer
3. Zone Pattern- Elevation Dependent
- Whenever diameter of sewer changes
4. Fan pattern- Outward-inward
- Whenever direction of sewer line changes
5. Radial Pattern- inside out
- When sewer of diff. Elev. Join together
Manhole Details
QUANTIFYING
- Cover and frame : 50 55 cm
- Access shaft
Dry Weather Flow (DWF)
- Steps and ladder : 30 cm interval
- Working Chamber : 1.2 m min , 0.9x1.2 m min
- The flow only sanitary sewage in the absence of
- Bottom shaft : 15 30 cm thick
storm in dry Season
Classification of Manhole
=
Shallow Manhole
- Depth of 0.75m to 0.9m w/ tight cover
= ( )() Normal Manhole
If population data is not available the following - Depth of 1.5m w/ heavy cover at top
densities can be used for different sizes of town Deep Manhole
- Depth greater than 1.5m w/ heavy cover
Residential Areas, Special Manholes
100 250 persons/ha
Detached Houses Junction Chamber
Multi Story Apartment 500- 1000 persons/ha Drop Manholes
Mercantile Area 30-70 persons/ha Flushing manholes
Industrial Ares 15-30 persons/ha
2. Lamp Hole intervals to clean the sewers of chocking
- Opening constructed on the straight sewer and obstruction.
lines bet. Manholes w\c are far apart and 8. Inverted siphons
permit the intersection of lamp into the - Sometimes called or depressed sewers.
sewer to find out obstruction if any inside - A sewer that runs full under gravity flow at
the sewers from the next manhole. a pressure above atmosphere.
3. Clean outs - Used to pass sewer lines under obstacles
- It is a pipe like lamp holes the only such ass buried pipes, subways and stream
difference being that clean out pipe is not bed.
vertical but inclined. 9. Storm water Regulators & weirs
- One end is of the inclined pipe is - Used to divert a part of the flow of sewage
connected to the sewer while other end is from a combined sewer. This is reqd to
brought up to the ground level. prevent the overcharging of the sewer
- Generally provided at the upper end of mainly to allow only that much sewage to
lateral sewer and is used for flushing. flow to sewage treatment.
4. Catch basins Commonly used Regulator
- Used to interrupt the velocity of storm 1. Leaping Weir
water before it enters the sewer 2. Over-flow or side weir
- Cause retention of suspended grit, sullage, 3. siphon spillway
and floating rubbish from rain water w/c Ventilation of sewers
otherwise might have entered the sewer a. laying sewer lines at proper gradient
and close it. b. running sewer at 2/3 full
- They are small settling chamber s of c. providing manholes w/ gratings
diameter 60-90cm and 60-75cm deep. d. proper house drainage
5. Inlets/street inlets e. Providing ventilation columns or shaft.
- Openings through w/c surface runoff is
admitted and conveyed to the storm sewer WASTEWATER ENGINEERIN
or combines sewer. - Branch of Environmental Engineering in which
- The inlets are located by the side of the the basic principles of science and engineering
pavement and has a maximum 30m are applied to the problems of water pollution
spacing. control, and issues associated with the
Based on position treatment and reuse of wastewater (Metcalf &
Curb inlets vertical opening in the road Eddy).
curb, w/ grating at the top and curb side
Wastewater
through w/c storm water flows into the
sewer and they are preferred where heavy - The spent or used water of a community or
traffic is anticipated. industry containing dissolved and suspended
Gutter inlets these are horizontal matters.
openings in the gutter w/c are lifted w/ - Any liquid wastes collected in sewer system and
gratings or bars through w/c flow passes. conveyed to a treatment plant for processing.
6. Oil & Grease Trap - Also termed as sewage.
- Device w/c is provided on the sewer lines
coming from kitchen, hotel etc. to intercept
oil and grease from sewage before it enters
the main sewer line.
7. Flushing tanks
- Provided to flush the sewers. They are not
always reqd they are provided to suitable
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Basic Principles of Sanitary DesignDokument16 SeitenBasic Principles of Sanitary DesignDeniell Kahlil Kyro Gabon100% (2)
- Design of Surfaces and Guideways Geometric Design REV 1Dokument11 SeitenDesign of Surfaces and Guideways Geometric Design REV 1Princess Joy Villareal EncinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Engineering Exam 1Dokument92 SeitenStructural Engineering Exam 1Renz Pagcaliwagan100% (1)
- Highway and Railroad Engineering Course GuideDokument27 SeitenHighway and Railroad Engineering Course GuideFrancis Ko Badongen-Cawi Tabaniag Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analyzing Gravity DamsDokument38 SeitenAnalyzing Gravity DamsMerwin Andrew UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sodium Hypochlorite MsdsDokument6 SeitenSodium Hypochlorite Msdssherif9000Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Practice of Civil EngineeringDokument31 SeitenThe Practice of Civil EngineeringDaniella Mae De GraciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wild Foods and Medicines of Forest Garden TransylvaniaDokument41 SeitenWild Foods and Medicines of Forest Garden Transylvaniadanut_doc100% (1)
- CE 425 - Engineering HydrologyDokument32 SeitenCE 425 - Engineering HydrologyCiel RonquilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Making Surrey tanks safeDokument6 SeitenMaking Surrey tanks safeEko KurniawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- FluidsDokument12 SeitenFluidsKris TejereroNoch keine Bewertungen
- HYDRAULICS - Module 1 Lesson 2Dokument57 SeitenHYDRAULICS - Module 1 Lesson 2Rey Angelo Carbilledo Jr.100% (2)
- Assignment IIDokument2 SeitenAssignment IIhabtamu100% (2)
- Flow of Open ChannelDokument61 SeitenFlow of Open Channelmr_sam91100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Building CostsDokument20 SeitenFundamentals of Building CostsEric John IsidoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 8 - Q4 - Week 6Dokument23 SeitenScience 8 - Q4 - Week 6EyphRhylle100% (1)
- How Do Refrigerators WorkDokument33 SeitenHow Do Refrigerators Worksushant3240Noch keine Bewertungen
- Project Work - Written ReportDokument56 SeitenProject Work - Written Reportu_bhalraam93% (14)
- 2631-RD Calc (MSMA II) - 19.10.25Dokument98 Seiten2631-RD Calc (MSMA II) - 19.10.25azwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - CMPM, Contracts & Specifications (Edmodo)Dokument15 Seiten1 - CMPM, Contracts & Specifications (Edmodo)jhuascute06100% (1)
- WASA Wastewater and Potable Water Design Requirements PDFDokument233 SeitenWASA Wastewater and Potable Water Design Requirements PDFYassin AlkadyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis of Garments Solid Waste GazipurDokument34 SeitenThesis of Garments Solid Waste GazipurMd BaizidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 005a - Plumbing ToolsDokument159 Seiten005a - Plumbing ToolsdinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aggregate PresentationDokument34 SeitenAggregate PresentationRahsaan KirtonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 6 - The Rational Method and Intro To Stormwater Drainage Structures - The Rational Method and Intro To Stormwater Drainage StructuresDokument16 SeitenLecture 6 - The Rational Method and Intro To Stormwater Drainage Structures - The Rational Method and Intro To Stormwater Drainage StructuresNavjotSingh100% (1)
- Ce 408Dokument30 SeitenCe 408Liaqat ZaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sewerage SystemDokument19 SeitenSewerage SystemSujan Singh50% (2)
- Module 3 SW5Dokument13 SeitenModule 3 SW5hgfhfghfghgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master Plumber Code of EthicsDokument1 SeiteMaster Plumber Code of EthicsDreiSanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Document 1Dokument3 SeitenDocument 1rauff ridwan akmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tsunami RXN 10-4Dokument5 SeitenTsunami RXN 10-4Ricca Valdez BaudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce161p A88 q1 MakeupDokument1 SeiteCe161p A88 q1 MakeupRam RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wells and Well HydraulicsDokument110 SeitenWells and Well HydraulicsSaqalain HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 10: Non-Uniform Flow: University of Nueva Caceres College of Engineering and ArchitectureDokument5 SeitenWeek 10: Non-Uniform Flow: University of Nueva Caceres College of Engineering and ArchitectureAngelica LosaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement of PrecipitationDokument8 SeitenMeasurement of PrecipitationYo Boi KatakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- HydrologyDokument34 SeitenHydrologyMichaelViloria100% (1)
- Lab ExerciseDokument22 SeitenLab ExerciseOnelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plumbing Arithmetic 20-30Dokument2 SeitenPlumbing Arithmetic 20-30Philip JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bernoulli'S Theorem Demonstration: Experiment No. 04Dokument3 SeitenBernoulli'S Theorem Demonstration: Experiment No. 04ChristopherHiladoNoch keine Bewertungen
- River Navigation GuideDokument7 SeitenRiver Navigation GuideIntan MadiaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Report 2 (Soil Sampling) Fajardo Bsce3aDokument6 SeitenActivity Report 2 (Soil Sampling) Fajardo Bsce3aGuilbert FajardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Item 803Dokument8 SeitenItem 803Ester MarianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4. Selection of The Civil EngineerDokument4 SeitenChapter 4. Selection of The Civil EngineerJenirose EndayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.5.2 Two Envelope System Inguillo and ZoletsDokument1 Seite3.5.2 Two Envelope System Inguillo and ZoletsXyrile ß IngilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explain Briefly The Evaporation ProcessDokument4 SeitenExplain Briefly The Evaporation ProcessChristian GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow Demonstration ExperimentDokument5 SeitenFlow Demonstration ExperimentVictoria SooknananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Bench OperationDokument2 SeitenHydraulic Bench OperationAneeqMustafa GhumroNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Site Sewage Treatment (Alternative Waste Systems)Dokument6 SeitenOn Site Sewage Treatment (Alternative Waste Systems)JhyneJazarenoAtutuboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6Dokument31 SeitenChapter 6Camille LardizabalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traffic & Highway Engineering: Nicholas Garber and Lester Hoel,, 5 Edition.. Cengage Learning, 2015Dokument11 SeitenTraffic & Highway Engineering: Nicholas Garber and Lester Hoel,, 5 Edition.. Cengage Learning, 2015Mohammed SaffariniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 02 Lesson 01 - The Derivative (Rates of Change and Delta Process)Dokument12 SeitenModule 02 Lesson 01 - The Derivative (Rates of Change and Delta Process)Kiziahlyn Fiona BibayNoch keine Bewertungen
- (E) Chapter 1 - Origin of Soil and Grain SizeDokument23 Seiten(E) Chapter 1 - Origin of Soil and Grain SizeLynas Beh TahanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Highway Engineering Drainage and Slope ProtectionDokument3 SeitenHighway Engineering Drainage and Slope ProtectionscrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Friction ApparatusDokument6 SeitenPipe Friction ApparatusShubham MauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Weight and Voids of AggregateDokument4 SeitenUnit Weight and Voids of AggregateKevin P Mendoza100% (1)
- Technical Specifications 1. GeneralDokument12 SeitenTechnical Specifications 1. GeneralBuoyancyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compre Hydraulics PSDokument5 SeitenCompre Hydraulics PSAlvin Lualhati0% (1)
- Lab Report No. 7 Plastic and Liquid Limit of SoilDokument52 SeitenLab Report No. 7 Plastic and Liquid Limit of Soilkim suarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulics 1-2-3Dokument4 SeitenHydraulics 1-2-3veeveegarcia_0% (1)
- Plumbing ExamDokument218 SeitenPlumbing ExamJhobs BesmonteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key Assumptions of Darcy's LawDokument19 SeitenKey Assumptions of Darcy's LawFah EemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Hydrology and Hydraulics in Wre PDFDokument9 SeitenRole of Hydrology and Hydraulics in Wre PDFGeraldine Galing75% (4)
- Determine Concrete Slump with Slump TestDokument7 SeitenDetermine Concrete Slump with Slump Testayat1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 5.1-5.5 Coefficients To TubesDokument18 SeitenMODULE 5.1-5.5 Coefficients To TubesFrancis HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids M3F1Dokument4 SeitenFluids M3F1Ej ParañalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE 8 Highway Engineering and Bridge Design #3Dokument20 SeitenCE 8 Highway Engineering and Bridge Design #3Vicky ZambranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 1. Basic Principles of Sanitary DesignDokument5 SeitenMODULE 1. Basic Principles of Sanitary DesignKervin SangalangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wastewater and Solid Waste Management NoteDokument403 SeitenWastewater and Solid Waste Management NoteAbebawNoch keine Bewertungen
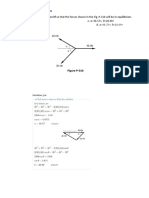
- Moment of Mass SMTBDokument1 SeiteMoment of Mass SMTBRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2. Determine the center of mass for the region bounded by y=2sin (2x), y=0 on the interval (0,π/2)Dokument2 Seiten2. Determine the center of mass for the region bounded by y=2sin (2x), y=0 on the interval (0,π/2)Renz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculating soil properties and forces in geotechnical engineering problemsDokument10 SeitenCalculating soil properties and forces in geotechnical engineering problemsRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural SeatworkDokument2 SeitenStructural SeatworkRenz Pagcaliwagan100% (1)
- Total Force Exerted by Liquids BamDokument1 SeiteTotal Force Exerted by Liquids BamRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics For ExamDokument21 SeitenMathematics For ExamRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spring Related Problems-EJMO1Dokument1 SeiteSpring Related Problems-EJMO1Renz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Probability Integral SLPDokument3 SeitenProbability Integral SLPRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
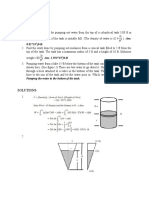
- Pumping Liquids: 8.82 10 FT-LBDokument3 SeitenPumping Liquids: 8.82 10 FT-LBRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Region Bounded by Curves DLCDokument2 SeitenRegion Bounded by Curves DLCRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 1 - Hydro GeoDokument9 SeitenExam 1 - Hydro GeoRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thickness Length Height PCS.: For Roof DeckDokument14 SeitenThickness Length Height PCS.: For Roof DeckRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seatwork 1 Mathematics: Specific WeightDokument5 SeitenSeatwork 1 Mathematics: Specific WeightRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- For Vertical Elements of Area: SetworkDokument4 SeitenFor Vertical Elements of Area: SetworkRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regions Bounded by CurvesDokument2 SeitenRegions Bounded by CurvesRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- TranspirationDokument14 SeitenTranspirationRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- For Earthquake-Gf PDFDokument1 SeiteFor Earthquake-Gf PDFRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- c4 SemisDokument4 Seitenc4 SemisRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- c6 SemisDokument5 Seitenc6 SemisRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conceptual: Four Stages of DesignDokument3 SeitenConceptual: Four Stages of DesignRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- DphiloDokument1 SeiteDphiloRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis and Design of Two-Way Slab With BeamsDokument63 SeitenAnalysis and Design of Two-Way Slab With BeamsChoco Mucho Cruzado100% (1)
- TabulationDokument2 SeitenTabulationRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beam DesignDokument6 SeitenBeam DesignRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Design (Gellisania)Dokument227 SeitenSteel Design (Gellisania)Renz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materials Used in Pre-Stressed ConcreteDokument1 SeiteMaterials Used in Pre-Stressed ConcreteRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seismic retrofit improves RC building performanceDokument4 SeitenSeismic retrofit improves RC building performanceRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Formal and Informal OrganizationDokument11 SeitenThe Formal and Informal OrganizationRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Formal And Informal Organization Structure ExplainedDokument12 SeitenThe Formal And Informal Organization Structure ExplainedRenz PagcaliwaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Task 3 Plant Adaptation Factsheets For PrintingDokument5 SeitenTask 3 Plant Adaptation Factsheets For PrintingBenjamin WatsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASETON Sciencelab - Com, Inc.Dokument5 SeitenASETON Sciencelab - Com, Inc.Kang IsurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sea Ice Impact On Naval OperationsDokument9 SeitenSea Ice Impact On Naval OperationsLaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banjir Bandang SentaniDokument4 SeitenBanjir Bandang SentaniFadhilah Hayyu AuliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accutek Product Guide 2011-2012Dokument78 SeitenAccutek Product Guide 2011-2012Ahmet MetinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sodium Chromate Anhydrous PDFDokument6 SeitenSodium Chromate Anhydrous PDFErika WidiariniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Bend Activity GuideDokument238 SeitenBig Bend Activity GuideDanny GriffinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Condensate Trapping Design Flaws - TraneDokument8 SeitenCondensate Trapping Design Flaws - Tranesuat yilmazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mercury Di Sungai Kecamatan DimembeDokument4 SeitenMercury Di Sungai Kecamatan DimembeDanso AyhuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GREASE MsdsDokument6 SeitenGREASE Msdsazer AzerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual RKE2200B1-VW-G1 (EN) OrionDokument92 SeitenManual RKE2200B1-VW-G1 (EN) Orionlanchon666Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hey 22Dokument6 SeitenHey 22AM CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dams Quiz With AnswersDokument3 SeitenDams Quiz With AnswersAltheaPeriasNoch keine Bewertungen
- FM 21-18 Foot-MarchesDokument49 SeitenFM 21-18 Foot-MarchesMark CheneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 11 Term 3 PowerpointDokument75 SeitenGrade 11 Term 3 PowerpointYONDELA MbandezeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- GlacierDokument31 SeitenGlacierGalactic CrystalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm D1141 98 2021Dokument2 SeitenAstm D1141 98 2021NettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide to Raising Pilots Federation RanksDokument27 SeitenGuide to Raising Pilots Federation RanksscribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1204-Barge 2 Tech SpecsDokument13 Seiten1204-Barge 2 Tech SpecsmardiradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comissioning of de GreaserDokument14 SeitenComissioning of de GreaserprabathnilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TDS Panax Blue-770 UK-SEUNG-ChemicalDokument1 SeiteTDS Panax Blue-770 UK-SEUNG-ChemicalJuanNoch keine Bewertungen