Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Heat
Hochgeladen von
Hardo NewbieCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Heat
Hochgeladen von
Hardo NewbieCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
HEAT OF COMBUSTION
The heat of combustion of a substance at 25C can be calculated from the enthalpy of formation (fH) data in the table Standard Thermodynamic
Properties of Chemical Substances in this Section. We can write the general combustion reaction as
X + O 2 CO 2 (g) + H 2 O(l) + other products
For a compound containing only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, the reaction is simply
1
C a H b O c + a + b c O 2 a CO 2 (g) + b H 2 O(l)
1 1
4 2 2
and the standard heat of combustion cH, which is defined as the negative of the enthalpy change for the reaction (i.e., the heat released in the
combustion process), is given by
c H = a f H (CO 2 , g) b f H (H 2 O, l) + f H (C a H b O c )
1
2
393.51 a + 142.915 b + f H (C a H b O c )
This equation applies if the reactants start in their standard states (25C and one atmosphere pressure) and the products return to the same conditions.
The same equation applies to a compound containing another element if that element ends in its standard reference state (e.g., nitrogen, if the product
is N2); in general, however, the exact products containing the other elements must be known in order to calculate the heat of combustion.
The following table gives the standard heat of combustion calculated in this manner for a few representative substances.
Molecular Molecular
formula Name cH/kJ mol1 formula Name cH/kJ mol1
Inorganic substances C3H8O 1-Propanol (l) 2021.3
C3H8O3 Glycerol (l) 1655.4
C Carbon (graphite) 393.5 C4H10O Diethyl ether (l) 2723.9
CO Carbon monoxide (g) 283.0 C5H12O 1-Pentanol (l) 3330.9
H2 Hydrogen (g) 285.8 C6H6O Phenol (s) 3053.5
H3N Ammonia (g) 382.8
H4N2 Hydrazine (g) 667.1 Carbonyl compounds
N2O Nitrous oxide (g) 82.1
CH2O Formaldehyde (g) 570.7
Hydrocarbons C2H2O Ketene (g) 1025.4
C2H4O Acetaldehyde (l) 1166.9
CH4 Methane (g) 890.8 C3H6O Acetone (l) 1789.9
C2H2 Acetylene (g) 1301.1 C3H6O Propanal (l) 1822.7
C2H4 Ethylene (g) 1411.2 C4H8O 2-Butanone (l) 2444.1
C2H6 Ethane (g) 1560.7
C3H6 Propylene (g) 2058.0 Acids and esters
C3H6 Cyclopropane (g) 2091.3
C3H8 Propane (g) 2219.2 CH2O2 Formic acid (l) 254.6
C4H6 1,3-Butadiene (g) 2541.5 C2H4O2 Acetic acid (l) 874.2
C4H10 Butane (g) 2877.6 C2H4O2 Methyl formate (l) 972.6
C5H12 Pentane (l) 3509.0 C3H6O2 Methyl acetate (l) 1592.2
C6H6 Benzene (l) 3267.6 C4H8O2 Ethyl acetate (l) 2238.1
C6H12 Cyclohexane (l) 3919.6 C7H6O2 Benzoic acid (s) 3226.9
C6H14 Hexane (l) 4163.2
C7H8 Toluene (l) 3910.3 Nitrogen compounds
C7H16 Heptane (l) 4817.0
C10H8 Naphthalene (s) 5156.3 CHN Hydrogen cyanide (g) 671.5
CH3NO2 Nitromethane (l) 709.2
Alcohols and ethers CH5N Methylamine (g) 1085.6
C2H3N Acetonitrile (l) 1247.2
CH4O Methanol (l) 726.1 C2H5NO Acetamide (s) 1184.6
C2H6O Ethanol (l) 1366.8 C3H9N Trimethylamine (g) 2443.1
C2H6O Dimethyl ether (g) 1460.4 C5H5N Pyridine (l) 2782.3
C2H6O2 Ethylene glycol (l) 1189.2 C6H7N Aniline (l) 3392.8
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Opuscolo Pompeii Nov18 HiResDokument5 SeitenOpuscolo Pompeii Nov18 HiResnot a bookwormNoch keine Bewertungen
- Separating Mixtures PDFDokument4 SeitenSeparating Mixtures PDFDenise Adriene ParanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TECHNOLOGY1 Answer-1Dokument6 SeitenTECHNOLOGY1 Answer-1JlkKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced WatertekDokument2 SeitenAdvanced WatertekAnonymous whI91WzNoch keine Bewertungen
- As 2358-1990 Adhesives - For Fixing Ceramic TilesDokument8 SeitenAs 2358-1990 Adhesives - For Fixing Ceramic TilesSAI Global - APAC100% (1)
- PVC W Water Sto Pper - Ins Stallation GuideDokument4 SeitenPVC W Water Sto Pper - Ins Stallation GuideZankar R ParikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of MatterDokument41 SeitenClassification of MatterRicardo Jr. Uy100% (1)
- Antisol White (In)Dokument2 SeitenAntisol White (In)Budhi KurniawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry Lab Manual With DEMO DATADokument42 SeitenGeneral Chemistry Lab Manual With DEMO DATAshihab shoronNoch keine Bewertungen
- CARBOSORB NC 830 - Comelt - TDS - ENDokument1 SeiteCARBOSORB NC 830 - Comelt - TDS - ENilkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet 1x19 Stainless Steel Strand Wire RopeDokument1 SeiteDatasheet 1x19 Stainless Steel Strand Wire RopePrattyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quotation For Arc Gun With Power Source DC Drive 400amp ExportDokument5 SeitenQuotation For Arc Gun With Power Source DC Drive 400amp ExportClaudio Fica RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
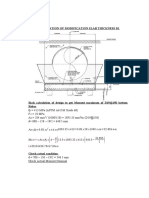
- CALCULATION OF MODIFICATION SLAB THICKNESS D1 v.2Dokument3 SeitenCALCULATION OF MODIFICATION SLAB THICKNESS D1 v.2Dica Rasyid MaulidhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyrolysis of WoodDokument42 SeitenPyrolysis of WoodCléo VieiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abs Ex58f - AsiaDokument4 SeitenAbs Ex58f - AsiaGiang CaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre Stressed Concrete Circular Hollow SectionDokument2 SeitenPre Stressed Concrete Circular Hollow SectionAndrew Black50% (2)
- Free Pattern 1037Dokument7 SeitenFree Pattern 1037Bet RomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- BituflamepDokument2 SeitenBituflamepnkhhhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basf MasterPozzolith 402R TdsDokument2 SeitenBasf MasterPozzolith 402R TdsValentino ToplesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Langelier IndexDokument6 SeitenLangelier IndexibruNoch keine Bewertungen
- NPTEL - Design of Machine Elements 1Dokument464 SeitenNPTEL - Design of Machine Elements 1Hardik Gupta75% (8)
- 5.pavement MaterialsDokument84 Seiten5.pavement MaterialssmaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 Sec 4 Pure Chem-12s PDFDokument591 Seiten2019 Sec 4 Pure Chem-12s PDFDewei LohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doi 10.15376 - Biores.5.3.1945-1954Dokument10 SeitenDoi 10.15376 - Biores.5.3.1945-1954trang đàmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dust/Gas/Air Filtration EquipmentDokument1 SeiteDust/Gas/Air Filtration EquipmentRogelioB.AlobIINoch keine Bewertungen
- Laurie Baker PresentedDokument33 SeitenLaurie Baker PresentedArnav DasaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2008 - 9 - Sandvik Coupling LDokument6 Seiten2008 - 9 - Sandvik Coupling LcanettijNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18-Inch Doll Hats-FinalDokument4 Seiten18-Inch Doll Hats-FinalGeorgie RedfordNoch keine Bewertungen
- Don't Test This One!! This One!!Dokument14 SeitenDon't Test This One!! This One!!Putu Agus SantosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GALA Valve LamindoDokument62 SeitenGALA Valve LamindoSyawalMaulanaNoch keine Bewertungen