Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Singh, Ramesh Prasad-Applied Welding Engineering, Second Edition - Processes, Codes, and Standards-Butterworth Heinemann (2016) PDF
Hochgeladen von
Braulio AtacusíOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Singh, Ramesh Prasad-Applied Welding Engineering, Second Edition - Processes, Codes, and Standards-Butterworth Heinemann (2016) PDF
Hochgeladen von
Braulio AtacusíCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
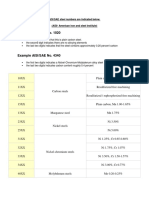
58 SECTION j 1 Introduction to Basic Metallurgy
AISI-SAE Designation Type of Steel with Typical Grades Nominal Alloy Content (%)
Carbon Steels
10xx Plain carbon steel: 1005, 1010, Manganese up to 1% max
1016, 1030 etc.
11xx Resulfurized: 1110, 1117, 1137
etc.
12xx Resulfurized and
Rephosphorized: 1211, 1212,
1213, 1215, 12L14 (this grade
include up to 0.35% lead)
15xx Plain carbon steel: 1513, 1522, Manganese range from 1% to
1526, 1548,1561 and 1566 etc. 1.65%
Manganese Steels
13xx Manganese 1.75%
Nickel Steels
23xx Nickel 3.5
Nickel 5
Nickel Chromium Steels
31xx Nickel 1.25, Cr 0.65 and 0.80
32xx Nickel 1.75, Cr 1.07
33xx Nickel 3.50, Cr 1.5 and 1.57
34xx Nickel 3.00, Cr 0.77
Molybdenum Steels
40xx 4023, 4024, 4027, 4028 etc. Mo 0.20 and 0.25
44xx Mo 0.40 and 0.52
Chromium Molybdenum Steels
41xx Cr Mo
4118 0.50 0.12
4130, 4137, 4140, 0.80 0.20
4142, 4145, 4147, 4150 0.95 0.25
4161 0.70-0.90 0.30
Nickel Chromium Molybdenum Steels
43xx 4320 Ni Cr Mo
1.65 to 0.40 to 0.20 to
2.00 0.60 0.30
4340 1.65 to 0.70 to 0.20 to
2.00 0.90 0.30
47xx 4720 0.90 to 0.35 to 0.15 to
1.20 0.55 0.25
81xx 0.30 0.40 0.12
86xx 0.55 0.50 0.20
87xx 0.55 0.50 0.25
88xx 0.55 0.50 0.35
93xx 3.25 1.20 0.12
94xx 0.45 0.40 0.12
97xx 0.55 0.20 0.20
98xx 1.00 0.80 0.25
Nickel Molybdenum Steels
46xx Ni Mo
0.85 0.20
1.82 0.25
48xx 3.50 0.25
Chromium Steels
50xx Cr 0.27, 0.40, 0.50, 0.65
51xx Cr 0.80, 0.87, 0.92, 1.00, 1.05
52xx Cr 0.50, Carbon 1.00
FIGURE 1-6-1 Classification of steel.
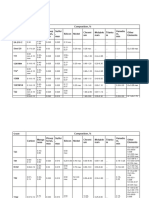
Classification of Steels Chapter j 6 59
Chromium Vanadium Steels
61xx Cr V
0.60, 0.80, 0.95 0.10, 0.15
Chromium Tungsten Steels
72xx Cr 0.75; W 1.75
Silicon Manganese Steels
92xx Si: 1.40, 2.00; Mn 0.65, 0.82,
0.85; Cr 0.65
High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steels
9xx Various SAE grades
xxBxx B indicates added Boron
xxLxx L indicates Lead addition
XX indicates steel designation for carbon steel and low alloys.
Stainless Steels
AISI designation SAE designation
2xx 302xx Chromium Manganese and
FIGURE 1-6-1 contd
LOW-CARBON STEELS
Low-carbon steels contain up to 0.30% carbon. The majority of this class of
steel is flat-rolled products such as sheet or strip; usually they are in the cold-
rolled and annealed condition. These steels have high formability because they
contain very low carbon, usually less than 0.10% C, with up to 0.4% Mn.
For rolled steel structural plates and sections, the carbon content is often
increased to approximately 0.30%, and the manganese content is increased to
1.5%. These materials are useful for stampings, forgings, seamless tubes, and
as boilerplates.
MEDIUM-CARBON STEELS
Medium-carbon steels are similar to low-carbon steels except that they contain
carbon from 0.30% to 0.60% and manganese from 0.60% to 1.65%. Increasing
the carbon content to approximately 0.5% with an accompanying increase in
manganese allows medium-carbon steels to be used in the quenched and
tempered condition. These steels are mainly used for making shafts, axles,
gears, crankshafts, couplings, and forgings. Steels with carbon ranging from
0.40% to 0.60% are used for rails, railway wheels, and rail axles.
HIGH-CARBON STEELS
High-carbon steels contain carbon from 0.60% to 1.00%; the manganese
content ranges from 0.30% to 0.90%. High-carbon steels are used for some
hand tools, spring materials, and high-strength wires.
ULTRAHIGH-CARBON STEELS
These steels are often experimental alloys containing 1.25% to 2.0% C. These
steels are often thermomechanically processed to produce consistent and
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- AISI Steel Numbers GuideDokument3 SeitenAISI Steel Numbers GuideSai ChandrasekharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polish Rod SpecificationsDokument1 SeitePolish Rod SpecificationsRisky PradikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Alloy DesignationsDokument2 SeitenSteel Alloy DesignationsVlad RytovNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM A 453/A 453M chemical and heat treatment requirementsDokument1 SeiteASTM A 453/A 453M chemical and heat treatment requirementsEderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ferrous Weld Metal Classification ChartDokument1 SeiteFerrous Weld Metal Classification ChartBruno SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- AcerosalCarbonoDokument5 SeitenAcerosalCarbonoEDGARD NESTOR VILCARINO ZELADANoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 4 - Fastener - MaterialsDokument33 SeitenSection 4 - Fastener - MaterialsChris MedeirosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buderus Edelstahl Presentation PDFDokument15 SeitenBuderus Edelstahl Presentation PDFMustafa Mert SAMLINoch keine Bewertungen
- Table 1 Chemical RequirementsDokument2 SeitenTable 1 Chemical RequirementsmoodydoodyNoch keine Bewertungen
- QW 442 A Number PDFDokument1 SeiteQW 442 A Number PDFMadidj_2014Noch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM A325 Heavy Hex Structural Bolt SpecificationDokument1 SeiteASTM A325 Heavy Hex Structural Bolt SpecificationAlberto CárdenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison Between Metal StandardsDokument16 SeitenComparison Between Metal StandardsS BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plate A36 (2016)Dokument4 SeitenPlate A36 (2016)eko kusumoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATERIALS FOR PRESSURE PARTS - CompositionDokument3 SeitenMATERIALS FOR PRESSURE PARTS - CompositionprabodhvkNoch keine Bewertungen
- QW-440 Weld Metal Chemical CompositionDokument1 SeiteQW-440 Weld Metal Chemical Compositionmetal treat ind.Noch keine Bewertungen
- CIPW Norm Hollacher Norm4Dokument2 SeitenCIPW Norm Hollacher Norm4Lucas CabelierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alloy Steel ChartDokument4 SeitenAlloy Steel Chartmodi_mihirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm A449Dokument1 SeiteAstm A449Vitor Rigueira de GodoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practica Calificada N°5 - Siderurgia NOMBRE: Magdalena Lucero Gómez Cabrera CODIGO: 20150203IDokument2 SeitenPractica Calificada N°5 - Siderurgia NOMBRE: Magdalena Lucero Gómez Cabrera CODIGO: 20150203ILucero Gomez CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOC DetailsDokument2 SeitenMOC DetailsrammaheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Plate Astm A36: Plates, Shapes, and Sheet PilingDokument4 SeitenStructural Plate Astm A36: Plates, Shapes, and Sheet Pilingeko kusumoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surface Roughness Comparison ChartDokument1 SeiteSurface Roughness Comparison ChartMilan JovanovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spring MaterialsDokument3 SeitenSpring MaterialsS. VeeravelNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Single Values Except EN8D Show Maximum Limit: Elements SR No Grade Carbon Manganese Phosphorus Sulfur SiliconDokument3 SeitenAll Single Values Except EN8D Show Maximum Limit: Elements SR No Grade Carbon Manganese Phosphorus Sulfur SiliconkartikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alloy Steel Designations and CompositionsDokument2 SeitenAlloy Steel Designations and CompositionsMohan Shyam PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Sheet For Hinged SystemsDokument6 SeitenData Sheet For Hinged SystemsMohsin KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM A449 Tech InfoDokument2 SeitenASTM A449 Tech InfoBoz Van DuynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aisi SteelDokument11 SeitenAisi SteelIlham SetiadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specific Heat MetalsDokument1 SeiteSpecific Heat Metalsagibson556Noch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of MaterialDokument1 SeiteComparison of Materialzohaib rafiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- HINGED 42MM SERIES PROFILESDokument120 SeitenHINGED 42MM SERIES PROFILESViswanathan Kannoor67% (3)
- API-2W Grade 50 PDFDokument2 SeitenAPI-2W Grade 50 PDFFYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Composition of Stainless Steels To BS EN 10088-2Dokument41 SeitenChemical Composition of Stainless Steels To BS EN 10088-2amit_91340% (1)
- SA-335 Chemical RequirementDokument1 SeiteSA-335 Chemical RequirementaruntpeNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIN 17174 SEAMLESS STEEL TUBES FOR LOW TEMP USEDokument7 SeitenDIN 17174 SEAMLESS STEEL TUBES FOR LOW TEMP USEdjmattmNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM A240 - A240M (Page 3)Dokument1 SeiteASTM A240 - A240M (Page 3)Yusuf KhoirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Arc Furnace SimulationDokument38 SeitenElectric Arc Furnace SimulationGilang Hermawan100% (1)
- 1993 - Recycled LeadDokument9 Seiten1993 - Recycled LeadgutobegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sections: I Rules For Construction of Power BoilersDokument23 SeitenSections: I Rules For Construction of Power BoilerssanketNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Composition of 1/3/5/6 Series AluminumDokument1 SeiteChemical Composition of 1/3/5/6 Series Aluminummukmin nbperkasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Titanium Alloys and Their PropertiesDokument14 SeitenTitanium Alloys and Their PropertiesMarno PrinslooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metals - Specific Heats: Metal Specific Heat - CDokument3 SeitenMetals - Specific Heats: Metal Specific Heat - CAzizah AmaliahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro Alloyed Steels Voestalpine EN 30102020Dokument4 SeitenMicro Alloyed Steels Voestalpine EN 30102020pierocarnelociNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book1 - KhaitanDokument2 SeitenBook1 - Khaitananirwan.duttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- +44 (0) 1786 475 662 Sales@amsmetals - Co.ukDokument2 Seiten+44 (0) 1786 475 662 Sales@amsmetals - Co.ukidontlikeebooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nickel Powder S GradeDokument1 SeiteNickel Powder S GradenvvsureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- THERMO-OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF MATERIALSDokument2 SeitenTHERMO-OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF MATERIALSMariela BaigorriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Din 17102 PDFDokument10 SeitenDin 17102 PDFEvriMert RüzgArdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alüminyum Alaşım Standartları Ve Element Içerikleri PDFDokument1 SeiteAlüminyum Alaşım Standartları Ve Element Içerikleri PDFFeratNoch keine Bewertungen
- N 1-Where An Ellipsis (... ) Appears in This Table, There Is No Requirement and The Element Need Neither Be Analyzed For or ReportedDokument1 SeiteN 1-Where An Ellipsis (... ) Appears in This Table, There Is No Requirement and The Element Need Neither Be Analyzed For or ReportedrajeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 742 PDFDokument1 Seite742 PDFrajeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - B - Chassis MaterialsDokument4 Seiten4 - B - Chassis MaterialszzirapovNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Uniqueness of Biological Materials: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Biology: ZoologyVon EverandThe Uniqueness of Biological Materials: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Biology: ZoologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pilana Metal Cutting Tools enDokument32 SeitenPilana Metal Cutting Tools enBryan ThorntonNoch keine Bewertungen
- IOC Metallurgy EDokument64 SeitenIOC Metallurgy EPriyanshu GehlotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 9 Cbse EnglishDokument8 SeitenClass 9 Cbse EnglishRoben SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solubility Rules - Chemistry LibreTextsDokument2 SeitenSolubility Rules - Chemistry LibreTextsKonoka KonoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- C. Mineral DepositsDokument8 SeitenC. Mineral DepositsShaina Mae Degal SaraumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 9 Science 3Dokument7 SeitenClass 9 Science 3chandralok_kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- G7Dokument21 SeitenG7Maame Ama FrempongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lubrication and Defects in ExtrusionDokument4 SeitenLubrication and Defects in ExtrusionmostafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salt Spray TestDokument13 SeitenSalt Spray TestSreedhar Patnaik.M100% (1)
- Nickel, gold, copper and other metals comparedDokument5 SeitenNickel, gold, copper and other metals comparedRofilR.AlbaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 용접의 개요Dokument26 Seiten용접의 개요박제영Noch keine Bewertungen
- Weicco Flexible ConnectorDokument2 SeitenWeicco Flexible ConnectormsmrizhwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metals and Their Uses C1 Revision HigherDokument31 SeitenMetals and Their Uses C1 Revision HigherHaziraAzlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAPE Chemistry 2017 U1 P1Dokument14 SeitenCAPE Chemistry 2017 U1 P1Ismadth2918388100% (1)
- Lab ManualDokument14 SeitenLab ManualBlair RogersNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5070 w16 QP 22Dokument20 Seiten5070 w16 QP 22Bun TeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyramid Inspection Procedure - Rev 0 - 010305Dokument42 SeitenPyramid Inspection Procedure - Rev 0 - 010305Ghazali Rahmat100% (5)
- Minerals Important To SocietyDokument56 SeitenMinerals Important To SocietyZay Salazar67% (3)
- Ebookonmineralsector635911539399033616 PDFDokument98 SeitenEbookonmineralsector635911539399033616 PDFRafath AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normalization and Temper Heat Treatment On P91Dokument6 SeitenNormalization and Temper Heat Treatment On P91Asad Bin Ala Qatari100% (2)
- Answers KISS Metals WorksheetsDokument6 SeitenAnswers KISS Metals WorksheetsDannyn ChenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ceramics 130515124855 Phpapp02Dokument111 SeitenCeramics 130515124855 Phpapp02Ajit Singh100% (1)
- Topic 7 - D BlockDokument47 SeitenTopic 7 - D Blockizz isalahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar Installation ManualDokument13 SeitenSolar Installation ManualShubham ArvikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is 13349Dokument20 SeitenIs 13349raji357100% (1)
- Preparing Thyroxine Sodium TabletsTITLEMaking Aspirin Capsules with Granules TITLEMethods of Formulating SuppositoriesDokument3 SeitenPreparing Thyroxine Sodium TabletsTITLEMaking Aspirin Capsules with Granules TITLEMethods of Formulating SuppositoriesDarwin MangabatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers Chapter 8Dokument3 SeitenAnswers Chapter 8Zoe SiewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certilas CatalogDokument308 SeitenCertilas CatalogLuiz Henrique Mourão InacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Austral Wright Metals Incoloy 800 Product Data SheetDokument2 SeitenAustral Wright Metals Incoloy 800 Product Data Sheetshashi_uit100% (1)
- External Corrosion of Buried Metal PipesDokument5 SeitenExternal Corrosion of Buried Metal PipesVinh Do ThanhNoch keine Bewertungen