Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Differentiate and Give Each Example. (Endemic, Pandemic, Sporadic and Epidemic)
Hochgeladen von
JuliusSerdeñaTrapal0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
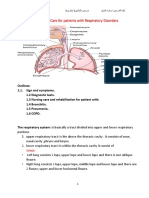
11 Ansichten2 SeitenCOPAR is a pneumonic used in emergency medicine to guide the assessment and management of patients with respiratory distress or failure. It stands for Compliance, Oxygenation, Perfusion, Airway, and Respiration. The phases include: assessing a patient's lung compliance and work of breathing; measuring oxygen levels and providing supplemental oxygen; evaluating perfusion by checking pulse, blood pressure, and skin signs; ensuring a patent airway; and determining the rate and depth of respiration.
Originalbeschreibung:
CA 417
Originaltitel
CA 417
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCOPAR is a pneumonic used in emergency medicine to guide the assessment and management of patients with respiratory distress or failure. It stands for Compliance, Oxygenation, Perfusion, Airway, and Respiration. The phases include: assessing a patient's lung compliance and work of breathing; measuring oxygen levels and providing supplemental oxygen; evaluating perfusion by checking pulse, blood pressure, and skin signs; ensuring a patent airway; and determining the rate and depth of respiration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
11 Ansichten2 SeitenDifferentiate and Give Each Example. (Endemic, Pandemic, Sporadic and Epidemic)
Hochgeladen von
JuliusSerdeñaTrapalCOPAR is a pneumonic used in emergency medicine to guide the assessment and management of patients with respiratory distress or failure. It stands for Compliance, Oxygenation, Perfusion, Airway, and Respiration. The phases include: assessing a patient's lung compliance and work of breathing; measuring oxygen levels and providing supplemental oxygen; evaluating perfusion by checking pulse, blood pressure, and skin signs; ensuring a patent airway; and determining the rate and depth of respiration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
1. Differentiate and give each example.
(Endemic, pandemic, sporadic and
epidemic)
Endemic - (of a disease or condition) regularly found among particular people or
in a certain area.
Diseases include chicken pox that occurs at a predictable rate among
young school children in the United States and malaria in some areas of
Africa.
Pandemic (of a disease) prevalent over a whole country or the world.
The severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) epidemic took the lives of
nearly 800 people worldwide.
Sporadic - occurring occasionally, or in scattered instances or only in a few places
Epidemic - a widespread occurrence of an infectious disease in a community at a
particular time.
2. Menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is the monthly series of changes a woman's body goes
through in preparation for the possibility of pregnancy. Each month, one of
the ovaries releases an egg a process called ovulation. At the same time,
hormonal changes prepare the uterus for pregnancy. If ovulation takes
place and the egg isn't fertilized, the lining of the uterus sheds through the
vagina. This is a menstrual period.
3. Pedia (TOF) Explain the 4 condition including (TOF).
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a congenital heart defect with four components:
1) large ventricular septal defect (VSD), which is a hole between the two
ventricles or pumping chambers in the heart; 2) pulmonary stenosis, which
is narrowing beneath or in the blood vessel leading to the lungs; 3)
overriding of the aorta, in which the aorta lies directly above the ventricular
septal defect; and 4) as a result of these events, the right ventricle becomes
thickened or hypertrophied.
4. Differentiate pulmonary to systemic circulation.
Pulmonary circulation refers to the circulation of blood in
which deoxygenated blood is pumped from the heart to the lungs
and oxygenated blood is returned to back to the heart. Pulmonary
circulation only occurs between the heart and the lungs.
Systemic circulation refers to the circulation of blood in
which oxygenated blood is pumped from the heart to the body
and deoxygenated blood is returned back to the heart. Systemic circulation
occurs between the heart and the entire body.
5. Hirschsprung Disease (explain)
Disease affects the large intestine (colon) of newborns, babies, and toddlers. The
condition which prevents bowel movements (stool) to pass through the
intestines due to missing nerve cells in the lower part of the colon is caused by
a birth defect.
6. What are the herbal medications and its uses?
Lagundi
- Asthma, cough and fever
Yerba (Hierba) Buena
- For pain in different parts of the body as headache and stomachache.
Sambong (Blumea Balsamifera)
- Anti edema, diuretic, anti urolithiasis
Tsaang Gubat (Carmona Retusa)
- Diarrhea
Niyog niyugan
- Anti helminthic
Bayabas/Guava
- For washing wounds
- For diarrhea
Akapulko
- Anti- fungal
Ulasimang Bato
- Lowers uric acid (rheumatism and gout)
Bawang
- For hypertension; toothache; to lower cholesterol levels in blood.
Ampalaya
- Lower blood sugar levels
Diabetes Mellitus (Mild non insulin dependent)
7. What is COPAR and its phases?
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Working Protcol KidsDokument6 SeitenWorking Protcol KidsAmy Rebekah Epstein MurrellNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS ShockDokument5 SeitenCS ShockJuliusSerdeñaTrapal0% (5)
- Must Have Nursing Mnemonics PDFDokument50 SeitenMust Have Nursing Mnemonics PDFJanus Lazaro100% (2)
- Module 1 Guidelines in Giving Emergency CareDokument2 SeitenModule 1 Guidelines in Giving Emergency CareJuliusSerdeñaTrapal100% (4)
- Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension CASE REPORTDokument31 SeitenPregnancy-Induced Hypertension CASE REPORTMylene Angelie Bognot100% (2)
- 50 Nursing Mnemonics and Acronyms You Need To Know NowDokument29 Seiten50 Nursing Mnemonics and Acronyms You Need To Know Nowtandz100% (19)
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Anatomy Physiology An Integrative Approach 3rd Edition PDF ScribdDokument41 SeitenInstant Download Ebook PDF Anatomy Physiology An Integrative Approach 3rd Edition PDF Scribdheidi.gomez888100% (48)
- Curriculum BS MLT IIMCDokument106 SeitenCurriculum BS MLT IIMCAmna Zafar100% (1)
- Trismed - Cardiapia 400 406N 406P 406R 406RS 406NH 406PH 406RH 406RSH PDFDokument65 SeitenTrismed - Cardiapia 400 406N 406P 406R 406RS 406NH 406PH 406RH 406RSH PDFDireccion Tecnica100% (2)
- MaternalDokument2 SeitenMaternalAileen May OlojanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tetralogy of Fallot Report 1Dokument9 SeitenTetralogy of Fallot Report 1Maricar EustaquioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hi Jam ADokument12 SeitenHi Jam Aelan sudjanamihardja100% (4)
- Magyawi Tetralogy of Fallot 1st PartDokument7 SeitenMagyawi Tetralogy of Fallot 1st PartJoanna Bee Rose MagyawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Medical Conditions 1 1Dokument87 SeitenSpecial Medical Conditions 1 1Kurt JanssenNoch keine Bewertungen
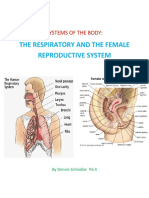
- Systems of The BodyDokument10 SeitenSystems of The BodyKatrina SchindlarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Cardiovascular System History & ExaminationDokument74 SeitenPediatric Cardiovascular System History & Examinationعبدالله Abdullah INoch keine Bewertungen
- ToF ScriptDokument6 SeitenToF ScriptCaity YoungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tetralogy of FallotDokument5 SeitenTetralogy of FallotCharity OaniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Odynophagia Is Painful SwallowingDokument21 SeitenOdynophagia Is Painful SwallowingVien CaagbayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ear (Inner)Dokument4 SeitenEar (Inner)magdangalmaryfrancessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dys CoDokument5 SeitenDys CoMinh Bui0% (1)
- History and Causology - DR - ShamolDokument265 SeitenHistory and Causology - DR - ShamolUmer Farooq100% (1)
- A Case of Pleural Effusion With Cardiomegaly Cured With HomoeopathyDokument9 SeitenA Case of Pleural Effusion With Cardiomegaly Cured With HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD Hom100% (1)
- Cyanotic Spells Blue Spells in Tetralogy of Fallot - PIAG 214Dokument2 SeitenCyanotic Spells Blue Spells in Tetralogy of Fallot - PIAG 214imil irsalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nephrotic Syndrome: Dinesh Kumar PDokument42 SeitenNephrotic Syndrome: Dinesh Kumar PRiya Sweetsolitude100% (1)
- Pediatric Clinical ExaminationDokument37 SeitenPediatric Clinical ExaminationHalema Al OkshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood StasisDokument5 SeitenBlood StasisiomastNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explanation Ko ItoDokument5 SeitenExplanation Ko ItoJoanna Bee Rose MagyawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tetralogy of FallotDokument38 SeitenTetralogy of FallotJohn Paul MedalloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy ReviewerDokument11 SeitenAnaphy ReviewerGlenn Giovan MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANAPHY111Dokument60 SeitenANAPHY111Gerlyn MortegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vital Signs or Cardinal SignsDokument5 SeitenVital Signs or Cardinal SignsMadelaine Mary Rose GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSCE Paeds Master Sheet Rachel AlbertDokument26 SeitenOSCE Paeds Master Sheet Rachel AlbertVahni SamarooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shortness of Breath NotesDokument7 SeitenShortness of Breath NotesChananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric CardiologyDokument30 SeitenPediatric CardiologyZahra AlaradiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approach To Pediatric HemoptysisDokument5 SeitenApproach To Pediatric HemoptysisAssma Haytham MuradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Human Respiratory & Circulatory System Class NotesDokument4 SeitenUnit Human Respiratory & Circulatory System Class NotesAiza SulemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Surgery ExamDokument48 SeitenGeneral Surgery ExamVarunavi SivakanesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vitalsignslecturenewbatch 160211000037Dokument8 SeitenVitalsignslecturenewbatch 160211000037faityneoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study: Mrs Sharon Mckenzie - : CausesDokument10 SeitenCase Study: Mrs Sharon Mckenzie - : CausesAnonymous NCDeTPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tetralogy of Fallot: Arianna Jasminemabunga Bsn-2BDokument30 SeitenTetralogy of Fallot: Arianna Jasminemabunga Bsn-2BArianna Jasmine MabungaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congestive Heart FailureDokument7 SeitenCongestive Heart FailureKeserovic AdmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 9 Student Handout2021 I - TaggedDokument12 SeitenUNIT 9 Student Handout2021 I - TaggedNia AvellanedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes on Diseases of Swine, Sheep, Poultry and the Dog: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentsVon EverandNotes on Diseases of Swine, Sheep, Poultry and the Dog: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Birth AsphyxiaDokument27 SeitenBirth AsphyxiaJaya Prabha100% (5)
- Differential Diagnosis and Approach To A Heart Murmur in Term InfantsDokument10 SeitenDifferential Diagnosis and Approach To A Heart Murmur in Term Infantsdeddy ekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prevention: Blood Pressure Body Weight Here BMIDokument8 SeitenPrevention: Blood Pressure Body Weight Here BMILuthfi Rama MaulanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7TH MEETING-Systems, Disease, and Symptoms 2Dokument20 Seiten7TH MEETING-Systems, Disease, and Symptoms 2FitriiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NUR040-SAS-Session3Dokument11 SeitenNUR040-SAS-Session3Jessa Maye A RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3,4,5 - Circulation, Respiration, and ExcretionDokument66 SeitenLesson 3,4,5 - Circulation, Respiration, and ExcretionJade Lawrence IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Disorders 1Dokument3 SeitenHealth Disorders 1sugandhdon77Noch keine Bewertungen
- resp د. وفاءDokument22 Seitenresp د. وفاءProf. Wafaa Mohammed Al-AttarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital AnomaliesDokument26 SeitenCongenital AnomaliesMaria VisitacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ipecac - GerryDokument7 SeitenIpecac - Gerryglenn johnstonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of LifestyleDokument33 SeitenEffects of LifestylePrincess Plamiano BenliroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1GP - Anaphy NotesDokument11 Seiten1GP - Anaphy NoteseriannenabazengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Automated External Defibrillation (AED) Training GuideVon EverandCardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Automated External Defibrillation (AED) Training GuideBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- RHD & H - Mole - Case PresDokument90 SeitenRHD & H - Mole - Case PresGhra CiousNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 118 - Emphsyema Pulmonary Embolism ARDS ALI VAP and Respiratory FailureDokument30 SeitenNCM 118 - Emphsyema Pulmonary Embolism ARDS ALI VAP and Respiratory Failurecabelin randy amenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiological Characteristics of NewbornDokument11 SeitenPhysiological Characteristics of Newbornbhawna67% (3)
- Pointers To ReadDokument10 SeitenPointers To ReadTrixie Jane P ManaayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tetralogy of Fallot SP B.inggrisDokument19 SeitenTetralogy of Fallot SP B.inggrisSoraya VerinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Report AsdDokument17 SeitenCase Report AsdTeuku Fauzan AtsariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of Blood Vessels (Autosaved)Dokument98 SeitenStructure of Blood Vessels (Autosaved)Lednew MatiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explanation LetterDokument1 SeiteExplanation LetterJuliusSerdeñaTrapal0% (1)
- Windows Keyboard Shortcuts OverviewDokument10 SeitenWindows Keyboard Shortcuts OverviewJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNoch keine Bewertungen
- FNCPDokument4 SeitenFNCPJuliusSerdeñaTrapal100% (1)
- Chapter IIIDokument3 SeitenChapter IIIJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument4 SeitenChapter 3JuliusSerdeñaTrapalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary, Conclusion and RecommendationDokument13 SeitenSummary, Conclusion and RecommendationJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNoch keine Bewertungen
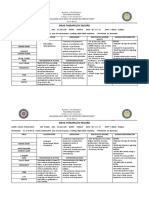
- Drug Therapeutic Record: Naval State UniversityDokument6 SeitenDrug Therapeutic Record: Naval State UniversityJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Status and Acceptability of Concrete Gravity Dam in Culaba, BiliranDokument1 SeiteStatus and Acceptability of Concrete Gravity Dam in Culaba, BiliranJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prediction TheoryDokument90 SeitenPrediction TheoryJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Nursing and Health Sciences DepartmentDokument6 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Nursing and Health Sciences DepartmentJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Therapeutic Record: Naval State UniversityDokument5 SeitenDrug Therapeutic Record: Naval State UniversityJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geriatric NursingDokument91 SeitenGeriatric NursingJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Myocardial InfarctionDokument2 SeitenMyocardial InfarctionJuliusSerdeñaTrapalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Updated Hesi Ap V1V2 Study GuideDokument10 SeitenUpdated Hesi Ap V1V2 Study GuideichelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Palpitations: DR Polamuri Tabitha PG First YrDokument37 SeitenPalpitations: DR Polamuri Tabitha PG First YrNinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR - Tahir Mahmood (PT) IIIRS, SialkotDokument40 SeitenDR - Tahir Mahmood (PT) IIIRS, SialkotRabia RaufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artery Vein CapillaryDokument1 SeiteArtery Vein CapillarynaduniNoch keine Bewertungen
- QP Code:111010 Reg. No: ........................ First Year B.SC Nursing Degree Examinations October 2017 Anatomy (2016 Scheme) Model Question PaperDokument6 SeitenQP Code:111010 Reg. No: ........................ First Year B.SC Nursing Degree Examinations October 2017 Anatomy (2016 Scheme) Model Question PaperdrsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers MediDokument443 SeitenAnswers MediAmine Younis100% (13)
- Cardiac Monitoring ChecklistDokument6 SeitenCardiac Monitoring Checklistdigdag100% (1)
- Aortic Regurgitation (Ar)Dokument18 SeitenAortic Regurgitation (Ar)rameshbmc100% (1)
- A Review of The Fundamental Principles and Evidence Base in The Use of Extracorporeal MembraneOxygenation (ECMO) in Critically Ill Adult PatientsDokument15 SeitenA Review of The Fundamental Principles and Evidence Base in The Use of Extracorporeal MembraneOxygenation (ECMO) in Critically Ill Adult PatientsGenaro MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Cycle 0Dokument28 SeitenCardiac Cycle 0ProfMarinho FisiologiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular Examination FinalDokument28 SeitenCardiovascular Examination FinalAllen Caine Taabbil100% (1)
- Anjleena: Curriculum VitaeDokument2 SeitenAnjleena: Curriculum Vitaetonny buddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of Endotoxin On Pacemaker Funny Current in Hek 293 CellsDokument190 SeitenEffects of Endotoxin On Pacemaker Funny Current in Hek 293 CellsNemo SecretNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Responsiveness in Mechanically Ventilated Patients A Review of Indices Used in Intensive CADokument9 SeitenFluid Responsiveness in Mechanically Ventilated Patients A Review of Indices Used in Intensive CAerwanNoch keine Bewertungen
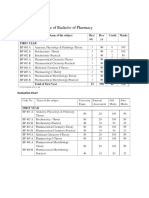
- Course of First Year BPharmDokument36 SeitenCourse of First Year BPharmpokhara144Noch keine Bewertungen
- Instruction Manual Model HCG-801Dokument56 SeitenInstruction Manual Model HCG-801MetalbetNoch keine Bewertungen
- UWORLD Notes by Subject Main Division Usmle GrassrootsDokument80 SeitenUWORLD Notes by Subject Main Division Usmle Grassrootsnashra bukhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiosave IAB Operation Transport Quick Reference Guide MCV00020163 - REVCDokument37 SeitenCardiosave IAB Operation Transport Quick Reference Guide MCV00020163 - REVCPrasong KotchakraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EKG Quick Reference Chart PDFDokument4 SeitenEKG Quick Reference Chart PDFrodney subaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN GRADE 6 BIOLOGY ExpirementDokument10 SeitenDETAILED LESSON PLAN GRADE 6 BIOLOGY ExpirementLoiweza Abaga100% (1)
- Answer - 2017 SPM Biology Trial PaperDokument8 SeitenAnswer - 2017 SPM Biology Trial PaperV. SundrramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fitz Cardiology Paces NotesDokument26 SeitenFitz Cardiology Paces NotesMuhammad BilalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory System of Animals PDFDokument18 SeitenCirculatory System of Animals PDFcheskja ramosNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Division (G.R. Nos. 94376-77, July 11, 1996)Dokument12 SeitenFirst Division (G.R. Nos. 94376-77, July 11, 1996)JB AndesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural Treatment & Home Remedies For Cardiac ArrhythmiaDokument3 SeitenNatural Treatment & Home Remedies For Cardiac ArrhythmiaHome Natural curesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Case Classification For The National Birth Defects Prevention StudyDokument9 SeitenGuidelines For Case Classification For The National Birth Defects Prevention Studyjorge davidNoch keine Bewertungen