Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
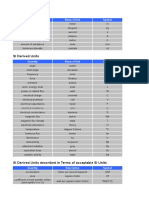
SI Unit Name Symbol British Unit Quantity Definition & Formula
Hochgeladen von
api-3569515700 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
20 Ansichten3 SeitenOriginaltitel
1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
20 Ansichten3 SeitenSI Unit Name Symbol British Unit Quantity Definition & Formula
Hochgeladen von
api-356951570Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
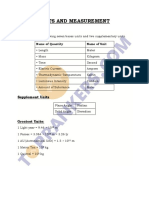
Physics Formulas
Base Units
SI Unit Name Symbol British Unit Quantity Definition & Formula
Kilogram kg Pounds Mass The unit to measure mass.
1kg = 3.28lb
Meter m Foot Length The unit to measure length.
1m=3.28ft
Second s Second Time The unit to measure time.
Ampere A Electric current The unit to measure the
charge of electrical current
per second.
Kelvin K Fahrenheit Temperature The degree of heat present
in matter.
1F = 255.91K
Mole mol Amount of The unit of measurement for
substance a substance.
Candela cd Luminous The measurement of
intensity luminous intensity in a
direction. It has a frequency
of 540 x 1012 Hz.
DERIVED UNITS
SI Unit Name Symbol British Unit Quantity Definition & Formula
Gray Gy Rad Absorbed dose The absorption of one joule
of radiation energy per
kilogram of matter.
1Gy= 1J/kg
Coulomb C Esu Charge Charge transferred by a
current of one ampere per
second.
C=As
Volt v Electric The difference in electrical
potential potential.
V=A
Sievert Sv Rem Dose equivalent The product of absorbed
dose, and the radiation
weighing factor.
1Sv = 100 rem
Joule J ft/lb Energy The work required to move
one coulomb through one
volt.
J=Cv
Coulomb/kilogram C/Kg Roentgen Exposure The quantity of X-rays or
gamma rays required to
produce a given amount of
ionization in a unit mass of
air.
2.58 x 10-4 C/kg
Hertz Hz Cycles/sec Frequency Unit of measurement for
frequency in cycles per
second.
Weber Wb Magnetic flux Unit to measure magnetic
flux.
Wb = field strength/area
Tesla T Gauss Magnetic flux The units to measure
density magnetic flux density.
T = 1WB/m2
Watt W Power The unit of measurement
for power.
1W = 1J/sec
Bequerel Bq Curie Radioactivity The unit of measurement of
radioactive material
undergoing decay.
1Bq = 1s-1
RADIOLOGIC UNITS
SI Unit Name Symbol British Unit Quantity Definition & Formula
Bequerel Bq Curie Radioactivity (A) The unit of measurement of
radioactive material
undergoing decay.
1Bq = 1s-1
Gray Gy Rad Absorbed dose The absorption of one joule
(D) of radiation energy per
kilogram of matter.
1Gy= 1J/kg
Sievert Sv Rem Dose equivalent The product of absorbed
(H) dose, and the radiation
weighing factor.
1Sv = 100 rem
Coulomb/Kilogram C/kg Exposure (X) The quantity of X-rays or
gamma rays required to
produce a given amount of
ionization in a unit mass of
air.
2.58 x 10-4 C/kg
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresVon EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Notebook 1: Lindsey ShrinerDokument3 SeitenNotebook 1: Lindsey Shrinerapi-338662480Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notebook 1Dokument4 SeitenNotebook 1api-338661748Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rte 142 Notebook 1 FinalDokument5 SeitenRte 142 Notebook 1 Finalapi-356719939Noch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix A: The International System of UnitsDokument8 SeitenAppendix A: The International System of UnitsIvan gheorgheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 Electric Circuit Theory BTDokument18 SeitenLecture 1 Electric Circuit Theory BTnjuraimelvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1: Units, Physical Quantities, and Vectors: Physics 1Dokument8 SeitenLesson 1: Units, Physical Quantities, and Vectors: Physics 1GM ShioriNoch keine Bewertungen
- PowerPoint PresentationDokument5 SeitenPowerPoint Presentationgzavalav2100Noch keine Bewertungen
- UnitsDokument16 SeitenUnitsVinayChowdaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Si UnitsDokument3 SeitenSi Unitsmouxritsa_83Noch keine Bewertungen
- UNITSDokument9 SeitenUNITSDhayane RedoquerioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conversion Factors PDFDokument3 SeitenConversion Factors PDFArbenson CNoch keine Bewertungen
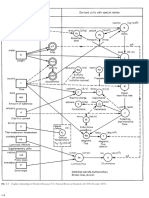
- Graphic Relationships of SI Units With Names (U.S. National Bureau of Standards, LC 1078, December 1976.)Dokument18 SeitenGraphic Relationships of SI Units With Names (U.S. National Bureau of Standards, LC 1078, December 1976.)annisa putriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electrical Engineering ModulesDokument243 SeitenBasic Electrical Engineering Modulesfaisal sbennaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm 02Dokument623 SeitenAstm 02Bilel RebaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Si Units PDFDokument4 SeitenSi Units PDFசெல்வ குமார்Noch keine Bewertungen
- SI Base Units: Quantity Name of Unit SymbolDokument6 SeitenSI Base Units: Quantity Name of Unit SymbolHazem SobhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiation Physics: Christensen's Physics of Diagnostic Radiology (4 Edition)Dokument14 SeitenRadiation Physics: Christensen's Physics of Diagnostic Radiology (4 Edition)Sarvesh ZambaulikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Igcse 2012 Exam Revision Notes-56395934Dokument34 SeitenPhysics Igcse 2012 Exam Revision Notes-56395934masairev8Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHEL04A - Transes in BiochemistryDokument7 SeitenCHEL04A - Transes in BiochemistryMikhaella GwenckyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SI Base UnitsDokument11 SeitenSI Base UnitsHasan BashoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Science 4 1Dokument44 SeitenGeneral Science 4 1J JNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Modern Metric System : Si Quick Reference Guide: International System of Units (SI)Dokument5 SeitenThe Modern Metric System : Si Quick Reference Guide: International System of Units (SI)Sama UmateNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK 1 Base and Derived UnitsDokument6 SeitenWEEK 1 Base and Derived UnitsannmarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Units: 3. U.S. Units of Measurement 4. Tables of EquivalentsDokument8 SeitenUnits: 3. U.S. Units of Measurement 4. Tables of EquivalentsAndré OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- AppendixDokument4 SeitenAppendixResham ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantity Unit Symbol: Base and Supplementary UnitsDokument6 SeitenQuantity Unit Symbol: Base and Supplementary UnitsRajkumar ANoch keine Bewertungen
- SI UNITS (Physics 5054)Dokument2 SeitenSI UNITS (Physics 5054)Haris ShaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPC - 1 Chp. Lec.Dokument17 SeitenCPC - 1 Chp. Lec.Latu BharaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Information: Engineering Units, Conversions & FormulaeDokument8 SeitenTechnical Information: Engineering Units, Conversions & FormulaePeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading 1Dokument11 SeitenReading 1shafyvonommyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of ElectricalDokument178 SeitenBasics of Electricaludayakumart50% (2)
- Technical Information: Back To Contents PagesDokument8 SeitenTechnical Information: Back To Contents PagesAditya PrasetyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Exam Quick Revision NotesDokument40 SeitenPhysics Exam Quick Revision NotesPinky Ann DanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector Scalar and Units ReviewDokument43 SeitenVector Scalar and Units ReviewGumball DumballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Units Associated With Basic Electrical QuantityDokument4 SeitenUnits Associated With Basic Electrical Quantitycaj7687100% (1)
- 1EQ - Science - Important Concept & Questions - EngDokument22 Seiten1EQ - Science - Important Concept & Questions - Engsachindv276Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electricians Licence 'A' (Domestic) - Maltese SyllabusDokument307 SeitenElectricians Licence 'A' (Domestic) - Maltese Syllabusdavidegrima100% (17)
- General Science: Career Point ShimlaDokument48 SeitenGeneral Science: Career Point ShimlaAnil SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Fundamentals of Radiologic ScienceDokument5 SeitenChapter 2 Fundamentals of Radiologic ScienceAnne LimpinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Date: 13/10/2003 Realm of Quantum Mechanics:: Remote ControlDokument3 Seiten1 Date: 13/10/2003 Realm of Quantum Mechanics:: Remote ControlHadi FakihNoch keine Bewertungen
- "The True Sign of Intelligence Is Not Knowledge But Imagination." - Albert Einstein (1879-1955)Dokument49 Seiten"The True Sign of Intelligence Is Not Knowledge But Imagination." - Albert Einstein (1879-1955)Ivan TNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Physics Definitions Needed by The Syllabus of 2009Dokument2 SeitenIB Physics Definitions Needed by The Syllabus of 2009mohsin771100% (1)
- CH-I ProjectDokument10 SeitenCH-I Projectzenebesleshi21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oil Field Trainee TestDokument102 SeitenOil Field Trainee TesteditinggroNoch keine Bewertungen
- V. Dimensions and Units For Physical Quantities Mechanical UnitsDokument4 SeitenV. Dimensions and Units For Physical Quantities Mechanical UnitsLei TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energies Radioactive Ionizing RadiationDokument9 SeitenEnergies Radioactive Ionizing RadiationDhuha MoyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Units and DimensionDokument18 SeitenUnits and DimensionnilusclassesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mole ObjectiveDokument26 SeitenMole ObjectiveDevil WalkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- GP1 Physical Quantities & MeasurementDokument6 SeitenGP1 Physical Quantities & MeasurementKatlo MokgethiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics GB Pllaning GuideDokument33 SeitenBasics GB Pllaning GuideNarcis PatrascuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Practicum-Lecture01Dokument16 SeitenEngineering Practicum-Lecture01Kelvin IgbodikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unidades para Formato ApaDokument4 SeitenUnidades para Formato ApaJaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latin Characters: Symbol Meaning SI Unit of MeasureDokument5 SeitenLatin Characters: Symbol Meaning SI Unit of MeasureChase CampbellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introductory Physics - Mashuri L. Warren - San Francisco, 1979 - W. H. Freeman - 9780716710080 - Anna's ArchiveDokument716 SeitenIntroductory Physics - Mashuri L. Warren - San Francisco, 1979 - W. H. Freeman - 9780716710080 - Anna's ArchiveNIpun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics 1 NotesDokument6 SeitenGeneral Physics 1 NotesJashley PanillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The International System of Units, Fundamental Constants, and Conversion FactorsDokument4 SeitenThe International System of Units, Fundamental Constants, and Conversion FactorsSamir ZaghloolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Units and MeasurementDokument2 SeitenUnits and MeasurementShanthi MarisettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles NotesDokument17 SeitenPrinciples NotesHuncho7Noch keine Bewertungen
- 48) Sistemul InternationalDokument5 Seiten48) Sistemul InternationalCosmin LTDANoch keine Bewertungen
- Particulate ElectromagneticDokument2 SeitenParticulate Electromagneticapi-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9Dokument3 Seiten9api-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arnoldbridgett PortfolioiDokument2 SeitenArnoldbridgett Portfolioiapi-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- 16Dokument3 Seiten16api-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- 10Dokument2 Seiten10api-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- 11Dokument1 Seite11api-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- 14Dokument2 Seiten14api-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8Dokument2 Seiten8api-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4Dokument1 Seite4api-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- 6Dokument3 Seiten6api-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
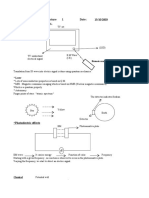
- (C) - Within The Main X-Ray Circuit There Are Two Sides, The Primary (Low Voltage) Side (A), and TheDokument2 Seiten(C) - Within The Main X-Ray Circuit There Are Two Sides, The Primary (Low Voltage) Side (A), and Theapi-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7Dokument1 Seite7api-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Circui 4Dokument2 SeitenElectrical Circui 4api-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2Dokument3 Seiten2api-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook9artifactsDokument2 SeitenArnoldbridgett Notebook9artifactsapi-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook8detaildistortionDokument2 SeitenArnoldbridgett Notebook8detaildistortionapi-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook10fluorosDokument4 SeitenArnoldbridgett Notebook10fluorosapi-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook12storageDokument1 SeiteArnoldbridgett Notebook12storageapi-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook11qcDokument2 SeitenArnoldbridgett Notebook11qcapi-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook7densitycontrastDokument2 SeitenArnoldbridgett Notebook7densitycontrastapi-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook4pspDokument2 SeitenArnoldbridgett Notebook4pspapi-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook6digitalprocessingDokument2 SeitenArnoldbridgett Notebook6digitalprocessingapi-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook5drDokument3 SeitenArnoldbridgett Notebook5drapi-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook3filmscreensDokument4 SeitenArnoldbridgett Notebook3filmscreensapi-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook1formulasDokument4 SeitenArnoldbridgett Notebook1formulasapi-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arnoldbridgett Notebook2gridsDokument6 SeitenArnoldbridgett Notebook2gridsapi-356951570Noch keine Bewertungen
- Raoult's LawDokument8 SeitenRaoult's LawHARSH DHOLAKIYANoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper Breadth in PhysicsDokument28 SeitenQuestion Paper Breadth in PhysicsRafay BilalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental of Power Electronics Week 8 Assignment SolutionsDokument4 SeitenFundamental of Power Electronics Week 8 Assignment SolutionsDeep Gandhi100% (1)
- KINEMATICSDokument7 SeitenKINEMATICSJhane AlvaradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sydney Grammar 2018 Physics Prelim Yearly & SolutionsDokument58 SeitenSydney Grammar 2018 Physics Prelim Yearly & SolutionsSpice Man100% (1)
- Unit1 MotionDokument11 SeitenUnit1 MotionGuai PlayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Physics Classnotes Midterm Sprint - 8th PDFDokument60 SeitenComplete Physics Classnotes Midterm Sprint - 8th PDFIbad ur Rehman gamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- E1 PDFDokument7 SeitenE1 PDFReinier Roman SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asymmetric Coupled Transmission Lines in An Inhomogeneous MediumDokument6 SeitenAsymmetric Coupled Transmission Lines in An Inhomogeneous MediumG P AnkushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fans and BlowersDokument11 SeitenFans and BlowerskennnNoch keine Bewertungen
- AN5141Dokument12 SeitenAN5141david_benavidez_3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Success Physics PDFDokument336 SeitenSuccess Physics PDFtranhuutuong0% (1)
- Kcse 2000 Physics Paper 2Dokument5 SeitenKcse 2000 Physics Paper 2Jones HildahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 25 AppendicesDokument23 Seiten25 AppendicesEmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plank's ConstantDokument4 SeitenPlank's ConstantRawan MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- How The Three Phase System Voltages Are Derived With Respect To ABC and CBA SequenceDokument13 SeitenHow The Three Phase System Voltages Are Derived With Respect To ABC and CBA SequenceRyan CortesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 - Distributed Forces - Centroids, Center of GravityDokument30 SeitenChapter 4 - Distributed Forces - Centroids, Center of GravityrushdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9th Class Physics Notes Chapter 2 AjkDokument2 Seiten9th Class Physics Notes Chapter 2 AjkAsher Kabir100% (4)
- Fluid Mechanics Question BankDokument6 SeitenFluid Mechanics Question BankPrashanth JagadeeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Load Sheet For: Additive Tank 03-TA-01Dokument7 SeitenProcess Load Sheet For: Additive Tank 03-TA-01WawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Laws ExercisesDokument26 SeitenGas Laws ExercisesAnonymousGodiswithyouNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResistorsDokument33 SeitenResistorsCaine de Leon100% (1)
- Basic Electronics Pre-TestDokument6 SeitenBasic Electronics Pre-TestShring HighbNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 Fuentes de poder-SITOPDokument24 Seiten13 Fuentes de poder-SITOPJosé PincayNoch keine Bewertungen
- AITS 2324 FT III JEEM TD SolDokument15 SeitenAITS 2324 FT III JEEM TD Soladoranto737Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tabella Riassuntiva T.A. Di Precisione High Accuracy Cts Selection TableDokument27 SeitenTabella Riassuntiva T.A. Di Precisione High Accuracy Cts Selection TableMEINARDONoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 10 Sinusoidal Steady-State Power CalculationsDokument30 SeitenCH 10 Sinusoidal Steady-State Power CalculationsMugerwa CharlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toaz - Info Electrical Machine Problems PRDokument2 SeitenToaz - Info Electrical Machine Problems PRJhan Edwards Pasiolan RectoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Phase Inductive LoadDokument40 SeitenSingle Phase Inductive LoadJULIET MOKWUGWONoch keine Bewertungen
- Opho2023 Open SolsDokument43 SeitenOpho2023 Open SolsNguyễn DũngNoch keine Bewertungen