Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
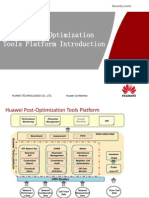
USN9810 V900R014C10 Capacity Assessment Guide
Hochgeladen von
BrunoCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
USN9810 V900R014C10 Capacity Assessment Guide
Hochgeladen von
BrunoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
USN9810 Unified Service Node
V900R014C10
Capacity Assessment Guide
Issue 01
Date 2015-06-18
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2015. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior
written consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and
the customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be
within the purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specified in the contract, all statements,
information, and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees
or representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address: Huawei Industrial Base
Bantian, Longgang
Shenzhen 518129
People's Republic of China
Website: http://www.huawei.com
Email: support@huawei.com
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential i
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node
Capacity Assessment Guide About This Document
About This Document
Purpose
This document describes how to assess and optimize capacity of the USN9810, and provides
guidelines on capacity assessment and optimization for network optimization and
maintenance engineers.
Intended Audience
This document is intended for:
Network optimization engineers
Maintenance engineers
Symbol Conventions
The symbols that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Symbol Description
Indicates a hazard with a high level of risk that, if not
avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a hazard with a medium or low level of risk
which, if not avoided, could result in minor or
moderate injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation that, if not
avoided, could cause equipment damage, data loss,
and performance degradation, or unexpected results.
Indicates a tip that may help you solve a problem or
save time.
Provides additional information to emphasize or
supplement important points of the main text.
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential ii
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node
Capacity Assessment Guide About This Document
Change History
Changes between document issues are cumulative. The latest document issue contains all the
changes made in earlier issues.
Issue 01 (2015-06-18)
This issue is used for first office application (FOA).
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential iii
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node V900R014C10
Capacity Assessment Guide Contents
Contents
About This Document....................................................................................................................ii
1 Overview.........................................................................................................................................1
1.1 Background.....................................................................................................................................................................1
1.2 Scope..............................................................................................................................................................................1
1.3 Networking Overview....................................................................................................................................................1
2 Assessment and Optimization Procedure................................................................................5
3 Capacity Assessment in EPC Scenarios....................................................................................6
3.1 Traffic Model..................................................................................................................................................................6
3.1.1 Definition of Peak Hour..............................................................................................................................................6
3.1.2 Traffic Model Acquisition...........................................................................................................................................7
3.2 Baseline..........................................................................................................................................................................8
3.3 License Capacity Assessment.........................................................................................................................................8
3.3.1 Assessment Principles.................................................................................................................................................8
3.3.2 Assessment Method.....................................................................................................................................................8
3.3.3 Assessment Conclusion...............................................................................................................................................9
3.4 Static Capacity Assessment............................................................................................................................................9
3.4.1 Assessment Principles.................................................................................................................................................9
3.4.2 Assessment Method.....................................................................................................................................................9
3.4.3 Assessment Conclusion.............................................................................................................................................10
3.5 Signaling Processing Resource Assessment.................................................................................................................10
3.5.1 Assessment Principles...............................................................................................................................................10
3.5.2 Assessment Method...................................................................................................................................................10
3.5.3 Assessment Conclusion.............................................................................................................................................10
3.6 Comprehensive Resource Assessment..........................................................................................................................11
3.6.1 Assessment Principles................................................................................................................................................11
3.6.2 Assessment Method...................................................................................................................................................11
3.6.3 Assessment Conclusion.............................................................................................................................................11
3.7 Interface Bandwidth Assessment..................................................................................................................................11
4 Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios........................................................12
4.1 Traffic Model................................................................................................................................................................12
4.1.1 Definition of Peak Hour............................................................................................................................................12
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential iv
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node V900R014C10
Capacity Assessment Guide Contents
4.1.2 Traffic Model Acquisition.........................................................................................................................................13
4.2 Baseline........................................................................................................................................................................25
4.3 License Capacity Assessment.......................................................................................................................................26
4.3.1 Assessment Principles...............................................................................................................................................26
4.3.2 Assessment Method...................................................................................................................................................26
4.3.3 Assessment Conclusion.............................................................................................................................................27
4.4 Static Capacity Assessment..........................................................................................................................................28
4.4.1 Assessment Principles...............................................................................................................................................28
4.4.2 Assessment Method...................................................................................................................................................28
4.4.3 Assessment Conclusion.............................................................................................................................................29
4.5 Signaling Processing Resource Assessment.................................................................................................................29
4.5.1 Assessment Method...................................................................................................................................................29
4.5.2 Assessment Conclusion.............................................................................................................................................29
4.6 Forwarding Resource Assessment................................................................................................................................30
4.6.1 Assessment Method...................................................................................................................................................30
4.6.2 Assessment Conclusion.............................................................................................................................................31
4.7 Comprehensive Resource Assessment.........................................................................................................................31
4.7.1 Assessment Method...................................................................................................................................................31
4.7.2 Assessment Conclusion.............................................................................................................................................32
4.8 Interface Bandwidth Assessment..................................................................................................................................32
4.8.1 Loading Rate.............................................................................................................................................................32
4.8.2 Assessment Procedure...............................................................................................................................................33
4.8.3 Calculation Formula for Interface Bandwidth Used on the Live Network...............................................................33
4.8.4 Calculation Formula for Configured Physical Bandwidths.......................................................................................35
4.8.5 Assessment Method...................................................................................................................................................38
4.8.6 Assessment Conclusion.............................................................................................................................................38
5 Capacity Assessment and Optimization Services.................................................................39
5.1 Overview......................................................................................................................................................................39
5.2 Services.........................................................................................................................................................................40
5.2.1 Evaluation on Phone Distribution and Traffic Models..............................................................................................40
5.2.2 Evaluation on Resource Usage of the Existing Network..........................................................................................40
5.2.3 Traffic Model Forecast..............................................................................................................................................41
5.2.4 Forecast on the Number of Users..............................................................................................................................41
5.2.5 Forecast on Resource Capacity Requirements..........................................................................................................42
A Acronyms and Abbreviations....................................................................................................43
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential v
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node
Capacity Assessment Guide OverviewOverview
1 Overview
1.1 Background
After deploying the EPC networks, carriers need to learn about support of the current
configurations for services and whether traffic models can be supported under specific events
and conditions.
In EPC networks, capacity of USN9810s functioning as MMEs directly affects quality of EPC
data services. Therefore, carriers urgently require USN9810 capacity assessment and
optimization.
1.2 Scope
This document is applicable to USN9810 capacity assessment and optimization.
This document is intended for network optimization and maintenance engineers.
1.3 Networking Overview
As the EPC network evolves, networking schemes become more complex. Different
assessment methods are required for different networking schemes. This section describes the
networking schemes in use and provides a reference for determining assessment methods for
other networking schemes.
GUL Convergence Networking
In GUL convergence scenarios, the USN9810 that functions as a combined MME/SGSN
supports GUL access. Figure 1.1 shows the typical networking scheme.
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 1
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node
Capacity Assessment Guide OverviewOverview
Figure 1.1 Networking where the USN9810 functions as both the Gn/Gp SGSN and the MME
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 2
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node
Capacity Assessment Guide OverviewOverview
LTE Networking
In EPC networks, the USN9810 that functions as an MME only supports EPC services and is
not involved in user-plane data forwarding. Figure 1.2 shows the typical networking scheme.
Figure 1.2 Networking where the USN9810 functions as an MME
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 3
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node
Capacity Assessment Guide OverviewOverview
GU Networking with USN9810
In GU networks, the USN9810 that functions as an SGSN only supports 2G and 3G services.
Figure 1.3 shows the typical networking scheme.
Figure 1.3 Networking where the USN9810 functions as a Gn/Gp SGSN
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 4
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Assessment and Optimization ProcedureAssessment and
Capacity Assessment Guide Optimization Procedure
2 Assessment and Optimization Procedure
To assess USN9810 capacity, perform the following steps:
Step 2 Assess license capacity.
Assess the proportions of the numbers of active subscribers and PDP contexts/dedicated
bearers on the live network to the numbers of subscribers and PDP contexts/bearers specified
in the license respectively and provide an assessment conclusion.
Step 3 Assess static capacity.
Assess the proportions of the numbers of active subscribers and PDP contexts/dedicated
bearers on the live network to the maximum numbers of subscribers and PDP contexts/bearers
supported by the hardware respectively and provide an assessment conclusion.
Step 4 Assess signaling resource usage.
Assess the proportions of the numbers of active subscribers and PDP contexts/bearers on the
live network to the maximum numbers of subscribers and PDP contexts/bearers supported by
the USN9810 respectively and provide an assessment conclusion.
Step 5 Assess forwarding resource usage.
Assess GSM/UMTS forwarding resource usage in GUL convergence scenarios.
Step 6 Assess interface bandwidth usage.
Assess the proportion of the interface bandwidth used on the live network to the configured
interface bandwidth. If the proportion exceeds a specified baseline, capacity expansion is
required.
----End
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 5
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in EPC ScenariosCapacity
Capacity Assessment Guide Assessment in EPC Scenarios
3 Capacity Assessment in EPC Scenarios
3.1 Traffic Model
3.1.1 Definition of Peak Hour
A peak hour is the hour in which signaling or traffic load on a device reaches a maximum
within an assessment period. Peak hours can be categorized as signaling peak hours and
traffic peak hours.
Signaling Peak Hour
A signaling peak hour is the hour in which signaling load on a device reaches a maximum
within an assessment period.
To calculate the signaling peak hour, perform the following steps:
Step 7 Sum the values of the counters listed in Table 1.1 of each hour within the assessment period.
Step 8 Compare the values calculated in Step 1. The hour in which the maximum sum is calculated is
the signaling peak hour.
----End
Table 1.1 Reference counters for calculating the signaling peak hour
No. Counter
1 S1 mode Attach request Times
2 S1 mode combined attach request times
3 PDN connect request Times
4 S1 mode Service request Times
5 S1 mode Paging request Times
6 S1 mode Attach request Times
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 6
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in EPC ScenariosCapacity
Capacity Assessment Guide Assessment in EPC Scenarios
Because the MME is not involved in user-plane data forwarding in EPC networks, assessment during the
traffic peak hour is not involved. Data for bandwidth assessment of the S1-MME interface can be
obtained from assessment during signaling peak hours.
3.1.2 Traffic Model Acquisition
Performance Measurement on Live Networks
Table 1.2 Performance measurement
Parameter Performance EPC Calculation Formula
Type Measurement
Signaling Number of attach (Value of "Attach request Times" + Value of "S1
parameters requests (k) mode combined attach request times")/1000
Average number of Value of "Average attached users"/1000
attached subscribers (k)
Average number of PDP (Value of "Average dedicated bearer number" +
contexts/bearers (k) Value of "Average PDN connection
number")/1000
Number of PDP Value of "Dedicated bearer active request
context/dedicated bearer Times"/1000
activation requests (k)
Number of service Value of "Service request Times"/1000
requests (k)
Number of intra- [Value of "Intra TAU request Times(SGW not
SGSN/MME RAUs or change)" + Value of "Intra TAU request
TAUs (k) Times(SGW change)" + Value of "S1 mode intra
combined TAU request times(S-GW not change)"
+ Value of "S1 mode intra combined TAU request
times(S-GW change)" + Value of "Period TAU
request Times(SGW not change)" + Value of
"Period TAU request Times(SGW
change)"]/1000
Number of inter- [Value of "Inter TAU request Times(SGW not
SGSN/MME RAUs or change)" + Value of "Inter TAU request
TAUs (k) Times(SGW change)" + Value of "S1 mode inter-
MME combined TAU request times(S-GW not
change)" + Value of "S1 mode inter-MME
combined TAU request times(S-GW
change)"]/1000
EPC Signaling Model
For details, see Table 1.5.
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 7
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in EPC ScenariosCapacity
Capacity Assessment Guide Assessment in EPC Scenarios
3.2 Baseline
Table 1.3 lists USN9810 capacity assessment baselines.
Table 1.3 USN9810 capacity assessment baselines
Assessment Item Baseline
License resource usage 70%
Static resource usage 70%
Signaling processing resource usage 70%
Interface bandwidth usage 70%
3.3 License Capacity Assessment
3.3.1 Assessment Principles
USN9810 license capacity is assessed from the following aspects:
License resource usage based on subscribers
License resource usage based on dedicated bearers
License resource usage based on forwarding bandwidths
The license resource usage based on forwarding bandwidths is only applicable to license
capacity assessment in GUL convergence scenarios.
3.3.2 Assessment Method
Calculate license resource usage based on EPC subscribers, bearers, and forwarding
bandwidths and check whether the obtained values exceed specified baselines.
License Resource Usage Based on Subscribers
EPC: Value of "Maximum attached users"/Value of "Maximum Number of 4G Subscribers"
specified in the license x 100%
License Resource Usage Based on Dedicated Bearers
EPC: (Value of "Maximum dedicated bearer number" + Value of "Maximum PDN connection
number")/Value of "Maximum Number of 4G Bearer Number" specified in the license x
100%
(Value of "Maximum dedicated bearer number" + Value of "Maximum PDN connection
number")/(Value of "Maximum Number of 4G Dedicated Bearer Number" specified in the
license + Value of "Maximum Number of 4G Subscribers" specified in the license) x 100%
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 8
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in EPC ScenariosCapacity
Capacity Assessment Guide Assessment in EPC Scenarios
The number of active subscribers/PDP contexts on the live network is the maximum number of
subscribers/PDP contexts on the live network during a measurement period. The number of active
subscribers or PDP contexts on the live network is always less than that permitted by the license.
Therefore, precise license resource usage can be calculated only based on the actual maximum number
of subscribers/PDP contexts.
The total number of subscribers on the live network is the maximum value of "Maximum attached
users" within the assessment period.
The value of "Maximum attached users" can be acquired by choosing S1 mode user resource >
Maximum attached users.
For EPS bearers, "Maximum Number of EPC Bearer Number" or "Maximum Number of EPC
Dedicated Bearer Number" can be configured in the license, but you cannot configure both of them.
Choose the corresponding algorithm for the assessment of either the license control item.
3.3.3 Assessment Conclusion
If the resource usage exceeds the baseline specified in section 3.2"Baseline", optimization is
required.
3.4 Static Capacity Assessment
3.4.1 Assessment Principles
USN9810 static capacity involves only the maximum numbers of subscribers and bearers
supported by a USN9810, which can be obtained based on the number of boards configured in
the USN9810 and the maximum numbers of subscribers and bearers supported per board.
USN9810 static capacity is assessed under no license control. If USN9810 static capacity
does not meet requirements, hardware must be expanded.
3.4.2 Assessment Method
Board Specifications
Calculate the number of subscribers and that of bearers supported by ECUs in the USN9810
based on the number of subscribers and that of bearers supported by each ECU.
Static resource specification for subscribers of ECUs = Total number of ECUs/2 x Static
resource specification for subscribers per ECU
Static resource specification for PDP contexts/bearers of ECUs = Total number of ECUs/2 x
Static resource specification for bearers per ECU
Contact the USN9810 product manager to obtain the numbers of subscribers and PDP contexts
supported by each board.
Resource Usage
ECU static resource usage (subscribers) in the system = (Value of "Gb mode average attached
users" + Value of "Iu mode average attached users" + Value of "Average attached
users")/Static resource specification for subscribers of ECUs x 100%
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 9
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in EPC ScenariosCapacity
Capacity Assessment Guide Assessment in EPC Scenarios
ECU static resource usage (PDP contexts/bearers) in the system = (Value of "Gb mode
average act PDP context" + Value of "Iu mode average active PDP context" + Value of
"Average dedicated bearer number" + Value of "Average PDN connection number")/Static
resource specification for PDP contexts/bearers of ECUs x 100%
The number of bearers activated on the live network during peak hours is the total number of dedicated
and default bearers. The value of "Average PDN connection number" replaces the average number of
default bearers because one default bearer is set up each time one PDN connection is set up.
3.4.3 Assessment Conclusion
If the resource usage exceeds the baseline specified in section 3.2"Baseline", optimization is
required for the static resource.
3.5 Signaling Processing Resource Assessment
3.5.1 Assessment Principles
For details, see section 4.5"Signaling Processing Resource Assessment."
3.5.2 Assessment Method
Board Specifications
ECU subscriber specification = Subscriber specification per ECU x Number of ECU pairs
ECU bearer specification = Bearer specification per ECU x Number of ECU pairs
Contact Huawei product manager to obtain the board specifications.
Resource Usage
ECU signaling resource usage (SAU) in the system = Value of "Average attached users"/ECU
subscriber specification x 100%
ECU signaling resource usage (PDP contexts) in the system = (Value of "Average dedicated
bearer number" + Value of "Average PDN connection number")/ECU subscriber specification
x 100%
3.5.3 Assessment Conclusion
If the resource usage exceeds the baseline specified in section 3.2"Baseline", optimization is
required for the resource.
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 10
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in EPC ScenariosCapacity
Capacity Assessment Guide Assessment in EPC Scenarios
3.6 Comprehensive Resource Assessment
3.6.1 Assessment Principles
The comprehensive capacity assessment is implemented by summarizing all the factors
affecting the system capacity and identifying the resource bottleneck. The comprehensive
capacity assessment includes the license capacity assessment, static capacity assessment, and
signaling processing resource assessment. The resource bottleneck determines the capacity of
the entire system, such as the maximum number of subscribers or that of bearers supported by
the system.
3.6.2 Assessment Method
Summarize assessment conclusions for the number of subscribers and number of bearers to
obtain the resource bottleneck of the entire system. The bottleneck determines the
specifications of the USN9810.
Table 1.4 Assessment conclusions
License Static Signaling Processing Resource
Resource Resource Resource Bottleneck
SAU ECU SAU ECU SAU ECU SAU
BEARER ECU BEARER ECU BEARER ECU BEARER
Resource usage = Statistics on the live network/Bottleneck specification x 100%
Resource usage based on the number of subscribers = Value of "Average attached
users"/Bottleneck specification for the number of subscribers x 100%
Resource usage based on the number of bearers = (Value of "Average dedicated bearer
number" + Value of "Average PDN connection number")/Bottleneck specification for the
number of bearers x 100%
3.6.3 Assessment Conclusion
If resource usage exceeds the baseline specified in section 3.2"Baseline", optimization for the
bottleneck resource is required.
3.7 Interface Bandwidth Assessment
Because the MME is not involved in user-plane data forwarding in EPC scenarios, only the
bandwidth of the S1-MME interface is assessed. For details about the assessment method, see
section 4.8"Interface Bandwidth Assessment."
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 11
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
4 Capacity Assessment in GUL
Convergence Scenarios
4.1 Traffic Model
4.1.1 Definition of Peak Hour
A peak hour is the hour in which signaling or traffic load on a device reaches a maximum
within an assessment period. Peak hours can be categorized as signaling peak hours and
traffic peak hours.
Signaling Peak Hour
A signaling peak hour is the hour in which signaling load on a device reaches a maximum
within an assessment period.
To calculate the signaling peak hour, perform the following steps:
Step 9 Sum the values of the reference counters listed in Table 1.1 of each hour within the
assessment period.
Step 10 Compare the values calculated in Step 1. The hour in which the maximum sum is calculated is
the signaling peak hour.
----End
Table 1.1 Reference counters for calculating the signaling peak hour
No. Counter
1 Gb mode GPRS attach request times
2 Gb mode MS init PDP context act
3 Gb mode Inter-SGSN RAU request times
4 Gb mode Intra-SGSN RAU request times
5 Gb mode packet paging request times
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 12
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
No. Counter
6 Iu mode GPRS attach request times
7 Iu mode MS init PDP context act
8 Iu mode Inter-SGSN RAU request times
9 Iu mode Intra-SGSN RAU request times
10 Iu mode packet paging request times
11 Iu mode Service Request times
12 S1 mode Attach request Times
13 S1 mode combined attach request times
14 PDN connect request Times
15 S1 mode Service request Times
16 S1 mode Paging request Times
Traffic Peak Hour
A traffic peak hour is the hour in which the service traffic reaches a maximum within the
assessment period, the hour in which the sum of values of the counter "Gn Mean Throughput"
reaches a maximum. The value of "Gn Mean Throughput" can be acquired by choosing
GTPU data packet transfer > Gn Mean Throughput.
Because the MME is not involved in user-plane data forwarding in EPC networks, the traffic peak hour
is only used to acquire 2G and 3G traffic models in GUL convergence scenarios.
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 13
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
4.1.2 Traffic Model Acquisition
Performance Measurement on Live Networks
Table 1.2 Performance measurement
Parameter Performance 2G 3G EPC Remarks
Type Measurement Calculation Calculation Calculation
Formula Formula Formula
Signaling Number of Value of "Gb Value of "Iu (Value of "Attach The value of "Gb
parameters attach requests mode GPRS mode GPRS request Times" + mode GPRS attach
(k) attach request attach request Value of "S1 request times" can
times"/1000 times"/1000 mode combined be acquired by
attach request choosing Gb mode
times")/1000 attach > Gb mode
GPRS attach
request times.
The value of "Iu mode
GPRS attach request
times" can be
acquired by
choosing Iu mode
attach > Iu mode
GPRS attach
request times.
Average Value of "Gb Value of "Iu Value of The value of "Gb
number of mode average mode average "Average mode average
attached attached attached attached attached users" can
subscribers (k) users"/1000 users"/1000 users"/1000 be acquired by
choosing Gb mode
radio resource >
Gb mode average
attached users.
The value of "Iu mode
average attached
users" can be
acquired by
choosing Iu mode
radio resource > Iu
mode average
attached users.
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 14
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
Parameter Performance 2G 3G EPC Remarks
Type Measurement Calculation Calculation Calculation
Formula Formula Formula
Average Value of "Gb Value of "Iu (Value of The value of "Gb
number of PDP mode average mode average "Average mode average act
contexts/bearer act PDP active PDP dedicated bearer PDP context" can be
s (k) context"/1000 context"/1000 number" + Value acquired by
of "Average PDN choosing Gb mode
connection SM resource > Gb
number")/1000 mode average act
PDP context.
The value of "Iu mode
average active PDP
context" can be
acquired by
choosing Iu mode
SM resource > Iu
mode average
active PDP context.
Number of Value of "Gb Value of "Iu Value of The value of "Gb
PDP mode MS init mode MS init "Dedicated mode MS init PDP
context/dedicat PDP context PDP context bearer active context act" can be
ed bearer act"/1000 act"/1000 request acquired by
activation Times"/1000 choosing Gb mode
requests (k) PDP context
activation > Gb
mode MS init PDP
context act.
The value of "Iu mode
MS init PDP context
act" can be acquired
by choosing Iu
mode PDP context
activation > Iu
mode MS init PDP
context act.
Number of N/A Value of "Iu Value of "Service The value of "Iu mode
service requests mode Service request Service Request
(k) Request Times"/1000 times" can be
times"/1000 acquired by
choosing Iu mode
service request > Iu
mode Service
Request times.
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 15
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
Parameter Performance 2G 3G EPC Remarks
Type Measurement Calculation Calculation Calculation
Formula Formula Formula
Number of Value of "Gb Value of "Iu [Value of "Intra The value of "Gb
intra- mode intra- mode intra- TAU request mode intra-SGSN
SGSN/MME SGSN RAU SGSN RAU Times(SGW not RAU request times"
RAUs or TAUs request request change)" + Value can be acquired by
(k) times"/1000 times"/1000 of "Intra TAU choosing Gb mode
request intra-SGSN RAU >
Times(SGW Gb mode intra-
change)" + Value SGSN RAU request
of "S1 mode times.
intra combined The value of "Iu mode
TAU request intra-SGSN RAU
times(S-GW not request times" can
change)" + Value be acquired by
of "S1 mode choosing Iu mode
intra combined intra-SGSN RAU >
TAU request Iu mode intra-
times(S-GW SGSN RAU request
change)" + Value times.
of "Period TAU
request
Times(SGW not
change)" + Value
of "Period TAU
request
Times(SGW
change)"]/1000
Number of Value of "Gb Value of "Iu [Value of "Inter The value of "Gb
inter- mode Inter- mode Inter- TAU request mode Inter-SGSN
SGSN/MME SGSN RAU SGSN RAU Times(SGW not RAU request times"
RAUs or TAUs request request change)" + Value can be acquired by
(k) times"/1000 times"/1000 of "Inter TAU choosing Gb mode
request inter-SGSN RAU >
Times(SGW Gb mode Inter-
change)" + Value SGSN RAU request
of "S1 mode times.
inter-MME The value of "Iu mode
combined TAU Inter-SGSN RAU
request times(S- request times" can
GW not change)" be acquired by
+ Value of "S1 choosing Iu mode
mode inter-MME inter-SGSN RAU >
combined TAU Iu mode Inter-
request times(S- SGSN RAU request
GW times.
change)"]/1000
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 16
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
Parameter Performance 2G 3G EPC Remarks
Type Measurement Calculation Calculation Calculation
Formula Formula Formula
Traffic Forwarding Value of (Value of "3G N/A The value of "LLC
parameters rate (Mbit/s) "LLC Peak Uplink Data Peak Throughput"
(in GU Throughput" from RNC can be acquired by
scenarios) x 8/1024 Peak choosing SGSN
Throughput" LLC > LLC Peak
+ Value of Throughput.
"3G The value of "3G
Downlink Uplink Data from
Data Sent to RNC Peak
RNC Peak Throughput" can be
Throughput") acquired by
x 8/1024 choosing GTPU
bearer > 3G Uplink
Data from RNC
Peak Throughput.
The value of "3G
Downlink Data Sent
to RNC Peak
Throughput" can be
acquired by
choosing GTPU
bearer > 3G
Downlink Data
Sent to RNC Peak
Throughput.
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 17
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
Parameter Performance 2G 3G EPC Remarks
Type Measurement Calculation Calculation Calculation
Formula Formula Formula
Total traffic (Value of "Gb (Value of "Iu N/A The value of "Gb
(GB) mode uplink mode uplink mode uplink
Kbytes" + Kbytes" + Kbytes" can be
Value of "Gb Value of "Iu acquired by
mode mode choosing GTPU
downlink downlink data packet
Kbytes")/102 Kbytes")/102 transfer > Gb mode
4/1024 4/1024 uplink Kbytes.
The value of "Gb
mode downlink
Kbytes" can be
acquired by
choosing GTPU
data packet
transfer > Gb mode
downlink Kbytes.
The value of "Iu mode
uplink Kbytes" can
be acquired by
choosing GTPU
data packet
transfer > Iu mode
uplink Kbytes.
The value of "Iu mode
downlink Kbytes"
can be acquired by
choosing GTPU
data packet
transfer > Iu mode
downlink Kbytes.
Total Value of "Max UE transfer N/A The value of "Max
forwarding rate bandwidth" x 8/1024 UE transfer
(Mbit/s) bandwidth" can be
acquired by
choosing UE
transfer bandwidth
> Max UE transfer
bandwidth.
GU Signaling Model
Table 1.3 GU signaling model
Traffic Model Calculation Formula Remarks
Proportion of 2G: Value of "Gb mode The value of "Gb mode average act
activation to average act PDP PDP context" can be acquired by
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 18
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
Traffic Model Calculation Formula Remarks
attachment context"/Value of "Gb choosing Gb mode SM resource >
mode average attached Gb mode average act PDP context.
users" The value of "Gb mode average
3G: Value of "Iu mode attached users" can be acquired by
average active PDP choosing Gb mode radio resource >
context"/Value of "Iu mode Gb mode average attached users.
average attached users" The value of "Iu mode average active
PDP context" can be acquired by
choosing Iu mode SM resource > Iu
mode average active PDP context.
The value of "Iu mode average
attached users" can be acquired by
choosing Iu mode radio resource >
Iu mode average attached users.
Number of attach 2G: (Value of "Gb mode The value of "Gb mode GPRS attach
requests of a GPRS attach request request times" can be acquired by
subscriber times" + Value of "Gb choosing Gb mode attach > Gb
mode combined attach mode GPRS attach request times.
request times")/Value of The value of "Gb mode combined
"Gb mode average attached attach request times" can be acquired
users" by choosing Gb mode attach > Gb
3G: (Value of "Iu mode mode combined attach request
GPRS attach request times.
times" + Value of "Iu mode The value of "Gb mode average
combined attach request attached users" can be acquired by
times")/Value of "Iu mode choosing Gb mode radio resource >
average attached users" Gb mode average attached users.
The value of "Iu mode GPRS attach
request times" can be acquired by
choosing Iu mode attach > Iu mode
GPRS attach request times.
The value of "Iu mode combined
attach request times" can be acquired
by choosing Iu mode attach > Iu
mode combined attach request
times.
The value of "Iu mode average
attached users" can be acquired by
choosing Iu mode radio resource >
Iu mode average attached users.
Average duration 2G: Value of "Gb mode The value of "Gb mode average act
for an activated average act PDP PDP context" can be acquired by
PDP context context"/Value of "Gb choosing Gb mode SM resource >
(min) mode MS init PDP context Gb mode average act PDP context.
act" x 60 The value of "Gb mode MS init PDP
3G: Value of "Iu mode context act" can be acquired by
average active PDP choosing Gb mode PDP context
context"/Value of "Iu mode activation > Gb mode MS init PDP
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 19
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
Traffic Model Calculation Formula Remarks
MS init PDP context act" x context act.
60 The value of "Iu mode average active
PDP context" can be acquired by
choosing Iu mode SM resource > Iu
mode average active PDP context.
The value of "Iu mode MS init PDP
context act" can be acquired by
choosing Iu mode PDP context
activation > Iu mode MS init PDP
context act.
Number of 2G: Value of "Gb mode The value of "Gb mode MS init PDP
activation MS init PDP context context act" can be acquired by
requests of a act"/Value of "Gb mode choosing Gb mode PDP context
subscriber average attached users" activation > Gb mode MS init PDP
3G: Value of "Iu mode MS context act.
init PDP context act"/Value The value of "Gb mode average
of "Iu mode average attached users" can be acquired by
attached users" choosing Gb mode radio resource >
Gb mode average attached users.
The value of "Iu mode MS init PDP
context act" can be acquired by
choosing Iu mode PDP context
activation > Iu mode MS init PDP
context act.
The value of "Iu mode average
attached users" can be acquired by
choosing Iu mode radio resource >
Iu mode average attached users.
Number of Value of "Iu mode Service The value of "Iu mode Service Request
service requests Request times"/Value of times" can be acquired by choosing
of a subscriber "Iu mode average attached Iu mode service request > Iu mode
users" Service Request times.
The value of "Iu mode average
attached users" can be acquired by
choosing Iu mode radio resource >
Iu mode average attached users.
Number of Iu 3G: Value of "Release The value of "Release Requests
release requests Requests received"/Value received" can be acquired by
of a subscriber of "Iu mode average choosing RANAP > Release
attached users" Requests received.
The value of "Iu mode average
attached users" can be acquired by
choosing Iu mode radio resource >
Iu mode average attached users.
Number of intra- 2G: (Value of "Gb mode The value of "Gb mode intra-SGSN
SGSN RAU intra-SGSN RAU request RAU request times" can be acquired
requests of a times" + Value of "Gb by choosing Gb mode intra-SGSN
subscriber mode intra-SGSN Com- RAU > Gb mode intra-SGSN RAU
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 20
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
Traffic Model Calculation Formula Remarks
RAU request times")/Value request times.
of "Gb mode average The value of "Gb mode intra-SGSN
attached users" Com-RAU request times" can be
3G: (Value of "Iu mode acquired by choosing Gb mode
intra-SGSN RAU request intra-SGSN RAU > Gb mode intra-
times" + Value of "Iu mode SGSN Com-RAU request times.
intra-SGSN COM-RAU The value of "Gb mode average
request times")/Value of attached users" can be acquired by
"Iu mode average attached choosing Gb mode radio resource >
users" Gb mode average attached users.
The value of "Iu mode intra-SGSN
RAU request times" can be acquired
by choosing Iu mode intra-SGSN
RAU > Iu mode intra-SGSN RAU
request times.
The value of "Iu mode intra-SGSN
COM-RAU request times" can be
acquired by choosing Iu mode intra-
SGSN RAU > Iu mode intra-SGSN
COM-RAU request times.
The value of "Iu mode average
attached users" can be acquired by
choosing Iu mode radio resource >
Iu mode average attached users.
Number of inter- 2G: (Value of "Gb mode The value of "Gb mode Inter-SGSN
SGSN RAU Inter-SGSN RAU request RAU request times" can be acquired
requests of a times" + Value of "Gb by choosing Gb mode inter-SGSN
subscriber mode Inter-SGSN Com- RAU > Gb mode Inter-SGSN RAU
RAU request times")/Value request times.
of "Gb mode average The value of "Gb mode Inter-SGSN
attached users" Com-RAU request times" can be
3G: (Value of "Iu mode acquired by choosing Gb mode
Inter-SGSN RAU request inter-SGSN RAU > Gb mode Inter-
times" + Value of "Iu mode SGSN Com-RAU request times.
Inter-SGSN COM-RAU The value of "Gb mode average
request times")/Value of attached users" can be acquired by
"Iu mode average attached choosing Gb mode radio resource >
users" Gb mode average attached users.
The value of "Iu mode Inter-SGSN
RAU request times" can be acquired
by choosing Iu mode inter-SGSN
RAU > Iu mode Inter-SGSN RAU
request times.
The value of "Iu mode Inter-SGSN
COM-RAU request times" can be
acquired by choosing Iu mode inter-
SGSN RAU > Iu mode Inter-SGSN
COM-RAU request times.
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 21
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
Traffic Model Calculation Formula Remarks
The value of "Iu mode average
attached users" can be acquired by
choosing Iu mode radio resource >
Iu mode average attached users.
Number of 2G: Value of "Gb mode The value of "Gb mode packet paging
paging requests packet paging request request times" can be acquired by
of a subscriber times"/Value of "Gb mode choosing Gb mode paging > Gb
average attached users" mode packet paging request times.
3G: Value of "Iu mode The value of "Gb mode average
packet paging request attached users" can be acquired by
times"/Value of "Iu mode choosing Gb mode radio resource >
average attached users" Gb mode average attached users.
The value of "Iu mode packet paging
request times" can be acquired by
choosing Iu mode paging > Iu mode
packet paging request times.
The value of "Iu mode average
attached users" can be acquired by
choosing Iu mode radio resource >
Iu mode average attached users.
GU Traffic Model
Table 1.4 GU traffic model
Traffic Calculation Formula Remarks
Model
Average size 2G: Value of "Gb mode The value of "Gb mode downlink Kbytes"
of a downlink Kbytes" x can be acquired by choosing GTPU data
downlink 1000/Value of "Gb mode packet transfer > Gb mode downlink
packet downlink packets" Kbytes.
(Byte) 3G: Value of "Iu mode The value of "Gb mode downlink packets"
downlink Kbytes" x can be acquired by choosing GTPU data
1000/Value of "Iu mode packet transfer > Gb mode downlink
downlink packets" packets.
The value of "Iu mode downlink Kbytes" can
be acquired by choosing GTPU data
packet transfer > Iu mode downlink
Kbytes.
The value of "Iu mode downlink packets" can
be acquired by choosing GTPU data
packet transfer > Iu mode downlink
packets.
Average size 2G: Value of "Gb mode The value of "Gb mode uplink Kbytes" can
of an uplink uplink Kbytes" x be acquired by choosing GTPU data
packet 1000/Value of "Gb mode packet transfer > Gb mode uplink
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 22
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
Traffic Calculation Formula Remarks
Model
(Byte) uplink packets" Kbytes.
3G: Value of "Iu mode The value of "Gb mode uplink packets" can
uplink Kbytes" x be acquired by choosing GTPU data
1000/Value of "Iu mode packet transfer > Gb mode uplink
uplink packets" packets.
The value of "Iu mode uplink Kbytes" can be
acquired by choosing GTPU data packet
transfer > Iu mode uplink Kbytes.
The value of "Iu mode uplink packets" can be
acquired by choosing GTPU data packet
transfer > Iu mode uplink packets.
Average 2G: (Value of "Gb mode The value of "Gb mode uplink Kbytes" can
forwarding uplink Kbytes" + Value be acquired by choosing GTPU data
rate for an of "Gb mode downlink packet transfer > Gb mode uplink
activated Kbytes") x 8/3600/Value Kbytes.
PDP context of "Gb mode average act The value of "Gb mode downlink Kbytes"
(kbps) PDP context" can be acquired by choosing GTPU data
3G: (Value of "Iu mode packet transfer > Gb mode downlink
uplink Kbytes" + Value Kbytes.
of "Iu mode downlink The value of "Gb mode average act PDP
Kbytes") x 8/3600/Value context" can be acquired by choosing Gb
of "Iu mode average mode SM resource > Gb mode average
active PDP context" act PDP context.
The value of "Iu mode uplink Kbytes" can be
acquired by choosing GTPU data packet
transfer > Iu mode uplink Kbytes.
The value of "Iu mode downlink Kbytes" can
be acquired by choosing GTPU data
packet transfer > Iu mode downlink
Kbytes.
The value of "Iu mode average active PDP
context" can be acquired by choosing Iu
mode SM resource > Iu mode average
active PDP context.
EPC Signaling Model
Table 1.5 EPC signaling model
Traffic Model Calculation Remarks
Formula
Proportion of Value of "Average The value of "Average dedicated bearer
activated dedicated dedicated bearer number" can be acquired by choosing S1
bearers to attached number"/Value of mode bearer resource > Average
subscribers "Average attached dedicated bearer number.
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 23
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
Traffic Model Calculation Remarks
Formula
users" The value of "Average attached users" can
be acquired by choosing S1 mode user
resource > Average attached users.
Number of attach (Value of "Attach The value of "Attach request Times" can
requests of a request Times" + be acquired by choosing S1 mode attach
subscriber in peak Value of "S1 mode > Attach request Times.
hours combined attach The value of "S1 mode combined attach
request times")/Value request times" can be acquired by
of "Average attached choosing S1 mode attach > S1 mode
users" combined attach request times.
The value of "Average attached users" can
be acquired by choosing S1 mode user
resource > Average attached users.
Number of Value of "Dedicated The value of "Dedicated bearer active
dedicated bearer bearer active request request Times" can be acquired by
activation requests Times"/Value of choosing S1 mode bearer activation >
of a subscriber in "Average attached Dedicated bearer active request Times.
peak hours users" The value of "Average attached users" can
be acquired by choosing S1 mode user
resource > Average attached users.
Average duration Value of "Average The value of "Average dedicated bearer
for a dedicated dedicated bearer number" can be acquired by choosing S1
bearer (min) in number"/Value of mode bearer resource > Average
peak hours "Dedicated bearer dedicated bearer number.
active request Times" The value of "Dedicated bearer active
x 60 request Times" can be acquired by
choosing S1 mode bearer activation >
Dedicated bearer active request Times.
Number of service Value of "Service The value of "Service request Times" can
requests of a request Times"/Value be acquired by choosing S1 mode
subscriber in peak of "Average attached service request > Service request
hours users" Times.
The value of "Average attached users" can
be acquired by choosing S1 mode user
resource > Average attached users.
Number of S1 [Value of "eNodeB The value of "eNodeB initiated S1 release
release requests of initiated S1 release request Times(UE inactive cause)" can
a subscriber in request Times(UE be acquired by choosing S1 interface >
peak hours inactive cause)" + eNodeB initiated S1 release request
Value of "eNodeB Times(UE inactive cause).
initiated S1 release The value of "eNodeB initiated S1 release
request Times(Others request Times(Others cause)" can be
cause)"]/Value of acquired by choosing S1 interface >
"Average attached eNodeB initiated S1 release request
users" Times(Others cause).
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 24
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
Traffic Model Calculation Remarks
Formula
The value of "Average attached users" can
be acquired by choosing S1 mode user
resource > Average attached users.
Number of intra- [Value of "Intra TAU The value of "Intra TAU request
MME TAU request Times(SGW Times(SGW not change)" can be
requests of a not change)" + Value acquired by choosing S1 mode intra-
subscriber in peak of "Intra TAU request MME tracking area update > Intra
hours Times(SGW change)" TAU request Times(SGW not change).
+ Value of "S1 mode The value of "Intra TAU request
intra combined TAU Times(SGW change)" can be acquired by
request times(S-GW choosing S1 mode intra-MME tracking
not change)" + Value area update > Intra TAU request
of "S1 mode intra Times(SGW change).
combined TAU
request times(S-GW
The value of "S1 mode intra combined
change)" + Value of TAU request times(S-GW not change)"
"Period TAU request can be acquired by choosing S1 mode
Times(SGW not intra-MME tracking area update > S1
change)" + Value of mode intra combined TAU request
"Period TAU request times(S-GW not change).
Times(SGW The value of "S1 mode intra combined
change)"]/Value of TAU request times(S-GW change)" can
"Average attached be acquired by choosing S1 mode intra-
users" MME tracking area update > S1 mode
intra combined TAU request times(S-
GW change).
The value of "Period TAU request
Times(SGW not change)" can be
acquired by choosing S1 mode intra-
MME tracking area update > Period
TAU request Times(SGW not change).
The value of "Period TAU request
Times(SGW change)" can be acquired by
choosing S1 mode intra-MME tracking
area update > Period TAU request
Times(SGW change).
The value of "Average attached users" can
be acquired by choosing S1 mode user
resource > Average attached users.
Number of inter- [Value of "Inter TAU The value of "Inter TAU request
MME TAU request Times(SGW Times(SGW not change)" can be
requests of a not change" + Value acquired by choosing S1 mode inter-
subscriber in peak of "Inter TAU request MME tracking area update > Inter
hours Times(SGW change)" TAU request Times(SGW not change).
+ Value of "S1 mode The value of "Inter TAU request
inter-MME combined Times(SGW change)" can be acquired by
TAU request times(S- choosing S1 mode inter-MME tracking
GW not change)" + area update > Inter TAU request
Value of "S1 mode Times(SGW change).
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 25
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
Traffic Model Calculation Remarks
Formula
inter-MME combined The value of "S1 mode inter-MME
TAU request times(S- combined TAU request times(S-GW not
GW change)"]/Value change)" can be acquired by choosing S1
of "Average attached mode inter-MME tracking area
users" update > S1 mode inter-MME
combined TAU request times(S-GW
not change).
The value of "S1 mode inter-MME
combined TAU request times(S-GW
change)" can be acquired by choosing S1
mode inter-MME tracking area
update > S1 mode inter-MME
combined TAU request times(S-GW
change).
The value of "Average attached users" can
be acquired by choosing S1 mode user
resource > Average attached users.
Number of paging [Value of "Paging The value of "Paging request Times" can
requests of a request Times" + be acquired by choosing S1 mode
subscriber in peak Value of "Paging paging > Paging request Times.
hours (PS data) request repeat The value of "Paging request repeat
Times"]/Value of Times" can be acquired by choosing S1
"Average attached mode paging > Paging request repeat
users" Times.
The value of "Average attached users" can
be acquired by choosing S1 mode user
resource > Average attached users.
4.2 Baseline
Table 1.6 lists USN9810 capacity assessment baselines.
Table 1.6 USN9810 capacity assessment baselines
Assessment Item Baseline
License resource usage 70%
Static resource usage 70%
Signaling processing resource usage 70%
Forwarding resource usage (SAU/PDP) 70%
Forwarding bandwidth usage (Mbps/pps) 70%
Interface bandwidth usage 70%
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 26
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
4.3 License Capacity Assessment
4.3.1 Assessment Principles
USN9810 license capacity is assessed from the following aspects:
License resource usage based on subscribers
License resource usage based on dedicated bearers
License resource usage based on forwarding bandwidths
The license resource usage based on forwarding bandwidths is only applicable to license
capacity assessment in GUL convergence scenarios.
4.3.2 Assessment Method
Calculate license resource usage based on EPC subscribers, bearers, and forwarding
bandwidths and check whether the obtained values exceed specified baselines.
License Resource Usage Based on Subscribers
2G: Value of "Gb mode maximum attached users"/(Value of "Maximum Number of 2.5G
Subscribers" specified in the license + Value of "Maximum Number of 2.5G/3G Common
Subscribers" specified in the license) x 100%
3G: Value of "Iu mode maximum attached users"/(Value of "Maximum Number of 3G
Subscribers" specified in the license + Value of "Maximum Number of 2.5G/3G Common
Subscribers" specified in the license) x 100%
EPC: Value of "Maximum attached users"/Value of "Maximum Number of 4G Subscribers"
specified in the license x 100%
License resource usage based on total number of subscribers: (Value of "Gb mode maximum
attached users" + Value of "Iu mode maximum attached users" + Value of "Maximum
attached users")/(Value of "Maximum Number of 2.5G Subscribers" specified in the license +
Value of "Maximum Number of 3G Subscribers" specified in the license + Value of
"Maximum Number of 2.5G/3G Common Subscribers" specified in the license + Value of
"Maximum Number of 4G Subscribers" specified in the license) x 100%
License Resource Usage Based on PDP Contexts/Dedicated Bearers
2G: Value of "Gb mode maximum act PDP context"/(Value of "Maximum Number of 2.5G
Active PDPs" specified in the license + Value of "Maximum Number of 2.5G/3G Common
Active PDPs" specified in the license) x 100%
3G: Value of "Iu mode maximum active PDP context"/(Value of "Maximum Number of 3G
Active PDPs" specified in the license + Value of "Maximum Number of 2.5G/3G Common
Active PDPs" specified in the license) x 100%
EPC: (Value of "Maximum dedicated bearer number" + Value of "Maximum PDN connection
number")/Value of "Maximum Number of 4G Bearer Number" specified in the license x
100%
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 27
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
(Value of "Maximum dedicated bearer number" + Value of "Maximum PDN connection
number")/(Value of "Maximum Number of 4G Dedicated Bearer Number" specified in the
license + Value of "Maximum Number of 4G Subscribers" specified in the license) x 100%
License resource usage based on total number of PDP contexts/bearers: (Value of "Gb mode
maximum act PDP context" + Value of "Iu mode maximum active PDP context" + Value of
"Maximum dedicated bearer number" + Value of "Maximum PDN connection number")/
(Value of "Maximum Number of 2.5G Active PDPs" specified in the license + Value of
"Maximum Number of 3G Active PDPs" specified in the license + Value of "Maximum
Number of 2.5G/3G Common Active PDPs" specified in the license + Value of "Maximum
Number of 4G Bearer Number" specified in the license + Value of "Maximum Number of 4G
Dedicated Bearer Number" specified in the license)
The number of active subscribers/PDP contexts on the live network is the maximum number of
subscribers/PDP contexts on the live network during a measurement period. The number of active
subscribers or PDP contexts on the live network is always less than that permitted by the license.
Therefore, precise license resource usage can be calculated only based on the actual maximum number
of subscribers/PDP contexts.
The total number of subscribers on the live network is the maximum sum of the values of "Gb mode
maximum attached users", "Iu mode maximum attached users", and "Maximum attached users" within
the assessment period.
For EPS bearers, "Maximum Number of EPC Bearer Number" or "Maximum Number of EPC
Dedicated Bearer Number" can be configured in the license, but you cannot configure both of them.
Choose the corresponding algorithm for the assessment of either the license control item.
License Resource Usage Based on Forwarding Bandwidths
The formula for calculating the license resource usage based on forwarding bandwidths:
License resource usage based on forwarding bandwidths = Value of "Max UE transfer
bandwidth" x 8/1024/Value of "Maximum Transmit Capability of User Plane(Mbit/s)"
specified in the license x 100%
The maximum value of "Max UE transfer bandwidth" within the assessment period must be used in the
formula.
4.3.3 Assessment Conclusion
If the resource usage exceeds the baseline specified in section 4.2"Baseline", optimization is
required.
4.4 Static Capacity Assessment
4.4.1 Assessment Principles
USN9810 static capacity involves only the maximum numbers of subscribers and bearers
supported by a USN9810, which can be obtained based on the number of boards configured in
the USN9810 and the maximum numbers of subscribers and bearers supported per board.
USN9810 static capacity is assessed under no license control. If USN9810 static capacity
does not meet requirements, hardware must be expanded.
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 28
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
4.4.2 Assessment Method
Board Specifications
Calculate the number of subscribers and that of bearers supported by ECUs in the USN9810
based on the number of subscribers and that of bearers supported by each ECU.
Static resource specification for subscribers of ECUs = Total number of ECUs/2 x Static
resource specification for subscribers per ECU
Static resource specification for PDP contexts/bearers of ECUs = Total number of ECUs/2 x
Static resource specification for bearers per ECU
Static resource specification for PDP contexts of EPUs = Total number of EPUs/2 x Static
resource specification for PDP contexts per EPU
Contact the USN9810 product manager to obtain the numbers of subscribers and PDP contexts
supported by each board.
Run the following commands to obtain the numbers of ECUs and EPUs installed in an USN9810:
ADD
BRD:SRN=0,SN=1,METYPE=SGSN,FBRDHTYP=UPBA3,APPTYPE=ECU,MOG="PUBLIC",REFERABLE=Y
ES;
ADD
BRD:SRN=0,SN=11,METYPE=SGSN,FBRDHTYP=MSPB0,BBRDHTYP=PFIA0,APPTYPE=EPU,BUPDBRDT
YPE=EEC,BDOWNDBRDTYPE=EEC,MOG="PUBLIC",REFERABLE=YES;
APPTYPE specifies the board type in the commands.
Resource Usage
ECU static resource usage (subscribers) in the system = (Value of "Gb mode average attached
users" + Value of "Iu mode average attached users" + Value of "Average attached
users")/Static resource specification for subscribers of ECUs x 100%
ECU static resource usage (PDP contexts/bearers) in the system = (Value of "Gb mode
average act PDP context" + Value of "Iu mode average active PDP context" + Value of
"Average dedicated bearer number" + Value of "Average PDN connection number")/Static
resource specification for PDP contexts/bearers of ECUs x 100%
EPU static resource usage (PDP contexts/bearers) in the system = (Value of "Gb mode
average act PDP context" + Value of "Iu mode average active PDP context" + Value of
"Average dedicated bearer number" + Value of "Average PDN connection number")/Static
resource specification for PDP contexts of EPUs x 100%
The number of bearers activated on the live network during peak hours is the total number of dedicated
and default bearers. The value of "Average PDN connection number" replaces the average number of
default bearers because one default bearer is set up each time one PDN connection is set up.
4.4.3 Assessment Conclusion
If the resource usage exceeds the baseline specified in section 4.2"Baseline", optimization is
required for the static resource.
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 29
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
4.5 Signaling Processing Resource Assessment
4.5.1 Assessment Method
Board Specifications
ECU subscriber specification = Subscriber specification per ECU x Number of ECU pairs
ECU bearer specification = Bearer specification per ECU x Number of ECU pairs
EPU subscriber specification = Subscriber specification per EPU x Number of EPU pairs
EPU bearer specification = Bearer specification per EPU x Number of EPU pairs
System subscriber specification = MIN(ECU subscriber specification,EPU subscriber
specification)
System bearer specification = MIN(ECU bearer specification,EPU bearer specification)
Contact Huawei product manager to obtain the board specifications.
Resource Usage
ECU resource usage (SAU) in the system = (Value of "Gb mode average attached users" +
Value of "Iu mode average attached users" + Value of "Average attached users")/ECU
subscriber specification x 100%
EPU resource usage (SAU) in the system = (Value of "Gb mode average attached users" +
Value of "Iu mode average attached users")/EPU subscriber specification x 100%
ECU resource usage (PDP contexts) in the system = (Value of "Gb mode average act PDP
context" + Value of "Iu mode average active PDP context" + Value of "Average dedicated
bearer number" + Value of "Average PDN connection number")/ECU subscriber specification
x 100%
EPU resource usage (PDP contexts) in the system = (Value of "Gb mode average act PDP
context" + Value of "Iu mode average active PDP context")/EPU subscriber specification x
100%
4.5.2 Assessment Conclusion
If the resource usage exceeds the baseline specified in section 4.2"Baseline", optimization is
required for the resource.
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 30
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
4.6 Forwarding Resource Assessment
4.6.1 Assessment Method
User-plane Forwarding Resource Usage Assessment
Assess the usage of user-plane forwarding resources based on the traffic and packet
forwarding rate. The forwarding traffic on a board can be calculated based on the forwarding
procedures in different networking schemes.
Usage of user-plane forwarding resources = Statistics on the live network/Forwarding
capacity of the entire system x 100%
Table 1.7 User-plane forwarding resource usage assessment
Assessment Statistics on the Live Network Forwarding Capacity of
Item the Entire System
ECU forwarding (Value of "Gb mode uplink Kbytes" + Data forwarding capacity
traffic (Mbit/s) Value of "Gb mode downlink (Mbit/s) per ECU x Number
Kbytes") x 8/1024/3600 of ECUs/2
ECU packet (Value of "Gb mode uplink packets" + Packet forwarding capacity
forwarding rate Value of "Gb mode downlink (pps) per ECU x Number of
(pps) packets")/3600 ECUs/2
EPU forwarding (Value of "Gb mode uplink Kbytes" + Data forwarding capacity
traffic (Mbit/s) Value of "Gb mode downlink (Mbit/s) per EPU x Number
Kbytes") x 8/1024/3600 x (1 + Gb of EPUs/2
over IP proportion) + (Value of "Iu
mode uplink Kbytes" + Value of "Iu
mode downlink Kbytes") x
8/1024/3600
EPU packet (Value of "Gb mode uplink packets" + Packet forwarding capacity
forwarding rate Value of "Gb mode downlink (pps) per EPU x Number of
(pps) packets") x 8/1024/3600 x (1 + Gb EPUs/2
over IP proportion) + (Value of "Iu
mode uplink packets" + Value of "Iu
mode downlink packets") x
8/1024/3600
Data collected during peak hours is used in performance measurement.
Contact the project management office (PMO) to obtain the data forwarding capacity of each ECU or
EPU.
Gb over IP proportion = 1 (Value of "NS Kbytes sent to FR" + Value of "NS Kbytes received from
FR")/(Value of "NS Kbytes sent to FR" + Value of "NS Kbytes received from FR" + Value of "NS
Downlink data Kbytes sent to IP" + Value of "NS Uplink data Kbytes received from IP")
The value of "NS Kbytes sent to FR" can be acquired by choosing SGSN NS > NS Kbytes sent to FR.
The value of "NS Kbytes received from FR" can be acquired by choosing SGSN NS > NS Kbytes
received from FR.
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 31
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
The value of "NS Downlink data Kbytes sent to IP" can be acquired by choosing IP NS > NS Downlink
data Kbytes sent to IP.
The value of "NS Uplink data Kbytes received from IP" can be acquired by choosing IP NS > NS
Uplink data Kbytes received from IP
Board Specifications
Forwarding resource specification = Board specification x Number of board pairs
The board resource specification includes:
Board specification for the number of subscribers
Board specification for the number of PDP contexts
Contact Huawei product manager to obtain the board specifications.
Resource Usage
Resource usage based on the number of subscribers = Number of active subscribers on
the live network/Specification for the number of subscribers per USN9810 x 100%
Resource usage based on the number of PDP contexts = Number of PDP contexts on the
live network/Specification for the number of PDP contexts per USN9810 x 100%
4.6.2 Assessment Conclusion
If the user-plane forwarding resource usage exceeds the baseline specified in section
4.2"Baseline", optimization is required.
If the forwarding resource usage based on the number of subscribers exceeds the
baseline specified in section 4.2"Baseline", optimization is required.
If the forwarding resource usage based on the number of PDP contexts exceeds the
baseline specified in section 4.2"Baseline", optimization is required.
4.7 Comprehensive Resource Assessment
4.7.1 Assessment Method
Summarize assessment conclusions for the number of subscribers, number of PDP contexts,
and traffic to obtain the resource bottleneck of the entire system. The bottleneck determines
the specifications of the USN9810.
Table 1.8 Assessment conclusions
Assessment License Static Signaling and Bottleneck
Item Resource Resource Forwarding Specification
Specification Specification Resource
Specifications
Number of Specification Specification Specifications for Bottleneck
subscribers for the total for the total the total number of specification
number of number of subscribers for the number
subscribers subscribers of subscribers
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 32
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
Assessment License Static Signaling and Bottleneck
Item Resource Resource Forwarding Specification
Specification Specification Resource
Specifications
Number of Specification Specification Specifications for Bottleneck
PDP contexts for the total for the total the total number of specification
number of PDP number of PDP PDP contexts for the number
contexts contexts of PDP
contexts
Traffic Specification N/A Specifications for Bottleneck
for total traffic total traffic specification
for traffic
Resource usage = Statistics on the live network/Bottleneck specification x 100%
Resource usage based on the number of subscribers = (Value of "Gb mode average attached
users" + Value of "Iu mode average attached users" + Value of "Average attached
users")/Bottleneck specification for the number of subscribers x 100%
Resource usage based on the number of PDP contexts = (Value of "Gb mode average act PDP
context" + Value of "Iu mode average active PDP context" + Value of "Average dedicated
bearer number" + Value of "Average PDN connection number")/Bottleneck specification for
the number of PDP contexts x 100%
Traffic usage = (Value of "Gb mode uplink Kbytes" + Value of "Gb mode downlink Kbytes")
x 8/1024/3600 x (1 + Gb over IP proportion) + (Value of "Iu mode uplink Kbytes" + Value of
"Iu mode downlink Kbytes") x 8/1024/3600/Bottleneck specification for traffic x 100%
4.7.2 Assessment Conclusion
If resource usage exceeds the baseline specified in section 4.2"Baseline", optimization for the
bottleneck resource is required.
4.8 Interface Bandwidth Assessment
4.8.1 Loading Rate
If the size of each packet is 420 bytes, the recommended default loading rates are described in
Table 1.9.
Table 1.9 Recommended default loading rate
Category Payload Loading Rate
GB&Gr over FR 0.38
Iu over ATM 0.45
Gb&Iu&Gr&Gn&Ga over IP 0.50
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 33
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
Category Payload Loading Rate
Gi 0.54
4.8.2 Assessment Procedure
To assess the bandwidth of each interface, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Determine the loading rate according to the bearer type.
Step 2 Calculate the bandwidths of different interfaces using formulas in section 4.8.3"Calculation
Formula for Interface Bandwidth Used on the Live Network."
Step 3 Obtain the configured physical bandwidths of different interfaces based on section
4.8.4"Calculation Formula for Configured Physical Bandwidths."
Step 4 Calculate bandwidth usage of each interface using the following formula:
Bandwidth usage of an interface = Interface bandwidth used on the live network/Configured
interface bandwidth
Step 5 Compare bandwidth usage of different interfaces except the Gr over TDM interface with the
baseline.
----End
4.8.3 Calculation Formula for Interface Bandwidth Used on the
Live Network
Bandwidth Calculation Formula for the Gb Interface
Assess respectively the bandwidth of the IP-based Gb interface and that of the FR-based Gb
interface on the live network.
Bandwidth of the FR-based Gb interface (Mbit/s) = Value of "NS kbytes sent to FR" x
8/Performance measurement period (in seconds)/Loading rate/1024
Bandwidth of the IP-based Gb interface (Mbit/s) = Value of "NS Downlink data Kbytes sent
to IP" x 8/Performance measurement period (in seconds)/Loading rate/1024
Uplink traffic is far lighter than downlink traffic. Therefore, downlink traffic is used for interface
bandwidth calculation. For loading rates in the preceding formulas, see section 4.8.1"Loading Rate."
Bandwidth Calculation Formula for the Iu Interface
Bandwidth of the Iu interface = MAX(Downlink bandwidth of the Iu interface,Uplink
bandwidth of the Iu interface)
Downlink bandwidth of the Iu interface = Value of "Iu mode downlink Kbytes" x
8/Performance measurement period (in seconds)/Loading rate
Uplink bandwidth of the Iu interface = Value of "Iu mode uplink Kbytes" x 8/Performance
measurement period (in seconds)/Loading rate
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 34
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
Bandwidth Calculation Formula for the Gn Interface
Bandwidth of the Gn interface on the SGSN
Bandwidth of the Gn interface (Mbit/s) = Value of "Gn Mean Received Throughput " x
8/Loading rate/1024
Bandwidth Calculation Formula for the Ga Interface
Bandwidth of the Ga interface (kbit/s) = Value of "Kbytes of CDRs sent to CG" x
8/Performance measurement period (in seconds)/Loading rate
Bandwidth Calculation Formula for the Gr Interface
When the Gr interface uses M3UA bearers, the bandwidth of this interface is calculated as
follows:
Bandwidth of the Gr interface (Mbit/s) = MAX(Value of "M3UA link OCTETS sent",Value of
"M3UA link OCTETS received") x 8/Performance measurement period (in seconds)/Loading
rate/1024
If the Gr interface uses TDM bearers, perform the following steps to assess the bandwidth of
this interface:
Step 6 Calculate load of each link using the formula MAX(Value of "MTP3 link send load",Value of
"MTP3 link receive load"). Check whether the obtained value exceeds the specified baseline.
If the value exceeds the baseline, the load of the link is high and optimization is required. The
load assessment baselines for TDM 64K links and TDM 2M links are respectively 0.4 erlang
and 0.2 erlang.
Step 7 Assess a load balance among signaling links in the same link set and calculate standard
deviation coefficients for sent and received load of MTP3 signaling links.
The calculation formulas are as follows:
Standard deviation =
xx 2
n
Standard deviation coefficient = x x 100%
where
N indicates the number of links to the same destination signaling point (DSP).
X 1 , X 2 .... X N indicate sent or received load of each link.
X = X 1 X 2 ... X N /N
Step 8 Check whether the obtained value of a standard deviation coefficient exceeds the baseline
25%. If the obtained value exceeds 25%, load among links in the link set is unbalanced, and
therefore load adjustment is required.
----End
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 35
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
Performance statistics in signaling peak hours are used for Gr interface bandwidth assessment because
the Gr interface only carries signaling. Performance statistics in traffic peak hours are used for
bandwidth assessment of other interfaces.
Bandwidth Calculation Formula for the S1-MME Interface
Uplink bandwidth of the S1-MME interface (Mbit/s) = (Value of "Uplink message kbytes
received in S1 interface" + Value of "Uplink message packets received in S1 interface" x
62/1024)/1024 x 8/0.86/Performance measurement period (in seconds)
Downlink bandwidth of the S1-MME interface (Mbit/s) = (Value of "Downlink message
kbytes sent in S1 interface" + Value of "Downlink message packets sent in S1 interface" x
62/1024)/1024 x 8/0.86/Performance measurement period (in seconds)
Bandwidth of the S1-MME interface (Mbit/s) = MAX(Uplink bandwidth of the S1-MME
interface,Downlink bandwidth of the S1-MME interface)
Only control-plane traffic is transmitted over the S1-MME interface. Therefore, traffic on the interface is
low and the bandwidths cannot be the bottleneck. The preceding calculation formulas are used for
monitoring. In the formulas, 62 is the length of the packet header and 0.86 is default physical bandwidth
usage.
The USN9810 of the current version does not support calculation of S6a and S11 interface bandwidths
because traffic volumes on S6a and S11 interfaces cannot be measured.
4.8.4 Calculation Formula for Configured Physical Bandwidths
Configured physical bandwidths vary according to the physical ports in use. For example, if
the ports for the Gn interface are a pair of GE ports that work in active/standby mode, the
physical bandwidth is 1 Gbit/s. If 10 E1 cables compose the FR-based Gb interface and each
bearer channel (BC) on an E1 cable has 32 time slots, the bandwidth of each E1 cable is 2
Mbit/s and the physical bandwidth of a GB interface is 20 Mbit/s.
Bandwidth Calculation for the IP-based Gb (Iu, Gn, Ga, or Gr) Interface
Bandwidths of IP-based interfaces are calculated using the same method. The IP-based Gn
interface is used as an example.
Step 9 Query the subrack number and slot number of the Gn interface using the ADD IFIP
command in the MML configuration file, for example:
ADD IFIP: SRN = 0, SN = 11, PN = 4, IPT = PRI, IP = "180.214.235.196", MSK =
"255.255.255.240", DESC = "Gn";
In the preceding example, port 4 in slot 11 of subrack 1 is used as the port for the Gn
interface. Count the active physical ports configured in the system.
A physical port can be identified as the port for an Iu, Gn, Gb, or Ga interface from the
information in MML files, but such an identification result is not reliable. You need to obtain
information about network segments of interfaces based on networking schemes or by
contacting frontline personnel for confirmation.
Step 10 Query port status. Run the following command in the MML Command - CGP window to
query actual bandwidths of all active ports that are located in subracks housing EPUs:
DSP PORT: SRN = 0, STATE = ACTIVE;
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 36
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
Step 11 Based on the actual bandwidth obtained in Step 2, use the following formula to calculate
configured bandwidth of the Gn interface on the live network:
Configured bandwidth of the port for the Gn interface on the live network (Mbit/s) = N x
1000
Where
N is the number of active physical ports configured in the system.
----End
Bandwidth Calculation for the FR-based Gb Interface
In Gb over FR networking, view the number of timeslots that each BC has in the ADD BC
command settings in the MML configuration file. Then multiply the number with 64 kbit/s to
obtain physical bandwidth of the FR-based Gb interface.
Step 1 Calculate configured bandwidth of each BC by using the following formula:
Configured bandwidth of each BC (Mbit/s) = (Value of End time slot No. Value of Begin
time slot No. + 1) x 64/1024
The parameter IDs ETS and BTS indicate respectively End time slot No. and Begin time
slot No. The values of these parameters can be obtained from the information in the MML
configuration file, for example:
ADD BC: SRN = 0, SN = 8, PRON = 4, PN = 3, BCID = 0, BTS = 1, ETS = 31, DLCIT = 1,
PROTOCOL = Q933, BWCNTL = NO, BCMODE = DCE, NETN392 = 3, NETN393 = 4, NETT392 =
15, BCN = "BC_Bone(ZTE)_50411";
Step 2 Calculate the configured bandwidth of the FR-based Gb interface in the entire system using
the following formula:
Configured bandwidth of the FR-based Gb interface = SUM (Configured bandwidth of each
BC)
----End
Bandwidth Calculation for the ATM-based Iu Interface
Step 1 Query the values of flow parameter index (TRAF) of IPoA links in the ADD IPOA
command settings in the MML configuration file. The following is an example in which flow
parameter index is 73.
ADD IPOA: SRN = 3, SN = 2, PN = 0, VPI = 8, VCI = 40, TP = STATIC_MAP, BT = FALSE,
ETP = LLC, IP = "172.29.143.253", TRAF = 73, F5 = FALSE, DESC = "RNC_Leipzig_3_A";
Step 2 Calculate the bandwidth of an IPoA link
Based on the obtained value of flow parameter index in Step 1, find the corresponding value
of service categories (SC) for each IPoA link in ADD TRAFFIC command in the MML
configuration file, for example:
ADD TRAFFIC: IDX = 73, SC = UBR, PCR = 235000, CDVT = 1500;
If SC = CBR:
Bandwidth (bit/s) of an IPoA link = Value of Peak cell rate (cells/s) (PCR) x 53 bytes x 8
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 37
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
If SC = UBR+:
Bandwidth (bit/s) of an IPoA link = Value of Minimum desired cell rate(cells/s) (MDCR) x
53 bytes x 8
If SC = UBR:
Bandwidth (bit/s) of an IPoA link = Value of Peak cell rate (cells/s) (PCR) x 53 bytes x 8
If SC = RTVBR:
Bandwidth (bit/s) of an IPoA link = Value of Sustainable cell rate(cells/s) (SCR) x 53 bytes x
8
If SC = NRTVBR:
Bandwidth (bit/s) of an IPoA link = Value of Sustainable cell rate(cells/s) (SCR) x 53 bytes x
8
Every ATM cell is composed of 53 bytes. There are 14 sets of flow parameters defined in SGSN by
default. Among these sets of parameters, the tenth set is applied in SAAL links and the fourth set is used
in IPoA PVCs by default. If flow parameter index is 4 in the ADD IPOA commands in the MML
configuration file, values of service categories and Peak cell rate (cells/s) are respectively UBR and
353207 cells/s by default. You do not need to view their values in the ADD TRAFFIC commands in the
MML configuration file.
Step 3 Calculate bandwidth of ATM interfaces. (One or more IPoA links can be configured on an
ATM interface.)
Bandwidth of an ATM interface = MIN(SUM [bandwidth of each IPoA link],Maximum
physical bandwidth of the ATM interface)
Physical bandwidth of the STM-1 interface is configured as 155 Mbit/s, and physical
bandwidth of the STM-4 interface is configured as 622 Mbit/s.
Step 4 Sum configured bandwidths of ATM interfaces in the system to obtain the configured physical
bandwidth.
Step 5 Configured physical bandwidth = SUM (Bandwidth of each ATM interface)
----End
Physical Bandwidth of an S1-MME Interface
Step 1 Identify the subrack number, slot number, and port number of the S1 interface.
Obtain information about network segments of interfaces based on networking schemes or by
contacting frontline personnel and query the information in the ADD IFIP command settings
in MML configuration files for confirmation.
Step 2 Run DSP PORT to query port status. The value of Ethernet attribute indicates the working
mode of the port and is generally the same as the working mode attribute of the port. When
Work mode is Auto, port working status is displayed based on actual working mode.
----End
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 38
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment in GUL Convergence ScenariosCapac
Capacity Assessment Guide ity Assessment in GUL Convergence Scenarios
4.8.5 Assessment Method
Obtain the actual bandwidth of each interface using the preceding formulas and use the
following formula to calculate the bandwidth usage:
Bandwidth usage of an interface = Actual bandwidth of the interface/Physical bandwidth of
the interface x 100%
4.8.6 Assessment Conclusion
If interface bandwidth usage is lower than the baseline, bandwidth resources are sufficient.
Otherwise, link bandwidths must be increased.
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 39
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment and Optimization ServicesCapacity
Capacity Assessment Guide Assessment and Optimization Services
5 Capacity Assessment and Optimization
Services
5.1 Overview
Huawei capacity assessment and optimization services are customized services provided only
for Huawei devices. These services are implemented based on radio access technology (RAT)
types, network elements (NEs), software versions, or hardware versions, forecast traffic
models, the number of users, and resource capacity requirements, and provide capacity
optimization proposals. These services analyze data on live networks, signaling models in use,
and traffic models in use and based on these models, assess the dynamic capacity of live
networks. Based on the analysis results and development trend of the models, these services
also forecast capacity requirements and provide a reference for network risk prewarning and
capacity planning.
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 40
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment and Optimization ServicesCapacity
Capacity Assessment Guide Assessment and Optimization Services
5.2 Services
5.2.1 Evaluation on Phone Distribution and Traffic Models
5.2.2 Evaluation on Resource Usage of the Existing Network
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 41
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment and Optimization ServicesCapacity
Capacity Assessment Guide Assessment and Optimization Services
5.2.3 Traffic Model Forecast
5.2.4 Forecast on the Number of Users
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 42
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node Capacity Assessment and Optimization ServicesCapacity
Capacity Assessment Guide Assessment and Optimization Services
5.2.5 Forecast on Resource Capacity Requirements
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 43
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node
Capacity Assessment Guide A Acronyms and Abbreviations
A Acronyms and Abbreviations
Numerics
3G 3rd Generation
3GPP2 3rd Generation Partnership Project 2
B
BOSS business and operation support system
E
ETSI European Telecommunications Standards Institute
G
GIS geographical information system
I
IDEA Integrated Data Environment of Applications
M
MDSP Mobile Data Service Platform
MM multimedia message
O
OSS operation support system
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 44
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
USN9810 Unified Service Node
Capacity Assessment Guide A Acronyms and Abbreviations
S
SGIP Short Message Gateway Interface Protocol
SMSC short message service center
SP service provider
U
URL uniform resource locator
USSD unstructured supplementary service data
W
WAP Wireless Application Protocol
WAP GW Wireless Application Protocol gateway
Issue 01 (2015-06-18) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 45
Copyright Huawei Technologies Co.,
Ltd.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionVon EverandCross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traffic Analysis: Security LevelDokument29 SeitenTraffic Analysis: Security Levelanon_757794657Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To CDMA Documentation V1.2 (20100809)Dokument44 SeitenIntroduction To CDMA Documentation V1.2 (20100809)Alaa Mahmoud Ali Al-dawoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM-To-UMTS Training Series 02 - WCDMA Radio Network Coverage Planning - V1.0Dokument86 SeitenGSM-To-UMTS Training Series 02 - WCDMA Radio Network Coverage Planning - V1.0AliKaiserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei Post-Optimization Tools Platform Introduction-PRS Part 20110530 PDFDokument12 SeitenHuawei Post-Optimization Tools Platform Introduction-PRS Part 20110530 PDFWaqas KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delivery Report: Delivering DealerDokument2 SeitenDelivery Report: Delivering DealerBrayan Calcina BellotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acceptance TestingDokument51 SeitenAcceptance TestingAuliaRamadhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drive Test Report: Site Name: Site ID: Regional: Type of Work: Customer: Prepared byDokument7 SeitenDrive Test Report: Site Name: Site ID: Regional: Type of Work: Customer: Prepared byIrsan JayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HCIP-LTE-RNP - RNO V1.0 Exam OutlineDokument6 SeitenHCIP-LTE-RNP - RNO V1.0 Exam OutlineSemirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics WCDMA PDFDokument164 SeitenBasics WCDMA PDFAndrewNoch keine Bewertungen
- OT SurveyDokument21 SeitenOT SurveyStefan Natanael PardedeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ibca (GBSS14.0 03) PDFDokument68 SeitenIbca (GBSS14.0 03) PDFVincenzo Guglielmi0% (1)
- Acceptance Test Report MA5600 Per ProvinceDokument4 SeitenAcceptance Test Report MA5600 Per ProvinceBinh Nguyen HuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSC6900 UMTS Parameter Reference (V900R012C01 - 03)Dokument931 SeitenBSC6900 UMTS Parameter Reference (V900R012C01 - 03)snsingh_ecNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS Fallback (ERAN12.1 03)Dokument314 SeitenCS Fallback (ERAN12.1 03)CosminDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Counter Related UMTS To LTE Statistic MeasurementDokument14 SeitenCounter Related UMTS To LTE Statistic Measurementdanangbayuaji76Noch keine Bewertungen
- Breezemax Si 4000 Cpe PDFDokument135 SeitenBreezemax Si 4000 Cpe PDFLong Tai-YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wimax-dt&Cqt Test GuideDokument45 SeitenWimax-dt&Cqt Test GuidefourwheelergamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3G Optimization Defense: Date: 22/05/2015Dokument35 Seiten3G Optimization Defense: Date: 22/05/2015Kaka NarcisseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Testing StandardsDokument22 SeitenSoftware Testing StandardsChandra RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMPak LTE Single Site Verification SSV ENodeB - ID 9070Dokument52 SeitenCMPak LTE Single Site Verification SSV ENodeB - ID 9070Hameed Khan Khattak100% (3)
- CBS (RAN16.0 - Draft A)Dokument51 SeitenCBS (RAN16.0 - Draft A)Sam FicherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepared By: Melvin Cuadrante: Genex AssistantDokument10 SeitenPrepared By: Melvin Cuadrante: Genex AssistantMelvin Diones CuadranteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedure For Binning Using XcalDokument13 SeitenProcedure For Binning Using XcalHazamir HamzahNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTCTE PROCEDURE Ver 2.1 Release May 2021Dokument51 SeitenMTCTE PROCEDURE Ver 2.1 Release May 2021srinivasa B R100% (1)
- WCDMA RAN FundamentalsDokument56 SeitenWCDMA RAN FundamentalsowuorjaredNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09 Introduction To GENEX Probe (Ver1.4)Dokument111 Seiten09 Introduction To GENEX Probe (Ver1.4)Rafael Andres Rodriguez MarulandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- I NOCDokument23 SeitenI NOCIkhtiander IkhtianderNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 WCDMA Power ControlDokument77 Seiten2 WCDMA Power ControlrogertehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei RAN15 Documentation ImprovementsDokument22 SeitenHuawei RAN15 Documentation Improvementsİsmail AkkaşNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-WCDMA Handover PrincipalDokument62 Seiten3-WCDMA Handover PrincipalsaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- RF Acceptance Document (GP-Huawei) - Modified - 290410Dokument22 SeitenRF Acceptance Document (GP-Huawei) - Modified - 290410Raju_RNO EnggNoch keine Bewertungen
- GENEX Probe Operation Guide (LTEDokument82 SeitenGENEX Probe Operation Guide (LTEAtok Enteng DigzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Impact Report 2016 04Dokument273 SeitenNetwork Impact Report 2016 04juliosantanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nemo Analyze 8.31 User Guide PDFDokument496 SeitenNemo Analyze 8.31 User Guide PDFDarko LekicNoch keine Bewertungen
- BA5131Dokument14 SeitenBA5131Abhay17120% (1)
- BSC6900 UMTS Guide To Avoiding Network Problems (V900R012) - 20110524-A-V1.40Dokument173 SeitenBSC6900 UMTS Guide To Avoiding Network Problems (V900R012) - 20110524-A-V1.40Anonymous g8YR8b9Noch keine Bewertungen
- EID SWAP PROCESS, CO Checklist During 2G - Cutover SWAPDokument44 SeitenEID SWAP PROCESS, CO Checklist During 2G - Cutover SWAPNangNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Handover in ZTE System - : Fahmida AfrinDokument14 SeitenGSM Handover in ZTE System - : Fahmida AfrinRakibul HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Completed Corrected Feasibility and Analysis MatrixDokument8 SeitenCompleted Corrected Feasibility and Analysis Matrixapi-238992918Noch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei Dual Cell HSDPA Technology White Paper V1 (1) .0 (20100128)Dokument21 SeitenHuawei Dual Cell HSDPA Technology White Paper V1 (1) .0 (20100128)Salvador Cristobal LLanca100% (2)
- GSM HuaweiDokument30 SeitenGSM HuaweiSri Datta Sameer AchantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Call Admission Control (RAN19.1 - 02)Dokument295 SeitenCall Admission Control (RAN19.1 - 02)anthony100% (1)
- VOIP Troubleshooting Whitepaper FinalDokument8 SeitenVOIP Troubleshooting Whitepaper FinalThiago HenriqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- GENEX Probe V300R014Voice Quality Evaluation MOS Test GuideDokument14 SeitenGENEX Probe V300R014Voice Quality Evaluation MOS Test GuideCannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Networks OverviewDokument104 SeitenMobile Networks OverviewHessam Alemohammad100% (1)
- WCDMA PS Service Optimization GuideDokument215 SeitenWCDMA PS Service Optimization GuideEfosa AigbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- WLAN High-Level Solution1Dokument24 SeitenWLAN High-Level Solution1hernandez.josedomingo6804Noch keine Bewertungen
- 21CFR11 Assessment FAQ Metler Toledo STAREDokument51 Seiten21CFR11 Assessment FAQ Metler Toledo STAREfurqan.malikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercises: WCDMA Air InterfaceDokument16 SeitenExercises: WCDMA Air InterfaceMohamed ShabanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow ControlDokument87 SeitenFlow Controlibrahim_nfsNoch keine Bewertungen
- NIST LinkBudgetCalc 2 4Dokument13 SeitenNIST LinkBudgetCalc 2 4abraamoffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iq Ahu-01Dokument26 SeitenIq Ahu-01yogendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Railway Operational Communication Solution GTSOFTX3000V200R001C01 Product Description V1.0 (20130311)Dokument89 SeitenRailway Operational Communication Solution GTSOFTX3000V200R001C01 Product Description V1.0 (20130311)Leonardo MorallosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft PowerPoint - 6-OHD906241 SingleSDB Maintenance andDokument22 SeitenMicrosoft PowerPoint - 6-OHD906241 SingleSDB Maintenance andGeni Evans100% (1)
- 2G Huawei Performance MonitoringDokument70 Seiten2G Huawei Performance MonitoringBatool FatimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wcdma RNP Rno ConspectusDokument77 SeitenWcdma RNP Rno ConspectusAbderrazekHmidetNoch keine Bewertungen
- DX200 MML CommandDokument3 SeitenDX200 MML Commanddedeputra01Noch keine Bewertungen
- 5G Terminology: (Updated - Feb 2019)Dokument23 Seiten5G Terminology: (Updated - Feb 2019)BrunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commissioning Data For Interworking With The P-GWDokument3 SeitenCommissioning Data For Interworking With The P-GWBrunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Features HuaweiDokument11 SeitenFeatures HuaweiBruno100% (1)
- Semi SmartDokument135 SeitenSemi SmartBrunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4-Port Dual-Beam Antenna Frequency Range Dual Polarization HPBW Adjust. Electr. DT Azimuth Beam Direction Optimized Horizontal SidelobesDokument9 Seiten4-Port Dual-Beam Antenna Frequency Range Dual Polarization HPBW Adjust. Electr. DT Azimuth Beam Direction Optimized Horizontal SidelobesBrunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MimoDokument4 SeitenMimoBrunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- (All Information in One Picture) CSFB Solution Poster PDFDokument1 Seite(All Information in One Picture) CSFB Solution Poster PDFBrunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELTE2.2 DBS3900 LTE TDD Product Description 01 (20130630)Dokument30 SeitenELTE2.2 DBS3900 LTE TDD Product Description 01 (20130630)BrunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 86B 3647 NPDokument14 Seiten86B 3647 NPBrunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HetNet Network Deployment and PlanningDokument17 SeitenHetNet Network Deployment and PlanningBrunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei Wcdma Call Drop Counter and Kpi IntroductionDokument34 SeitenHuawei Wcdma Call Drop Counter and Kpi IntroductionBrunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei WCDMA RAN 14 Capacity GuideDokument45 SeitenHuawei WCDMA RAN 14 Capacity GuideagvavrssNoch keine Bewertungen
- ERICSSON Business Objects KPIs Generation Process DocumentationDokument13 SeitenERICSSON Business Objects KPIs Generation Process DocumentationAbhishek Sharma100% (2)
- GSM Security Concerns: OperatorsDokument36 SeitenGSM Security Concerns: Operatorsgkutty9Noch keine Bewertungen
- B.E Electrical and Electronics Engineering Curriculum 2012 Batch OnwardsDokument7 SeitenB.E Electrical and Electronics Engineering Curriculum 2012 Batch Onwardskarthick_mariner92Noch keine Bewertungen
- Limited Edition Limited Edition Limited EdDokument4 SeitenLimited Edition Limited Edition Limited EdWiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 31026316-BTS3X Technical Manual-System Principle (V3.30)Dokument56 Seiten31026316-BTS3X Technical Manual-System Principle (V3.30)williamNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTE Interview Questions 1Dokument12 SeitenLTE Interview Questions 1Ashish Gupta100% (2)
- Sfs Det Chart-Eid-RfsebdiDokument1 SeiteSfs Det Chart-Eid-Rfsebdiherbster28Noch keine Bewertungen
- FT-817 Softw Adjustment Menu Tabela Com Valores DefaultDokument6 SeitenFT-817 Softw Adjustment Menu Tabela Com Valores DefaultDaniel CoslovskyNoch keine Bewertungen
- HBXX-3319DS-VTM - HBXX-3319DS-A2M: General SpecificationsDokument4 SeitenHBXX-3319DS-VTM - HBXX-3319DS-A2M: General SpecificationsakiselNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Radio Astronomy Observatory, New MexicoDokument30 SeitenNational Radio Astronomy Observatory, New MexicoMuhaamad Haseeb KhokharNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 - D-ATKS - Airborne - EngDokument13 Seiten02 - D-ATKS - Airborne - EngJack58Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9 LineDokument2 Seiten9 LineTina SabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Ucs 6324 Fabric Interconnect Spec SheetDokument26 SeitenCisco Ucs 6324 Fabric Interconnect Spec Sheetsergio chacon luizagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atc 1000 DS PDFDokument2 SeitenAtc 1000 DS PDFKapil GalwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Walker Ultrasonic Wind Sensor2080Dokument2 SeitenWalker Ultrasonic Wind Sensor2080bobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei 2G HandoverDokument32 SeitenHuawei 2G HandoverRizal Mambaul AsnawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gallien Krueger ManualDokument12 SeitenGallien Krueger ManualAntonio LombardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exploded View Part ListDokument9 SeitenExploded View Part ListJosé MacedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Controller - Two Hand Control Station - Contactor - Cat.4 PL E - SIL 3 - Stop Category 0Dokument4 SeitenSafety Controller - Two Hand Control Station - Contactor - Cat.4 PL E - SIL 3 - Stop Category 0davidcristian2009100% (1)
- NAD T751 Service ManualDokument64 SeitenNAD T751 Service ManualIrving AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- WISOLAppNote WSSFM10R HW Design Guide R03 170320 PDFDokument6 SeitenWISOLAppNote WSSFM10R HW Design Guide R03 170320 PDFRegis DantasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simatic Configuration Communication - 2Dokument18 SeitenSimatic Configuration Communication - 2Sam eagle goodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet 1205CXBDokument4 SeitenDatasheet 1205CXBCPPS Comércio de Produtos, Peças e Serviços LtdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Security Analysis of India's Electronic Voting MachinesDokument25 SeitenSecurity Analysis of India's Electronic Voting MachinesSrikanth SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- HL-740 (TM) 7-5Dokument17 SeitenHL-740 (TM) 7-5REMZONANoch keine Bewertungen
- Phương Pháp Dòng Mắc LướiDokument20 SeitenPhương Pháp Dòng Mắc LướiKise RyotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAS001Dokument7 SeitenDAS001JLTorres50% (2)
- What Is Mho Relay - Description & Its Operating Characteristic - Circuit GlobeDokument4 SeitenWhat Is Mho Relay - Description & Its Operating Characteristic - Circuit GlobeAbdul RafaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iqan-Md3 Instruction Book: Publ No HY33-8395-IB/UK Edition 2016-06-17Dokument37 SeitenIqan-Md3 Instruction Book: Publ No HY33-8395-IB/UK Edition 2016-06-17baggo81Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tebevert Iii Modular 5-25 Kva Inverter System: Key FeaturesDokument2 SeitenTebevert Iii Modular 5-25 Kva Inverter System: Key FeaturesФарид СаулебаевNoch keine Bewertungen