Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pleural Effusion
Hochgeladen von
Carlos H. AcuñaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pleural Effusion
Hochgeladen von
Carlos H. AcuñaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
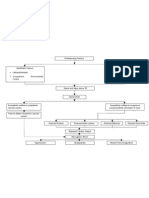
A pleural effusion is an accumulation of fluid between the layers of tissue that line the lungs
and chest cavity.
Causes
Your body produces pleural fluid in small amounts to lubricate the surfaces of the pleura, the
thin tissue that lines the chest cavity and surrounds the lungs. A pleural effusion is an abnormal,
excessive collection of this fluid.
Two different types of effusions can develop:
Transudative pleural effusions are caused by fluid leaking into the pleural space. This is
caused by elevated pressure in, or low protein content in, the blood vessels. Congestive
heart failure is the most common cause.
Exudative effusions usually result from leaky blood vessels caused by inflammation
(irritation and swelling) of the pleura. This is often caused by lung disease. Examples
include lung cancer, lung infections such as tuberculosis and pneumonia, drug reactions,
and asbestosis.
Symptoms
Chest pain, usually a sharp pain that is worse with cough or deep breaths
Cough
Fever
Hiccups
Rapid breathing
Shortness of breath
Sometimes there are no symptoms.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- TICKLER-PRINT Pedia PDFDokument8 SeitenTICKLER-PRINT Pedia PDFCarlos H. AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tickler Print PediaDokument8 SeitenTickler Print PediaCarlos H. AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TICKLER-PRINT-2 Pedia PDFDokument7 SeitenTICKLER-PRINT-2 Pedia PDFCarlos H. AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 'Batangas Medical Center Case Report by PGI Carlos H. AcuñaDokument7 Seiten'Batangas Medical Center Case Report by PGI Carlos H. AcuñaCarlos H. AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UST-PREV MED (3rd Handout) - Dr. PinedaDokument14 SeitenUST-PREV MED (3rd Handout) - Dr. PinedaCarlos H. AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rabies Lay ForumDokument40 SeitenRabies Lay ForumCarlos H. AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nephro - CKDDokument6 SeitenNephro - CKDCarlos H. AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology of Chronic Inflammation: Robbins' Basic Pathology 2-20 7 EdDokument17 SeitenHistology of Chronic Inflammation: Robbins' Basic Pathology 2-20 7 EdCarlos H. AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 4-CT - PUDDokument7 SeitenCase 4-CT - PUDCarlos H. AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evidence Based MedicineDokument10 SeitenEvidence Based MedicineCarlos H. AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Physical Examination Silverman Transcribed Notes (Chapter 6) General CommentsDokument8 SeitenGeneral Physical Examination Silverman Transcribed Notes (Chapter 6) General CommentsCarlos H. AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem List: Problem Date Identified Date Resolved ManagementDokument1 SeiteProblem List: Problem Date Identified Date Resolved ManagementCarlos H. AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micromonospora Purpurea. Action IsDokument3 SeitenMicromonospora Purpurea. Action IsCarlos H. AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PathoDokument1 SeitePathoCarlos H. AcuñaNoch keine Bewertungen