Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
OSHA 10 Slides 06 - Electrical Safety
Hochgeladen von
asteinb10 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
618 Ansichten64 SeitenOSHA
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenOSHA
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
618 Ansichten64 SeitenOSHA 10 Slides 06 - Electrical Safety
Hochgeladen von
asteinb1OSHA
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 64
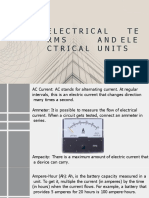
Key Terms
Amperes: The volume or intensity of the current flow.
AWG: American wire gauge (AWG), which is one measurement standard used to size wire.
Circuit: Complete path of the current; including a voltage source, conductors, and the load (such as, a lamp, tool, or
heater).
Conductors: Materials that contain free electrons that allow current to flow through the material.
Current: Electron movement (measured in amperes).
Electric Shock: The effects of current flowing through the body.
GFCI: Ground-Fault Circuit Interrupter.
Grounding: An intentional conductive connection to the earth that provides a path back to the source for any fault
current that may occur in a circuit.
Insulators: Materials with few free electrons. Current does not easily flow through insulators, if at all.
Resistance: Opposition to current flow.
Volts: The electrical pressure (measure of electrical force).
Watts: Measurement of electrical power.
Wire Gauge: System used to measure the physical size of wire.
LOW VOLTAGE DOES NOT MEAN LOW HAZARD!
*mA = milliampere =
1/1,000 of an ampere
Ground-Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI)
Fuses
Circuit Breakers
If a GFCI keeps tripping while you are using a
power tool, there is a problem. Don’t keep
resetting the GFCI and continue work. You
must evaluate the “clue” and decide what
action should be taken to control the
hazard.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- OSHA 10 Slides 07 - Struck by and Caught in Between HazardsDokument40 SeitenOSHA 10 Slides 07 - Struck by and Caught in Between Hazardsasteinb1Noch keine Bewertungen
- OSHA 10 Slides 10 - Hand and Power ToolsDokument79 SeitenOSHA 10 Slides 10 - Hand and Power Toolsasteinb1Noch keine Bewertungen
- OSHA 10 Slides 04 - Hazardous MaterialsDokument40 SeitenOSHA 10 Slides 04 - Hazardous Materialsasteinb1Noch keine Bewertungen
- OSHA 10 Slides 05 - Cranes and RiggingDokument66 SeitenOSHA 10 Slides 05 - Cranes and Riggingasteinb1100% (1)
- OSHA 10 Slides 09 - Personal Protective EquipmentDokument106 SeitenOSHA 10 Slides 09 - Personal Protective Equipmentasteinb1Noch keine Bewertungen
- OSHA 10 Slides 11 - Scaffolds PDFDokument80 SeitenOSHA 10 Slides 11 - Scaffolds PDFasteinb1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Osha StudyguideDokument107 SeitenOsha StudyguideGerman Marte Pepén50% (4)
- 30-Hr Construction SG 1.2Dokument177 Seiten30-Hr Construction SG 1.2c2hardman100% (5)
- OSHA Construction Pre-TestanswersDokument2 SeitenOSHA Construction Pre-TestanswersAgencia Privada de Investigacion33% (6)
- WWW - Osha.gov Pre Test Answer Key2Dokument3 SeitenWWW - Osha.gov Pre Test Answer Key2raul_bsu100% (6)
- Osha StandardsDokument18 SeitenOsha Standardsmojback100% (3)
- OSHA 10-30 Hour Course List-1Dokument9 SeitenOSHA 10-30 Hour Course List-1kabir0% (1)
- OSHA-30 General Industry Training for ForemenDokument1 SeiteOSHA-30 General Industry Training for ForemenAldrin33% (3)
- OSHA 10 Hour Construction Course Fact SheetDokument1 SeiteOSHA 10 Hour Construction Course Fact SheetMaurice Anthony0% (1)
- OSHADokument244 SeitenOSHApicottNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osha 30 HR Outreach Study GuideDokument290 SeitenOsha 30 HR Outreach Study GuideRich Perez80% (5)
- OSHA 500 Post TestDokument5 SeitenOSHA 500 Post TestMughees Ali67% (3)
- Study Guide OSHA 30 Construction Focus Four Electrocuction HazardsDokument86 SeitenStudy Guide OSHA 30 Construction Focus Four Electrocuction HazardssuperpiojoNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSHA 10 Test AnswerDokument3 SeitenOSHA 10 Test AnswerRana Muhammad Zeeshan41% (39)
- 10 Hours OshaDokument247 Seiten10 Hours OshaJose BastidasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osha Questions and AnswersDokument5 SeitenOsha Questions and AnswersOsueni Aitiemigele91% (11)
- OSHA - 30-Hr Construction - StudyGuide - v2 PDFDokument175 SeitenOSHA - 30-Hr Construction - StudyGuide - v2 PDFRoberto Polanco100% (4)
- 30-Hr Construction Safety Certification Study GuideDokument176 Seiten30-Hr Construction Safety Certification Study GuideMichael Kovach100% (1)
- Introduction To OshaDokument44 SeitenIntroduction To Oshafettane100% (1)
- BCSP CP ExamGuideDokument36 SeitenBCSP CP ExamGuideYogendra SasankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXAM OSHA With Ans PDFDokument4 SeitenEXAM OSHA With Ans PDFJunel Christian Delos Angeles59% (17)
- OSHA 2013 AnswersDokument3 SeitenOSHA 2013 Answerslacurva67% (3)
- Career Research Essay 1Dokument4 SeitenCareer Research Essay 1api-554074391Noch keine Bewertungen
- OSHA SHIPS: Preventing Injuries in ShipyardsDokument33 SeitenOSHA SHIPS: Preventing Injuries in ShipyardsAmr MoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Confined Space ProgramDokument80 SeitenConfined Space ProgramRoberto Teekersingh100% (2)
- 30Hr Construction Study GuideDokument105 Seiten30Hr Construction Study GuideMuhammad Younas100% (12)
- Accident Prevention Manual Administration & Programs, 14th Ed.-Answers To Review QuestionsDokument50 SeitenAccident Prevention Manual Administration & Programs, 14th Ed.-Answers To Review QuestionsGukan DoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working Safe With ElectricityDokument68 SeitenWorking Safe With ElectricityocernnNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSHA 1910 - General Industry Standards 2016Dokument989 SeitenOSHA 1910 - General Industry Standards 2016Dan100% (1)
- OSHA 30 ManualDokument440 SeitenOSHA 30 ManualNina Bays100% (3)
- OSHA 30 HR Construction Outline - 2009-1Dokument23 SeitenOSHA 30 HR Construction Outline - 2009-1Kashif Nadeem Rana100% (1)
- Osha 30Dokument49 SeitenOsha 30juliki1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Osha 2226Dokument27 SeitenOsha 2226Marco Ernesto Llerena SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ergonomics Analysis Tools Used in IndustryDokument10 SeitenErgonomics Analysis Tools Used in IndustryMyle26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Osha Focus 4Dokument95 SeitenOsha Focus 4Raoul Njie100% (1)
- CIH EXAM Equations 2020 Explained by Expert Dr. Daniel FarcasDokument36 SeitenCIH EXAM Equations 2020 Explained by Expert Dr. Daniel FarcasDaniel FarcasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osha 29 CFR 1910.268Dokument41 SeitenOsha 29 CFR 1910.268André Ricardo Silva100% (1)
- OHST Complete GuideDokument24 SeitenOHST Complete GuideFuzail Ayaz100% (1)
- Board of Certified Safety Professionals - Career - Guide To The Safety ProfessionDokument54 SeitenBoard of Certified Safety Professionals - Career - Guide To The Safety Professionsobemile100% (4)
- BCRSP Examination Candidate Handbook: Doc.024 Last Revision: June 2021Dokument39 SeitenBCRSP Examination Candidate Handbook: Doc.024 Last Revision: June 2021rob mclellanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final ExamDokument784 SeitenFinal Examdancofffey5Noch keine Bewertungen
- OSHA Safety ManualDokument278 SeitenOSHA Safety ManualHall26100% (9)
- CIH Exam Equation Fully ExplainedDokument35 SeitenCIH Exam Equation Fully ExplainedDaniel FarcasNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCSP ASP Exam GuideDokument28 SeitenBCSP ASP Exam Guidernp24600067% (3)
- Osha RequirementsDokument55 SeitenOsha RequirementsHasan Shakeel100% (1)
- CSP App GuideDokument16 SeitenCSP App GuideSAYED100% (4)
- OSHA Construction Pre-TestDokument1 SeiteOSHA Construction Pre-TestAgencia Privada de Investigacion50% (2)
- Electrical Terms and UnitsDokument28 SeitenElectrical Terms and UnitsMichael PachecoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject: 2es103 Basic Electrical Engineering (Bee)Dokument30 SeitenSubject: 2es103 Basic Electrical Engineering (Bee)Jay SathvaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Electricity 1.1Dokument23 SeitenIntroduction To Electricity 1.1August DuqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Services Book 2Dokument237 SeitenBuilding Services Book 2Africana RoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 1Dokument51 SeitenPresentation 1Workineh AsefaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW 1Dokument5 SeitenHW 1asteinb1Noch keine Bewertungen
- OSHA 10 Slides 12 - Stairways and LaddersDokument82 SeitenOSHA 10 Slides 12 - Stairways and Laddersasteinb1100% (1)
- OSHA 10 Slides 11 - Scaffolds PDFDokument80 SeitenOSHA 10 Slides 11 - Scaffolds PDFasteinb1Noch keine Bewertungen
- OSHA 10 Slides 08 - Fall ProtectionDokument75 SeitenOSHA 10 Slides 08 - Fall Protectionasteinb1100% (1)
- OSHA 10 Slides 01 - Intro To OSHADokument62 SeitenOSHA 10 Slides 01 - Intro To OSHAasteinb1Noch keine Bewertungen
- OSHA 10 Slides 03 - Hazard CommunicationDokument54 SeitenOSHA 10 Slides 03 - Hazard Communicationasteinb1Noch keine Bewertungen
- OSHA 10 Slides 02 - General Safety and Health ProvisionsDokument48 SeitenOSHA 10 Slides 02 - General Safety and Health Provisionsasteinb1Noch keine Bewertungen
- OSHA 10 Slides 00 - Preliminary InfoDokument20 SeitenOSHA 10 Slides 00 - Preliminary Infoasteinb1Noch keine Bewertungen