Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
A Review On Different Digital Watermarking Techniques
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
A Review On Different Digital Watermarking Techniques
Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Volume 2, Issue 10, October 2017 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456 2165
A Review on Different Digital Watermarking
Techniques
Vasudha B. Sankpal1, Prof.R.N.Patil2
[1]Student, Department of Electronics Engg, DKTE's Textile and Engineering Institute, Ichalkarnji, Maharashtra
[2]Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics Engg, DKTE's Textile and Engineering Institute, Ichalkarnji, Maharashtra
vasudhasankpal12@gmail.com1, rnpatil@dktes.com2
AbstractNow a days it is very easy to use digital the various watermarking techniques. Section III describes the
information available on internet because of the fast Features and requirements .Section IV describes the various
development in Information Communication Technology parameters used to evaluate the performance of watermarked
(ICT) sector. To provide facility of data authentication, image and watermarking applications. Section V is the
security and copyright protection of digital media the Conclusion.
technology being developed is a Digital Watermarking.
For text or image, audio, video digital watermarking can
be applied. In this paper it is focused only on image
watermarking. In general, watermark can be embedded in
transform domain or spatial domain technique of an
image. A review of various watermarking techniques is
presented in this paper. The paper also includes
definition of watermarking features, requirements and
performance of various watermarking techniques.
KeywordsDigitalWatermarking, Techniques,DCT,,DWT
,SVD.
I. INTRODUCTION
The rapid growth of internet technology increased, also
exchange and transmission of digital information increased,
the prevention of tampering and illegal distribution of the
digital data is becomes very essential. Digital watermarking
Fig.1: Watermark Embedding Process
one of the techniques used to achieve copyright protection and
authenticity of digital data. Digital watermarking is the
process of hiding a data associated to a digital signal (i.e.
video, song, and image) inside the signal itself. It tries to hide
a message associated to the actual content of the digital signal
[1].Digital Watermarking has several applications such as
Broadcast Monitoring, Owner Identification, Proof
Ownership, Transaction Tracking and Content Authentication
[2] [3].It has become a very important to study about
information hiding. Watermarking consists of two modules;
watermark embedding module and watermark detection &
extraction module .These two modules are same for all types
of watermarking techniques. Fig 1. Shows the watermark
embedding process in which the watermark is embedded on
the cover image by using the embedding algorithm and the
embedded watermark is recovered by using detection
algorithm is as shown in Fig 2.watermark detection process.
This paper shows the core technologies of digital Fig. 2: Watermark Detection Process
watermarking and explores the application in the digital
image. The paper is structured as follows: Section II describes
IJISRT17OC167 www.ijisrt.com 453
Volume 2, Issue 10, October 2017 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456 2165
II. WATERMARKING TECHNIQUES frequency domain. It needs more computation as compared to
spatial domain methods but it can provide better robustness
from different attacks [6].
The watermarking techniques fall into two categories as
shown in Fig 3. Spatial - Domain methods and Frequency According to differentiation, the watermarking system can be
Transform Domain methods [4] [5]. In Spatial Domain, it classified as Blind, Semi-Blind and Non-Blind [7].
directly handles digital data to hide the watermark. Its main
advantage is low computational complexity. Blind:
The Blind watermarking scheme is called as public:
However, this method is susceptible to various attacks. In
frequency domain, data to be protected are changed into a
Fig.3: Classification of Watermarking Techniques
The watermark may be spread throughout the image or that the relationship between the numbers of different keys
Watermarking scheme. The most challenging type of will be very low [8].
watermarking system is blind watermarking as it does not
requires the cover (original data), or the embedded watermark b). Least Significant Bit:
, n bits of the watermark data is extracted from the Least Significant Bit [16] is a spatial domain technique which
watermarked data (i.e. the watermarked image) by this system. is a very simple and straight forward method. The least
significant bits of the original image is used to embed the
Semi-blind: watermark. It requires very less time to embed image
It is called as semi-private watermarking scheme. This system (watermark). This technique has many drawbacks, a simple
does not need original data for detection. attacks can destroy or remove watermark but sometime it may
survive against some of the transformations. Recently some of
Non-Blind: improvements on LSB substitution suggested like embed
It is also known as private watermarking scheme. This system watermark at single bit rate, multi bit rate or using a pseudo-
requires at least original data for detection. The System random number generator. Pixel can also be selected with help
extracts the watermark from the possibly distorted data and of key. Performing loss in compression and addition of noise
uses the original data as a hint. [17] can easily degrade the image quality or remove or disrupt
or destroy watermark.
A. Spatial Domain Watermarking Methods:
It lacks the basic strength. In case, if the algorithm is
a). Additive Watermarking: discovered, it becomes very easy for attacker to modify or
To add pseudo random noise pattern to the intensity of image remove watermark.
pixels is the most straight forward method to embed the
watermark in spatial domain. The noise signal is floating point c). SSM Modulation Based Technique:
numbers or usually integers like (-1, 0, 1).To ensure that the In this technique the least significant bits are used for
watermark can be noticed, the noise is made by a key, such embedding watermarks. This method is robust against
different attacks and is very easy for implementation. By
IJISRT17OC167 www.ijisrt.com 454
Volume 2, Issue 10, October 2017 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456 2165
selecting a group of pixels the embedding operation is captured by the spectral coefficients [11] ,so frequency
performed and replaces this selected group with the pixels of domain method is popularly used for watermarking. That is
watermarks. But this technique does not stand for common human eye is less sensitive against high frequency component
signal processing attacks and is not suitable for practical and more sensitive against low frequency component. The
applications. most commonly used transformations are Discrete Wavelet
Transform (DWT), Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT), and
d). Texture mapping coding Technique: Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT). Some of its main
It is useful for those images which have some texture part in it. algorithms are discussed below:
In this method the watermark embedded in the texture part of
the image. This algorithm is only suitable for those areas with a). Discrete Cosine Transforms (DCT):
large number of arbitrary texture images (disadvantage) [9], DCT is a Fourier Transform; it represents data in terms of
and cannot be done automatically. This method hides data in frequency space rather than an amplitude space. Compared to
the continuous random texture patterns of a picture. spatial domain techniques DCT based watermarking
techniques are more robust. Such algorithms are robust against
e). Patchwork Algorithm: simple image processing operations like low pass filtering,
Patchwork is a data hiding method proposed by Bender et al blurring, brightness and contrast adjustment, etc. However,
and published on IBM Systems Journal, 1996[10]. It is based they are very difficult for implementation and are more
on a pseudorandom, statistical model. Patchwork expensive. Along with this, they are weak against Geometric
imperceptibly inserts a watermark with a particular statistic attacks like scaling, rotation, cropping etc. DCT domain
using a Gaussian distribution. A pseudo randomly selection of watermarking can be classified into Block based DCT
two patches is carried out where the first one is A and the watermarking and Global DCT watermarking. Embedding in
second is B. Patch A image data is brightened where as that of the perceptually significant portion of the image has its own
patch B is darkened (for purposes of this illustration this is advantages because most compression schemes remove the
magnified). perceptually insignificant portion of the image.
B. Frequency Domain Watermarking Methods: b). Discrete Wavelet Transforms (DWT):
The multi resolution representation of an image is produced by
These methods are more widely applied than others. The discrete wavelet transform (DWT) of the image.
characteristics of the human visual system (HVS) are better
a) Host image b) DWT Transform
Fig.4: Two Level Decomposition
The multi resolution representation provides a simple contains horizontal details of the image, the one bottom left
framework for interpreting the image information. The DWT contains vertical details of the original image, the bottom right
analyses the signal at multiple resolution. DWT divide the contains high frequency of original image. The low frequency
image into low frequency quadrants and high frequency coefficients are more robust to embed watermark because it
quadrants .The low frequency quadrants is again split into two contains more information of original image [12].The
more parts of low and high frequencies and this process is reconstruct of the original image from the decomposed image
repeated until the signal is entirely decomposed. The signal is performed by IDWT. The digital wavelet transform are
DWT transformed two dimensional image into four parts: one scalable in nature. DWT more frequently used in digital image
part is the low frequency of the original image, the top right watermarking because of excellent spatial localization and
IJISRT17OC167 www.ijisrt.com 455
Volume 2, Issue 10, October 2017 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456 2165
multi resolution techniques. To recognize the area in the cover Small Variation in singular values does not affect the
image in which the watermark is embedded efficiently the quality of image and
excellent spatial localization property is very convenient. Singular Values of an image have high stability so; they
dont change after various attacks.
The DWT is applied on host image to decompose the image
into four non overlapping multi resolution coefficients is as III. FEATURES AND REQUIREMENTS
shown in Fig 4.
And then the detector is used to extract the embedded spread A. Features of Digital watermarking Invisible/Inaudible
spectrum watermark [13] The DFT is used for the periodic
digital signal or discrete-time f(x). Information is embedded without digital content degradation,
because of the level of embedding operation is too small for
c). Discrete Fourier Transforms (DFT) human to notice the change.
Discrete Fourier Transforms (DFT) offers robustness against
geometric attacks like rotation, scaling, cropping, translation a). Inseparable
etc. DFT decomposes an image in sine and cosine form .The The embedded information can survive after some processing,
DFT based watermark embedding techniques are divided in compression and format transformation.
two types: one is the direct embedding technique and the other
one is the template embedding. b). Unchanging Data File
Information is embedded directly into the media due to which
By modifying DFT magnitude and phase coefficients the data size of the media is not changed before and after
watermark is embedded in direct embedding technique. The embedding operation.
concept of templates is introduced by template based
embedding technique. In DFT domain a template is structure B. Requirements of Digital watermarking
which is embedded to estimate the transformation factor. Once
the image undergoes a transformation this template is searched A watermark can exhibit a number of important
to resynchronize the image, And then the detector is used to characteristics. The most important properties of digital
extract the embedded spread spectrum watermark [13] watermarking techniques are transparency, robustness,
The DFT is used for the periodic digital signal or discrete-time security, capacity, invert ability (reversibility) and complexity
f(x). and possibility of verification. Transparency relates to the
properties of the human sensory. A transparent watermark
d). Singular Value Decomposition (SVD): causes no artifacts.
Singular Value Decomposition transform is a linear algebra
transform which is used for factorization of a real or complex a). Robustness:
matrix. Which has numerous applications in various fields of Watermarked in image should survive basic image processing
image processing? As a digital image, can be represented in a operation such as contrast or brightness enhancement, gamma
matrix form with its entries giving the intensity value of each correction etc.
pixel in the image, SVD of an image M with dimension in
mxm is given by. b). Perceptual transparency:
The algorithm must embed data without affecting the
perceptual quality of the underlying host signal.
M=U*S* V Eqn.
c). Security:
Where, U and V are orthogonal matrices and S is called as
A secure data embedding procedure cannot be broken unless
singular matrix is a diagonal matrix which carries non-
the unauthorized user access to a secret key that controls the
negative singular values of matrix M. The columns of U and V
insertion of the data in the host signal.
are call left and right singular vectors of M, respectively. They
basically specify the geometry details of the original image.
d). Complexity:
Left singular matrix, i.e. V represents the vertical details of the
This is important property considering in Real time
original image, i.e.,U represents the horizontal details and
applications like video. Complexity property is concerned
right singular matrix, The diagonal value of Matrix S is
with amount of effort needed to extract or retrieve the
arranged in decreasing order which shows that importance of
watermark from content.
the entries is decreasing from the first singular value for the
last one, this feature is working in SVD based compression
e). Capacity:
methods. [15] There are two main properties of SVD to
This factor shows the maximum amount of data, which can be
employ in digital watermarking scheme.
embedded into an image without noticeably reducing image
quality. The influence of capacity on the robustness and
IJISRT17OC167 www.ijisrt.com 456
Volume 2, Issue 10, October 2017 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456 2165
imperceptibility of watermarked image is not negligible; for m and n are height of the image
instance, by increasing the data payload, the robustness will H , is the pixel value of cover image.
decrease and the Imperceptibility will increase. H , is the pixel value of embed image.
Capacity requirement always struggle against two other Normalized Cross Correlation (NC)-
important requirements, that is, imperceptibility and
robustness (Fig 5). A higher capacity is usually obtained at the Normalized Cross Correlation (NC) can be used to evaluate
expense of either robustness strength or imperceptibility, or the robustness of the watermarking method.
both.
Bit error ratio(BER)-
The difference between the original image and watermarked
images is manipulated using the Bit- Error-Rate (BER).
.
BER = Eqn.
P
A. Applications of Digital Watermarking
a). Copyright protection - Watermarking can be used to
protect digital material distributed on internet to verify the
ownership of material.
Fig 5: The Tradeoffs among Imperceptibility, Robustness, and b). Content Achieving - It can hide identity of digital material
Capacity such as image, video, audio etc. within its material reduce
possibility of tempering it.
f). Imperceptibility:
c). Mete-data insertion - Meta-data is the data that describe the
This factor is about the amount of distortion that appears on a
data. This data can be inserted using watermarking such as
watermarked image after inserting a watermark. For invisible
audio file can carry singer name or video file carry the
watermarks, this factor should be low.
subtitle.
g). Reliability: d). Broadcast monitoring - Broadcast monitoring refers to the
To ensure that the project application returns the correct technique of cross verifying whether the content that was
watermark each time. In spite of the loss of watermarking supposed to be broadcasted has really been broadcasted or not.
information by the optimizer, we should always be able to e). Tamper detection - Data transfer over internet can be
obtain correct and accurate results from the project. tamper or alter by other party which is detect by
watermarking.
IV. PERFORMANCE PARAMETERS f). Medical Applications: digital watermarking provide both
confidentiality and authentication without affecting the
Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR)- medical data.
It measures the similarity between images before and after
watermarking. PSNR is defined in the following way: V. CONCLUSION
ax2 This paper gives a detailed study on various digital water
PSNR = Xlog dB Eqn. marking techniques spatial domain and transform domain
E
(DCT, DWT, DFT) and their applications. We have presented
Mean Squared Error (MSE)- various aspects of digital watermarking like overview,
It is simplest function to measure the perceptual distance techniques and requirements. Apart from it a brief analysis of
between watermarked and original image. MSE can be watermarking techniques is presented which can help the new
defined as: researchers in related area.
We tried to provide the comprehensive information regarding
MSE = H , H , Eqn. the digital watermarking which will assist the new researchers
to acquire the maximum knowledge in this domain.
Where,
IJISRT17OC167 www.ijisrt.com 457
Volume 2, Issue 10, October 2017 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456 2165
REFERENCES [14]. N. Bisla and P. Chaudhary, "Comparative Study of
DWT and DWT-SVD Image Watermarking Techniques,"
[1]. M. Durvey and D. Satyarthi, "A Review Paper on Digital International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer
Watermarking," International Journal of Emerging Trends Science and Software Engineering, vol. 3, no. 6, pp. 821-
& Technology in Computer Science (IJETTCS), vol. 3, 825, 2013.
no. 4, pp. 99-105, 2014. [15]. D. Samanta, A. Basu, T. S. Das, V. H. Mankar,
[2]. Cox, M. L. Miller and J. A. Bloom, "Digital Ankush Ghosh, Manish Das and Subir K Sarkar, SET
Watermarking," Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 2002. Based Logic Realization of a Robust Spatial Domain
[3]. R. G. Schyndel, A. Z. Tirkel and C. F. Osborne, "A Image Watermarking, Proc. in 5th International
Digital Watermark," in Proceedings of 1994 International Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering-
Conference, Austin, Texas, 1994. ICECE 2008, Dhaka, Bangladesh, pp. 986-993, Dec.
[4]. H. Daren, L. J. H. Jiwu and L. Hongmei, "A DWT Based 2008.
Image Watermarking Algorithm," in Proceedings of the [16]. J. L., Dugelay, S. Roche, C. Rey, G. Dorr, "Still-
IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, image watermarking robust to local geometric
2001. distortions," IEEE Trans. on Image Proc., vol. 15, no. 9,
[5]. M. Barni, F. Bartolini, V. CappeAini and A. Piva, "A pp. 2831- 2842, 2006.
DCT-Domain System for Robust Image Watermarking," [17]. Dhanalakshmi and Dr.T.Ravichandran, A SURVEY
Vols. 66, No.3, pp. 357-372, 1998. OF WATERMARKING PROCESS, S. Dhanalakshmi et
[6]. S. Madhesiya and S. Ahmed, "Advanced Technique of al. / IJAIR Vol. 2 Issue 2 ISSN: 2278-7844. [5] Mr.
Digital Watermarking based on SVD-DWT-DCT and Gaurav N Mehta, Mr. Yash Kshirs.
Arnold Transform," International Journal of Advanced
Research in Computer Engineering & Technology
(IJARCET), Vols. 2, No 5, May 2013.
[7]. H. Jahankhani, D. L. Watson, G. Me and F. Leonhardt,
"Authentication," in Handbook of Electronic Security and
Digital Forensics, Singapore, World Scientific Publishing
Co. Pte. Ltd, 2010, p. 40.
[8]. CHAPTER 2: LITERATURE REVIEW, Source: Internet
Jiang Xuehua, Digital Watermarking and Its
Application in Image Copyright Protection, 2010
International Conference on Intelligent Computation
Technology and Automation.
[9]. http://ippr-practical.blogspot.in
[10]. Manpreet kaur, Sonia Jindal, Sunny behal, A
Study of Digital image watermarking, Volume2, Issue 2,
Feb 2012.
[11]. N.Tiwari, M.k. Ramaiya and Monika Sharma,
Digital Watermarking using DWT and
DES,IEEE(2013).
[12]. V.M. Potdar , S.Han and E.Chang , A Survey of
Digital Watermarking Techniques,2005 3rd IEEE
International Conference on Industrial Informatics
(INDIN).
[13]. Manpreet kaur, Sonia Jindal, Sunny behal, A Study
of Digital image watermarking, Volume2, Issue 2, Feb
2012.
IJISRT17OC167 www.ijisrt.com 458
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Ijset 2014 803Dokument4 SeitenIjset 2014 803Editorijset IjsetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compusoft, 2 (4), 97-102Dokument6 SeitenCompusoft, 2 (4), 97-102Ijact EditorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cts Image Watermarking Based On DWT and Des: Issue 03, Volume 4 (March 2017)Dokument8 SeitenCts Image Watermarking Based On DWT and Des: Issue 03, Volume 4 (March 2017)sparsh jainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Image Authentication Subject ReviewDokument6 SeitenImage Authentication Subject Revieweditor ijeratNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Image Watermarking Using 3 Level Discrete Wavelet TransformDokument5 SeitenDigital Image Watermarking Using 3 Level Discrete Wavelet Transformtjdandin1Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Block Based Novel Digital Video Watermarking Scheme Using DCTDokument11 SeitenA Block Based Novel Digital Video Watermarking Scheme Using DCTInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ijcet: International Journal of Computer Engineering & Technology (Ijcet)Dokument12 SeitenIjcet: International Journal of Computer Engineering & Technology (Ijcet)IAEME PublicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wavelet Based Watermarking Technique Using Simple Preprocessing MethodsDokument5 SeitenWavelet Based Watermarking Technique Using Simple Preprocessing Methodsvol1no2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Recent Water1Dokument8 SeitenRecent Water1Jeet SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- VLSI Implementation of Online Digital Watermarking Technique With Difference Encoding For 8-Bit Gray Scale ImagesDokument6 SeitenVLSI Implementation of Online Digital Watermarking Technique With Difference Encoding For 8-Bit Gray Scale ImagesMOHAMMAD AWAISNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Survey: Digital Image Watermarking TechniquesDokument14 SeitenA Survey: Digital Image Watermarking Techniquesvidhyasree123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ijert Ijert: VLSI Implementation of Digital Image WatermarkingDokument6 SeitenIjert Ijert: VLSI Implementation of Digital Image WatermarkingVenkataramanLakshminarayananNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Review On Digital Image Watermarking Using 3-Level Discrete Wavelet TransformDokument7 SeitenA Review On Digital Image Watermarking Using 3-Level Discrete Wavelet TransformShahid RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hurrah 2017Dokument5 SeitenHurrah 2017ناصرھرەNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Imperceptible Blind Image Watermarking Scheme For Image Authentication Using DNA Encoding and Multi-Resolution Wavelet DecompositionDokument8 SeitenAn Imperceptible Blind Image Watermarking Scheme For Image Authentication Using DNA Encoding and Multi-Resolution Wavelet DecompositionInternational Journal of Engineering Inventions (IJEI)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ijct V2i6p5Dokument11 SeitenIjct V2i6p5IjctJournalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Watermarking TrendsDokument7 SeitenDigital Watermarking TrendsWhite Globe Publications (IJORCS)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Robust Image Watermarking Theories and Techniques: A Review: Vol.12, February2014Dokument17 SeitenRobust Image Watermarking Theories and Techniques: A Review: Vol.12, February2014evergreenman55Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Semi-Blind Reference Video Watermarking Using: Satyanarayana Murty. P K. Venkatesh Rajesh Kumar. PDokument11 SeitenA Semi-Blind Reference Video Watermarking Using: Satyanarayana Murty. P K. Venkatesh Rajesh Kumar. PMaharani MeidyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.1 Classification of Digital Watermarking TechniquesDokument30 Seiten7.1 Classification of Digital Watermarking TechniquesLong Đào HảiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Review Paper On Digital WatermarkingDokument7 SeitenA Review Paper On Digital WatermarkingInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Normalized Content System For Efficient WatermarkingDokument7 SeitenIntegrated Normalized Content System For Efficient Watermarkingstephenlim7986Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Survey Work On Digital WatermarkingDokument4 SeitenA Survey Work On Digital WatermarkingNguyễn Văn Hùng DũngNoch keine Bewertungen
- DWT-SVD and DCT Based Robust and Blind: Durgesh Singh Sanjay K. SinghDokument24 SeitenDWT-SVD and DCT Based Robust and Blind: Durgesh Singh Sanjay K. SinghWalid El-ShafaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Watermarking Using Machine LearningDokument7 SeitenDigital Watermarking Using Machine LearningIJRASETPublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Article: FPGA Implementation of Digital Images Watermarking System Based On Discrete Haar Wavelet TransformDokument18 SeitenResearch Article: FPGA Implementation of Digital Images Watermarking System Based On Discrete Haar Wavelet TransformSanjana M PNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCT Based Video Watermarking in MATLAB PDFDokument11 SeitenDCT Based Video Watermarking in MATLAB PDFKamlesh DahiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 I026 CamerareadyDokument6 Seiten15 I026 CamerareadyARUN CHILUKURINoch keine Bewertungen
- Towards Optimal Copyright Protection Using Neural Networks Based Digital Image WatermarkingDokument7 SeitenTowards Optimal Copyright Protection Using Neural Networks Based Digital Image WatermarkingEditor IJRITCCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Image Watermarking Techniques in Spatial Domain: A ReviewDokument7 SeitenImage Watermarking Techniques in Spatial Domain: A ReviewCannyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dual Image Watermarking Scheme Based On DWT-SVD: D. M. Gaikwad A. R. KarwankarDokument6 SeitenDual Image Watermarking Scheme Based On DWT-SVD: D. M. Gaikwad A. R. Karwankarrahul sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arise'14 IjertDokument41 SeitenArise'14 IjertAnand RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- DWT Based Invisible Image Watermarking AbstractDokument2 SeitenDWT Based Invisible Image Watermarking AbstractMichael BenilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics: A Hidden DCT-Based Invisible Watermarking Method For Low-Cost Hardware ImplementationsDokument25 SeitenElectronics: A Hidden DCT-Based Invisible Watermarking Method For Low-Cost Hardware ImplementationsARUN CHILUKURINoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Watermarking: A TutorialDokument12 SeitenDigital Watermarking: A TutorialJiawei LinNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Review Study On Image Digital Watermarking: Charles Way Hun Fung Ant Onio Gortan Walter Godoy JuniorDokument5 SeitenA Review Study On Image Digital Watermarking: Charles Way Hun Fung Ant Onio Gortan Walter Godoy JuniorAmoon Al HarbiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Must ReadDokument16 SeitenMust ReadSheela ShivaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robust Video Watermarking Using DWT and PCA Analysis: IPASJ International Journal of Electronics & Communication (IIJEC)Dokument6 SeitenRobust Video Watermarking Using DWT and PCA Analysis: IPASJ International Journal of Electronics & Communication (IIJEC)International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijcet: International Journal of Computer Engineering & Technology (Ijcet)Dokument8 SeitenIjcet: International Journal of Computer Engineering & Technology (Ijcet)IAEME PublicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improved Wavelet-Based Watermarking ThroughDokument9 SeitenImproved Wavelet-Based Watermarking ThroughJerald RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minor Project Synopsis of Digital Watermarking Using DCT and Genetic AlgorithmDokument6 SeitenMinor Project Synopsis of Digital Watermarking Using DCT and Genetic AlgorithmVipul RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- LSB Based Digital Watermarking TechniqueDokument4 SeitenLSB Based Digital Watermarking TechniqueInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Paper On Non Blind Image WatermarkingDokument4 SeitenA Paper On Non Blind Image WatermarkingIJSTENoch keine Bewertungen
- Ownership Protection of Shape Datasets With Distance Based PreservationDokument4 SeitenOwnership Protection of Shape Datasets With Distance Based PreservationerpublicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Robust Optimal Zero-Watermarking Technique For Secret Watermark SharingDokument12 SeitenA Robust Optimal Zero-Watermarking Technique For Secret Watermark SharingzaidsaebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijaiem 2014 06 04 1Dokument6 SeitenIjaiem 2014 06 04 1International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- LSB PDFDokument4 SeitenLSB PDFMaharani MeidyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robust Image Watermarking Based On Generative Adversarial NetworkDokument10 SeitenRobust Image Watermarking Based On Generative Adversarial NetworkbamshadpotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCT-DWT Based Digital Watermarking and Extraction Using Neural NetworksDokument5 SeitenDCT-DWT Based Digital Watermarking and Extraction Using Neural Networkshmm raniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Image Watermarking of Compressed Image Using Jpeg 2000 and Encryption TechniquesDokument13 SeitenDigital Image Watermarking of Compressed Image Using Jpeg 2000 and Encryption TechniquesIJIERT-International Journal of Innovations in Engineering Research and TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER)Dokument4 SeitenInternational Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER)International Journal of computational Engineering research (IJCER)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Water Mark 2-9Dokument19 SeitenDigital Water Mark 2-9Sandip AjmireNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Novel Digital Watermarking Technique For Video Copyright ProtectionDokument9 SeitenA Novel Digital Watermarking Technique For Video Copyright ProtectionCS & ITNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toward Robust Logo Watermarking Using Multiresolution Image Fusion PrinciplesDokument14 SeitenToward Robust Logo Watermarking Using Multiresolution Image Fusion PrinciplesGobinda RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Watermarking: First A. Author, Second B. Author, JR., and Third C. Author, Member, IEEEDokument2 SeitenDigital Watermarking: First A. Author, Second B. Author, JR., and Third C. Author, Member, IEEENishanthShanmugamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Watermarking Using Ant Colony OptimizationDokument11 SeitenDigital Watermarking Using Ant Colony OptimizationNavdeep GoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Research Review On Different Data Hiding Techniques: Dr.K.Sathiyasekar, S.Karthick Swathy Krishna K SDokument5 SeitenA Research Review On Different Data Hiding Techniques: Dr.K.Sathiyasekar, S.Karthick Swathy Krishna K SManish PaliwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Watermarking: Michael StumpflDokument10 SeitenDigital Watermarking: Michael StumpflNaren DranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grayscale Image Watermark DetectionDokument7 SeitenGrayscale Image Watermark DetectionMurilo Vasconcelos AndradeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embedded Deep Learning: Algorithms, Architectures and Circuits for Always-on Neural Network ProcessingVon EverandEmbedded Deep Learning: Algorithms, Architectures and Circuits for Always-on Neural Network ProcessingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Stress and Emotional Reactions due to the Covid-19 Pandemic in IndiaDokument6 SeitenImpact of Stress and Emotional Reactions due to the Covid-19 Pandemic in IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Utilization of Waste Heat Emitted by the KilnDokument2 SeitenUtilization of Waste Heat Emitted by the KilnInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detection and Counting of Fake Currency & Genuine Currency Using Image ProcessingDokument6 SeitenDetection and Counting of Fake Currency & Genuine Currency Using Image ProcessingInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (9)
- Entrepreneurial Creative Thinking and Venture Performance: Reviewing the Influence of Psychomotor Education on the Profitability of Small and Medium Scale Firms in Port Harcourt MetropolisDokument10 SeitenEntrepreneurial Creative Thinking and Venture Performance: Reviewing the Influence of Psychomotor Education on the Profitability of Small and Medium Scale Firms in Port Harcourt MetropolisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Overview of Lung CancerDokument6 SeitenAn Overview of Lung CancerInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ambulance Booking SystemDokument7 SeitenAmbulance Booking SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designing Cost-Effective SMS based Irrigation System using GSM ModuleDokument8 SeitenDesigning Cost-Effective SMS based Irrigation System using GSM ModuleInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unmasking Phishing Threats Through Cutting-Edge Machine LearningDokument8 SeitenUnmasking Phishing Threats Through Cutting-Edge Machine LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Finance-Fintech and it’s Impact on Financial Inclusion in IndiaDokument10 SeitenDigital Finance-Fintech and it’s Impact on Financial Inclusion in IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auto Tix: Automated Bus Ticket SolutionDokument5 SeitenAuto Tix: Automated Bus Ticket SolutionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Solid Waste Management on Socio-Economic Development of Urban Area: A Case of Kicukiro DistrictDokument13 SeitenEffect of Solid Waste Management on Socio-Economic Development of Urban Area: A Case of Kicukiro DistrictInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Vision Gestures Recognition System Using Centralized Cloud ServerDokument9 SeitenComputer Vision Gestures Recognition System Using Centralized Cloud ServerInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Predictive Analytics for Motorcycle Theft Detection and RecoveryDokument5 SeitenPredictive Analytics for Motorcycle Theft Detection and RecoveryInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Assessing Viability of Installing 20kw Solar Power For The Electrical & Electronic Engineering Department Rufus Giwa Polytechnic OwoDokument6 SeitenStudy Assessing Viability of Installing 20kw Solar Power For The Electrical & Electronic Engineering Department Rufus Giwa Polytechnic OwoInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forensic Advantages and Disadvantages of Raman Spectroscopy Methods in Various Banknotes Analysis and The Observed Discordant ResultsDokument12 SeitenForensic Advantages and Disadvantages of Raman Spectroscopy Methods in Various Banknotes Analysis and The Observed Discordant ResultsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Industry That Capitalizes Off of Women's Insecurities?Dokument8 SeitenAn Industry That Capitalizes Off of Women's Insecurities?International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyber Security Awareness and Educational Outcomes of Grade 4 LearnersDokument33 SeitenCyber Security Awareness and Educational Outcomes of Grade 4 LearnersInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors Influencing The Use of Improved Maize Seed and Participation in The Seed Demonstration Program by Smallholder Farmers in Kwali Area Council Abuja, NigeriaDokument6 SeitenFactors Influencing The Use of Improved Maize Seed and Participation in The Seed Demonstration Program by Smallholder Farmers in Kwali Area Council Abuja, NigeriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parastomal Hernia: A Case Report, Repaired by Modified Laparascopic Sugarbaker TechniqueDokument2 SeitenParastomal Hernia: A Case Report, Repaired by Modified Laparascopic Sugarbaker TechniqueInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blockchain Based Decentralized ApplicationDokument7 SeitenBlockchain Based Decentralized ApplicationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insights Into Nipah Virus: A Review of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Therapeutic AdvancesDokument8 SeitenInsights Into Nipah Virus: A Review of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Therapeutic AdvancesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implications of Adnexal Invasions in Primary Extramammary Paget's Disease: A Systematic ReviewDokument6 SeitenImplications of Adnexal Invasions in Primary Extramammary Paget's Disease: A Systematic ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Silver Nanoparticles Infused in Blood in A Stenosed Artery Under The Effect of Magnetic Field Imp. of Silver Nano. Inf. in Blood in A Sten. Art. Under The Eff. of Mag. FieldDokument6 SeitenImpact of Silver Nanoparticles Infused in Blood in A Stenosed Artery Under The Effect of Magnetic Field Imp. of Silver Nano. Inf. in Blood in A Sten. Art. Under The Eff. of Mag. FieldInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Health Care SystemDokument8 SeitenSmart Health Care SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visual Water: An Integration of App and Web To Understand Chemical ElementsDokument5 SeitenVisual Water: An Integration of App and Web To Understand Chemical ElementsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Quality Index Prediction Using Bi-LSTMDokument8 SeitenAir Quality Index Prediction Using Bi-LSTMInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Predict The Heart Attack Possibilities Using Machine LearningDokument2 SeitenPredict The Heart Attack Possibilities Using Machine LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compact and Wearable Ventilator System For Enhanced Patient CareDokument4 SeitenCompact and Wearable Ventilator System For Enhanced Patient CareInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Cities: Boosting Economic Growth Through Innovation and EfficiencyDokument19 SeitenSmart Cities: Boosting Economic Growth Through Innovation and EfficiencyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parkinson's Detection Using Voice Features and Spiral DrawingsDokument5 SeitenParkinson's Detection Using Voice Features and Spiral DrawingsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 - Lecture 3Dokument31 SeitenModule 2 - Lecture 3lvrevathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Malware PredictionDokument16 SeitenMicrosoft Malware Predictionvikram k100% (1)
- Nature of Mathematics FinalDokument4 SeitenNature of Mathematics FinalDennis ZamoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Time Series Forecasting by Combining Anfis With Various Aggregation OperatorsDokument48 SeitenFinancial Time Series Forecasting by Combining Anfis With Various Aggregation OperatorsAmit SamdarshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment 01 - Introduction To Descrete Probability: Probability of Cyan - GeneralizedDokument2 SeitenAssessment 01 - Introduction To Descrete Probability: Probability of Cyan - Generalizedashishamitav123Noch keine Bewertungen
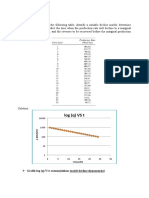
- Problems: Log (Q) VS TDokument8 SeitenProblems: Log (Q) VS TDianita ZuamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control in LabVIEW PDFDokument104 SeitenControl in LabVIEW PDFJuan PabloNoch keine Bewertungen
- DM Ch6 (Classification and Prediction)Dokument39 SeitenDM Ch6 (Classification and Prediction)Baljinder Kumar SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- VHDL Implementation of 128 Bit Pipelined Blowfish AlgorithmDokument5 SeitenVHDL Implementation of 128 Bit Pipelined Blowfish AlgorithmAnonymous lPvvgiQjRNoch keine Bewertungen
- ) Resolution:: Solution: A.) Sampling Period: TDokument5 Seiten) Resolution:: Solution: A.) Sampling Period: TDennis Jefferson AMORANoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument16 SeitenUntitledJenny CaballeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Rubel - Data MiningDokument12 SeitenAssignment Rubel - Data Miningto.jaharkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Mathematician's Survival GuideDokument18 SeitenA Mathematician's Survival GuideKenny SngNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Case) CatDokument14 Seiten(Case) CatFarah Andayani RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control System Design Process by VisSimDokument6 SeitenControl System Design Process by VisSimSreedhar MadichettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Model of Reactive Power Optimization For Distributed Photovoltaic Distribution NetworkDokument5 SeitenMathematical Model of Reactive Power Optimization For Distributed Photovoltaic Distribution NetworkNicolas LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAS BF Q3 Week 6 7 8 IGLDokument6 SeitenLAS BF Q3 Week 6 7 8 IGLdaisymae.buenaventuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To ControlDokument507 SeitenIntroduction To Controlnaderjsa100% (2)
- 4 - Looping StatementsDokument2 Seiten4 - Looping StatementsAdvika LakshmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Given An ArrayDokument5 SeitenGiven An ArrayCh SubhashNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIDokument8 SeitenAImohamed haniNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Important Questions 2022-23 PDFDokument42 SeitenCBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Important Questions 2022-23 PDFShaunak BasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minimax Algorithm & Alpha-Beta PruningDokument35 SeitenMinimax Algorithm & Alpha-Beta PruninganyangupreciousNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Chinese University of Hong Kong: Data StructuresDokument2 SeitenThe Chinese University of Hong Kong: Data Structuresenergy0124Noch keine Bewertungen
- Past Paper Quests. For C++Dokument4 SeitenPast Paper Quests. For C++Musa AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autonomous College Under VTU - Accredited by NBA - Approved by AICTEDokument3 SeitenAutonomous College Under VTU - Accredited by NBA - Approved by AICTESureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stanford University Computer Science Department Solved CS347 Spring 2001 Mid-TermDokument5 SeitenStanford University Computer Science Department Solved CS347 Spring 2001 Mid-TermErwan SetiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristics of Tasks and Task InteractionsDokument11 SeitenCharacteristics of Tasks and Task InteractionsRishabh NagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 11 - Z-Transform (Exercises)Dokument2 SeitenTutorial 11 - Z-Transform (Exercises)Taylor Andres Amaya100% (1)
- Ex of Goal ProgrammingDokument13 SeitenEx of Goal ProgrammingSubir ChakrabartyNoch keine Bewertungen