Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
The Textile Industry
Hochgeladen von
abdelbarr0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
18 Ansichten4 SeitenThe textile industry produces wastewater that requires treatment through a multi-stage process including preliminary treatment, biological treatment, and sometimes tertiary treatment. Preliminary treatment involves screening, homogenization, and neutralization. Biological treatment can include physical-chemical treatment, trickling filters, or activated sludge processes to remove BOD5. Tertiary treatment through methods like chemical precipitation or ozonation can further remove non-biodegradable COD and color. Produced sludge is then thickened and dewatered.
Originalbeschreibung:
op
Originaltitel
1429_1431
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe textile industry produces wastewater that requires treatment through a multi-stage process including preliminary treatment, biological treatment, and sometimes tertiary treatment. Preliminary treatment involves screening, homogenization, and neutralization. Biological treatment can include physical-chemical treatment, trickling filters, or activated sludge processes to remove BOD5. Tertiary treatment through methods like chemical precipitation or ozonation can further remove non-biodegradable COD and color. Produced sludge is then thickened and dewatered.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
18 Ansichten4 SeitenThe Textile Industry
Hochgeladen von
abdelbarrThe textile industry produces wastewater that requires treatment through a multi-stage process including preliminary treatment, biological treatment, and sometimes tertiary treatment. Preliminary treatment involves screening, homogenization, and neutralization. Biological treatment can include physical-chemical treatment, trickling filters, or activated sludge processes to remove BOD5. Tertiary treatment through methods like chemical precipitation or ozonation can further remove non-biodegradable COD and color. Produced sludge is then thickened and dewatered.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
7.
The textile industry
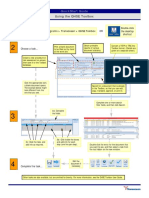
7. THE TEXTILE INDUSTRY
According to the imposed purification two may be used. The treatment proce-
Rates, physical-chemical or biological dure (figure 975) includes the stages
treatment or even a combination of the described below:
7.1. It is vital to provide for a buffer capacity
offering a volume corresponding to 6-12
PRELIMINARY hours storage time for the average flow
TREATMENT treated. This makes it possible to spread
over 24 hours the treatment of waste that is
Screening - straining usually produced over 16 hours (two
The presence of fluff and cotton flock shifts). Air stirring of the buffer tank can
also be useful.
means that fine straining has to be carried
out after routine screening. Oil removal, in
the event of large quantities of white spirit, Neutralisation
may also be necessary. After homogenisation, the pH of
effluents generally remains alkaline,
Homogenisation between 9 and 10. Neutralisation is
therefore necessary. It is carried out either
by sulphuric acid or available flue gas.
Chap. 26: Industrial processes and the treatment of wastewater
7.2. TREATMENT avoid dogging of filter packing. Owing to this
constraint, it is advisable to precede the
trickling filter process with physical-chemical
7.2.1. Physical-chemical treatment treatment with flocculation-settling. Once the
trickling filter stage has been completed, a
This treatment is only useful if the raw final clarifier may be used, depending on the
effluent contains a large quantity of SS, toxic end result needed.
substances (sulphides, chromates, etc.), or if
it requires a high degree of colour removal. Activated sludge
Treatment may include one or several of the Due to the type of pollution, it is advisable
following stages:
to size the facility with a low F/M ratio. The
- catalytic oxidation of sulphides in an settling tank must be sufficiently large to
aerated tank, with controlled addition of iron account for poor activated sludge settleability
or manganese salts, owing to the high content of surface-active
- flocculation in a slowly mixed reactor with agents in wastewater to be treated.
dosage of iron or aluminium salts followed BOD5 removal rates reach 90% to 95%.
by addition of an organic polymer to enhance
settling yield,
7.2.3. Tertiary treatment
- clarification by settling (Turbocirculator) or
flotation (Flotazur).
Tertiary treatment is useful for the removal
of non-biodegradable COD and more
7.2.2. Biological treatment
especially for colour removal. It includes:
chemical precipitation, ozonation, adsorption
Depending on the pollutant load and on activated carbon, etc.
purification level required, several treatment It is also preferable to carry out a
processes are available: treatabiliry test to choose and size the most
suitable procedure.
Trickling filter, followed by settling if
needed Sludge
This is the simplest technique and allows a Produced sludge is thickened and then
BOD5 removal rate of between 50% and dewatered either by a belt filter (Superpress
70%. It does, however, require raw water to or GDPresse), or filter press.
be completely free of any fibrous content to
7. The textile industry
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Work Permits FormatsDokument17 SeitenWork Permits FormatsAjay khatriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slings Instruction ManualDokument20 SeitenSlings Instruction ManualCris SuyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical, Chemical & Biological: Design of Facilities For Treatment of Waste WaterDokument118 SeitenPhysical, Chemical & Biological: Design of Facilities For Treatment of Waste WaterAseem Vivek Masih100% (1)
- Heavy Fuel OilsDokument114 SeitenHeavy Fuel Oilsrenatomico2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Iron Ore Processing 2009 PDFDokument41 SeitenIron Ore Processing 2009 PDFglz1100% (2)
- Treatment On Petrochemical Industry Waste WaterDokument28 SeitenTreatment On Petrochemical Industry Waste WaterRimeli RoychoudhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- SP 1099Dokument34 SeitenSP 1099Muthu KumaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crude Oil ProcessingDokument8 SeitenCrude Oil Processingmarcomaciel3061Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ball MillDokument8 SeitenBall MillHumbulaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effluent Treatment PlantDokument67 SeitenEffluent Treatment PlantSWATHI ACHARNoch keine Bewertungen
- #Biogas ScrubbingDokument13 Seiten#Biogas ScrubbingLai Mei EeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digester Design2Dokument16 SeitenDigester Design2Pragathees WaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sequencing Batch Reactor Technology For Biological Wastewater Treatment: A ReviewDokument9 SeitenSequencing Batch Reactor Technology For Biological Wastewater Treatment: A ReviewDiliptiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sludge Treatment & DisposalDokument78 SeitenSludge Treatment & DisposalAirish Navera67% (3)
- Sludge TreatmentDokument9 SeitenSludge Treatmentrollrams100% (1)
- Separation and Processing and Transformation of Solid WasteDokument10 SeitenSeparation and Processing and Transformation of Solid WasteKind Red50% (2)
- Objectives: Chapter 4 Sludge Treatment and DisposalDokument37 SeitenObjectives: Chapter 4 Sludge Treatment and Disposalashe zinabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil Gas Industry Waste ManagementDokument29 SeitenOil Gas Industry Waste ManagementFtr RizkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling, Control, and Optimization of Natural Gas Processing PlantsVon EverandModeling, Control, and Optimization of Natural Gas Processing PlantsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- 1 CAM Intro FinalDokument41 Seiten1 CAM Intro FinalSourav MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final - STP ReportDokument39 SeitenFinal - STP ReportSatyavijet Chilakapati100% (1)
- Methods For UASB Reactor DesignDokument5 SeitenMethods For UASB Reactor Designecotechconsultants100% (1)
- Hydrogen Sulfide Removal From BiogasDokument4 SeitenHydrogen Sulfide Removal From BiogasAbdussyukur Rila SubektiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sludge Treatment: 1-Thickening 2-Stabilization 3-DewateringDokument11 SeitenSludge Treatment: 1-Thickening 2-Stabilization 3-Dewateringomar alasadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Submitted by Natthu Shrirame: Under The Guidance ofDokument48 SeitenSubmitted by Natthu Shrirame: Under The Guidance ofKamran Rana100% (2)
- PERTAMINA COMPATIBILITY TEST Method PDFDokument27 SeitenPERTAMINA COMPATIBILITY TEST Method PDFm_asad_a50% (2)
- Week 9-CHEM4015-CIVE4140-2023-2024Dokument44 SeitenWeek 9-CHEM4015-CIVE4140-2023-2024Nitin RautNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyclic Activated Sludge TechnologyDokument8 SeitenCyclic Activated Sludge TechnologyNavin GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wastewater TreatmentDokument10 SeitenWastewater Treatmentهاجر صالح جبارNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effluent TreatmentDokument21 SeitenEffluent TreatmentRadhika AnandkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Choise of Sewage Treatment ProcessDokument24 SeitenChoise of Sewage Treatment Processerkarthik85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dizayee Et Al, 2023Dokument16 SeitenDizayee Et Al, 2023Simon JuddNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of The Upflow Sludge Blanket (USB) ReactorDokument36 SeitenUse of The Upflow Sludge Blanket (USB) ReactorinscNoch keine Bewertungen
- HYDRANAUTICS - Technical Service BulletinDokument50 SeitenHYDRANAUTICS - Technical Service Bulletindpahomi1Noch keine Bewertungen
- 26.1. Industrial Processes and The Treatment of Waste Water - Description of Treatment TechniquesDokument6 Seiten26.1. Industrial Processes and The Treatment of Waste Water - Description of Treatment TechniquesWafa A. NasserNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHT 303 Module 3 To S5Dokument144 SeitenCHT 303 Module 3 To S5jonasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaerobic Biological Wastewater TreatmentDokument4 SeitenAnaerobic Biological Wastewater TreatmentKhalilRoumaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- H2S Paper AD 10Dokument3 SeitenH2S Paper AD 10Ajit HaridasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Wastewater Treatment-DisposalDokument37 SeitenIndustrial Wastewater Treatment-DisposalSajedur Rahman SetuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerobic Digestion-Deo KnjigeDokument16 SeitenAerobic Digestion-Deo Knjigemilenaknezevic.mikanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 4.0 WW PorcessingDokument26 SeitenTopic 4.0 WW PorcessingikhwanstorageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wastewater Treatment: On Completion of This Segment You Should BeDokument57 SeitenWastewater Treatment: On Completion of This Segment You Should BeGourav MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agua DeclorinacionDokument8 SeitenAgua DeclorinacionpepitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Activated Sludge ProcessDokument32 SeitenOverview of Activated Sludge ProcesssoorajTVMNoch keine Bewertungen
- H. Zhang Et Al. Separation and Purification Technology 63 (2008) 264-268Dokument5 SeitenH. Zhang Et Al. Separation and Purification Technology 63 (2008) 264-268ZIA UR REHMANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanism of Precipitate Formation NewDokument12 SeitenMechanism of Precipitate Formation NewAnonymous atBeojaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treatment Anaerobic 2004Dokument9 SeitenTreatment Anaerobic 2004ASK REDANoch keine Bewertungen
- AGF Potato ProcessingDokument8 SeitenAGF Potato Processinganil_049Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sludge TreatmentDokument8 SeitenSludge TreatmentHausland Const. Corp.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Science and EngineeringDokument4 SeitenEnvironmental Science and Engineeringmenma JintanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2Dokument28 SeitenModule 2ikhwanstorageNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOme InfoDokument7 SeitenSOme InfoJITENDRA CARPENTERNoch keine Bewertungen
- M19L25 PDFDokument7 SeitenM19L25 PDFJade BobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glycol Treating During The Pipeline Transport of Natural GasDokument4 SeitenGlycol Treating During The Pipeline Transport of Natural GasWidiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture-06: Sludge Treatment and Disposal: Ce 333: Environmental Engineering IiDokument6 SeitenLecture-06: Sludge Treatment and Disposal: Ce 333: Environmental Engineering IiMirza Md. Nazmus SakibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture4 PDFDokument7 SeitenLecture4 PDFmisbul hadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harrelkas2009 PDFDokument10 SeitenHarrelkas2009 PDFRohan ChauguleNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Industrial HygieneDokument23 SeitenHistory of Industrial HygieneJohnCarloTolibasNoch keine Bewertungen
- NAWTEC - New Trends On Flue Gas CleaningDokument14 SeitenNAWTEC - New Trends On Flue Gas CleaningADalPozzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Removal of Hydrogen Sulfide From Biogas Using Dry Desulfurization Systems PDFDokument4 SeitenRemoval of Hydrogen Sulfide From Biogas Using Dry Desulfurization Systems PDFLương Hữu BắcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imp ZLD System Tamil NaduDokument4 SeitenImp ZLD System Tamil Naduneeraj sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil & Gas Industry Waste Management: Prof. Dr. Mamdouh F. Abdel-SabourDokument28 SeitenOil & Gas Industry Waste Management: Prof. Dr. Mamdouh F. Abdel-SabourKawooya AloysiusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesage 23709Dokument8 SeitenLesage 23709حاتم غيدان خلفNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesage 23709Dokument8 SeitenLesage 23709حاتم غيدان خلفNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treatability and Kinetics Studies of Mes PDFDokument8 SeitenTreatability and Kinetics Studies of Mes PDFwilfredo suarez torresNoch keine Bewertungen
- STP Secondary Treatment Sept 27 2018Dokument26 SeitenSTP Secondary Treatment Sept 27 2018Mulberry PlaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- FILMTEC Membranes: Tech Manual ExcerptsDokument5 SeitenFILMTEC Membranes: Tech Manual ExcerptsgsaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suspended Growth Biological TreatmentDokument21 SeitenSuspended Growth Biological Treatmentsaiful islamNoch keine Bewertungen
- gdwq4 With Add1 Annex5Dokument19 Seitengdwq4 With Add1 Annex5Keile Brugés PinedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charge LourdeDokument3 SeitenCharge LourdeabdelbarrNoch keine Bewertungen
- QHSE Toolbox PDFDokument88 SeitenQHSE Toolbox PDFabdelbarrNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuickStart - Using The QHSE ToolboxDokument1 SeiteQuickStart - Using The QHSE ToolboxabdelbarrNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuickStart - Importing From THINKDokument1 SeiteQuickStart - Importing From THINKabdelbarrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surface Treatment: 10.1. RecyclingDokument6 SeitenSurface Treatment: 10.1. RecyclingabdelbarrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1. HP CondensatesDokument9 Seiten2.1. HP CondensatesabdelbarrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 103Dokument52 Seiten103Món Quà Vô Giá100% (1)
- Puzwm 50 VhaDokument86 SeitenPuzwm 50 Vhamoreds1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Green Cosmos AKS Lining PDFDokument8 SeitenGreen Cosmos AKS Lining PDFMeng WaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stripper Bolt, Coil Spring, Dowel PinDokument3 SeitenStripper Bolt, Coil Spring, Dowel Pinmuhamad laaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gke10 Spirax SarcoDokument2 SeitenGke10 Spirax SarcoEMANoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 SinteringDokument32 Seiten2 SinteringGopikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Database of Embodied Energy and Water Values For MaterialsDokument3 SeitenDatabase of Embodied Energy and Water Values For MaterialsMax Yanac TelleriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON 7 - Quality of Manufacturing ProcessDokument21 SeitenLESSON 7 - Quality of Manufacturing Processcelestetorino1Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S1359835X05003957 Main PDFDokument14 Seiten1 s2.0 S1359835X05003957 Main PDFabiliovieiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Septic TanksDokument6 SeitenSeptic TanksJustin MusopoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Installation For Second Floor For G+2Dokument1 SeiteElectrical Installation For Second Floor For G+2Welday GebremichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEBECO I LINE COST (As of July 2006)Dokument24 SeitenCEBECO I LINE COST (As of July 2006)Sugar RayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burnit Comfort PM PM/BDokument56 SeitenBurnit Comfort PM PM/BAleksandar GuskovNoch keine Bewertungen
- AWS D1 Visual InspectionDokument2 SeitenAWS D1 Visual InspectionBHUSHAN KALENoch keine Bewertungen
- 4327 Corrosive Sulphur Flyer PDFDokument2 Seiten4327 Corrosive Sulphur Flyer PDFMichael Angelo VidalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swaged and Lightweight Welding NozzlesDokument5 SeitenSwaged and Lightweight Welding NozzlesDries VandezandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Suction Hose - 10 Bar: Application: FeaturesDokument2 SeitenWater Suction Hose - 10 Bar: Application: FeaturesShyam BKNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-2 Spot WeldingDokument24 Seiten3-2 Spot Weldingsrikanth_aravamuthanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensus WP Dynamic Cold Water Meter (DN40-300)Dokument4 SeitenSensus WP Dynamic Cold Water Meter (DN40-300)Roderikus Rendy MNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Silica FumeDokument2 SeitenWhat Is Silica FumeAmmarNoch keine Bewertungen