Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Reviewer: Animal Cell
Hochgeladen von
Josua Garcia0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
25 Ansichten1 SeiteThis document discusses cell biology and the structure and function of cells. It covers the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including that eukaryotic cells have a nucleus while prokaryotic cells do not. It also summarizes the main types of cell structures found in eukaryotic cells like the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and mitochondria. Finally, it briefly outlines the major types of tissues in the body including epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissues.
Originalbeschreibung:
tgfg
Originaltitel
Botany
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis document discusses cell biology and the structure and function of cells. It covers the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including that eukaryotic cells have a nucleus while prokaryotic cells do not. It also summarizes the main types of cell structures found in eukaryotic cells like the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and mitochondria. Finally, it briefly outlines the major types of tissues in the body including epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissues.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
25 Ansichten1 SeiteReviewer: Animal Cell
Hochgeladen von
Josua GarciaThis document discusses cell biology and the structure and function of cells. It covers the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including that eukaryotic cells have a nucleus while prokaryotic cells do not. It also summarizes the main types of cell structures found in eukaryotic cells like the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and mitochondria. Finally, it briefly outlines the major types of tissues in the body including epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissues.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
Reviewer
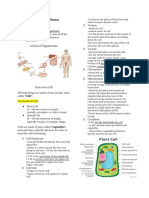
BOTANY 5. CELL DIVISION
Animal Cell Flagellum some single celled
CYTOLOGY Cell Biology The study of E.Organism have flagellum
cell structure and activity 3 types of cell division
Micrometer Unit of Measurement (1/1000 mn) 1. Binary Fission
with the symbol of (um) 2. Meiosis
Nanometer (nm) most often used (1000nm=1 um; 3. Mitosis
1nm= 10 A) Binary fission the method used by prokaryotes, produces
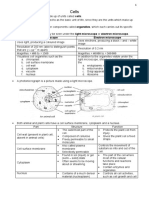
Two catergories of CELL STRUCTURE two identical cells from one cell
Prokaryotic Cell Mitosis which also produces two genetically identical cells
Eukaryotic Cell from a single cell
Prokaryotice Cell Found only in Bacteria and Meiosis sexually reproducting organisms include
archaebacteria Components of DNA seaweeds,fungi,plants&animals
DNAMingle freely in the cells Meiosis differ from Mitosis
DNA Dioxi Nucle Acid Zygote Cell resulting from the union contains the full
RNA Raivo Nucle Acid number of chromosomes.
RER Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Tissue Group of associated
Eukaryotic Cell Found in Fungi, Animals and all other Life Histology/Microscopic Anatomy study of the arrangement
forms of tissues in organs
The DNA of Eukaryotic Cells is enclosed in a special Gross Anatomy This deals with organ system by dissection
organelle Nucleus 5 Major Groups of Somatic cell
Epithelial or Covering
Prokaryote before nucleus or Prenucleus Connective or Supporting
Eukaryote means true nucleus Vascular or Circulatory
Eukaryote 10x Larger than Prokaryotic cells Muscular or Contractile
The Nucleus largest organelle in an animal cell. Nervous
- Sorrounded by Double Layered
Endoplasmic Reticulum attached to the 1. Epithelial or Covering Color enhanced microscopic
Nuclear membrane is an elongated membranous sac photograph reveals the distribution of structure and
(2 forms of E.R) substances
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) Tissue
Appears bumpy under a microscope Simple with cell in one layer
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) Stratified with Multiple Layer
Prominent in liver cells, serves to detoxify subs. such as 2. Connective tissues and Supportive Tissues
alcohol, drugs, and other poisons. Support and hold parts of the body together
Golgi apparatus organelle that resembles a stack of deflated Reticular Tissue framework stellate reticular cell
balloons Fibrous Tissue consist of scattered cells.
Lysosomes small, often spherical organelles that function as Adipose Tissue The cell rounded of polygonal w/ thin layers
the cells recycling center and garbage disposal Elastic Tissue found in legaments
Mitochondria the power houses of the cell Cartilage Firm yet elastic matrix (chrondrion)
ATP Adenosine TriphosPhate serves as an energy battery True Bone/Osseous Tissues occurs only in the skeleton of
for countless cellular processes, bony fishes and land vertebrates
Blood and Lymph often considered connective tissues.
CELL FUNCTION 3. Muscle Tissues/Contractile Tissue
Cell must be able to carry out a variety of function. Which contract and relax, comprise the striated, smooth
and cardiac muscles.
5 TYPES OF CELL FUNCTION Striated Muscles skeletal or voluntary muscles
1. MOVEMENTS Cardiac Muscles have characteristic of both striated and
2. NUTRITION smooth muscles
3. ENERGY 4. Nerve Tissues transmit information from one part of
4. PROTEINSYNTHESIS the body to another
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Quarter 1 - Module 1: Cells: The Building Blocks of LifeDokument7 SeitenQuarter 1 - Module 1: Cells: The Building Blocks of LifeCharmaine PamesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology 1Dokument7 SeitenGeneral Biology 1Charmaine PamesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells and Tissues & Integumentary SystemDokument21 SeitenCells and Tissues & Integumentary SystemTaehyung KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epithelial Tissue: Absorption, Transport, Excretion, Protection, SecretionDokument7 SeitenEpithelial Tissue: Absorption, Transport, Excretion, Protection, SecretionKenneth Rodriguez HerminadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology 1Dokument3 SeitenBiology 1ever leighNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDokument12 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology ReviewerAnn Fenelope AniscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology 1 1Dokument9 SeitenGeneral Biology 1 1manansalastarringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 3 - GenBio1 CELLS 1st Term SY 2021-2022Dokument8 SeitenWeek 3 - GenBio1 CELLS 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINANoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cells: Cella - Small RoomDokument5 SeitenThe Cells: Cella - Small RoomSarah Grace CajucomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Y10 Ch2Dokument7 SeitenBiology Y10 Ch2zuhra123coolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology: The Study of TissuesDokument39 SeitenHistology: The Study of TissuesEla Santos100% (1)
- CELL PARTS and PROKARYOTESDokument6 SeitenCELL PARTS and PROKARYOTESHarry ParconNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell: The Building Blocks of Life: Awaluddin, M.KesDokument39 SeitenCell: The Building Blocks of Life: Awaluddin, M.KesNovanda D. PahleviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genbio ExamDokument13 SeitenGenbio Examharry pottahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - Module 1Dokument6 SeitenBiology - Module 1ASHLEY MONICA PLATANoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson1 CellDokument3 SeitenLesson1 CellClarisse De GuiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- STM 007Dokument11 SeitenSTM 007Carla PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)Dokument37 SeitenGeneral Biology Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)shieeesh.aNoch keine Bewertungen
- CG - Y9 - 02-03 Levels of Organisation & Cell StructureDokument39 SeitenCG - Y9 - 02-03 Levels of Organisation & Cell StructureCharlotte BurkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy PrelimsDokument17 SeitenAnaphy PrelimsEkoy TheRealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Bio Sem 1 NotesDokument12 SeitenGen Bio Sem 1 NotesFrances Chynna KhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACFrOgA SX2Dokument7 SeitenACFrOgA SX2Nadhine MacalinaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Characteristics of Living Things: M R S G R E NDokument10 Seiten7 Characteristics of Living Things: M R S G R E Nmcda100% (1)
- Cell Biology - Unit - 1Dokument19 SeitenCell Biology - Unit - 1shivangipurohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bab 2 Tingkatan 1Dokument58 SeitenBab 2 Tingkatan 1azizahembong84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pointers To Review in GenbioDokument5 SeitenPointers To Review in GenbioLouie BarrientosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Form 4Dokument9 SeitenBiology Form 4Ashlyn OoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Alvi Milliana Risma Aprinda K. UIN Maliki MalangDokument90 SeitenDr. Alvi Milliana Risma Aprinda K. UIN Maliki MalangFaridNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy PrelimsDokument20 SeitenAnaphy PrelimsEkoy TheRealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy Prelims 1Dokument20 SeitenAnaphy Prelims 1Ekoy TheRealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Tissues 2023Dokument70 SeitenAnimal Tissues 2023yxcz.rzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Lesson 4Dokument4 SeitenBiology Lesson 4Medija FamilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- All About Animal Cells: Presentation byDokument32 SeitenAll About Animal Cells: Presentation byMarifer Dapat100% (1)
- Spgbio NotesDokument22 SeitenSpgbio NotesKaycee HeokkaidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biol 266 - Cell Biology Unit 1 "Cells and Organelles - I"Dokument78 SeitenBiol 266 - Cell Biology Unit 1 "Cells and Organelles - I"Volodymyr KravchenkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Cell and TissueDokument45 Seiten2 Cell and Tissuemandefro2Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Cells (Theory, Types and Ultrastructure)Dokument6 Seiten1.1 Cells (Theory, Types and Ultrastructure)Ivan RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer in Biology 1Dokument6 SeitenReviewer in Biology 1CameronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Types 1Dokument28 SeitenCell Types 1IngridNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zikri Aiman-Cell Organization in AnimalsDokument37 SeitenZikri Aiman-Cell Organization in AnimalsZikriAimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology 1 "CELL": Postulates of The Cell TheoryDokument9 SeitenGeneral Biology 1 "CELL": Postulates of The Cell TheoryLaika LaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selina Concise Biology Solutions Class 7 Chapter 1 Plant and Animal TissuesDokument12 SeitenSelina Concise Biology Solutions Class 7 Chapter 1 Plant and Animal TissuesAKSHAJ AGGARWALNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.4.1-2.4.3 Cell DiversityDokument8 Seiten2.4.1-2.4.3 Cell Diversity13593678Noch keine Bewertungen
- ZoologyDokument4 SeitenZoologyremolador.carengraceNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology-Lesson 4 Plant and Animal TissuesDokument4 SeitenGeneral Biology-Lesson 4 Plant and Animal TissuesHaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Notes Chapter 4 Cells and Tissue: 4.2 Cellular Structures and FunctionsDokument10 SeitenBiology Notes Chapter 4 Cells and Tissue: 4.2 Cellular Structures and FunctionsFatima Zulqarnain100% (1)
- Structure and TaxonomyDokument4 SeitenStructure and Taxonomymhiee maaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- تخدير المحاضرة الاولىDokument7 Seitenتخدير المحاضرة الاولىXcv FfgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: The Cell: Cell-Is The Simplest Unit of Matter That Is AliveDokument5 SeitenChapter 1: The Cell: Cell-Is The Simplest Unit of Matter That Is AliveScarlet VillamorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells NoteDokument6 SeitenCells NoteYolanda JesslinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Study Guide - TeacherDokument11 SeitenUnit 2 Study Guide - Teacherapi-198603477Noch keine Bewertungen
- BIO1 - Lessons3J4J5 - Prokaryotic Vs EukaryoticJ Plant Vs Animal CellJ Cell ModificationsDokument49 SeitenBIO1 - Lessons3J4J5 - Prokaryotic Vs EukaryoticJ Plant Vs Animal CellJ Cell Modificationsraphaelleflorenog1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cells StudentDokument24 SeitenCells Studentfeliciamichelle200Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer 2016 - 2017Dokument8 SeitenReviewer 2016 - 2017VivaMapwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trans EsDokument5 SeitenTrans EsSOLIS, John Ernest S.Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology Cells1Dokument6 SeitenGeneral Biology Cells1Kristine CarvajalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Animal's Specialized StructuresDokument58 Seiten1.1 Animal's Specialized StructuresNathaliabee100% (1)
- Module 2 - Bio SyllabusDokument13 SeitenModule 2 - Bio SyllabusChamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3 Cell Parts and FunctionDokument60 SeitenLecture 3 Cell Parts and FunctionEsther Suan-LancitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- COT-RSP RubricDokument10 SeitenCOT-RSP RubricJosua Garcia100% (4)
- Grade 11 (First Semester) SY: 2018 - 2019 Grade 11 (Second Semester) Sy: 2018 - 2019Dokument1 SeiteGrade 11 (First Semester) SY: 2018 - 2019 Grade 11 (Second Semester) Sy: 2018 - 2019Josua GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (PDF) 21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDokument7 Seiten(PDF) 21st Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldJosua GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan For ObservationDokument3 SeitenLesson Plan For ObservationJosua GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of MediaDokument11 SeitenTypes of MediaJosua GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of MediaDokument11 SeitenTypes of MediaJosua GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module For Pr1Dokument2 SeitenModule For Pr1Josua GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PointersDokument2 SeitenPointersJosua GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate of AppreciationDokument1 SeiteCertificate of AppreciationJosua GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boracay UK - English A5-Brochure August-2019 WebDokument4 SeitenBoracay UK - English A5-Brochure August-2019 WebJosua GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HeheDokument5 SeitenHeheJosua GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Other Lit Genres LPDokument9 SeitenC Other Lit Genres LPJosua GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Letter To The ParentDokument1 SeiteLetter To The ParentJosua GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21st Century Literature Pre-TestDokument2 Seiten21st Century Literature Pre-TestJosua GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHS Applied Research 2 CGDokument3 SeitenSHS Applied Research 2 CGJosua GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PointersDokument2 SeitenPointersJosua GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9 SampleDokument1 SeiteF9 SampleJosua GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS - RS12 Id e 2Dokument8 SeitenCS - RS12 Id e 2Josua GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Area Chart Presentation Slides: Lorem Ipsum Dolor Sit Amet, Consectetur Adipiscing Elit. Aliquam Eu Lobortis ErosDokument14 SeitenArea Chart Presentation Slides: Lorem Ipsum Dolor Sit Amet, Consectetur Adipiscing Elit. Aliquam Eu Lobortis ErosRahman IskandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potential Environmental Impacts of Quarrying Stone in Karst - A Literature ReviewDokument39 SeitenPotential Environmental Impacts of Quarrying Stone in Karst - A Literature ReviewJohn Dale IbaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Letter For Feild Compressive Strength Test 1Dokument2 SeitenLetter For Feild Compressive Strength Test 1Pja Shantha100% (1)
- 3 JSA For SealantDokument11 Seiten3 JSA For SealantAkbar SyahrezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S1110863017300228 MainDokument5 Seiten1 s2.0 S1110863017300228 Mainmaria melayantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wei Sun, P.EDokument36 SeitenWei Sun, P.EharishupretiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dialogue Unit 8: Example of A DialogueDokument4 SeitenDialogue Unit 8: Example of A DialogueIsfaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GINA Severe Asthma Pocket Guide v2.0 Wms 1 PDFDokument22 SeitenGINA Severe Asthma Pocket Guide v2.0 Wms 1 PDFPhuong HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lapres ProteinDokument65 SeitenLapres ProteinPutri AnggreaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Madness Rules For RPGDokument20 SeitenMadness Rules For RPGKaiser Julianus Apostata100% (1)
- Natural Gas EngineeringDokument51 SeitenNatural Gas EngineeringMusa favourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smartgoalsws NNDokument1 SeiteSmartgoalsws NNapi-569332192Noch keine Bewertungen
- Use of Alternative Energy Sources For The Initiation and Execution of Chemical Reactions and ProcessesDokument21 SeitenUse of Alternative Energy Sources For The Initiation and Execution of Chemical Reactions and ProcessesNstm3Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 M2-Prinsip Dan Penerapan Diagram FasaDokument62 Seiten2 M2-Prinsip Dan Penerapan Diagram FasaAhmad WildanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Đề 05Dokument26 SeitenĐề 05Tu CandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calc. Hid. ManguerasDokument8 SeitenCalc. Hid. ManguerasJonahtan A. Navas G.Noch keine Bewertungen
- AHA - Working On Slope RoofDokument2 SeitenAHA - Working On Slope RoofTopsun EnergyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Running Head: Sleep and Misbehavior 1Dokument31 SeitenRunning Head: Sleep and Misbehavior 1api-271305500Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis. Rehabilitation Center. Meta Project Fot The BlindDokument126 SeitenThesis. Rehabilitation Center. Meta Project Fot The Blindshikha chugh0% (1)
- Investigations in Environmental Geology 3rd Edition Foley Solutions ManualDokument18 SeitenInvestigations in Environmental Geology 3rd Edition Foley Solutions Manualjesselact0vvk100% (33)
- ASTM - D888 Oxigeno DisueltoDokument14 SeitenASTM - D888 Oxigeno DisueltoAngel MurilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- GED 104 Contemporary World - Reviewer ofDokument2 SeitenGED 104 Contemporary World - Reviewer ofsiriusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proposal Letter New1Dokument2 SeitenProposal Letter New1api-242445476Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2023 03 The Role of MTHFR Polymorphisms in The Risk of LipedemaDokument9 Seiten2023 03 The Role of MTHFR Polymorphisms in The Risk of LipedemaAndreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Pure Copper - A Comparison of Analytical MethodsDokument12 SeitenAnalysis of Pure Copper - A Comparison of Analytical Methodsban bekasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potato ProjectDokument10 SeitenPotato Projectkillerfox70Noch keine Bewertungen
- 05.08 Saidkhasan SadievDokument2 Seiten05.08 Saidkhasan SadievjaborNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waukesha Mobileflex l5794 L7044gsi Epa Product Sheet PDFDokument4 SeitenWaukesha Mobileflex l5794 L7044gsi Epa Product Sheet PDFDODONoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Customer ServiceDokument16 SeitenUnit 1 Customer ServiceGillian Delos ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speech For FMCGDokument2 SeitenSpeech For FMCGNitin DhantoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeVon EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainVon EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (65)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityVon EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceVon EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (18)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsVon EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessVon Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (33)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldVon EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (598)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseVon EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (52)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomVon EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (217)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondVon EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (4)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedVon EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (11)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceVon EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (517)
- Change Your Brain, Change Your Life (Before 25): Change Your Developing Mind for Real-World SuccessVon EverandChange Your Brain, Change Your Life (Before 25): Change Your Developing Mind for Real-World SuccessBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (18)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorVon EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainVon EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (111)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionVon EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (812)
- The Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceVon EverandThe Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (633)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueVon EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (38)
- Minds Make Societies: How Cognition Explains the World Humans CreateVon EverandMinds Make Societies: How Cognition Explains the World Humans CreateBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (24)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildVon EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (44)
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightVon EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (5)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouVon EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (62)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveVon EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (66)
- Remnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsVon EverandRemnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (3)
- Lymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthVon EverandLymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (13)