Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Current Vs Static Electricity
Hochgeladen von
Naushaba Rangoonwala0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
20 Ansichten1 SeiteOriginaltitel
intro to electric current.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
20 Ansichten1 SeiteCurrent Vs Static Electricity
Hochgeladen von
Naushaba RangoonwalaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
Difference Between Current and Static Electricity
Current vs Static Electricity
Can you imagine a world without TVs, computers, cell phones, cars, and the light
bulb?
Electricity is an amazing thing. It is such a wide field of study, and many people
are still confused by it. Electricity has made a huge impact on our way of life. I
cant imagine a life without electricity. We have become dependent on its
applications that have made our lives enormously comfortable, enjoyable, and
livable.
Most of us just enjoy the benefits of electricity, but dont really understand the
science behind it, and the phenomena associated with it. For now, lets try to
grasp two phenomena in electricity Static Electricity and Current Electricity.
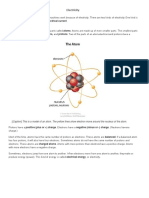
Technically, electricity is actually a phenomenon in itself, which involves the
displacement or movement of electrons.
When electricity is at rest, it is called static electricity. It refers to the electric
charges that build up on the surface of materials or substances. These so-called
static charges remain until they are grounded, or discharged.
Static electricity is generated by friction, or sudden contact for instance,
rubbing two materials against each other. Ordinarily, atoms are uncharged.
These are considered neutral substances, but they can lose or gain electrons
through friction.
The rubbing procedure can cause the atoms of particular substances to lose their
electrons. This loss of electrons will make the substance or material become
positively charged. The excess protons caused the substance have a positive
charge. Conversely, the substance that gains the electrons is said to be negatively
charged.
Certain atoms readily lose electrons, and it goes the same way with particular
atoms which have the tendency to accept them. When these two substances are
rubbed together, the potential of generating static electricity is great. Basically,
the phenomenon of static electricity is achieved when there is a separation of
positive and negative charges.
Current electricity, on the other hand, is a phenomenon of moving electrons in a
particular path, or direction, such as a stream of them flowing through
conducting materials. Current electricity can come from various sources. The
most commonly used source of current electricity is from batteries. These
batteries rely on the chemical reactions within them to produce electricity.
Current electricity, in huge amounts, is typically brought about by generators.
Power plants have many of these to produce enormous quantities of current
electricity. The phenomenon is usually controlled, and requires a flow of
electrons along a path, which is fittingly called the electric current.
Summary:
1. Static electricity is caused by the build up of electrical charges on the surface of
objects, while current electricity is a phenomenon from the flow of electrons
along a conductor.
2. When objects are rubbed, a loss and/or gain of electrons occurs, which results
in the phenomenon of static electricity.
3. Current electricity is normally controlled, and it is the more used phenomenon
of electricity, in countless applications.
4. Static electricity is usually uncontrolled, and just happens sporadically.
5. Current electricity is generated by batteries and power plants.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Physics AssignmentDokument3 SeitenPhysics AssignmentHussein BoffuNoch keine Bewertungen
- GP ProjectDokument19 SeitenGP ProjectdhurgeshmalothNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Current PresentationDokument10 SeitenElectric Current PresentationMalik AyazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity: ElectromagnetismDokument18 SeitenElectricity: ElectromagnetismShajara Anglacer AnacanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sourav Physics ProjectsDokument16 SeitenSourav Physics ProjectsT VpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy: The Ability To Do Work: ElectricityDokument14 SeitenEnergy: The Ability To Do Work: ElectricityAbdulkhadarJilani ShaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1 Physics 2Dokument4 SeitenWeek 1 Physics 2Stephanie Gwynette Almirol LalasNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectricityDokument4 SeitenElectricityRusul MajidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report in Ia4Dokument22 SeitenReport in Ia4CORONADO, EULENE MAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksVon EverandPhysics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- By Areez Anwar Class: 8 Cambridge Subject: Science Mid-Year ExaminationsDokument14 SeitenBy Areez Anwar Class: 8 Cambridge Subject: Science Mid-Year ExaminationsAreez SaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETM 10 Basic Electricity: Engr. Romano A. Pimentel InstructorDokument17 SeitenETM 10 Basic Electricity: Engr. Romano A. Pimentel InstructorWynne LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectricityDokument1 SeiteElectricityMarcus CambridgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electricity NotesDokument2 SeitenBasic Electricity Noteszaidkadiri9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Effect of Electric... Class 8thDokument7 SeitenChemical Effect of Electric... Class 8thAyush Soni 7:- परिश्रम 3678Noch keine Bewertungen
- Liceo de Apodaca: Name of The Student: Sofia Fernanda Cuevas MendezDokument9 SeitenLiceo de Apodaca: Name of The Student: Sofia Fernanda Cuevas MendezSofiaa FernandaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rina B. InggrisDokument9 SeitenRina B. InggrisRidwan Alfian NoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Our Ancestors RDokument16 SeitenOur Ancestors RAachal SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Current The Flow of ChargeDokument6 SeitenElectric Current The Flow of ChargePournima AmbikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Utilities (Electrical)Dokument18 SeitenBuilding Utilities (Electrical)damsaishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Static ElectricityDokument10 SeitenStatic ElectricityJohn MillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Static Electiricity Vs Human Harnessed ElectricityDokument5 SeitenStatic Electiricity Vs Human Harnessed ElectricityRyan RosenquistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Well Come To Session On Basic Electrical Theory: Prolific Systems and Technologies PVT LTDDokument103 SeitenWell Come To Session On Basic Electrical Theory: Prolific Systems and Technologies PVT LTDsiddharth1996Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acitivity 2Dokument1 SeiteAcitivity 2Precious PontaweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity Is The Set of Physical Phenomena Associated With The Presence andDokument2 SeitenElectricity Is The Set of Physical Phenomena Associated With The Presence andMathew EspantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contact-Induced Charge SeparationDokument2 SeitenContact-Induced Charge SeparationMohanie D SudamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity BasicsDokument8 SeitenElectricity BasicsMauritzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric ChargesDokument31 SeitenElectric ChargesJeorge QuiboyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phys 3Dokument5 SeitenPhys 3Wyndle PachecaNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Elektron" This Is The Origin of The Terms Electricity andDokument7 Seiten"Elektron" This Is The Origin of The Terms Electricity andstudy for KNOWLEDGENoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 Nature and Concept of Electricity and Electronics Part 1Dokument33 Seiten3.1 Nature and Concept of Electricity and Electronics Part 1ANGELYN TI-ADNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Currenttopic 1Dokument5 SeitenElectric Currenttopic 1julie ann amihanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity: Complete The FollowingDokument2 SeitenElectricity: Complete The FollowingDanissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guia 1 Ingles AngeloDokument13 SeitenGuia 1 Ingles AngeloAlejandroDuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity From The Power Station To The HomeDokument52 SeitenElectricity From The Power Station To The HomeShantanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Reviewer Grade TenDokument3 SeitenScience Reviewer Grade Tenanon_523095838Noch keine Bewertungen
- Task 1Dokument5 SeitenTask 1Marfe Salamat ManilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jose Gerardo Farias Electricity Tuesday December 18 2012 France Myp 2Dokument8 SeitenJose Gerardo Farias Electricity Tuesday December 18 2012 France Myp 2Gerardo FariasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suplemen of Static ElectricityDokument10 SeitenSuplemen of Static ElectricityIndra CesaryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Electricity and MagnetismDokument1 SeiteLecture Electricity and MagnetismSheesh AbleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity: Prepared by Soumit Dey, Arinab Dev Roy Anubhav Mazumdar, Rishov Khan Sourav Dutta, Subhankar DasDokument41 SeitenElectricity: Prepared by Soumit Dey, Arinab Dev Roy Anubhav Mazumdar, Rishov Khan Sourav Dutta, Subhankar DasArup DeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity & Magnetism - A1 - Masing - RichelleDokument2 SeitenElectricity & Magnetism - A1 - Masing - RichelleRichelle MasingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 11 Elctrical Hazards ControlDokument42 SeitenUnit 11 Elctrical Hazards Controlbabusureshdev5639Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carl John B. Pacana Assignment No.11 Electrostatics Electrostatics, The Study of Electromagnetic Phenomena That Occur When There Are NoDokument9 SeitenCarl John B. Pacana Assignment No.11 Electrostatics Electrostatics, The Study of Electromagnetic Phenomena That Occur When There Are NoAllen PacanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectricDokument318 SeitenElectricdenokNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELECTRICITYDokument6 SeitenELECTRICITYsamuel rojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Consideration: Case-Studies On Electrocution Incidences in Nigeria - Exploring Technical SolutionsDokument40 SeitenGeneral Consideration: Case-Studies On Electrocution Incidences in Nigeria - Exploring Technical SolutionsBhausaheb Patil100% (1)
- TVE 1 (Basic ElectricityElectronics) LessonsDokument14 SeitenTVE 1 (Basic ElectricityElectronics) LessonssorcererpcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elementary Electrical Engineering MODULES in WORDSDokument7 SeitenElementary Electrical Engineering MODULES in WORDSRubdubRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction in Electricity and MagnetismDokument1 SeiteIntroduction in Electricity and Magnetismjoe_boyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itVon EverandELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectricityDokument30 SeitenElectricityJopie ArandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics-Static and Current ElectricityDokument10 SeitenPhysics-Static and Current ElectricityCodeen WhiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- BasicDokument20 SeitenBasicG Sandeep KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction ElectricityDokument41 SeitenIntroduction ElectricityAloiza FababaerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Larry Ferlazzo - GamesDokument6 SeitenLarry Ferlazzo - GamesNaushaba RangoonwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Theory Timeline ActivityDokument4 SeitenCell Theory Timeline ActivityJojebelle Kate Iyog-cabanletNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuestionBank of Light PDFDokument17 SeitenQuestionBank of Light PDFNaushaba Rangoonwala100% (1)
- Word Puzzles PDFDokument5 SeitenWord Puzzles PDFNaushaba RangoonwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Sheet For Class ViiDokument4 SeitenRevision Sheet For Class ViiNaushaba RangoonwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teachers Lesson Plan - Sorting Materials Into GroupsDokument20 SeitenTeachers Lesson Plan - Sorting Materials Into GroupsNaushaba Rangoonwala67% (3)
- BED 1st Year English 2012Dokument4 SeitenBED 1st Year English 2012sonal236Noch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank of HeatDokument13 SeitenQuestion Bank of HeatNaushaba Rangoonwala100% (1)
- BBC Teachers Ks2 Science Worksheet ForcesDokument1 SeiteBBC Teachers Ks2 Science Worksheet ForcesNaushaba RangoonwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ready Set Potty v2Dokument9 SeitenReady Set Potty v2Naushaba RangoonwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion Graphs: Graphs Help Make Motion Easier To Picture, and Therefore UnderstandDokument11 SeitenMotion Graphs: Graphs Help Make Motion Easier To Picture, and Therefore Understandpooja24aggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top and Tunic PurseDokument4 SeitenTop and Tunic PurseNaushaba RangoonwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Vs Static ElectricityDokument1 SeiteCurrent Vs Static ElectricityNaushaba RangoonwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elements Compounds MixturesDokument34 SeitenElements Compounds Mixturesapi-245307849Noch keine Bewertungen
- LifeSkills For Classroom ManagementDokument5 SeitenLifeSkills For Classroom ManagementNaushaba RangoonwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem ArticlesDokument4 SeitenChem ArticlesNaushaba RangoonwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surface ChemistryDokument17 SeitenSurface ChemistryNaushaba RangoonwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE CBSE Class 9 Science Question Paper SA II Set 1 2014Dokument14 SeitenCBSE CBSE Class 9 Science Question Paper SA II Set 1 2014Naushaba RangoonwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adopt An Element Project GuidelinesDokument4 SeitenAdopt An Element Project GuidelinesChip ChaseNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Science Diversity in Living Organisms Test 03 PDFDokument1 Seite9 Science Diversity in Living Organisms Test 03 PDFNaushaba RangoonwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Tiny PineconesDokument2 Seiten1 Tiny PineconesNaushaba RangoonwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artskills Poster HandbookDokument99 SeitenArtskills Poster HandbookioanamitrofNoch keine Bewertungen
- AcetoneDokument9 SeitenAcetoneNaushaba RangoonwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Large Seashell1Dokument3 Seiten1 Large Seashell1Naushaba RangoonwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- VSEPR Shapes WorksheetDokument1 SeiteVSEPR Shapes WorksheetNaushaba RangoonwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan16Dokument13 SeitenLesson Plan16Kathir MuruganNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 DolphinDokument4 Seiten1 DolphinNaushaba Rangoonwala100% (2)
- AffirmationsDokument1 SeiteAffirmationsNaushaba RangoonwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ic-F310 f320 f410 f420Dokument24 SeitenIc-F310 f320 f410 f420zikamaxiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Cylinder DeactivationDokument7 SeitenReport On Cylinder Deactivationsanchit333Noch keine Bewertungen
- User'S Manual: MODEL: MMA160/200Dokument9 SeitenUser'S Manual: MODEL: MMA160/200Vlaovic GoranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ip SelctionDokument22 SeitenIp SelctionHATEM68Noch keine Bewertungen
- MXR Evh5150 Overdrive Manual 479917Dokument2 SeitenMXR Evh5150 Overdrive Manual 479917Μαριτίνα ΑλεξίουNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Note On Solar Panel InstallationDokument3 SeitenComplete Note On Solar Panel InstallationtowfiqeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACS880 Long Motor Cables Product Notice6Dokument5 SeitenACS880 Long Motor Cables Product Notice6Alejandro Zanella100% (1)
- DIY FM Radio TransmitterDokument23 SeitenDIY FM Radio TransmitterJames Bryan Eugenio Abaño0% (1)
- MSE - ChapterDokument42 SeitenMSE - ChapterFaisal MumtazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Security Door Controls SDC 413NDokument4 SeitenSecurity Door Controls SDC 413NJMAC SupplyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Disk Memory Storage DevicesDokument74 SeitenOptical Disk Memory Storage DevicesM.WASEEM YOUSAF100% (2)
- DEPT. of Computer Science Engineering SRM IST, Kattankulathur - 603 203Dokument5 SeitenDEPT. of Computer Science Engineering SRM IST, Kattankulathur - 603 203nielabh GireyNoch keine Bewertungen
- KiSS DVD PLAYER Manual DP 508 3966 PDFDokument1 SeiteKiSS DVD PLAYER Manual DP 508 3966 PDFGurkan12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Antena 12 26 AP861014Dokument4 SeitenAntena 12 26 AP861014FusilInsurgenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inertial Navigation IntroductionDokument10 SeitenInertial Navigation Introductionedwin_killedlaw100% (1)
- Uquran How ToDokument4 SeitenUquran How Togw1921Noch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo MotorpactDokument50 SeitenCatalogo MotorpactAlexander Moisés Saldaña AcevedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACES Journal - Infinite Periodic Boundary Conditions in FEKODokument8 SeitenACES Journal - Infinite Periodic Boundary Conditions in FEKOthe_jaberwockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cnt-Fet A ReviewDokument5 SeitenCnt-Fet A ReviewEr Ashish BahetiNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Syed Ubed - For UpdationDokument1 SeiteTo Syed Ubed - For Updationshrikanth5singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plano Antena Yagi Frecuencia 850 MHZDokument2 SeitenPlano Antena Yagi Frecuencia 850 MHZageroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 445 - Guide - For - Transformer - Maintenance CIGRE A2 - 34 PDFDokument123 Seiten445 - Guide - For - Transformer - Maintenance CIGRE A2 - 34 PDFJohnDoe100% (10)
- Samsung 633nw Ls16cmy SCH PDFDokument10 SeitenSamsung 633nw Ls16cmy SCH PDFeugenio bravataNoch keine Bewertungen
- IES 2004 EE Conventional Paper01Dokument4 SeitenIES 2004 EE Conventional Paper01Shubham KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bateria Leoch 100ahDokument2 SeitenBateria Leoch 100ahAlba Car MarNoch keine Bewertungen
- GDM 500-650 Juction BoxDokument2 SeitenGDM 500-650 Juction BoxPatron MixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waterproof and Cleanroom Luminaires PDFDokument13 SeitenWaterproof and Cleanroom Luminaires PDFdwi wahyu sugiartoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Easergy Range - VD23Dokument4 SeitenEasergy Range - VD23crysty24Noch keine Bewertungen
- TIL306, TIL307 Numeric Displays With LogicDokument9 SeitenTIL306, TIL307 Numeric Displays With LogicAndy ScriptorNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS Samsung Slim Duct PDFDokument2 SeitenMS Samsung Slim Duct PDFMacSparesNoch keine Bewertungen