Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
RI Table Insulation Testing
Hochgeladen von
Danail DachevOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
RI Table Insulation Testing
Hochgeladen von
Danail DachevCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Guide to modern insulation testing Typical problems during measurements
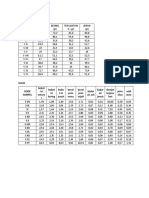
Table 11: Temperature correction factors for insulation resistance
Rotating
cables
equipment
heat resist perform. GR-
natural
oil-filled transformers
performance natural
impregnated paper
varnished cambric
heat resist natural
temperature ( C)
resist
code natural
code GR-S
class A
class B
ozone
GR-S
S
0 0,21 0,4 0,25 0,25 0,12 0,47 0,42 0,22 0,14 0,1 0,28
5 0,31 0,5 0,36 0,4 0,23 0,6 0,56 0,37 0,26 0,2 0,43
10 0,45 0,63 0,5 0,61 0,46 0,76 0,73 0,58 0,49 0,43 0,64
15, 0,71 0,81 0,74 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
6
20 1 1 1 1,47 1,83 1,24 1,28 1,53 1,75 1,94 1,43
25 1,48 1,25 1,4 2,27 3,67 1,58 1,68 2,48 3,29 4,08 2,17
30 2,2 1,58 1,98 3,52 7,32 2 2,24 4,03 6,20 8,62 3,2
35 3,24 2 2,8 5,45 14,6 2,55 2,93 6,53 11,65 18,2 4,77
40 4,8 2,5 3,95 8,45 29,2 3,26 3,85 10,7 25 38,5 7,15
45 7,1 3,15 5,6 13,1 54 4,15 5,08 17,1 41,4 81 10,7
50 10,4 3,98 7,85 20 116 5,29 6,72 27,8 78 170 16
5 5
55 15,5 5 11,2 6,72 8,83 45 345 24
60 22,8 6,3 15,8 8,58 11,6 73 775 36
5 2
65 34 7,9 22,4 15,4 118
0
70 50 10 31,7 20,3 193
5 0
75 74 12,6 44,7 26,6 313
Example:
A motor with class A insulation has a winding temperature of 40 C. The result of
measurement at this temperature is 2 M.
The value of resistance corrected to 20 C:
R20 = R40 k40 = 2 M 4,8 = 9,6 M Eq. 13
Hint
For a very rough estimation the correction can be made by the following thumb rule:
For every 10 C increase in temperature halve the resistance; or for every 10 C
decrease double the resistance.
25
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Acara 2 Sedimen BudiDokument22 SeitenAcara 2 Sedimen BudiAlfon HertantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Round 1 - Question Paper - Class III: SampleDokument1 SeiteRound 1 - Question Paper - Class III: Sample28 MD Arham AdeelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nace Paper 477-Servicos Sist en AñosDokument12 SeitenNace Paper 477-Servicos Sist en AñosmartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- ERGA04-08DVA Capheat 3D112789D ENDokument1 SeiteERGA04-08DVA Capheat 3D112789D ENPeter TitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weekly Free Live Mocksongoing Live Mockscgl 19 Tier 2 Quant Ait 28 2059942solution 1&session 18060094Dokument1 SeiteWeekly Free Live Mocksongoing Live Mockscgl 19 Tier 2 Quant Ait 28 2059942solution 1&session 18060094Nitesh kumar ShrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uy - Weekly Report 39Dokument51 SeitenUy - Weekly Report 39Santiago MangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alarm List Gas Oil SystemDokument13 SeitenAlarm List Gas Oil SystemprojectManagement exirsanatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Round 1 - Question Paper - Class III: SampleDokument1 SeiteRound 1 - Question Paper - Class III: SampleAnuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elbows According To DIN 2605-1 Steel Grades St37.0, St35.8, St45.8, S235, P235Dokument4 SeitenElbows According To DIN 2605-1 Steel Grades St37.0, St35.8, St45.8, S235, P235Purushoth ChinnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22-05-2021 SR - Super60 (In Coming) Jee-Main WTM-31 Key & Sol'sDokument12 Seiten22-05-2021 SR - Super60 (In Coming) Jee-Main WTM-31 Key & Sol'sRohan k sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autofilettanti - Self TappingDokument2 SeitenAutofilettanti - Self TappingFranco FranchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Booklet Series - 'A'Dokument4 SeitenQuestion Booklet Series - 'A'sgpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jee-Main - WTM-13 - Key & Sol'sDokument8 SeitenJee-Main - WTM-13 - Key & Sol'stheju13052006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Threads StandardDokument5 SeitenThreads StandardAhmed IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 001 Ratios ArquitecturaDokument1 Seite001 Ratios Arquitecturaclovis.contreras.pNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: SR - Super60Dokument14 SeitenSri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: SR - Super60roshni nekkantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- JASELL TAM T. DACUP Educ 201 Activity No. 2Dokument4 SeitenJASELL TAM T. DACUP Educ 201 Activity No. 2DinahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proctor TestDokument1 SeiteProctor TestGlobal EngineeringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Oil Storage Tank Dada SheetDokument3 SeitenGas Oil Storage Tank Dada SheetprojectManagement exirsanatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Major Test - V, - 24.03.2020Dokument4 SeitenSolution Major Test - V, - 24.03.2020DrNaresh SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal 1: Metode MomentDokument9 SeitenSoal 1: Metode MomentMuh FaisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- DATOS CONTINUA - MergedDokument8 SeitenDATOS CONTINUA - MergedJaime Alberto Poveda AriasNoch keine Bewertungen
- PAS-JBG-400-D-002 Pipe Stress Report For Line Pipe Fuel Gas System Supply To GTCP 2020B Rev DDokument7 SeitenPAS-JBG-400-D-002 Pipe Stress Report For Line Pipe Fuel Gas System Supply To GTCP 2020B Rev DElias EliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kapasitas Daya Dukung Tanah Terzaghi: PondasiDokument5 SeitenKapasitas Daya Dukung Tanah Terzaghi: PondasiRaihan Naxx HotudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 2Dokument1 SeiteClass 2priyanka gargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal 1 AdiDokument1 SeiteSoal 1 AdiRizal rindawunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Radiators Conversion Tables and ConnectionsDokument2 SeitenDesign Radiators Conversion Tables and ConnectionsSean WalshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Al Conductor Stranded 6Dokument4 SeitenAl Conductor Stranded 6Ankit AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module IIDokument47 SeitenModule IIt7kv6wmvkcNoch keine Bewertungen
- TIME SCHEDULE - PEK - RELAYOUT - RK - SAI - PLAZA BNI - INTERIOR & MEP WORKS - 16th - REV - 25.10.2022Dokument2 SeitenTIME SCHEDULE - PEK - RELAYOUT - RK - SAI - PLAZA BNI - INTERIOR & MEP WORKS - 16th - REV - 25.10.2022SatyagrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnalysisDokument3 SeitenAnalysisvishnukumarsharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabel Comparativ Izolatii TermiceDokument1 SeiteTabel Comparativ Izolatii TermiceDaniel StanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sieves: Rekord / Ondula Tria / Serpenti Harp ScreensDokument12 SeitenSieves: Rekord / Ondula Tria / Serpenti Harp ScreensArnab MannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fabrication & Erection ProcedureDokument17 SeitenFabrication & Erection ProcedureAndreas Schlager100% (1)
- 07-02-16 - Sr. IIT-IZ-CO-SPARK - Ph-I - Jee-Main - GTM-4 - Key & Sol'sDokument13 Seiten07-02-16 - Sr. IIT-IZ-CO-SPARK - Ph-I - Jee-Main - GTM-4 - Key & Sol'sUppu EshwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Control and Safety System (ICSS) TGS Bill of MaterialDokument9 SeitenIntegrated Control and Safety System (ICSS) TGS Bill of MaterialFatholla SalehiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: JEE-MAIN (WTM-1)Dokument1 SeiteSri Chaitanya IIT Academy., India.: JEE-MAIN (WTM-1)Kumkum KumbarahalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ilovepdf MergedDokument51 SeitenIlovepdf MergedHema BNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABG InterpretationDokument4 SeitenABG InterpretationjessamineNoch keine Bewertungen
- 60Hz ZP32K3E-TFD R410A: Evaporating Temperature °CDokument2 Seiten60Hz ZP32K3E-TFD R410A: Evaporating Temperature °CJoão Felipe Chueh BejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KPSC Sda Key AnswerDokument8 SeitenKPSC Sda Key AnswerMahe GowdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figure 1. (Left) Geometry For Vertical Arrangement (Right) Geometry For Horizontal ArrangementDokument13 SeitenFigure 1. (Left) Geometry For Vertical Arrangement (Right) Geometry For Horizontal ArrangementLuis PerdomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Coalescer SizingDokument6 SeitenGas Coalescer SizingAde IskandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key - Solution - Haryana - Ntse Stage 1 2020-21 - MatDokument13 SeitenAnswer Key - Solution - Haryana - Ntse Stage 1 2020-21 - MatArchana YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16..01.24 - SR - STAR CO-SC (MODEL-A, B&C) - Jee - Main - GTM-18 (N) - KEY&SOLDokument1 Seite16..01.24 - SR - STAR CO-SC (MODEL-A, B&C) - Jee - Main - GTM-18 (N) - KEY&SOLtiwariakhilesh21361Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mean Soil Resistance Ohm Mean Soil Resistance Oh-MDokument7 SeitenMean Soil Resistance Ohm Mean Soil Resistance Oh-MRahul SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- L-Js1 - Features L-Ol - FeaturesDokument4 SeitenL-Js1 - Features L-Ol - FeaturesEdderNoch keine Bewertungen
- 358-3130 (800) 638-1830 Faxes: (410) 358-3142 (800) 872-9329 Technical Information and DataDokument1 Seite358-3130 (800) 638-1830 Faxes: (410) 358-3142 (800) 872-9329 Technical Information and DataRenny DevassyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analisis Hasil Mid Semester 1 PJOK Kls VDokument1 SeiteAnalisis Hasil Mid Semester 1 PJOK Kls Vsdn017 smduluNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnomalyDokument2 SeitenAnomalyA AzlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table According To DIN 7985Dokument4 SeitenTable According To DIN 7985SidharthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabla Conversion DB V DBFSDokument1 SeiteTabla Conversion DB V DBFSHector CardosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A (Mean)Dokument3 SeitenA (Mean)meena201122Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Paper - I Junior Engineer (Civil & Mechanical) - 2017Dokument4 SeitenGeneral Paper - I Junior Engineer (Civil & Mechanical) - 2017Hari PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Consolidation Test-Halaman-1Dokument1 SeiteData Consolidation Test-Halaman-1Muhammad Tiasy IdrusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Booklet Series - 'C'Dokument1 SeiteQuestion Booklet Series - 'C'Sushanth PoojaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon Steel Pipe Price List IndonesiaDokument8 SeitenCarbon Steel Pipe Price List Indonesiaiandegs2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- Evidencias 5152890049 7986624 RemovedDokument39 SeitenEvidencias 5152890049 7986624 RemovedJoshua emanuel GallegosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math, Grade 1: Strengthening Basic Skills with Jokes, Comics, and RiddlesVon EverandMath, Grade 1: Strengthening Basic Skills with Jokes, Comics, and RiddlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rev02 Transformer Modelling Guide1Dokument304 SeitenRev02 Transformer Modelling Guide1Danail DachevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement Comparisons in The Cipm MraDokument29 SeitenMeasurement Comparisons in The Cipm MraDanail DachevNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISH99 CommonDokument5 SeitenISH99 CommonDanail DachevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Automatic Recovery Voltage Meter For Diagnosis of Oil Paper InsulationDokument4 SeitenAdvanced Automatic Recovery Voltage Meter For Diagnosis of Oil Paper InsulationDanail DachevNoch keine Bewertungen
- TD 2014 P OmicronDokument36 SeitenTD 2014 P OmicronDanail DachevNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1Dokument106 Seiten1Danail DachevNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRODokument4 SeitenCROboopathy566Noch keine Bewertungen
- Indicative Solutions: Institute of Actuaries of IndiaDokument9 SeitenIndicative Solutions: Institute of Actuaries of IndiaeuticusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge International A Level: Mathematics 9709/31 May/June 2020Dokument13 SeitenCambridge International A Level: Mathematics 9709/31 May/June 2020Mubashir AsifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1 - Getting Started On EnergyPlus - 20120618 - 0Dokument28 SeitenTutorial 1 - Getting Started On EnergyPlus - 20120618 - 0PaulaErikaMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Tos Ce-4-IDokument14 SeitenTos Ce-4-Ilucifer.the.morning.star.4141Noch keine Bewertungen
- Footings PDFDokument80 SeitenFootings PDFHamza RasheedNoch keine Bewertungen
- PW and Wfi Storage and Distribution Systems Design and OperationDokument33 SeitenPW and Wfi Storage and Distribution Systems Design and Operationmanojdhamne5802Noch keine Bewertungen
- ATA 21. Air Conditioning As-05-02 (PLAN-09)Dokument81 SeitenATA 21. Air Conditioning As-05-02 (PLAN-09)faisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emission LabDokument2 SeitenEmission LabFederico PiñeyroNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Source Book in APLDokument146 SeitenA Source Book in APLhungbkpro90100% (1)
- Catalog Copeland KCLDokument40 SeitenCatalog Copeland KCLIsidro MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6362Dokument19 Seiten6362Amit VijayvargiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- L298 Dual H-Bridge Motor Driver DatasheetDokument3 SeitenL298 Dual H-Bridge Motor Driver DatasheetSuresh LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review On Thermomechanical Processing of Advanced High Strength SteelsDokument130 SeitenReview On Thermomechanical Processing of Advanced High Strength SteelsharishNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0654 s04 MsDokument29 Seiten0654 s04 MsJeneshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 3 Physics MagnetsDokument6 SeitenForm 3 Physics MagnetsChibale Mchere BandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elevator Traction Machine 20131018 Elevator Traction MachineDokument8 SeitenElevator Traction Machine 20131018 Elevator Traction MachineTh NattapongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cs Ba-Bsc 3rd Sem 2016Dokument4 SeitenCs Ba-Bsc 3rd Sem 2016So RvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scia Engineer 2014 - Advanced Concept Training - FEM PDFDokument102 SeitenScia Engineer 2014 - Advanced Concept Training - FEM PDFericfgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Iv. Analysis of The Structure at The Ultimate Limit StateDokument17 SeitenChapter Iv. Analysis of The Structure at The Ultimate Limit StateisaacssebulibaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stroke Width Chart For Fountain Pens (Version 2.0.3, Revised February 5, 2010)Dokument1 SeiteStroke Width Chart For Fountain Pens (Version 2.0.3, Revised February 5, 2010)kishore13Noch keine Bewertungen
- PrefaceDokument45 SeitenPrefaceaddy_callsoutNoch keine Bewertungen
- MiniPUR Melter SystemDokument2 SeitenMiniPUR Melter SystemNordson Adhesive Dispensing SystemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design properties of HEA profiles for S235 steel class (γ = 1.00, units = mm)Dokument18 SeitenDesign properties of HEA profiles for S235 steel class (γ = 1.00, units = mm)scarto08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spheerol LMMDokument2 SeitenSpheerol LMMArnaldo BenitezNoch keine Bewertungen
- E.C.G Machine: by Er.U.Karthik Premkumar, H.O.D - Biomedical Engineering DepartmentDokument36 SeitenE.C.G Machine: by Er.U.Karthik Premkumar, H.O.D - Biomedical Engineering DepartmentAch ThungNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDMS Commands 1Dokument25 SeitenPDMS Commands 1Perdana KusumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nucl - Phys.B v.646Dokument538 SeitenNucl - Phys.B v.646buddy72Noch keine Bewertungen