Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Engine Fundamental Introduction
Hochgeladen von
Hezdrye AkbcOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Engine Fundamental Introduction
Hochgeladen von
Hezdrye AkbcCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
UNI-KL MALAYSIA FRANCE INSTITUTE
AUTOMOTIVE MAINTENANCE TECHNOLOGY
SUBJECT: Engine Fundamental TITLE: Introduction
Automotive History.
The automobile as we know it was not invented in a single day by a single inventor. The history of
the automobile reflects an evolution that took place world wide Starting with the first theoretical
plans for a motor vehicle that had been drawn up by both Leonardo da Vinci and Isaac Newton.
The first automotive vehicles were steam drive. The following dates show the development
of engine:
1769 Nicolas Joseph Cugnot - the first self-propelled road vehicle was a military
tractor
1876 Otto and Langen - Four stroke engine
1883 Carburetor engine with preheat ignition and higher engine speeds by
Diamler
1884 Daimler mounts engine (1/2 hp) on the first motorcycle
1897 Rudolf Diesel - Diesel engine
1936 Otto cycle aviation engine with fuel injection, from 1950 on for motor car
1957 Wankel rotary piston engine
WHAT IS AN ENGINE?
An engine is a related group of parts assembled in a specific order.
Designed to convert the energy given off by burning fuel into a useful form.
There are many parts in a modern engine, each one being essential to the engine operation.
Chemical energy in fuel is converted to heat by the burning of the fuel at a controlled rate, which
called combustion.
If engine combustion occurs within the power chamber, the engine is called an internal
combustion engine. An external combustion engine is an engine that burns fuel outside of the
engine itself, such as a steam engine.
Character of engine
External combustion engine
Internal combustion engine
Internal combustion engine
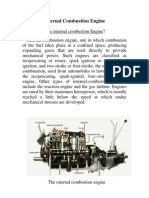
An internal combustion engine is an engine that is powered by the expansion of hot
combustion products of fuel directly acting within an engine. A piston internal combustion
engine works by burning hydrocarbon or hydrogen fuel that presses on a piston
UNI-KL MALAYSIA FRANCE INSTITUTE
AUTOMOTIVE MAINTENANCE TECHNOLOGY
SUBJECT: Engine Fundamental TITLE: Introduction
External combustion engine
An external combustion engine is an engine which burns its fuel outside of the engine.
External combustion engines are large and less powerful.
External combustion engines produce hot gases that transfer heat energy to another
fluid. The heat energy in this fluid, in turn, is changed into mechanical energy. Such
engines include gas and steam turbines and reciprocating steam engines.
A Stirling engines and steam turbine are a good example of an external-combustion
engine. Heat from burning fuel changes water in a boiler to steam. Pipes carry the steam
into the turbine, which has a series of bladed wheels attached to a shaft. The steam
expands through the turbine and so pushes on the blades and causes them to turn the
shaft. The spinning shaft can drive an electric generator, move a ship's propeller, or do
other useful work.
Automotive Engine
Engines used are internal combustion heat engines.
Convert the chemical energy of the gasoline into heat within a power chamber that is
called a combustion chamber.
Heat energy released in the combustion chamber raises the temperature of the
combustion gases within the chamber.
The pressure developed within the combustion chamber is applied to the head of a piston
or a turbine wheel to produce a usable mechanical force. This force is converted into
useful mechanical power.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Internal Combustion EngineDokument4 SeitenInternal Combustion Enginesari hafizhNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConceptsDokument8 SeitenConceptsLouis Feliph RuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principle of Operation:: Unit IiiDokument20 SeitenPrinciple of Operation:: Unit Iiilakshmigsr6610Noch keine Bewertungen
- Project Intro Internal Combustion EngineDokument4 SeitenProject Intro Internal Combustion EngineAmit Kumar PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument8 SeitenUnit 1Shivajee YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jimma University Jimma Institute of Technology Faculty of Mechanical EngineeringDokument52 SeitenJimma University Jimma Institute of Technology Faculty of Mechanical EngineeringSofoniyas FeysaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bhs Inggris Teknik: Oleh: Fajar Tri Yulianto Farid KoviananDokument8 SeitenBhs Inggris Teknik: Oleh: Fajar Tri Yulianto Farid KoviananFajarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Combustion EngineDokument16 SeitenInternal Combustion EngineHamzeh Al-QaisiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENGINEDokument7 SeitenENGINEayesha amjadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation Internal Combustion EngineDokument25 SeitenPresentation Internal Combustion EngineAbderrazak ZahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Combustion EngineDokument13 SeitenInternal Combustion EngineNAITAJINoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment AT 112Dokument4 SeitenAssignment AT 112Zamora Enguerra EmmalyneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Combustion Engine: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Jump ToDokument7 SeitenInternal Combustion Engine: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Jump ToAbdullah KhaledNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument42 SeitenChapter 1Naol EmanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EngineDokument23 SeitenEngineVardaan ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icgt Unit-II MaterialDokument34 SeitenIcgt Unit-II MaterialA Rahul KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Engine: Name: Joezel A. Entienza Date:May 1, 2018 Lab 4Dokument11 SeitenHeat Engine: Name: Joezel A. Entienza Date:May 1, 2018 Lab 4joshua jan allawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Heat Engines: What Is The Heat Engine?Dokument46 SeitenTypes of Heat Engines: What Is The Heat Engine?Mozammel HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Types of Engines emDokument9 SeitenDifferent Types of Engines emJose Albert MacayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo Fluids Ime-241L Lab Report: Prof. DR Salman Habib Hassan Ali Butt 2017-IM-39Dokument19 SeitenThermo Fluids Ime-241L Lab Report: Prof. DR Salman Habib Hassan Ali Butt 2017-IM-39Mahrukh ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- b4 GroupDokument11 Seitenb4 GroupdevmarineacademyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On Petrol Engine: Presented By-Mridul Mudai Sec-B4004 Roll No-B64Dokument12 SeitenPresentation On Petrol Engine: Presented By-Mridul Mudai Sec-B4004 Roll No-B64mridulmudai1991Noch keine Bewertungen
- LAB Report 01 Meen 20110104Dokument13 SeitenLAB Report 01 Meen 20110104Zohaib Arif MehmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19me02033 I.C Engines ReportDokument18 Seiten19me02033 I.C Engines ReportNagapavan MarisettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hand Made CarDokument33 SeitenHand Made CarSahil DhirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument39 SeitenChapter 1Flanc100% (1)
- Introduction To IC EnginesDokument76 SeitenIntroduction To IC Engineskedirabduri88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Project PresentationDokument24 SeitenMini Project PresentationHarshit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FilayDokument22 SeitenFilayROHITH GAMERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Combustion Engine-2016Dokument27 SeitenInternal Combustion Engine-2016ZerotheoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 2 AssignemntDokument9 SeitenPhysics 2 AssignemntMuhammad JohaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Engineering 1: Lecture NotesDokument17 SeitenThermal Engineering 1: Lecture NotesAndy LoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is EngineDokument25 SeitenWhat Is EngineSajib Chandra RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comsats: Assignment #3Dokument8 SeitenComsats: Assignment #3thunder riderNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10-Piston-Engine Based Power PlantsDokument27 Seiten10-Piston-Engine Based Power PlantsSaif YounusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hod LabDokument32 SeitenHod LabPrashant MehraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ice Notes1 PDFDokument124 SeitenIce Notes1 PDFDiyar NezarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ic Engine and Turbo MachineryDokument25 SeitenIc Engine and Turbo MachineryEyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept of An Internal Combustion EngineDokument9 SeitenConcept of An Internal Combustion EngineDiego Andrée ArmasNoch keine Bewertungen
- I.C EnginesDokument23 SeitenI.C EngineskolappanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of EngineDokument11 SeitenTypes of Enginejoshua jan allawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnergyDokument14 SeitenEnergyNirmal DharavathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Combustion EngineDokument16 SeitenInternal Combustion EngineNarayana Sarma Marthi0% (1)
- Unit5 - Heat Engine-Notes1Dokument17 SeitenUnit5 - Heat Engine-Notes1Krishna AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance of IC's EngineDokument45 SeitenPerformance of IC's EngineNandhakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Fabrication Stirling EngineDokument54 SeitenDesign and Fabrication Stirling Engineermias100% (1)
- Heat Engine DesignDokument25 SeitenHeat Engine DesignEamonn McStravickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siege Engine Electric Engine: NomenclatureDokument11 SeitenSiege Engine Electric Engine: NomenclatureZülfüNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam EngineDokument13 SeitenSteam EngineMuhammad Bin RiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abhay Mini InternshipDokument23 SeitenAbhay Mini InternshipAbhay Raaj YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ic EngineDokument23 SeitenIc EngineGanesh kumar100% (1)
- 26.performance and Characteristics Analysis Triangular Shaped Shape Piston CrownDokument44 Seiten26.performance and Characteristics Analysis Triangular Shaped Shape Piston CrowneshuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal CombustionDokument16 SeitenInternal CombustionWojtek PolisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report 12Dokument8 SeitenLab Report 12mamoona noreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICE UnitDokument88 SeitenICE UnitsuhasNoch keine Bewertungen
- In Which Stroke Does The Engine Produce PowerDokument2 SeitenIn Which Stroke Does The Engine Produce PowerJohn MarcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hand Cranked EngineDokument37 SeitenHand Cranked EngineEngineering ProjectNoch keine Bewertungen
- Four Stroke EngineDokument5 SeitenFour Stroke Enginemnoorulain80Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vroom! How Does A Car Engine Work for KidsVon EverandVroom! How Does A Car Engine Work for KidsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Cummins Data Sheet C550D5Dokument3 SeitenCummins Data Sheet C550D5fahad pirzadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repair Manual Mercedes Benz Mbe 900 Doc211myadhaco - 59c57c3e1723dddf92db5865Dokument2 SeitenRepair Manual Mercedes Benz Mbe 900 Doc211myadhaco - 59c57c3e1723dddf92db5865luiyel0% (1)
- SHB 1404 en 1000166693 1 1Dokument162 SeitenSHB 1404 en 1000166693 1 1Alberto100% (1)
- MultiGas 488 ManualDokument75 SeitenMultiGas 488 ManualOleg ZhbanovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annajaf City Naphtha As A Commercial Alternative Fuel For S.I. Engines in IraqDokument10 SeitenAnnajaf City Naphtha As A Commercial Alternative Fuel For S.I. Engines in IraqAjaykumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruction Manual: Instruction Manual of H30 Self Loading Concrete Mixer MixerDokument27 SeitenInstruction Manual: Instruction Manual of H30 Self Loading Concrete Mixer MixerElang SabunganNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Engine Management System For Gasoline EnginesDokument17 SeitenThe Engine Management System For Gasoline EnginesUpendraChaudhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2007 Honda Civic Type R (FN2) 2.0 (201 HP) Technical Specs, Data, Fuel Consumption, DimensionsDokument1 Seite2007 Honda Civic Type R (FN2) 2.0 (201 HP) Technical Specs, Data, Fuel Consumption, DimensionslanceNoch keine Bewertungen
- RR300 Recuperadora de PavimentoDokument16 SeitenRR300 Recuperadora de PavimentoJulio Cesar Izquierdo MadrigalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mazda Fe & 2 Sevice DataDokument5 SeitenMazda Fe & 2 Sevice Datazanio100% (1)
- Ldce 2022Dokument13 SeitenLdce 2022Ramesh TammineniNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCG2020 Technical SpecificationDokument4 SeitenTCG2020 Technical SpecificationJoy DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Storage and Assy SpecDokument14 SeitenStorage and Assy SpecGaurav DatarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hybrid ScooterDokument1 SeiteHybrid ScooterSrinivasAkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical File D16-Mg Krs D2E2 04: According To Marpol 73/78 Annex Vi and Nox Technical CodeDokument12 SeitenTechnical File D16-Mg Krs D2E2 04: According To Marpol 73/78 Annex Vi and Nox Technical CodeinforlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- I44v2 Technical SpecificationDokument7 SeitenI44v2 Technical SpecificationFredy RoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Powerful Delivery: 250 Series Engine Family of Stationary GensetsDokument2 SeitenPowerful Delivery: 250 Series Engine Family of Stationary Gensetsguichen wangNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Ju6h Models Ads RevbDokument2 SeitenNew Ju6h Models Ads RevbMarcos Nayib Brito100% (1)
- Borr Drilling - L1112Dokument2 SeitenBorr Drilling - L1112Carlos MunizagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proposed Rule: Airworthiness Directives: Honeywell International Inc.Dokument3 SeitenProposed Rule: Airworthiness Directives: Honeywell International Inc.Justia.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kurt Saxon - The Poor Mans James Bond - Vol 3 - TextDokument414 SeitenKurt Saxon - The Poor Mans James Bond - Vol 3 - TextCritical Damage100% (3)
- Mbe 4000 DiagramaDokument4 SeitenMbe 4000 DiagramaEduardo TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Triplex Pump Part 1Dokument30 SeitenTriplex Pump Part 1Rodolfo Castro86% (7)
- Final ReportDokument28 SeitenFinal Reportsnekanvns344Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wartsila Pumps Centrifugal Dolphin RangeDokument2 SeitenWartsila Pumps Centrifugal Dolphin RangeJoseph Alexander BorgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diya Grade IX Term I History ProjectDokument14 SeitenDiya Grade IX Term I History ProjectĎıʏɑNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overall Vehicle SysyemsDokument40 SeitenOverall Vehicle Sysyemsrajdrkl100% (4)
- Diesel Fire Pump EnginesDokument26 SeitenDiesel Fire Pump EnginesShakeel Ahmed0% (1)
- NIT W ThermalDokument78 SeitenNIT W ThermalKharaPrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Western Technology and Soviet Economic Development 1945 To 1965 Vol 3Dokument502 SeitenWestern Technology and Soviet Economic Development 1945 To 1965 Vol 3FOX K9Noch keine Bewertungen