Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Types of Insulators: Pin Type Insulator
Hochgeladen von
Gary M TrajanoOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Types of Insulators: Pin Type Insulator
Hochgeladen von
Gary M TrajanoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
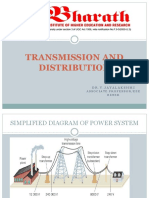
An overhead power line is a structure used in electric power transmission and distribution to
transmit electrical energy along large distances. It consists of one or more conductors(commonly
multiples of three) suspended by towers or poles. Since most of the insulation is provided by air,
overhead power lines are generally the lowest-cost method of power transmission for large
quantities of electric energy.
Types of insulators[edit]
These are the common classes of insulator:[citation needed]
Pin type insulator - As the name suggests, the pin type insulator is mounted on a pin on the
cross-arm on the pole. There is a groove on the upper end of the insulator. The conductor
passes through this groove and is tied to the insulator with annealed wire of the same material
as the conductor. Pin type insulators are used for transmission and distribution of
communications, and electric power at voltages up to 33 kV. Insulators made for operating
voltages between 33kV and 69kV tend to be very bulky and have become uneconomical in
recent years.
Post insulator - A type of insulator in the 1930s that is more compact than traditional pin-type
insulators and which has rapidly replaced many pin-type insulators on lines up to 69kV and in
some configurations, can be made for operation at up to 115kV.
Suspension insulator - For voltages greater than 33 kV, it is a usual practice to use suspension
type insulators, consisting of a number of glass or porcelain discs connected in series by metal
links in the form of a string. The conductor is suspended at the bottom end of this string while
the top end is secured to the cross-arm of the tower. The number of disc units used depends on
the voltage.
Strain insulator - A dead end or anchor pole or tower is used where a straight section of line
ends, or angles off in another direction. These poles must withstand the lateral (horizontal)
tension of the long straight section of wire. In order to support this lateral load, strain insulators
are used. For low voltage lines (less than 11 kV), shackle insulators are used as strain
insulators. However, for high voltage transmission lines, strings of cap-and-pin (suspension)
insulators are used, attached to the crossarm in a horizontal direction. When the tension load in
lines is exceedingly high, such as at long river spans, two or more strings are used in parallel.
Shackle insulator - In early days, the shackle insulators were used as strain insulators. But
nowaday, they are frequently used for low voltage distribution lines. Such insulators can be used
either in a horizontal position or in a vertical position. They can be directly fixed to the pole with a
bolt or to the cross arm.
Bushing - enables one or several conductors to pass through a partition such as a wall or a tank,
and insulates the conductors from it.[9]
Line post insulator
Station post insulator
Cut-out
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Types of Insulators: Pin Type InsulatorDokument11 SeitenTypes of Insulators: Pin Type InsulatorGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insulator Power TrueDokument11 SeitenInsulator Power TrueGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of InsulatorsDokument2 SeitenTypes of InsulatorsRasheed ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insulators: Eee. Department, B V C Engg CollegeDokument38 SeitenInsulators: Eee. Department, B V C Engg CollegeRahul OhriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation 130309031327 Phpapp02 PDFDokument38 SeitenNewmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation 130309031327 Phpapp02 PDFtaiptc4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Slide Share Auxilary Electrical Power EquipmentDokument38 SeitenSlide Share Auxilary Electrical Power EquipmentHamza AteeqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of InsulatorDokument10 SeitenTypes of InsulatorlegasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- XLineDokument38 SeitenXLineMuhammad BilalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overhead Power Line: StructuresDokument8 SeitenOverhead Power Line: Structuresarvind_3aprilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of OH InsulatoresDokument10 SeitenTypes of OH InsulatoresShahrukh SaleemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-6 Over Head Transmission LinesDokument35 SeitenChapter-6 Over Head Transmission LinesGidey GebrehiwotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insulators: Yoseph Mekonnen (PH.D.)Dokument30 SeitenInsulators: Yoseph Mekonnen (PH.D.)Kalab TenadegNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insulators and Circuit BreakersDokument29 SeitenInsulators and Circuit Breakersdilja aravindanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emeng 3131 Electrical Power Systems: Overhead Line InsulatorsDokument30 SeitenEmeng 3131 Electrical Power Systems: Overhead Line InsulatorsmichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Power Transmission 1Dokument5 SeitenElectrical Power Transmission 1FaisalSoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week10 - OH Line InsulatorsDokument37 SeitenWeek10 - OH Line InsulatorsRiccardo BurowsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6NDokument34 SeitenChapter 6NawrexNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEE 441 Transmission & Distribution of Electrical Power: Mechanical Design of Overhead LinesDokument22 SeitenEEE 441 Transmission & Distribution of Electrical Power: Mechanical Design of Overhead LinesAreyan HaqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overhead Power LineDokument13 SeitenOverhead Power LineVinay SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insulators & String EfficiencyDokument17 SeitenInsulators & String Efficiencyketan adhwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEE - BEE601 - TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION - Dr. V. JayalakshmiDokument21 SeitenEEE - BEE601 - TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION - Dr. V. JayalakshmikrishnandrkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Electrical InsulatorDokument7 SeitenTypes of Electrical InsulatorsathyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insulator ReportDokument5 SeitenInsulator ReportHANAN TARIQ QASURIANoch keine Bewertungen
- Substation ReportDokument23 SeitenSubstation ReportLanz de la CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH-7 InsulatorDokument13 SeitenCH-7 InsulatorMerera TaresaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insulator of Overhead Transmission LineDokument13 SeitenInsulator of Overhead Transmission LineElias BeyeneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insulator of Overhead Transmission LineDokument13 SeitenInsulator of Overhead Transmission LineElias BeyeneNoch keine Bewertungen
- T&D Lab Manual 4th Sem EeDokument20 SeitenT&D Lab Manual 4th Sem Ee993276757060% (5)
- Insulator PDFDokument12 SeitenInsulator PDFSimran KushwahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission Line InsulatorsDokument2 SeitenTransmission Line InsulatorsSachintha EpasingheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Power Transmission (EE-352) : Presenter: Dr. Umbrin Sultana Assistant Professor Eed, NeduetDokument29 SeitenElectrical Power Transmission (EE-352) : Presenter: Dr. Umbrin Sultana Assistant Professor Eed, NeduetFaizan ShaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- LECTUREDokument4 SeitenLECTUREmuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Workshop - ExperimentsDokument7 SeitenElectrical Workshop - ExperimentsMirza Bilal100% (1)
- To Study About Insulation Coordination and Different Types of Insulators Used in Transmission Line and SubstationDokument6 SeitenTo Study About Insulation Coordination and Different Types of Insulators Used in Transmission Line and SubstationApurva Christian100% (1)
- Unit III: Line InsulatorsDokument48 SeitenUnit III: Line InsulatorsVenkatesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Insulators String Efficiency ProblemDokument71 Seiten1 - Insulators String Efficiency ProblemVeera Vamsi Yejju100% (1)
- Lecture - 08 Lecture - 08: EEN-206: Power Transmission and Distribution EEN-206: Power Transmission and DistributionDokument20 SeitenLecture - 08 Lecture - 08: EEN-206: Power Transmission and Distribution EEN-206: Power Transmission and Distributionguddu guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Transmission and DistributionDokument34 SeitenElectrical Transmission and DistributionJessica Laine Tumbaga100% (2)
- Transmission Line IDokument58 SeitenTransmission Line IOdellien SajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Power Transmission and DistributionDokument29 SeitenElectrical Power Transmission and DistributionEngrAneelKumarAkhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- G H Patel College of Engineering & Technology: Electrical Power System-1 (2150908)Dokument21 SeitenG H Patel College of Engineering & Technology: Electrical Power System-1 (2150908)Chintan PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- InsulatorsDokument17 SeitenInsulatorsMizanur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strain Type InsulatorDokument3 SeitenStrain Type InsulatorSindhu ManchukondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical ConsiderationsDokument36 SeitenMechanical ConsiderationsRafi JonNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMPONENTS OF OVERHEAD LINES-modified 1Dokument14 SeitenCOMPONENTS OF OVERHEAD LINES-modified 1Rane SiddeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overhead DistributionDokument31 SeitenOverhead DistributionZvandaziva NelisherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3Dokument32 SeitenLecture 3Muhammad AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nexans MV Cables UK Brochure - 1Dokument48 SeitenNexans MV Cables UK Brochure - 1Ra'fat HerzallahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Underground Power Cables Catalogue 03-2010Dokument48 SeitenUnderground Power Cables Catalogue 03-2010Edgar Sierra Rodriguez100% (1)
- Overhead Distribution LinesDokument53 SeitenOverhead Distribution LinesJunry Tatoy MonterolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Parameters of Overhead LinesDokument8 SeitenDifferent Parameters of Overhead LinesRohan Sharma75% (4)
- Power1 Chapter-7 PDFDokument33 SeitenPower1 Chapter-7 PDFEnyewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Over Head Line Conductor: Experiment No. 9Dokument6 SeitenOver Head Line Conductor: Experiment No. 9Faiza IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- InsulatorDokument16 SeitenInsulatorMohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingVon EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insulation Co-ordination in High-voltage Electric Power SystemsVon EverandInsulation Co-ordination in High-voltage Electric Power SystemsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (5)
- The History of The Philippines From 1521 To 1898Dokument9 SeitenThe History of The Philippines From 1521 To 1898Gary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Petty CashDokument1 SeitePetty CashGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covid On The GoDokument1 SeiteCovid On The GoGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Research: Development of The TraditionDokument2 SeitenComparative Research: Development of The TraditionGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Humanities: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument2 SeitenHumanities: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of The PhilippinesDokument10 SeitenHistory of The PhilippinesGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maypakung Ikaw PresDokument2 SeitenMaypakung Ikaw PresGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- In The News: Hurricane IrmaDokument2 SeitenIn The News: Hurricane IrmaGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- In The News: Featured TopicsDokument2 SeitenIn The News: Featured TopicsGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benedict Arnold Led An ExpeditionDokument2 SeitenBenedict Arnold Led An ExpeditionGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vasco Da Gama: Opera House in ChemnitzDokument2 SeitenVasco Da Gama: Opera House in ChemnitzGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- In The News: Hurricane IrmaDokument2 SeitenIn The News: Hurricane IrmaGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prehistory (Pre-900) : Awidon Mesa Formation Callao Limestone FormationDokument9 SeitenPrehistory (Pre-900) : Awidon Mesa Formation Callao Limestone FormationGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DDokument1 SeiteDGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FDokument12 SeitenFGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProgramsDokument2 SeitenProgramsGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperbolic Trigonometry: A Slide RuleDokument2 SeitenHyperbolic Trigonometry: A Slide RuleGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Controls: Transmission Fluid Oil PumpDokument2 SeitenHydraulic Controls: Transmission Fluid Oil PumpGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 1Dokument2 SeitenThe 1Gary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Etymology: Pre-20th CenturyDokument2 SeitenEtymology: Pre-20th CenturyGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Good Job PresDokument6 SeitenGood Job PresGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- History: Horseless Carriage Boston MassachusettsDokument1 SeiteHistory: Horseless Carriage Boston MassachusettsGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dota 2Dokument3 SeitenDota 2Gary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clutch Stalling Torque Converter Fluid Coupling Torque Impeller Turbine StatorDokument1 SeiteClutch Stalling Torque Converter Fluid Coupling Torque Impeller Turbine StatorGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts and Operation: DynaflowDokument1 SeiteParts and Operation: DynaflowGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gago ItoDokument1 SeiteGago ItoGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic (Where N Is Its Number of Forward Gear Ratios), or AT, Is A Type ofDokument2 SeitenAutomatic (Where N Is Its Number of Forward Gear Ratios), or AT, Is A Type ofGary M TrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Index: © Christopher Pitt 2018 C. Pitt, The Definitive Guide To AdonisjsDokument5 SeitenIndex: © Christopher Pitt 2018 C. Pitt, The Definitive Guide To AdonisjsZidi BoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writ Petition 21992 of 2019 FinalDokument22 SeitenWrit Petition 21992 of 2019 FinalNANDANI kumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHS G11 Reading and Writing Q3 Week 1 2 V1Dokument15 SeitenSHS G11 Reading and Writing Q3 Week 1 2 V1Romeo Espinosa Carmona JrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essays of Warren Buffett - Lessons For Corporate America by Lawrence Cunningham - The Rabbit HoleDokument3 SeitenEssays of Warren Buffett - Lessons For Corporate America by Lawrence Cunningham - The Rabbit Holebrijsing0% (1)
- This Is A Short Presentation To Explain The Character of Uncle Sam, Made by Ivo BogoevskiDokument7 SeitenThis Is A Short Presentation To Explain The Character of Uncle Sam, Made by Ivo BogoevskiIvo BogoevskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Music Production EngineeringDokument1 SeiteMusic Production EngineeringSteffano RebolledoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Not CE 2015 Version R Series 1t-3.5t Operating Manua 2015-08Dokument151 SeitenNot CE 2015 Version R Series 1t-3.5t Operating Manua 2015-08hocine gherbiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Our Story Needs No Filter by Nagarkar SudeepDokument153 SeitenOur Story Needs No Filter by Nagarkar SudeepKavya SunderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Densha: Memories of A Train Ride Through Kyushu: By: Scott NesbittDokument7 SeitenDensha: Memories of A Train Ride Through Kyushu: By: Scott Nesbittapi-16144421Noch keine Bewertungen
- JIMMA Electrical&ComputerEngDokument219 SeitenJIMMA Electrical&ComputerEngTewodros71% (7)
- Equilibrium of A Rigid BodyDokument30 SeitenEquilibrium of A Rigid BodyChristine Torrepenida RasimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Education Deteriorating - EditedDokument3 SeitenPhilippine Education Deteriorating - EditedRukimi Yamato100% (1)
- Creating A Research Space (C.A.R.S.) ModelDokument5 SeitenCreating A Research Space (C.A.R.S.) ModelNazwa MustikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ubicomp PracticalDokument27 SeitenUbicomp Practicalvikrant sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- French Cuisine RecipeDokument6 SeitenFrench Cuisine RecipeJimmy AchasNoch keine Bewertungen
- MegaMacho Drums BT READ MEDokument14 SeitenMegaMacho Drums BT READ MEMirkoSashaGoggoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ode To The West WindDokument4 SeitenOde To The West WindCharis Mae DimaculanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Suppurative Otitis MediaDokument41 SeitenAcute Suppurative Otitis Mediarani suwadjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-Ii Syllabus: Basic Elements in Solid Waste ManagementDokument14 SeitenUnit-Ii Syllabus: Basic Elements in Solid Waste ManagementChaitanya KadambalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo PukangDokument41 SeitenCatalogo PukangClarita Muller LeigueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 30 - HypertensionDokument70 SeitenChapter 30 - HypertensionSakaC.TanayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Law of AttractionDokument2 SeitenLaw of AttractionKate SummersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post Renaissance Architecture in EuropeDokument10 SeitenPost Renaissance Architecture in Europekali_007Noch keine Bewertungen
- OBOE GougerDokument2 SeitenOBOE GougerCarlos GaldámezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 19 Code Standards and ReviewDokument27 SeitenLecture 19 Code Standards and ReviewAdhil Ashik vNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.ed - Eng6 - q1 - Mod3 - Make Connections Between Information Viewed and Personal ExpiriencesDokument32 Seiten2.ed - Eng6 - q1 - Mod3 - Make Connections Between Information Viewed and Personal ExpiriencesToni Marie Atienza Besa100% (3)
- Learning English Through The Educational Games of Wordwall Website For Elementary Students by Group 1 (R4E)Dokument6 SeitenLearning English Through The Educational Games of Wordwall Website For Elementary Students by Group 1 (R4E)NurulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rdramirez Aota 2018 Poster For PortfolioDokument1 SeiteRdramirez Aota 2018 Poster For Portfolioapi-437843157Noch keine Bewertungen
- ManualDokument50 SeitenManualspacejung50% (2)
- 1572 - Anantha Narayanan FFS CalculationDokument1 Seite1572 - Anantha Narayanan FFS CalculationAnantha NarayananNoch keine Bewertungen