Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
"Nagtatae Siya 4 Days Na" As Verbalized by The Mother. Inatake of Causative Agents Irritation of The Stomach Inflammation of The Stomach Increase GI Motility Diarrrhea
Hochgeladen von
Melissa MhelOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
"Nagtatae Siya 4 Days Na" As Verbalized by The Mother. Inatake of Causative Agents Irritation of The Stomach Inflammation of The Stomach Increase GI Motility Diarrrhea
Hochgeladen von
Melissa MhelCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
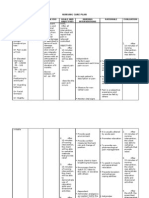
NURSING ANALYSIS/HEALTH GOAL AND
CUES NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS IMPLICATION OBJECTIVES
INTERACTION Diarrhea Inatake of causative After 4 hours of Observe and record stool Helps differentiate After 4 hours of
“Nagtatae siya 4 related to agents nursing frequency, individual disease and nursing
days na” As infectious ↓ interventions, the characteristics, amount assesses severity of interventions, the
verbalized by the processes as Irritation of the client will report client was able to
and precipitating factors. episode.
mother. stomach
manifested by reduction in report reduction in
↓
OBSERVATION
passage of Inflammation of the
frequency of Promote bed rest. Rest decreases frequency of
loose watery stomach passage of stool. intestinal motility and passage of stool.
WBC count stool ↓ reduces metabolic rate.
10.4 Increase GI motility
↓ Identify foods and fluids Avoiding intestinal
Lymphocytes
Diarrrhea that precipitate diarrhea. irritants promotes
0.167
Hyperactive intestinal rest.
bowel
movements Restart oral fluid intake Provides colon rest by
gradually. Offer clear omitting or decreasing
liquids hourly, and avoid stimulus of foods or
fluids.
Encourage to eat foods Fruits that are stool
like banana and apple. former.
Avoid foods that are oily, Foods that may
spicy and caffeine. precipitate gastric
cramping.
Administer antidiarrheals Decreases G.I motility
as prescribed by the or peristalsis and
physician. diminishes digestive
secretions to relieve
cramping and diarrhea.
NURSING ANALYSIS/HEALTH GOAL AND
CUES NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS IMPLICATION OBJECTIVES
OBSERVATION Nutrition, less intestinal fluid After 3 days of > Measured height and > for initial data base and After 3 days of
than body output overwhelms Nursing Intervention weight everyday and to see gain or lose in nursing
(+) poor skin requirements the absorptive the patient will: isplay compared it each day. weight. intervention the
turgor related to capacity of the GI physical growth and goal was partially
(+)muscle excessive fluid tract Gain weigth > Note status of fontanels, > Inadequate fluid intake met. The patient
wasting
(+) sunken loss and ↓ appropriate for age production of mucus, and results in dehydration,
skin turgor, and number of
did not fully gain
fontanel malsabsorption damage to the and developmental number of wet diapers per wet diapers per day. weight necessary
as manifested villous brush stage. day. for her age
Wt.= 1.8 by poor skin border of the
kg(<2500 g) SGA turgor, muscle intestine, >Encourage continued use > Skim milk contains about half
wasting, ↓ of formula for first 12 mo. the number of calories in breast
sunken malabsorption of of life. Discourage or commercial formulas;
fontanel and intestinal contents, substitution of skim or
Wt.= 1.8 vitamins and whole cow’s milk.
kg(<2500 g) electrolytes > Determine color,
SGA frequency, consistency, > Altered elimination
and odor of stool. pattern may suggest
problem with digestion
and absorption.
> FTT infants who are
> Instruct in addition to breastfed may benefit
human milk fortifiers(HMF), from having the mother
as indicated, to milk bottlefeed breast until the
supplemented with extra infant is gaining weight
appropriately on a
calories breast milk, which consistent basis. Note:
is The morning and evening
pumped and stored for feeding may be from the
feedings. breast in order to support
the maternal
breastfeeding experience.
NURSING GOAL AND
CUES INFERENCE NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS OBJECTIVES
INTERACTION Knowledge Disease Process After 8 hours > Determine the mother’s >Establishes knowledge After 3 days of
“akala ko normal deficient related ↓ of Nursing perception of disease base and provides some nursing
lang namagtae Presence of Signs Intervention the
to unfamiliarity of patient’s parent/ process. insight into individual intervention the
siya, limang araw the condition and and symptoms watcher will: learning needs goal was met.
bago namin siya ↓
information The patient’s
dinala sa ospital”. Ignore signs and
misinterpretation >Verbalize > Review disease process, >Accurate knowledge base watcher
As verbalized by symptoms
the mother. . ↓ understanding of cause/effect relationship of provides opportunity for the verbalized
Aggravations of the disease factors that precipitate mother to make informed understanding of
OBSERVATION conditions processes, symptoms, and identify decisions/choices about disease
The statement ↓ possible ways to reduce contributing future and control of processes, and
supports the idea Knowledge Deficit complications factors. Encourage chronic disease. Although possible
that the parents questions. most others know about complications
have deficient their own disease process,
information they may have outdated
regarding the information or
illness of their
misconceptions.
child.
> Review medications,
purpose, frequency, > Promotes understanding
dosage, and possible side and may enhance
effects. cooperation with regimen
>Stress importance of good > Reduces spread of
skin care, e.g., proper bacteria and risk of skin
handwashing techniques irritation/breakdown,
and perineal skin care. infection.
> Patients with IBD are at
> Emphasize need for long-
risk for colon/rectal cancer,
term follow-up and periodic
and regular diagnostic
reevaluation.
evaluations may be
required
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cutaneous Anthrax Nursing Care PlanDokument2 SeitenCutaneous Anthrax Nursing Care PlanYayin Pestaño100% (1)
- Deficient KnowledgeDokument3 SeitenDeficient KnowledgeCamilleAnneRoseRabinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)Dokument2 SeitenCompartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)eunica16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: IndependentDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan: IndependentAdhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP PryllDokument6 SeitenNCP PryllpjcolitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patricia Mae T. Miranda: Assessment Family Nursing Care Diagnoses Planning Implementation EvaluationDokument2 SeitenPatricia Mae T. Miranda: Assessment Family Nursing Care Diagnoses Planning Implementation EvaluationPatricia Mae MirandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument4 SeitenNCPRachel PerandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP-fluid Volume DeficitDokument4 SeitenNCP-fluid Volume DeficitChrissa Mae Aranilla MayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ncp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasDokument4 SeitenNcp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasFran LanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glaucoma NCPDokument4 SeitenGlaucoma NCPChantal CaraganNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument8 SeitenNCPJoseph Anthony Benitez VerzosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ncp-Imbalance NutritionDokument2 SeitenNcp-Imbalance NutritionMariko BarbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Objectives: "Masakit Lagi Yung Lalamunan NyaDokument3 SeitenAssessment Objectives: "Masakit Lagi Yung Lalamunan Nyaangel_pearl413100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For LYING inDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan For LYING inKarissa CiprianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Pedia SleepapneaDokument2 SeitenNCP Pedia SleepapneaDavid Brillo100% (1)
- Fluid Volume Loss NCP - PediaDokument2 SeitenFluid Volume Loss NCP - PediaAdrian MallarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDokument1 SeiteNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument4 SeitenNCPyasayayasay yasayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Breast Cancer NCP PDFDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Breast Cancer NCP PDFMaina BarmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Er NCPDokument9 SeitenEr NCPEden Marie FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument7 SeitenNCPJo Chiko FlorendoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument4 SeitenNCPAndrea BroccoliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJennirose JingNoch keine Bewertungen
- SLCN Gazette Magazine, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2019Dokument20 SeitenSLCN Gazette Magazine, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2019Mayzelle RizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDokument3 SeitenAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDanica Kate GalleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Infection NewDokument3 SeitenNCP Infection NewXerxes DejitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument3 SeitenNCPeun kyung shinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Airway Clearance - PTBDokument2 SeitenIneffective Airway Clearance - PTBIrish Eunice FelixNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP DiarrheaDokument2 SeitenNCP DiarrheaBracel GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cholecystectomy Nursing Care Plan: Intraoperative Problem: Risk For AspirationDokument1 SeiteCholecystectomy Nursing Care Plan: Intraoperative Problem: Risk For AspirationJess GoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP 3Dokument2 SeitenNCP 3Richson Bacay100% (1)
- In Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Surgical Ward RotationDokument3 SeitenIn Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Surgical Ward RotationEdgie FabreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goboy - Risk For Infection NCPDokument3 SeitenGoboy - Risk For Infection NCPLouise GermaineNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Acute PainDokument3 SeitenNCP Acute Painmanoelsterg50% (2)
- Answer: 59.5 KG: Rationale: Although All of These Clients Might Experience Fluid Volume Deficit, TheDokument14 SeitenAnswer: 59.5 KG: Rationale: Although All of These Clients Might Experience Fluid Volume Deficit, TheMikeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument1 SeiteNCPnictan 140% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPDokument2 SeitenNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPpa3kmedina100% (1)
- NCP Nausea and VomitingDokument4 SeitenNCP Nausea and VomitingKingJayson Pacman06Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Hopelessness NCPDokument5 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Hopelessness NCPRammiel Saylo CarlosNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - Acute PainDokument2 SeitenNCP - Acute PainsAm_300% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationria_soriano_2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Volume Deficit BatuDokument2 SeitenFluid Volume Deficit Batumecz26Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Acute PainDokument3 SeitenNCP Acute PainSheene Lysethea Sioteco AguilosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Planjnx_anonymousNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument3 SeitenNCPChrisTine M. MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Problem: Acute Intermittent Moderate PainDokument1 SeiteNursing Care Plan Problem: Acute Intermittent Moderate PainDiana Laura Lei100% (3)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDokument1 SeiteAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationJames PajarilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP (Acute Pain)Dokument2 SeitenNCP (Acute Pain)jennilois100% (1)
- Homework 1: Developing A Health Teaching Program 1. What Insights and Reflections Do You Have Based On Your Understanding of The EssentialDokument2 SeitenHomework 1: Developing A Health Teaching Program 1. What Insights and Reflections Do You Have Based On Your Understanding of The EssentialRianne BaetiongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementio N EvaluationDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementio N EvaluationAndrew James Javier Quidez100% (1)
- HoplessnessDokument16 SeitenHoplessnessHamza IshtiaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity IntoleranceDokument2 SeitenActivity IntolerancedohbleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationKenj PereñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gout N C P BY BHERU LALDokument1 SeiteGout N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Age NCPDokument3 SeitenAge NCPMartin Allen ClaudioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity On Care PlanningDokument4 SeitenActivity On Care PlanningRichlle CortesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity On Care PlanningDokument4 SeitenActivity On Care PlanningRichlle CortesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For DiarrheaDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan For DiarrheaImang Dela Cruz100% (9)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokument4 SeitenAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluationliezel jane agramonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Diarrhea Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokument8 SeitenNursing Care Plan Diarrhea Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationKrah100% (1)
- ADV-885E-PAC-1 Quick Reference Guide Metric EU Version 1Dokument7 SeitenADV-885E-PAC-1 Quick Reference Guide Metric EU Version 1Alonso Rafael Vasquez ContrerasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sepsis Early Goal Directed Therapy (EGDT) Algorithm/Driver DiagramDokument1 SeiteSepsis Early Goal Directed Therapy (EGDT) Algorithm/Driver DiagramAngga AndriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FACTS: There Is No Cure & Complete: Sustained Remissions Are Rare. Principles of TherapyDokument12 SeitenFACTS: There Is No Cure & Complete: Sustained Remissions Are Rare. Principles of TherapyAzizan HannyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study: Observational Travelers' DiarrheaDokument5 SeitenStudy: Observational Travelers' DiarrheaFathah MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Child Psychopathology: Child Psychopathology Is The Manifestation of Psychological Disorders in Children andDokument7 SeitenChild Psychopathology: Child Psychopathology Is The Manifestation of Psychological Disorders in Children andMarvellous MunhuwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topical AntifungalsDokument14 SeitenTopical AntifungalsRasha Mohammad100% (1)
- Ankylosing SpondylitisDokument4 SeitenAnkylosing SpondylitisHenry TirtosuhartoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fin e 171 2014 PDFDokument66 SeitenFin e 171 2014 PDFRenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enteral NutritionDokument11 SeitenEnteral NutritionEso Soso0% (1)
- Gas Exchange in HumansDokument9 SeitenGas Exchange in HumanscherylrachelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study AnalysisDokument3 SeitenCase Study Analysisapi-241588828Noch keine Bewertungen
- Immunological Basis of Infertility in AnimalsDokument13 SeitenImmunological Basis of Infertility in AnimalsRamachandran Ram100% (3)
- Ahprn Getting Involved in Research A Pocket Guide 0 0 0Dokument215 SeitenAhprn Getting Involved in Research A Pocket Guide 0 0 0Rusnifaezah MusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contoh IjapDokument4 SeitenContoh IjapFarihaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calsium Supplementation With Rasbora Sp. To Prevent Loss of Bone Mineral Density During Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone Agonist Long-Term TreatmentDokument5 SeitenCalsium Supplementation With Rasbora Sp. To Prevent Loss of Bone Mineral Density During Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone Agonist Long-Term Treatmentfarad killaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bipolar DisordersDokument63 SeitenBipolar DisorderselvinegunawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerosol TherapyDokument10 SeitenAerosol Therapy04lubna_869632400Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer and Rationale Psychiatric NursingDokument23 SeitenAnswer and Rationale Psychiatric NursingCharles Gerard B. BeluanNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Protocolo) ACT For Psychosis. An 18 Session Group Therapy Protocol - Pearson & TingeyDokument82 Seiten(Protocolo) ACT For Psychosis. An 18 Session Group Therapy Protocol - Pearson & TingeyDavid Espinola100% (1)
- First Aid Cdrrmo 2019Dokument373 SeitenFirst Aid Cdrrmo 2019fenan sollanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Learning,, ,: Key WordsDokument8 SeitenE-Learning,, ,: Key WordsMaria MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 SoalDokument5 Seiten11 SoalHerman NasuhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP and CNPDokument37 SeitenNCP and CNPDen TupasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sewage Treatment PlantDokument12 SeitenSewage Treatment Plantanuj dhavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CD N Psoriasis GuidelinesDokument109 SeitenCD N Psoriasis GuidelinesMuhammad Ilham RafiudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Promise of Energy Psychology Nexus PDF by Brendan D. MurphyDokument7 SeitenThe Promise of Energy Psychology Nexus PDF by Brendan D. MurphyBrendan D. MurphyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A 3 Table of Surgical Procedures TOSP With Minor Surgical Procedures MSPs 1Dokument94 SeitenA 3 Table of Surgical Procedures TOSP With Minor Surgical Procedures MSPs 1Chee Yung NgNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITAT Holds That Charitable Trust Running Max Hospital Was Charitable To Only To Corporate Max Group of Companies and Uncharitable' Towards The Society or PublicDokument46 SeitenITAT Holds That Charitable Trust Running Max Hospital Was Charitable To Only To Corporate Max Group of Companies and Uncharitable' Towards The Society or PublicLive LawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vitamin EDokument11 SeitenVitamin EErvan Apsara BismakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MectaDokument29 SeitenMectakinantika nur dewantiNoch keine Bewertungen