Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Force and acceleration problem set
Hochgeladen von
Benedick Jayson P. Marti100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
368 Ansichten2 Seiten1. The document contains 14 physics problems involving kinetics, forces, accelerations, friction, inclined planes, and pulley systems. The problems provide mass values, initial conditions, coefficients of friction, and ask solver to determine values like acceleration, tension, distance, speed, or time.
2. Common concepts assessed include determining acceleration from applied forces, effects of friction on motion, and analyzing pulley systems and inclined planes to solve for unknown values.
3. Problem solving requires applying Newton's laws of motion, equations for acceleration, and principles of forces, friction and pulleys.
Originalbeschreibung:
[9[
Originaltitel
Problem Set ForceAndAccelerationV01
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument melden1. The document contains 14 physics problems involving kinetics, forces, accelerations, friction, inclined planes, and pulley systems. The problems provide mass values, initial conditions, coefficients of friction, and ask solver to determine values like acceleration, tension, distance, speed, or time.
2. Common concepts assessed include determining acceleration from applied forces, effects of friction on motion, and analyzing pulley systems and inclined planes to solve for unknown values.
3. Problem solving requires applying Newton's laws of motion, equations for acceleration, and principles of forces, friction and pulleys.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
368 Ansichten2 SeitenForce and acceleration problem set
Hochgeladen von
Benedick Jayson P. Marti1. The document contains 14 physics problems involving kinetics, forces, accelerations, friction, inclined planes, and pulley systems. The problems provide mass values, initial conditions, coefficients of friction, and ask solver to determine values like acceleration, tension, distance, speed, or time.
2. Common concepts assessed include determining acceleration from applied forces, effects of friction on motion, and analyzing pulley systems and inclined planes to solve for unknown values.
3. Problem solving requires applying Newton's laws of motion, equations for acceleration, and principles of forces, friction and pulleys.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
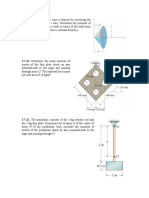
Problem Set No.
Kinetics : Force and Acceleration
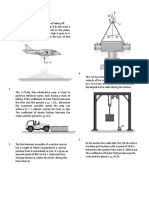
1 The casting has a mass of 4 Mg. Suspended in a
vertical position and initially at rest, it is given an
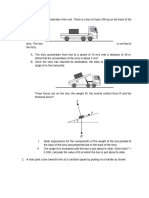
upward speed of 250 mm/ s in 0.4 s using a crane 4 The 3-Mg truck is traveling at 17 m /s when the
hook H. Determine the tension in cables AC and brakes on all its wheels are applied, causing it to
AB during this time interval if the acceleration is skid for a distance of 15 m before coming to rest.
constant. Determine the constant horizontal force developed
in the coupling C, and the frictional force developed
between the tires of the truck and the road during
this time. The total mass of the boat and trailer is 2
Mg.
5 If blocks A and B of mass 15 kg and 10 kg,
respectively, are placed on the inclined plane and
released, determine the force developed in the link.
The coefficients of kinetic friction between the
blocks and the inclined plane are A = 0.2 and B =
0.4. Neglect the mass of the link.
2 The 170-Mg train travels with a speed of 90 km/h
when it starts to climb the slope. If the engine
exerts a traction force F of 1/30 of the weight of the
train and the rolling resistance F D is equal to 1/600
of the weight of the train, determine the
deceleration of the train.
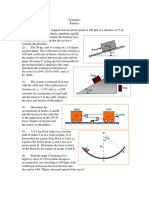
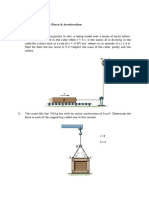
6 Motors A and B draw in the cable with the
accelerations shown. Determine the acceleration of
the 400-lb crate C and the tension developed in the
3 The 170-Mg train starts from rest and begins to cable. Neglect the mass of all the pulleys.
climb the slope as shown. If the engine exerts a
traction force F of 1/10 of the weight of the train,
determine the speed of the train when it has
traveled up the slope a distance of 1.2 km. Neglect
rolling resistance.
7 The van is traveling at 30 km h when the coupling
of the trailer at A fails. If the trailer has a mass of
350 kg and coasts 55 m before coming to rest,
determine the constant horizontal force F created
by rolling friction which causes
the trailer to stop.
12 The man pushes on the 60-lb crate with a force F.
The force is always directed down at 30 from the
horizontal as shown, and its magnitude is increased
8 If the 15-lb block A slides down the plane with a until the crate begins to slide. Determine the crates
constant velocity when = 40, determine the initial acceleration if the coefficient of static friction is
acceleration of the block when = 45. s = 0.7 and the coefficient of kinetic friction is k =
0.4.
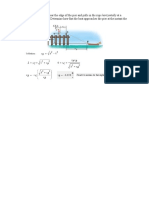
9 Each of the three barges has a mass of 40 Mg,
whereas the tugboat has a mass of 14 Mg. As the
barges are being pulled forward with a constant
velocity of 5 m/s, the tugboat must overcome the 13 A force of F = 20 lb is applied to the cord.
frictional resistance of the water, which is 3 kN for Determine how high the 40-lb block A rises in 4 s
each barge and 2.5 kN for the tugboat. If the starting from rest. Neglect the weight of the pulleys
cable between A and B breaks, determine the and cord.
acceleration of the tugboat.
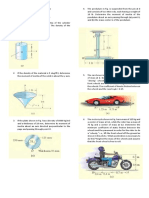
10 The crate has a mass of 90 kg and is being towed
by a chain which is always directed at 30 from the
horizontal as shown. If the magnitude of P is
increased until the crate begins to slide, determine
the crates initial acceleration if the coefficient of
static friction is s = 0.6 and the coefficient of
kinetic friction is k = 0.4. 14 The 70-kg crate shown below rests on a horizontal
surface for which the coefficient of kinetic friction is
k = 0.4. If the crate is subjected to a 400-N towing
force as shown, determine the velocity of the crate
in 3 s starting from rest.
11 Determine the acceleration of the system and the
tension in each cable. The inclined plane is
smooth, and the coefficient of kinetic friction
between the horizontal surface and block C is (k)C
= 0.3.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Entropy measure disorder physical chemistryDokument10 SeitenEntropy measure disorder physical chemistryBenedick Jayson P. Marti100% (2)
- Steam Table Problems PDFDokument5 SeitenSteam Table Problems PDFBenedick Jayson P. Marti100% (1)
- CO-4 Assignment QuestionsDokument7 SeitenCO-4 Assignment QuestionsrajeswariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Calculations 2nd Ed. - V. Venkataramani, N. Anantharaman & K.M. Meera Sheriffa Begum 2011 PDFDokument260 SeitenProcess Calculations 2nd Ed. - V. Venkataramani, N. Anantharaman & K.M. Meera Sheriffa Begum 2011 PDFantonino69100% (6)
- Student Exploration: Energy Conversion in A SystemDokument5 SeitenStudent Exploration: Energy Conversion in A SystemCassie BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determining Specific Gravity Through BuoyancyDokument7 SeitenDetermining Specific Gravity Through BuoyancyVincent Allen B. CorbillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 0910 Spring Set2Dokument3 SeitenAssignment 0910 Spring Set2Sarp Yiğit ŞirinNoch keine Bewertungen
- F at Each Wheel. Assume A Constant Deceleration For The 1500-kg CarDokument12 SeitenF at Each Wheel. Assume A Constant Deceleration For The 1500-kg CarAndre BocoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 7 8Dokument3 SeitenTutorial 7 8Zahida ParnisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addpro 7Dokument1 SeiteAddpro 7Mary Izere MutabaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetics of Particles Work and Energy ClassworkDokument2 SeitenKinetics of Particles Work and Energy ClassworkHarvey BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Energy-6Dokument2 SeitenWork Energy-6Zahida ParnisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics WorksheetDokument3 SeitenDynamics Worksheetgirma workuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set ImpulseMomentum 1Dokument2 SeitenProblem Set ImpulseMomentum 1Takayuki TakayukiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final 08 Engg SolDokument6 SeitenFinal 08 Engg SolyanelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics problems solved step-by-stepDokument6 SeitenMechanics problems solved step-by-stepAndrea 75Noch keine Bewertungen
- Review Module 11 Classical Physics Part 2Dokument2 SeitenReview Module 11 Classical Physics Part 2RamonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics RevisionDokument14 SeitenDynamics Revision地雷0% (1)
- Work Sheet G9 Unit 3&4Dokument2 SeitenWork Sheet G9 Unit 3&4Amarch BahiluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton 2nd law method (work and energy equation) RectilinearDokument9 SeitenNewton 2nd law method (work and energy equation) Rectilineardaniel hambissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DinmjgDokument10 SeitenDinmjghaker linkisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Particle Kinetics ProblemsDokument12 SeitenParticle Kinetics ProblemsAeon ReignNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument15 SeitenChapter 2Lhey Anne Dipasupil EstiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dinamik Final Örnek Sorular PDFDokument3 SeitenDinamik Final Örnek Sorular PDFgedikoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 3 WEDokument5 SeitenTutorial 3 WE2B Dai Ko DUPLICATENoch keine Bewertungen
- CE 222 Spring 2007-2008 Home Exercise #5: A. If The Rotor Always Maintains A Constant ClockwiseDokument2 SeitenCE 222 Spring 2007-2008 Home Exercise #5: A. If The Rotor Always Maintains A Constant ClockwiseSean TraverNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 4 (Chapter 3)Dokument5 SeitenUniversity of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 4 (Chapter 3)Vivin MathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 9 Solutions PDFDokument20 SeitenTutorial 9 Solutions PDFBharat SaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 3Dokument19 SeitenTutorial 3Maria CutajarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trabajo Energia en Una Partícula EjerciciosDokument7 SeitenTrabajo Energia en Una Partícula EjerciciosFabricio Espinoza GamarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit V - Unid End Questions - EMDokument6 SeitenUnit V - Unid End Questions - EMNaresh JonnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1: Energy and Momentum Methods of Particle: Applied Mechanics II, Ramesh Khanal, Nepal Engineering College, 2016Dokument5 SeitenTutorial 1: Energy and Momentum Methods of Particle: Applied Mechanics II, Ramesh Khanal, Nepal Engineering College, 2016Romharsh OliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics 1 Chapter 5 Connected Particles ExamplesDokument19 SeitenMechanics 1 Chapter 5 Connected Particles ExamplesRocketNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 5-1Dokument1 SeiteTutorial 5-1Zahida ParnisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics (Kinetics)Dokument2 SeitenDynamics (Kinetics)HeliosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 8 PDFDokument16 SeitenTutorial 8 PDFBharat SaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruction: Answer The Following Questions by Groups of 3, On Long Bond PaperDokument2 SeitenInstruction: Answer The Following Questions by Groups of 3, On Long Bond PaperDember PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rectangular CoordinatesDokument9 SeitenRectangular CoordinatesJhon Albert RobledoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap2 Q USTH Exercise B1 QuestionOnlyDokument7 SeitenChap2 Q USTH Exercise B1 QuestionOnlyTrần Hoàng Việt100% (1)
- TD statics particle and rigid bodyDokument5 SeitenTD statics particle and rigid bodyUng ChannoutdomNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEC107 Tutorial Sheet 6 Problems on Forces, Friction, Work, Energy and Moment of InertiaDokument2 SeitenMEC107 Tutorial Sheet 6 Problems on Forces, Friction, Work, Energy and Moment of Inertiasiddharth yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opción Múltiple: Ecuación de Movimiento Fuerza y AceleraciónDokument11 SeitenOpción Múltiple: Ecuación de Movimiento Fuerza y AceleraciónDiego Naspud UrgilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flip Problem SetDokument4 SeitenFlip Problem SetNikhole JaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- USTH B1 Exercise Part3 QuestionDokument7 SeitenUSTH B1 Exercise Part3 Questionbình minh trầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 17Dokument7 SeitenCH 17Amer JumahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planar Kinetics of Rigid Body Work, Energy, Impulse & Momentum TutorialDokument6 SeitenPlanar Kinetics of Rigid Body Work, Energy, Impulse & Momentum TutorialChin Tiong LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics problems spring force motionDokument3 SeitenDynamics problems spring force motionSaba RasouliNoch keine Bewertungen
- EM Assignment 19Dokument2 SeitenEM Assignment 19Rajat PullinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAK 217 2. ÖdevDokument2 SeitenMAK 217 2. ÖdevBünyamin TatarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial W12 Force & AccelerationDokument3 SeitenTutorial W12 Force & AccelerationSek Chin JiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetics of Particles Tutorial 2 ProblemsDokument4 SeitenKinetics of Particles Tutorial 2 ProblemsJackson TeohNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP 9 Take HomeDokument2 SeitenCP 9 Take HomeTidal SurgesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Engineering Dynamics ReviewDokument2 SeitenStructural Engineering Dynamics ReviewVincent NavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Danymics - Homeworks - Chapter 3 Kinetics of Particles - Energy and Momentum MethodsDokument3 SeitenDanymics - Homeworks - Chapter 3 Kinetics of Particles - Energy and Momentum MethodsRed DemonsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE222 Problem Set 2Dokument12 SeitenCE222 Problem Set 2Mehmet ArasNoch keine Bewertungen
- LOM-05 - (Cbse) LevelDokument3 SeitenLOM-05 - (Cbse) LevelRaju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Mechanics IIDokument4 SeitenApplied Mechanics IIsushilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Mechanics Practice ProblemsDokument6 SeitenApplied Mechanics Practice ProblemsVikrant SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Unit DynamicsDokument5 Seiten2 Unit DynamicsmanojNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screenshot 2024-01-23 at 18.20.55Dokument2 SeitenScreenshot 2024-01-23 at 18.20.55wfffs7bcr4Noch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument7 SeitenUntitledObiedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics 2 - HandoutsDokument7 SeitenDynamics 2 - HandoutsRomeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- WS - 6 DT PreparationDokument4 SeitenWS - 6 DT PreparationNathanael Anthony Haposan PasaribuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Manuscript (Breadnut Peel) - EditedDokument57 SeitenFinal Manuscript (Breadnut Peel) - EditedBenedick Jayson P. MartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Oils ChemistryDokument27 SeitenEssential Oils ChemistryTaleem CityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food Chemistry: Prof. DR - Fahim ShaltoutDokument29 SeitenFood Chemistry: Prof. DR - Fahim ShaltoutBenedick Jayson P. MartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Related Literature and StudiesDokument2 SeitenReview of Related Literature and StudiesBenedick Jayson P. Marti67% (3)
- Chapter 3 FinalDokument4 SeitenChapter 3 FinalBenedick Jayson P. MartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CheM 004 Assign 1Dokument2 SeitenCheM 004 Assign 1Benedick Jayson P. MartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apa Style Sample PaperDokument12 SeitenApa Style Sample Paperjoerunner407Noch keine Bewertungen
- IE 002-Reflection Paper Format - MacsDokument3 SeitenIE 002-Reflection Paper Format - MacsBenedick Jayson P. MartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Conceptual FrameworkDokument1 SeiteI. Conceptual FrameworkBenedick Jayson P. MartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Exam in Advanced MathDokument3 SeitenMidterm Exam in Advanced MathBenedick Jayson P. MartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sales, Abipiel Regina I. Bsche Environmental Engineering ES21FB2Dokument41 SeitenSales, Abipiel Regina I. Bsche Environmental Engineering ES21FB2Benedick Jayson P. MartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice Questions in Engineering Mathematics by Venancio I. Besavilla, Jr. Vol1Dokument122 SeitenMultiple Choice Questions in Engineering Mathematics by Venancio I. Besavilla, Jr. Vol1Lugabaluga100% (1)
- Nutrient Cycle LPCPDokument8 SeitenNutrient Cycle LPCPBenedick Jayson P. MartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EarthquakeDokument25 SeitenEarthquakeBenedick Jayson P. MartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW#5 - #3 Sol Real2Dokument7 SeitenHW#5 - #3 Sol Real2derping123456Noch keine Bewertungen
- HW#5 - #3 Sol Real2Dokument7 SeitenHW#5 - #3 Sol Real2derping123456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ReportDokument7 SeitenLab ReportBenedick Jayson P. MartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics WorksheetDokument6 SeitenKinematics WorksheetDIPAKSHINoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect2 - 2020 SEM2 1920Dokument46 SeitenLect2 - 2020 SEM2 1920Praven KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Definitions and ExplanationsDokument22 SeitenPhysics Definitions and ExplanationsOwen ZhaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improving productivity through motion economy principlesDokument38 SeitenImproving productivity through motion economy principlesMariver LlorenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Jee Advanced: Total Marks: 155 Max. Time: 168 MinDokument11 SeitenPhysics Jee Advanced: Total Marks: 155 Max. Time: 168 MinVanshaj GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gyroscope - Gyroscopic Effects On The Movement Of: Airplanes and Ships - Gyroscope StabilizationDokument25 SeitenGyroscope - Gyroscopic Effects On The Movement Of: Airplanes and Ships - Gyroscope StabilizationAbdur Rahman100% (1)
- Pennies Density LabDokument6 SeitenPennies Density LabHope Shelby RangelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sat Physics NotesDokument9 SeitenSat Physics NotesMartin CrnickiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 PDFDokument31 Seiten1 PDFhod meNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 101 Chapter 3Dokument29 SeitenPhysics 101 Chapter 3Andrew GoolsbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics for Engineers Course SyllabusDokument5 SeitenPhysics for Engineers Course SyllabusAlbert Patrick DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me Sci 8 q1 0201 SGDokument20 SeitenMe Sci 8 q1 0201 SGZyro Jay MonteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science8 q1 Mod1 Forces FINAL08052021Dokument23 SeitenScience8 q1 Mod1 Forces FINAL08052021Elyzza Wye AlbaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 3 PDFDokument2 SeitenPhysics 3 PDFNoor Ul Hudda MemonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8Dokument44 SeitenChapter 8Mohan ManickamNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Forces Are With Us: Name - ClassDokument4 SeitenThe Forces Are With Us: Name - ClassSapphire BlueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Concepts in Relativity and Early Quantum Theory (Resnick Halliday)Dokument353 SeitenBasic Concepts in Relativity and Early Quantum Theory (Resnick Halliday)Alex Costa100% (4)
- Electromagnetic InductionDokument8 SeitenElectromagnetic InductionDeen ZakariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work - Energy - and PowerDokument19 SeitenWork - Energy - and PowerNaimah GuroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jep Specific GravityDokument2 SeitenJep Specific Gravityjep castanedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2work and Energy v3Dokument62 SeitenModule 2work and Energy v3Dyas FerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Density and Buoyancy - Student WorksheetDokument9 SeitenDensity and Buoyancy - Student WorksheetLitzzy EspinozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIT Physics Lab Manual (Combined)Dokument34 SeitenIIT Physics Lab Manual (Combined)Victoria Aschebrook-KealiherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vertical water jet suspends plate; jet force on stationary plateDokument14 SeitenVertical water jet suspends plate; jet force on stationary plateMd RoknuzzamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TechTips SectionDokument7 SeitenTechTips SectionMuhammad Rifqi AninditoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass Weight Volume Density Review - Sheet1Dokument4 SeitenMass Weight Volume Density Review - Sheet1jstock112Noch keine Bewertungen