Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Cleft Lip: Neisseria Gonorrhoeae (May Cause Ulceration and Destruction) and Chlamydia Trachomatis
Hochgeladen von
teabagmanOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cleft Lip: Neisseria Gonorrhoeae (May Cause Ulceration and Destruction) and Chlamydia Trachomatis
Hochgeladen von
teabagmanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ophthalmia neonatorum is an eye infection that occurs at birth or during the first month.
Common cause: Neisseria gonorrhoeae(may cause ulceration and destruction) and Chlamydia
trachomatis
- contracted during birth (vaginal secretions)
Assessment: bilateral, eye with pus, edematous, red. Usually on 1-4 days of life.
Prevention: erythromycin(prevents both gonococcal and chlamydial conjunctivitis);
Mgt: if gonococci (penicillin and ceftriaxone); chlamydia (erythromycin); sterile saline solution for irrigation; mother
should also be treated;
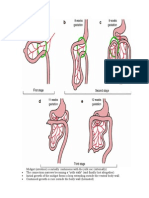
Cleft lip
The maxillary and median nasal processes normally fuse between weeks 5 and 8 of intrauterine
life.
Lip more common in boys than girls.
Cause: folic acid deficiency; genetics
Cleft Palate
The palatal process closes at approximately weeks 9 to 12 of intrauterine life
- it is an opening of the palate, is usually on the midline and may involve the anterior hard
palate, the posterior soft palate, or both
- more common in girls than boys
-maybe associated with other congenital anomalies
Assessment: Lip sonogram or upon birth; Palate- depress tongue and shine light on palate.
Mgt: surgery at 2-10weeks; A two-stage palate repair, with soft palate repair at 3 to 6 months of
age and hard palate repair at 15 to 18 months of age, may be recommended.
Nursing Dx: Risk for imbalanced nutrition, less than body requirements, related to feeding
problem caused by cleft lip or palate (post op: After surgery for cleft lip or palate, an infant is
kept NPO for approximately 4 hours. The infant is then introduced to liquids (plain water). Begin
the process with only a small amount to prevent vomiting.); avoiding tension helps keep the
sutures from pulling apart and leaving a large scar. After palate surgery, liquids are generally
continued
for the first 3 or 4 days, and then a soft diet is followed until healing is complete.
After a cleft palate repair, when children begin eating soft food, they should not use a spoon,
because they will invariably push it against the roof of the mouth and possibly disrupt sutures. If
being fed rather than being allowed to use a spoon himself evokes an intense reaction, it is
better to leave a child on a liquid diet until the sutures are removed. Be certain milk is not
included in the first fluids offered because milk curds tend to adhere to the suture line. After a
feeding, offer the child clear water to rinse the suture line and keep it as clean as possible.;
Impaired tissue integrity at incision
line related to cleft lip or cleft palate surgery; Risk for infection related to surgical incision; Risk for
ineffective airway clearance related to oral surgery;
Imperforate anus- stricture of anus
A wink reflex (touching the skin near the rectum should make it contract) will not be present if
sensory nerve endings in the rectum are not intact.; no stool passed
Before surgery, keep the infant
NPO to avoid further bowel distention. A nasogastric tube attached to low intermittent suction for
decompression will be inserted to relieve vomiting and prevent pressure on other abdominal organs or the
diaphragm from the distended intestine. Intravenous
therapy or total parenteral nutrition will be started to maintain fluid and electrolyte balance.
- Mgt: surgery anastomosis
Hydrocephalus is an excess of CSF in the ventricles or the subarachnoid space. Causes:
obstruction of passage (common cause), overproduction of fluid (rare); interference with
absorption of CSF.
Assessment: he infants fontanelles widen and appear tense, the suture lines on the skull
separate, and the head diameter enlarges; scalp becomes shiny and scalp veins become
prominent; increased ICP(decreased respiration and pulse, increased temp and BP, hyperactive
reflexes, strabismus and optic atrophy)
Mgt: if cause is overproduction of fluid, acetazolamide (Diamox), a diuretic; A
ventriculoperitoneal shunt removes excessive cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles and shunts
it to the peritoneum. A one-way valve is present in the tubing behind the ear; shunting procedure
involves threading a thin polyethylene catheter under the skin from the ventricles
to the peritoneum
Nsg Dx: Risk for ineffective cerebral tissue perfusion related to increased intracranial pressure
After a shunt is inserted, the infants bed is usually left flat or raised only about 30 degrees so the childs
head remains level with the body. This is because if the childs head is raised excessively, CSF may flow
too rapidly and decompression can then occur too rapidly, leading to possible tearing of cerebral arteries
Neural tube disorders:
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Physical and Developmental Disorders of The Gastrointestinal SystemDokument10 SeitenPhysical and Developmental Disorders of The Gastrointestinal SystemJo Marchianne PigarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Care and Feeding of Children - A Catechism for the Use of Mothers and Children’s NursesVon EverandThe Care and Feeding of Children - A Catechism for the Use of Mothers and Children’s NursesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peds ATI TakeawaysDokument4 SeitenPeds ATI TakeawaysNiki95% (19)
- Congenital Anomalies in Newborn (Critical)Dokument46 SeitenCongenital Anomalies in Newborn (Critical)Shereen Mohamed Soliman HammoudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cleft PalateDokument16 SeitenCleft PalateAnu Priya GopuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatrics Nclex Review PointersDokument14 SeitenPediatrics Nclex Review PointersCathryn Dominique Tan100% (1)
- Cleft Lip and Cleft PalateDokument8 SeitenCleft Lip and Cleft PalateRAJU33% (3)
- Choanal Atresia, Epistaxis & AspirationDokument12 SeitenChoanal Atresia, Epistaxis & Aspirationsubinj_350% (2)
- CNLDO JurnalDokument6 SeitenCNLDO JurnalKhairul FitrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Choanal AtresiaDokument32 SeitenChoanal AtresiaGreeshma ShajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal First Quiz ReviewerDokument15 SeitenMaternal First Quiz ReviewerRay Ann BorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate: College of Health Science Department of Midwifery Course Newborn Care For PostbasicDokument42 SeitenCleft Lip and Cleft Palate: College of Health Science Department of Midwifery Course Newborn Care For PostbasicmichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cleft Lip and Cleft PalateDokument22 SeitenCleft Lip and Cleft PalateOm VaishNav0% (1)
- Disorders of The Gastrointestinal SystemDokument12 SeitenDisorders of The Gastrointestinal SystemRonel ResurricionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care of The Child Born With PhysicalDokument55 SeitenNursing Care of The Child Born With PhysicalJoy kimmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Neonatal Problems - 085835Dokument39 SeitenCommon Neonatal Problems - 085835Jack AdamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cleft Lip and Cleft PalateDokument16 SeitenCleft Lip and Cleft PalateIsmail LubisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cleft Lip PalateDokument4 SeitenCleft Lip PalateMaricel DefiestaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pubdoc 4 14280 150Dokument6 SeitenPubdoc 4 14280 150jadarcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Nurs GI DisordersDokument9 SeitenPediatric Nurs GI DisordersVin Lorenzo CampbellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Health Problems InfancyDokument147 SeitenCommon Health Problems Infancymark OrpillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric G.I Disorders FinalDokument53 SeitenPediatric G.I Disorders FinalRashid Hussain0% (1)
- Lecture NCM 109Dokument11 SeitenLecture NCM 109Evangeline Anne MacanasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minor Disorder of NewbornDokument11 SeitenMinor Disorder of Newbornbiswaspritha.18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Common Health Problems - InfancyDokument76 SeitenCommon Health Problems - InfancyAmiel Francisco Reyes100% (1)
- Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate: Sharada Pathak M.Sc. Nursing Department of Medical Surgical Nursing 2014 BatchDokument20 SeitenCleft Lip and Cleft Palate: Sharada Pathak M.Sc. Nursing Department of Medical Surgical Nursing 2014 Batchurmila dewanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mal RotationDokument13 SeitenMal RotationkavyarkrnagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal in ChildrenDokument10 SeitenGastrointestinal in ChildrenANNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Cleft Lip and PalateDokument20 SeitenCleft Lip and Palatejapzee1988100% (1)
- Imperforate AnusDokument17 SeitenImperforate AnusNalzaro Emyril100% (1)
- Cleft and Lip PalateDokument6 SeitenCleft and Lip PalateShane PangilinanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cleft Lip / Cleft Palate: Predisposing FactorsDokument15 SeitenCleft Lip / Cleft Palate: Predisposing FactorsMabesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal Danger SignsDokument6 SeitenNeonatal Danger Signsmarkus_danusantosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nur 218 Peds Exam 1 Study Guide Role of The Pediatric NurseDokument9 SeitenNur 218 Peds Exam 1 Study Guide Role of The Pediatric NurseNurseme13Noch keine Bewertungen
- In Partial Fulfillment For The Requirements in R.L.E: Submitted By: Elaine Blanche R. GonzalezDokument6 SeitenIn Partial Fulfillment For The Requirements in R.L.E: Submitted By: Elaine Blanche R. GonzalezBlanche GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary and Conclusion Esophageal Atresia (Or Oesophageal AtresiaDokument3 SeitenSummary and Conclusion Esophageal Atresia (Or Oesophageal AtresiaSanket TelangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infection of Umbilicus Laksamana Abimanyu B 14-134Dokument26 SeitenInfection of Umbilicus Laksamana Abimanyu B 14-134BimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baba Jaswant Singh Dental College and Research Institute, LudhianaDokument40 SeitenBaba Jaswant Singh Dental College and Research Institute, LudhianaPalak VashistNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Hydrocele Is A Collection of Watery Fluid Around The TesticleDokument6 SeitenA Hydrocele Is A Collection of Watery Fluid Around The TesticleZeeham EscalonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrocephalus PresentationDokument49 SeitenHydrocephalus PresentationSourina BeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- AsomDokument40 SeitenAsomRachel RiordanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedia GiDokument10 SeitenPedia GiCam IbardolasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Be ConDokument53 SeitenTo Be ConLiza AingelicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coanal AtresiaDokument4 SeitenCoanal AtresiaBkas GrgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 27Dokument22 SeitenChapter 27zbestgurlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Content Congenital DisorderDokument20 SeitenContent Congenital DisorderKaka SalvatoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- AtresiaDokument5 SeitenAtresiakirtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TracheoesophagealDokument2 SeitenTracheoesophagealLuigi GeduqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indications For TonsillectomyDokument4 SeitenIndications For TonsillectomyRimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ob Seminar Amniotic Fluid-1Dokument25 SeitenOb Seminar Amniotic Fluid-1Aleena Davis100% (1)
- Seminar On Choanal AtresiaDokument16 SeitenSeminar On Choanal AtresiaGreeshma ShajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cleft Lip PalateDokument29 SeitenCleft Lip PalatelisalovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyloric Stenosis WDokument11 SeitenPyloric Stenosis WKlaue Neiv CallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intussuseption and Hirschprung's DiseaseDokument5 SeitenIntussuseption and Hirschprung's DiseaseAris Magallanes100% (2)
- Cleft Lip and PalateDokument19 SeitenCleft Lip and PalateJuviely PremacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Nasolacrimal Duct ObstructionDokument43 SeitenCongenital Nasolacrimal Duct ObstructionAnumeha JindalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory SystemDokument24 SeitenRespiratory SystemHani El-asferNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kelainan Kongenital Sistem RespirasiDokument54 SeitenKelainan Kongenital Sistem RespirasiBhima PerdanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19-Pediatric SurgeryDokument39 Seiten19-Pediatric Surgerycallisto3487Noch keine Bewertungen
- Health Assessment LectureDokument16 SeitenHealth Assessment LectureteabagmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Nursing TheoriesDokument5 SeitenClassification of Nursing Theoriesteabagman70% (10)
- Biostat FinalsDokument3 SeitenBiostat FinalsteabagmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology Exam 1st GradingDokument4 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology Exam 1st Gradingteabagman100% (2)
- Endometab Exam 2018Dokument8 SeitenEndometab Exam 2018teabagmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Madeleine Leininger Transcultural NursingDokument5 SeitenMadeleine Leininger Transcultural Nursingteabagman100% (1)
- XV Ongoing Support For MothersDokument19 SeitenXV Ongoing Support For MothersteabagmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- XVII Making Hospital Baby FriendlyDokument18 SeitenXVII Making Hospital Baby FriendlyteabagmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz BioethicsDokument1 SeiteQuiz Bioethicsteabagman50% (2)
- XII Breast and Nipple ConditionsDokument23 SeitenXII Breast and Nipple ConditionsteabagmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Globe Mackay and Radio Corporation V CA: Civil CodeDokument2 SeitenGlobe Mackay and Radio Corporation V CA: Civil CodeteabagmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioethics Finals ExamDokument5 SeitenBioethics Finals Examteabagman100% (2)
- MOA Sample 1Dokument3 SeitenMOA Sample 1teabagmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 102 SyllabusDokument3 SeitenNCM 102 SyllabusteabagmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharma 2017 1st GradexamDokument4 SeitenPharma 2017 1st GradexamteabagmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz BioethicsDokument1 SeiteQuiz Bioethicsteabagman50% (2)
- RecipesDokument2 SeitenRecipesteabagmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid and Electrolyte ExamDokument1 SeiteFluid and Electrolyte Examteabagman0% (1)
- Spec Com FinalDokument151 SeitenSpec Com FinalteabagmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalance QuizDokument2 SeitenFluid and Electrolyte Imbalance QuizteabagmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCN QuizDokument2 SeitenMCN QuizteabagmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tesda Circular s.2016 Re Revised Process Cycle Time and Requirements For Program RegistrationDokument51 SeitenTesda Circular s.2016 Re Revised Process Cycle Time and Requirements For Program Registrationteabagman100% (3)
- HEALTH ED QUIZ Determinants of LearningDokument2 SeitenHEALTH ED QUIZ Determinants of LearningteabagmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter (1) The Accounting EquationDokument46 SeitenChapter (1) The Accounting Equationtunlinoo.067433100% (3)
- De Villa vs. Court of AppealsDokument1 SeiteDe Villa vs. Court of AppealsValerie Aileen AnceroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examination of Conscience Ten Commandments PDFDokument2 SeitenExamination of Conscience Ten Commandments PDFAntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Digest - de Roy Vs CoaDokument2 SeitenCase Digest - de Roy Vs CoaLei Lei LeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ramin Shamshiri Risk Analysis Exam2 PDFDokument8 SeitenRamin Shamshiri Risk Analysis Exam2 PDFRedmond R. ShamshiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Travel Smart: Assignment 1: Project ProposalDokument14 SeitenTravel Smart: Assignment 1: Project ProposalcattytomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Digest: Pedro Elcano and Patricia Elcano Vs - Reginald Hill and Marvin HillDokument5 SeitenCase Digest: Pedro Elcano and Patricia Elcano Vs - Reginald Hill and Marvin Hillshirlyn cuyongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theoretical Foundations of NursingDokument22 SeitenTheoretical Foundations of Nursingattilaabiidn100% (3)
- List of Festivals in India - WikipediaDokument13 SeitenList of Festivals in India - WikipediaRashmi RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Far 1 - Activity 1 - Sept. 09, 2020 - Answer SheetDokument4 SeitenFar 1 - Activity 1 - Sept. 09, 2020 - Answer SheetAnonn100% (1)
- Story of Their Lives: Lived Experiences of Parents of Children With Special Needs Amidst The PandemicDokument15 SeitenStory of Their Lives: Lived Experiences of Parents of Children With Special Needs Amidst The PandemicPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diplomatic Quarter New Marriott Hotel & Executive ApartmentsDokument1 SeiteDiplomatic Quarter New Marriott Hotel & Executive Apartmentsconsultnadeem70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lee Gwan Cheung Resume WeeblyDokument1 SeiteLee Gwan Cheung Resume Weeblyapi-445443446Noch keine Bewertungen
- Invoice Ce 2019 12 IVDokument8 SeitenInvoice Ce 2019 12 IVMoussa NdourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oscar Characterization TemplateDokument3 SeitenOscar Characterization Templatemqs786Noch keine Bewertungen
- F07 hw07Dokument2 SeitenF07 hw07rahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 13 ArqDokument6 SeitenCH 13 Arqneha.senthilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pitch PDFDokument12 SeitenPitch PDFJessa Mae AnonuevoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adobe Voice Assessment Tool-FinalDokument1 SeiteAdobe Voice Assessment Tool-Finalapi-268484302Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is GodDokument273 SeitenWhat Is GodBlankafloraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tuberculosis: Still A Social DiseaseDokument3 SeitenTuberculosis: Still A Social DiseaseTercio Estudiantil FamurpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Armor MagazineDokument56 SeitenArmor Magazine"Rufus"100% (2)
- Percussion Digital TWDokument26 SeitenPercussion Digital TWAlberto GallardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- (These Are Taken From The Hics Infectious Disease Incident Response Guide Available atDokument2 Seiten(These Are Taken From The Hics Infectious Disease Incident Response Guide Available atDavid MitchellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reseller Handbook 2019 v1Dokument16 SeitenReseller Handbook 2019 v1Jennyfer SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument6 SeitenChapter 1Alyssa DuranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2teeth and Its Care: Worksheet - 1Dokument11 SeitenChapter 2teeth and Its Care: Worksheet - 1RPJNoch keine Bewertungen
- The EagleDokument4 SeitenThe EagleJunkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Psychometricians Licensure Exam RevieweDokument1 SeitePhilippine Psychometricians Licensure Exam RevieweKristelle Mae C. Azucenas0% (1)
- Seventh Day Adventist Quiz by KnowingTheTimeDokument4 SeitenSeventh Day Adventist Quiz by KnowingTheTimeMiiiTheart100% (3)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Von EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDVon EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityVon EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (29)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionVon EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (404)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsVon EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedVon EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (81)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeVon EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessVon EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (328)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossVon EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaVon EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (42)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsVon EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (4)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsVon EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeVon EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (253)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Von EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (110)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityVon EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryVon EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsVon EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (170)
- Summary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedVon EverandSummary: Thinking, Fast and Slow: by Daniel Kahneman: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (61)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesVon EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (1412)
- How to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingVon EverandHow to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlVon EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (59)