Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Final NCP1 2
Hochgeladen von
hahahahaaaaaaa0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
30 Ansichten2 Seitenvomiting
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenvomiting
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
30 Ansichten2 SeitenFinal NCP1 2
Hochgeladen von
hahahahaaaaaaavomiting
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
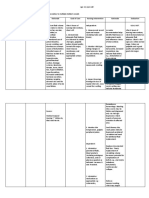
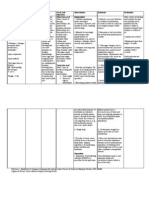
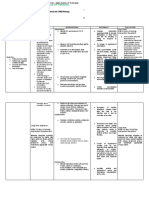
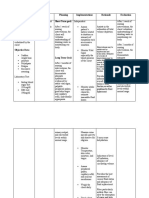
Nursing Care Plan 1
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Dehydration -After 8 hours of After 8 hrs of
S: andami niya na related to nursing Independent: nursing
pong isinuka, hindi ko vomiting as intervention, Monitor and document vital Decrease in circulating blood intervention
na po mabilang as manifested by clients vomiting signs especially BP and volume can the patient
verbalized by the poor skin turgor will stop and HR. cause hypotension and displayed
mother. and dry mucous reduced tachycardia. Alteration in HR is improvement
O: membranes. a compensatory mechanism to on the
dry mucous -After nursing maintain cardiac output. Objective cues
membranes intervention, a Usually, the pulse is weak and
poor skin slight decrease in may be irregular if electrolyte
turgor skin turgor will be imbalance also occurs.
observed.
Vital Signs: Assess Urine Color, Urine A normal urine output is
BP: 90/60mmHg Intake and Output every 4 considered normal not less than
HR: 120 hours. 30ml/hour and Gconcentrated
beats/minute urine means fluid deficit.
I&O:
4/18: 1,050
4/19: 1,200
Assess skin turgor and oral Signs of dehydration are also
mucous membranes for detected through skin.
signs of dehydration.
Assess color and amount of These factors influence the
urine. intake and output or any other
fluid needs.
Note the presence of To decrease the risk of
nausea and vomiting, and dehydrations complication and
fever. hypovolemia.
Dependent:
Encourage to increase fluid
intake. An accurate measure of fluid
intake and output is an
important indicator of patients
fluid status.
Collaborative:
Give/supervise administ
ration of IV fluids. To decrease the risk of
dehydrations complication and
hypovolemia.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hypo-Pigmentation Of The Skin A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandHypo-Pigmentation Of The Skin A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDokument6 SeitenAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dermatitis Herpetiformis: A Concise Guide to Causes, Tests and Treatment OptionsVon EverandDermatitis Herpetiformis: A Concise Guide to Causes, Tests and Treatment OptionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Diabetes 2Dokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan Diabetes 2Ysun Espino100% (1)
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsVon EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument9 SeitenNCPYesha Mae MartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Disease Management for Small AnimalsVon EverandChronic Disease Management for Small AnimalsW. Dunbar GramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Diabetes 2Dokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan Diabetes 2inagasi83% (12)
- Cues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: IndependentDokument2 SeitenCues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: IndependentArabelle GONoch keine Bewertungen
- Lichen Planus, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandLichen Planus, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP HemothoraxDokument3 SeitenNCP Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (2)
- Haemorrhoids: Natural Treatments That Really Work!Von EverandHaemorrhoids: Natural Treatments That Really Work!Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ncp.-Fluid Volume DeficitDokument1 SeiteNcp.-Fluid Volume DeficitAdia Cavrinni De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Mnemonics: The Ultimate Tips and Notes For NursesVon EverandNursing Mnemonics: The Ultimate Tips and Notes For NursesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Dengue NCPDokument3 SeitenDengue NCPingridNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dengue NCPDokument3 SeitenDengue NCPnj_pink08179456% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective DataDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Subjective DataAbdallah AlasalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenCues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationKristiene Kyle AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPs Durano Aireen E.Dokument6 SeitenNCPs Durano Aireen E.Doneva Lyn MedinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For DM PatientDokument10 SeitenNursing Care Plan For DM PatientRainier Rhett Concha100% (5)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationHanz AlecNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan AmoebiasisDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Amoebiasisderic97% (35)
- NCP Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume PotentialDokument4 SeitenNCP Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume PotentialArian May Marcos100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: IndependentDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan: IndependentAdhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Noc: NIC: Fluid ManagementDokument10 SeitenCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Noc: NIC: Fluid ManagementSkyla FiestaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NURSING CARE PLAN - CholeraDokument2 SeitenNURSING CARE PLAN - Choleraderic87% (30)
- Nursing Diagnosis 1Dokument5 SeitenNursing Diagnosis 1Kim TangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume Best NCPDokument2 SeitenRisk For Deficient Fluid Volume Best NCPAlbean DelojeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetes Mellitus (DM)Dokument1 SeiteDiabetes Mellitus (DM)Bheru LalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care Plan 3Dokument2 SeitenCues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care Plan 3JP2001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Histolytica, ADokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Histolytica, AkristennemarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- As Fluid Volume Deficit (FVD), Hypovolemia) Is ADokument2 SeitenAs Fluid Volume Deficit (FVD), Hypovolemia) Is ATanya Alyssa Untalan AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Diabetes Mellitus Type 1Dokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Diabetes Mellitus Type 1deric85% (46)
- Prado NCPDokument4 SeitenPrado NCPalleah pradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 1Dokument3 SeitenModule 2 1Lacangan, Thea YvonneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument6 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationKRISTINE BULACANNoch keine Bewertungen
- But He Hated The Taste of Water: Nursing Assessment RationaleDokument4 SeitenBut He Hated The Taste of Water: Nursing Assessment RationaleJiv Rouziell DoroteoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PL WPS OfficeDokument3 SeitenNursing Care PL WPS OfficeDhan IvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)Dokument7 SeitenDeficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)jajalerNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP CaprichoDokument3 SeitenNCP CaprichoElishah CaprichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - DM - FatigueDokument12 SeitenNCP - DM - FatigueJisel-Apple BulanNoch keine Bewertungen
- College of Nursing: Maternal and Child NursingDokument2 SeitenCollege of Nursing: Maternal and Child NursingLeahmore Amor Padayhag AlineaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Actual and Potencial NCP Peptic Ulcer. Adepoju Iyinoluwa EDokument3 SeitenActual and Potencial NCP Peptic Ulcer. Adepoju Iyinoluwa EAdepoju IyinoluwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP CKDDokument5 SeitenNCP CKDDbktNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For Deficient Fluid VolumeDokument3 SeitenRisk For Deficient Fluid VolumeALEKS MONTECINO JIMENEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subjective Data: Long Term Goal: Diagnostic:: "I Was Trying To Vomit in The Emergency Department."Dokument5 SeitenSubjective Data: Long Term Goal: Diagnostic:: "I Was Trying To Vomit in The Emergency Department."Erle Gray CadangenNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For MedwardDokument11 SeitenNCP For MedwardTroy MirandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Volume Defict Ms. HicksDokument8 SeitenFluid Volume Defict Ms. HicksShenna RegaspiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Camba RLE3rd BloodTransfusionDokument9 SeitenCamba RLE3rd BloodTransfusionJOANNA MARIE CAMBANoch keine Bewertungen
- DM NCP - Trixia U. Almendral GRP 6Dokument3 SeitenDM NCP - Trixia U. Almendral GRP 6Trixia AlmendralNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP DengueDokument3 SeitenNCP DenguejhaninahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument11 SeitenNursing Care PlanKirstin del CarmenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan PediaDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan PediaLenie DegraciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BOX 17.4 NCP Postpartum HemorrhageDokument4 SeitenBOX 17.4 NCP Postpartum HemorrhageJam AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedia NCPDokument9 SeitenPedia NCPTyn TynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan, DeficientDokument5 SeitenNursing Care Plan, Deficientimee15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan TemplateDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan TemplateTricia LiporadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - AgeDokument5 SeitenNCP - Ageunsp3akabl386% (7)
- Oral: PO 50mg/day Alone Or: ND RDDokument2 SeitenOral: PO 50mg/day Alone Or: ND RDhahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guinea Pig Farm (Out)Dokument3 SeitenGuinea Pig Farm (Out)hahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CefuroximeDokument1 SeiteCefuroximehahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PantoprazoleDokument1 SeitePantoprazolehahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance, Posture and Body AlignmentDokument6 SeitenBalance, Posture and Body AlignmenthahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zamboanga Del Sur General Hospital: Staff Nurse Performance Evaluation SheetDokument5 SeitenZamboanga Del Sur General Hospital: Staff Nurse Performance Evaluation SheethahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hospital Budgeting: - Construction Materials - Construction Team and Workers - ElectricianDokument11 SeitenHospital Budgeting: - Construction Materials - Construction Team and Workers - ElectricianhahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHN Lecture SY2015-2016 1 SemesterDokument141 SeitenCHN Lecture SY2015-2016 1 SemesterhahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biodata and AnaphyDokument3 SeitenBiodata and AnaphyhahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug TableDokument1 SeiteDrug TablehahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids and Electrolytes: 2. Interstitial SpaceDokument13 SeitenFluids and Electrolytes: 2. Interstitial Spacehahahahaaaaaaa100% (1)
- FilariasisDokument11 SeitenFilariasishahahahaaaaaaa100% (1)
- Composition Qualifications and Terms of HRDokument2 SeitenComposition Qualifications and Terms of HRhahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Escavape Cloud RoomDokument2 SeitenEscavape Cloud RoomhahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Wall of The Heart Consists of Three Layers of TissueDokument4 SeitenThe Wall of The Heart Consists of Three Layers of TissuehahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Leadership and Management PDFDokument10 SeitenNursing Leadership and Management PDFhahahahaaaaaaa100% (9)
- Service Ward FebruaryDokument1 SeiteService Ward FebruaryhahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3C Drug StudyDokument2 Seiten3C Drug StudyhahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiologic Technologist Job DescriptionDokument1 SeiteRadiologic Technologist Job DescriptionhahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Ordog Effect DeadworldDokument59 SeitenThe Ordog Effect DeadworldJw SqNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.andersen: 2. BimlerDokument6 Seiten1.andersen: 2. BimlerRoxana ElenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensory Play Activities Kids Will LoveDokument5 SeitenSensory Play Activities Kids Will LoveGoh KokMingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formation of Faeces and DefecationDokument11 SeitenFormation of Faeces and Defecationbiologi88Noch keine Bewertungen
- TonsillectomyDokument6 SeitenTonsillectomyBen David0% (1)
- Listening Comprehension The Amish ParadiseDokument5 SeitenListening Comprehension The Amish ParadiseAngel Angeleri-priftis.100% (2)
- Fluid and Electrolytes1Dokument7 SeitenFluid and Electrolytes1Charl PabillonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agglutination ReactionsDokument28 SeitenAgglutination ReactionscyrhenmieNoch keine Bewertungen
- TerminologiesDokument65 SeitenTerminologiesErika Mae PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modic Type 1 Vs Tuberculous SpondylitisDokument5 SeitenModic Type 1 Vs Tuberculous SpondylitisAgnes JauwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overgranulation: A. Muhammad Reva A.MDokument21 SeitenOvergranulation: A. Muhammad Reva A.Mgalih widodoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Illustrated July-August 2008Dokument79 SeitenScience Illustrated July-August 2008lelo2k30% (1)
- Anatomical LandmarksDokument32 SeitenAnatomical Landmarksdrhari_omrdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Analysis - FractureDokument7 SeitenCase Analysis - FractureMichelle TeodoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- A French Reader Aldrich and Foster 1903Dokument324 SeitenA French Reader Aldrich and Foster 1903sandrabbit100% (1)
- Physiology of Mammalian IngestionDokument6 SeitenPhysiology of Mammalian IngestionEbooks For YouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics Icar1Dokument18 SeitenGenetics Icar1elanthamizhmaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- UH Kelas XIIDokument7 SeitenUH Kelas XIIElismawati AzmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Walt Disney: SpeechDokument2 SeitenWalt Disney: SpeechBuşuMihaiCătălinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Ni LagneDokument8 SeitenResearch Ni LagneqtiejeydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Housing and Maintenance of Ambystoma Mexicanum, The Mexican AxolotlDokument20 SeitenHousing and Maintenance of Ambystoma Mexicanum, The Mexican AxolotlAngela HurtadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Freon 11Dokument8 SeitenFreon 11JodyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENT - Ear-Nose-Throat PDFDokument15 SeitenENT - Ear-Nose-Throat PDFMa SakhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 MCNDokument14 SeitenChapter 1 MCNLawrence NemirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Clinical Parasitology PDF 4656784Dokument1 SeiteBasic Clinical Parasitology PDF 4656784Natalie EnriquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology of Heart and Vessels - ANAT3888 - 2023Dokument41 SeitenHistology of Heart and Vessels - ANAT3888 - 2023RachaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study About Cervical CancerDokument11 SeitenCase Study About Cervical CancerJisel-Apple Bulan100% (1)
- Medical Parasitology in The Philippines 3rd Ed PDFDokument535 SeitenMedical Parasitology in The Philippines 3rd Ed PDFroland mamburam75% (16)
- Comparative Anatomy of The Horse, Ox, and Dog-The Brain and Associated VesselsDokument11 SeitenComparative Anatomy of The Horse, Ox, and Dog-The Brain and Associated VesselsmichiparisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Keys of Comedk Pget-2008Dokument23 SeitenAnswer Keys of Comedk Pget-2008mobiled2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Sleep Hypnosis: Guided Meditation For Sleep & HealingVon EverandDeep Sleep Hypnosis: Guided Meditation For Sleep & HealingBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (104)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- Breaking the Habit of Being YourselfVon EverandBreaking the Habit of Being YourselfBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (1460)
- How to Talk to Anyone: Learn the Secrets of Good Communication and the Little Tricks for Big Success in RelationshipVon EverandHow to Talk to Anyone: Learn the Secrets of Good Communication and the Little Tricks for Big Success in RelationshipBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (1135)
- Peaceful Sleep Hypnosis: Meditate & RelaxVon EverandPeaceful Sleep Hypnosis: Meditate & RelaxBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (144)
- Aging Backwards: Reverse the Aging Process and Look 10 Years Younger in 30 Minutes a DayVon EverandAging Backwards: Reverse the Aging Process and Look 10 Years Younger in 30 Minutes a DayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of The 4-Hour Body: An Uncommon Guide to Rapid Fat-Loss, Incredible Sex, and Becoming Superhuman by Timothy FerrissVon EverandSummary of The 4-Hour Body: An Uncommon Guide to Rapid Fat-Loss, Incredible Sex, and Becoming Superhuman by Timothy FerrissBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (82)
- Forever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellVon EverandForever Strong: A New, Science-Based Strategy for Aging WellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allen Carr's Easy Way to Quit Vaping: Get Free from JUUL, IQOS, Disposables, Tanks or any other Nicotine ProductVon EverandAllen Carr's Easy Way to Quit Vaping: Get Free from JUUL, IQOS, Disposables, Tanks or any other Nicotine ProductBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (31)
- The Noom Kitchen: 100 Healthy, Delicious, Flexible Recipes for Every DayVon EverandThe Noom Kitchen: 100 Healthy, Delicious, Flexible Recipes for Every DayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Love Yourself, Heal Your Life Workbook (Insight Guide)Von EverandLove Yourself, Heal Your Life Workbook (Insight Guide)Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (40)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- The Longevity Book: The Science of Aging, the Biology of Strength, and the Privilege of TimeVon EverandThe Longevity Book: The Science of Aging, the Biology of Strength, and the Privilege of TimeBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (13)
- What to Expect When You’re Expecting (5th Edition)Von EverandWhat to Expect When You’re Expecting (5th Edition)Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningVon EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- Midnight Meditations: Calm Your Thoughts, Still Your Body, and Return to SleepVon EverandMidnight Meditations: Calm Your Thoughts, Still Your Body, and Return to SleepBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Body Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomVon EverandBody Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- 369: Manifesting Through 369 and the Law of Attraction - METHODS, TECHNIQUES AND EXERCISESVon Everand369: Manifesting Through 369 and the Law of Attraction - METHODS, TECHNIQUES AND EXERCISESBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (50)
- The Happiest Baby on the Block: The New Way to Calm Crying and Help Your Newborn Baby Sleep LongerVon EverandThe Happiest Baby on the Block: The New Way to Calm Crying and Help Your Newborn Baby Sleep LongerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (58)
- Chair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouVon EverandChair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (5)
- Instant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookVon EverandInstant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Glucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarVon EverandGlucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (352)
- The End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellVon EverandThe End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (82)
- Eat & Run: My Unlikely Journey to Ultramarathon GreatnessVon EverandEat & Run: My Unlikely Journey to Ultramarathon GreatnessNoch keine Bewertungen