Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Blood and Tissue Protozoan Blood and Tissue Protozoan Blood and Tissue Protozoan Urogenital Protozoa - Pear Shaped-Flagellated
Hochgeladen von
Mohamed Elserwy0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
5 Ansichten1 Seiteparasitology
Originaltitel
para 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenparasitology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
5 Ansichten1 SeiteBlood and Tissue Protozoan Blood and Tissue Protozoan Blood and Tissue Protozoan Urogenital Protozoa - Pear Shaped-Flagellated
Hochgeladen von
Mohamed Elserwyparasitology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
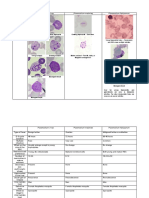
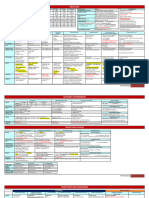
Trichomonas Vaginalis Trypanosoma T.
Gambiense & Leishmania donovani
cruzi Rhodesiense
Disease Trichomoniasis Chagas' disease Sleeping sickness Visceral leishmaniasis
(African trypanosomiasis) (Kala-azar)
Characteristics Urogenital protozoa pear shaped- flagellated Blood and tissue protozoan Blood and tissue protozoan Blood and tissue protozoan
trophozoites, No cysts or other forms Life cycle: Trypomastigotes in Life cycle: trypomastigotes in Life cycle: human macrophag
blood of reservoir host are the human blood or animal Containing amastigotes are
ingested by reduviid bug and are ingested by tsetse fly. Ingested by sandfly.
form epimastigotes and then They differentiate in the gut Amastigotes differentiate in
trypomastigotes in the gut. to form epimastigotes and The fly gut to promastigotes
When the bug bites, it then metacyclic Which migrate to pharynx.
defecates and feces containing trypomastigotes in salivary When fly bites promastigotes
trypomastigotes contaminate glands, when fly bites tryp Enter blood macrophages and
the wound. Organisms enter enter the blood. Repeated Form amastigotes. These can
the blood and form variation of surface antigen Infect reticuloendothelial cell
amastigotes within cells, these occur, which allow the Such in spleen and liver .
become trypomastigotes organism to evade immunity
Transmission Transmitted sexually . Human reservoir By reduviid bugs, Human and By tsetse fly , T. gambiense By sandfly ( phlebotomus or
many animals are reservoirs has a human reservoir Lutzomyia). Animal reservoir
And Occur in latin America T.rhodesiense has animal (dogs, carnivore, and rodent)
Epidemiology reservoir ( antelope) Human reservoir in india
pathogenesis Trophozoites attach to wall of vagina and cause Amastigotes kill cells, especially Trypomastigotes infect brain Amastigotes kill
inflammation and discharge cardiac muscle leading to causing encephalitis. reticuloendothelial cells, in
myocarditis also neuronal liver, spleen and bone
damage leading to megacolon marrow.
and megaesophagus
Laboratory Trophozoites visible in secretions Trypomastigoes visible in Trypomastigotes visible early Amastigotes visible in bone
blood in blood (early stage ) marrow smear .
Diagnosis Bone marrow biopsy- invitro- Cerebrospinal fluid ( late Skin test indicates prior
xenodiagnoses-serological test stage ) infection .
may be required
Treatment Metronidazole for both sexual partenrs Nifurtimox or benzidazole for Suramin (early) , suramin+ Sodium stibogluconate
acute disease-No one for melarsoprol ( CNS symptoms)
chronic disease
prevention Condoms limit transmission Protection from bite Protection from bite Protection from bite
Insect control Insect control Insect control
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Ospe ParasitologyDokument19 SeitenOspe Parasitologyaimi Batrisyia100% (1)
- Dr. Anas Yasin - MDDokument58 SeitenDr. Anas Yasin - MDMahfouzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasitology ReviewerDokument17 SeitenParasitology Reviewerlouie100% (1)
- 2024 04 04 SSCP Oversight EC Letter To Daszak 6c867682d6Dokument12 Seiten2024 04 04 SSCP Oversight EC Letter To Daszak 6c867682d6Jennifer Van LaarNoch keine Bewertungen
- For Review OAPDokument144 SeitenFor Review OAPKim John Rull NateNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Parasites and Their Common Names: Compiled Topics in Parasitology By: BNKLDokument47 SeitenList of Parasites and Their Common Names: Compiled Topics in Parasitology By: BNKLDIVINE GRACE FLORITA PEPITONoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Atlas of ParasitologyDokument650 SeitenElectronic Atlas of Parasitologystormyccs100% (7)
- Food and Toxicity-Natural ToxinsDokument47 SeitenFood and Toxicity-Natural Toxinsflorina.andreea100% (1)
- Oriental Breathing Terapy NakamuraDokument146 SeitenOriental Breathing Terapy Nakamurahcorzo100% (2)
- Blood and Tissue ProtozoansDokument12 SeitenBlood and Tissue ProtozoansHumayun ArshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Parasitology: Intestinal and Blood ParasitesDokument24 SeitenMedical Parasitology: Intestinal and Blood ParasitesSrijan BhattaraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dispensing, Incompatibilities, and Adverse Drug Reactions Answer Key-PINK PACOPDokument78 SeitenDispensing, Incompatibilities, and Adverse Drug Reactions Answer Key-PINK PACOPBilly Vince AlquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RAD RLE MCN 6 Case StudyDokument9 SeitenRAD RLE MCN 6 Case StudyCathleen Nasis Forrosuelo100% (2)
- Atlas Electrónico de ParasitologíaDokument650 SeitenAtlas Electrónico de ParasitologíaSoledad Rod100% (1)
- 3 Most Common Biochemical ImbalancesDokument4 Seiten3 Most Common Biochemical Imbalancescarlos100% (1)
- Domiciliary Midwifery RDokument16 SeitenDomiciliary Midwifery Rswillymadhu83% (6)
- Persuasive Speech Outline - Marijauna FinalDokument4 SeitenPersuasive Speech Outline - Marijauna Finalapi-34805003388% (17)
- Bio Parasite NotesDokument83 SeitenBio Parasite NotesosaydNoch keine Bewertungen
- PARA Master Notes by IbeDokument6 SeitenPARA Master Notes by IbePrimo GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood and Tissue Protozoa (Con't) : DR - Mehru Nisha Mehrunisha@unikl - Edu.myDokument35 SeitenBlood and Tissue Protozoa (Con't) : DR - Mehru Nisha Mehrunisha@unikl - Edu.myNida RidzuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name Morphology Epidemiology Pathogenicity Method of Diagnosis Vectors Life Cycle Life SpanDokument8 SeitenName Morphology Epidemiology Pathogenicity Method of Diagnosis Vectors Life Cycle Life SpanJhake Calvin ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- VPAR 101: Family of Protozoan Under The Order TrypanosomastidaDokument4 SeitenVPAR 101: Family of Protozoan Under The Order TrypanosomastidaAnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ParasitologyDokument1 SeiteParasitologyHawkar QadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 2 Blood and Tissue ProtozoansDokument42 SeitenActivity 2 Blood and Tissue ProtozoansRaven TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grp03ClinPara PDFDokument132 SeitenGrp03ClinPara PDFJeddhie MoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 & 3 Protozoa and MalariaDokument22 Seiten2 & 3 Protozoa and Malariaمصطفي خندقاويNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sistematika ParasitDokument30 SeitenSistematika ParasitFatmawati NadhyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1MicrobioTrans - EukaryotesDokument9 Seiten1MicrobioTrans - EukaryotesJeztin Faye Del RosarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasitology NotesDokument38 SeitenParasitology NotesEdoardo CitarellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Parasitology - B28Dokument23 SeitenIntroduction To Parasitology - B28Heswer RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrypanosomesDokument48 SeitenTrypanosomesdoubleyouem2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Concise Common Diseases TableDokument4 SeitenConcise Common Diseases Tableanushkasingh300806Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fungi Classification MapDokument3 SeitenFungi Classification MapShoaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Para Lab 11Dokument3 SeitenPara Lab 11api-3743217Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Parasitology Revision NotesDokument29 SeitenBiology Parasitology Revision NotesUsman Ali KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer in MicrobiologyDokument15 SeitenReviewer in MicrobiologyRonel ResurricionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Species Morphology Disease Caused: Trypanosoma Brucei RhodesienseDokument26 SeitenSpecies Morphology Disease Caused: Trypanosoma Brucei RhodesienseArielle VidalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protozoal Infections 29 April 2013Dokument87 SeitenProtozoal Infections 29 April 2013Nive KojNoch keine Bewertungen
- ParasitologyDokument53 SeitenParasitologyshakila786Noch keine Bewertungen
- Blood and Tissue FlagellatesDokument5 SeitenBlood and Tissue FlagellatesChristine BuenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasitology: An IntroductionDokument8 SeitenParasitology: An IntroductionRuthenie RedobleNoch keine Bewertungen
- LeishmaniaDokument78 SeitenLeishmaniaFatin AfinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasitology ClassificationDokument4 SeitenParasitology Classificationaparna viswanbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Book Dantes Russel C.Dokument8 SeitenOpen Book Dantes Russel C.Chrisha DangilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Human Parasites, Vectors, and Similar OrganismsDokument3 SeitenClassification of Human Parasites, Vectors, and Similar OrganismsWais Al-QorniNoch keine Bewertungen
- PROTOZOANS (Blood and Tissue Flagellates)Dokument4 SeitenPROTOZOANS (Blood and Tissue Flagellates)Eunice AndradeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plasm OdiumDokument12 SeitenPlasm OdiumtqurroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Para Lect Prelims (Reviewer) : Lumbricoides Is An Example of A/anDokument17 SeitenPara Lect Prelims (Reviewer) : Lumbricoides Is An Example of A/anJ Pao Bayro - LacanilaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ParaDokument2 SeitenParaAhmed FarahatNoch keine Bewertungen
- ParasiteDokument27 SeitenParasiteAbdullah AlkharsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 02Dokument58 SeitenLecture 02Lib PalmaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrematodesDokument16 SeitenTrematodesRenz Gerard AmorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasitology MidtermsDokument26 SeitenParasitology Midtermsstar220498Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 General Parasitology and Overview of Parasitic InfectionsDokument138 SeitenChapter 5 General Parasitology and Overview of Parasitic InfectionsAkbar SaleemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification, General Characteristics of Parasites and Medically Important ParasitesDokument30 SeitenClassification, General Characteristics of Parasites and Medically Important ParasitesSteph AsideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Para Revision1 2023Dokument21 SeitenPara Revision1 2023Amr Hasan Abdelfattah NasrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasites by Apple TanDokument16 SeitenParasites by Apple TanOlivia LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasitology Lec5Dokument13 SeitenParasitology Lec5ao868598Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trypanosoma-SppDokument4 SeitenTrypanosoma-SppVE NI CENoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasitology (Malaria)Dokument37 SeitenParasitology (Malaria)78255143Noch keine Bewertungen
- Microbio Act 05 10 2022Dokument2 SeitenMicrobio Act 05 10 2022Janna Niña ElementoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SLP Parasitic Diseases of Central Nervous System-ANSWER SGDokument13 SeitenSLP Parasitic Diseases of Central Nervous System-ANSWER SGDanial MazukiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasitology Review 1Dokument20 SeitenParasitology Review 1sdillon28Noch keine Bewertungen
- Farmakologi AntiprotozoaDokument32 SeitenFarmakologi AntiprotozoatriyantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tasks On Medical Biology 04.05.2020 - 08.05.2020Dokument2 SeitenTasks On Medical Biology 04.05.2020 - 08.05.2020hudamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trypanosoma EvansiDokument54 SeitenTrypanosoma Evansijoven delos santosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 5 (Zamudio)Dokument3 SeitenActivity 5 (Zamudio)Phobelyn ZamudioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasitology Table SummaryDokument3 SeitenParasitology Table SummaryIyah ChingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ob WARDDokument7 SeitenOb WARDNursingNooBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dalay Panishment of FormalinDokument4 SeitenDalay Panishment of Formalinmutiara defiskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Article: Duplex Ultrasound Evaluation of Hemodialysis Access: A Detailed ProtocolDokument8 SeitenReview Article: Duplex Ultrasound Evaluation of Hemodialysis Access: A Detailed ProtocolRenov BaligeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Full Crown Preparation On Pulpal Blood Flow in Man. Marisa Sukapattee. 2016. Archives of Oral BiologyDokument6 SeitenEffect of Full Crown Preparation On Pulpal Blood Flow in Man. Marisa Sukapattee. 2016. Archives of Oral BiologyValeria CrespoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnesium Sulphate InjDokument2 SeitenMagnesium Sulphate InjmahgadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia in Adults 2019 PDFDokument22 SeitenAutoimmune Hemolytic Anemia in Adults 2019 PDFKevin Mora BañosNoch keine Bewertungen
- PronounDokument8 SeitenPronounGhulam NabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CM2-CU10-Modification of Mendelian RatiosDokument17 SeitenCM2-CU10-Modification of Mendelian RatiosClaire GonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prezentare AromaDokument56 SeitenPrezentare AromaMamaliga LizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key Components of Industrial HygieneDokument2 SeitenKey Components of Industrial HygieneCharlotte LibreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paket B Soal Listening TO US MGMP B.Inggris DKI 2023Dokument14 SeitenPaket B Soal Listening TO US MGMP B.Inggris DKI 2023X MIPA-E /10 Garnis Trie AdistyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effects of Caffeine On Voice A Systematic ReviewDokument13 SeitenThe Effects of Caffeine On Voice A Systematic ReviewChrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pla423-Effects of Solid Waste On EnvironmentDokument6 SeitenPla423-Effects of Solid Waste On EnvironmentpaulineNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 HivDokument1 Seite2020 HivhenkNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia of India: Part - Ii (Formulations) Volume - I First Edition Monographs Ebook V.1.0Dokument187 SeitenThe Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia of India: Part - Ii (Formulations) Volume - I First Edition Monographs Ebook V.1.0VinitSharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planaria Lab ReportDokument3 SeitenPlanaria Lab Reportapi-201420026Noch keine Bewertungen
- Project On Veganism - by Aryan Raj - From KJ Somaiya Institute of ManagementDokument17 SeitenProject On Veganism - by Aryan Raj - From KJ Somaiya Institute of ManagementAryan RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Si 8Dokument1 SeiteSi 8ray72roNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal Gland Disorders: Addison's DiseaseDokument4 SeitenAdrenal Gland Disorders: Addison's DiseaseyoussraselimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal Aid Society Complaint Re Homeless YouthDokument65 SeitenLegal Aid Society Complaint Re Homeless YouthPaul SchindlerNoch keine Bewertungen