Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
15ME102 Engineering Mechanics
Hochgeladen von
MDR PRAPHUCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
15ME102 Engineering Mechanics
Hochgeladen von
MDR PRAPHUCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
L T P C
15ME102 ENGINEERING MECHANICS 3 2 0 4
Prerequisite
Nil
PURPOSE
To develop the ability, in the engineering student, to understand, formulate, and solve a given
problem in a logical manner and to apply it to solve a few basic problems in engineering
mechanics.
INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES
At the end of this course the student should be able to apply concepts of
1. Static equilibrium of particles and rigid bodies
2. Analysis of trusses and friction
3. Properties of surfaces and volumes
4. Dynamic equilibrium of particles
5. Dynamic equilibrium of rigid bodies
in solving basic problems in engineering mechanics
UNIT I: STATICS OF PARTICLES 16
Equilibrium of Particles: Fundamental concepts and principles of engineering mechanics -
Forces on particles vector addition- Concurrent forces in a plane - Resolution of forces -
Resultant of several concurrent forces - Free body diagram Forces in space. Equilibrium of rigid
bodies: Principles of transmissibility - Moment of a force - Varignon's theorem - Equivalent
system of forces - Reduction of system of forces into single force and couple-Equipollent system
of forces - Types of supports and corresponding reactions - Equilibrium of rigid bodies in two
dimensions.- Equilibrium of a two force body , statically determinate and indeterminate structures
UNIT II: ANALYSIS OF TRUSSES AND FRICTION 15
Trusses: Definition of a truss - Simple Trusses - Analysis of Trusses - Method of joints- Method
of sections. Friction: Laws of Friction - Angle of Friction Dry friction- Wedges - Rolling friction
- Belt Friction - Thrust and Journal bearings.
UNIT III: PROPERTIES OF SURFACES AND VOLUMES 14
Centre of Gravity: - Centroids of lines, areas, and volumes Determination of centroids by
integration - Theorem of Pappus-Guldinus - Moment of Inertia: Second moment or Moment of
inertia of an area- Determination of moment of inertia of area by integration - Radius of gyration
- Parallel and perpendicular axis theorems - Polar moment of inertia - Mass moment of inertia.
UNIT IV: DYNAMICS OF PARTICLES 15
Rectilinear motion uniform velocity and uniformly accelerated motion- Rectangular components
of velocity and acceleration- Curvilinear motion Normal and tangential components- Radial and
transverse components-Newton second law DAlemberts principle- Principle of work and
energy Applications- Conservative forces-Principle of impulse and momentum - Impulsive
motion - Impact of elastic bodies Direct central- Oblique central impact.
UNIT V: DYNAMICS OF RIGID BODIES 15
Introduction to Kinematics of rigid bodies - Translation and rotation of rigid bodies - Fixed axis
rotation General plane motion Absolute and Relative velocity in plane motion - Instantaneous
center of rotation in plane motion - Principle of work and energy for a rigid body - Principle of
impulse and momentum for the plane motion of a rigid body.
TOTAL 75
TEXT BOOKS
1. Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., David Mazurek, Philip J Cornwell, Vector
Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics , McGraw - Hill, New Delhi, Tenth Edition
2013
2. Palanichamy, M. S., and Nagan, S., Engineering Mechanics (Statics and Dynamics), Tata
McGraw Hill, New Delhi Eighth reprint 2011(Third edition)
REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Timoshenko, and Young, Engineering Mechanics, Tata Mc-Graw Hill Book Company,
Edition 4, New Delhi, 1988
2. Mclean, and Nelson, Theory and problems of Engineering Mechanics (Statics and Dynamics),
3rd Edition Schaum Series, 1980
3. Rajasekaran, S., & Sankarasubramanian, G., Engineering Mechanics, Vikas Publishing House
Pvt Ltd, 2011
4. Shames, I.H., and Krishna Mohana Rao, G., Engineering Mechanics (Statics and Dynamics),
Dorling Kindersley (India) Pvt. Ltd. (Pearson Education), 2006
5. Dr.R.K.Bansal & Sanjay Bansal, A Text book of Engineering Mechanics, Lakshimi
publications, Edition 7, 2011.
15ME102 - ENGINEERING MECHANICS
Course designed by Department of Mechanical Engineering
a b c d e f g h i j k
1 Student Outcome
Mapping of
instructional 1,2, 1,2,3, 1,2,3,
2
objectives with 3,4,5 4,5 4,5
student outcome
ENGINEERIN
G SCIENCES PROFESSIO
GENERAL BASIC
& NAL
(G) SCIENCES
3 Category TECHNICAL SUBJECTS
(B)
ART (P)
(E)
X
4 Approval 23rd meeting of the Academic Council , May 2013
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Factories Act, 1948: Labour LawsDokument7 SeitenThe Factories Act, 1948: Labour LawsMDR PRAPHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ajith ResumeDokument2 SeitenAjith ResumeMDR PRAPHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- CertifDokument8 SeitenCertifMDR PRAPHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk AssessmentDokument7 SeitenRisk AssessmentMDR PRAPHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- CertifDokument9 SeitenCertifMDR PRAPHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dip-Ii & Bsc-IiDokument3 SeitenDip-Ii & Bsc-IiMDR PRAPHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sasikala ResumeDokument4 SeitenSasikala ResumeMDR PRAPHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name List For Safety Quiz ProgramDokument1 SeiteName List For Safety Quiz ProgramMDR PRAPHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Quiz Program Name ListDokument1 SeiteSafety Quiz Program Name ListMDR PRAPHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naveen Kumar.B: ObjectiveDokument2 SeitenNaveen Kumar.B: ObjectiveMDR PRAPHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Quiz Program - 2015: Score ScheduleDokument1 SeiteSafety Quiz Program - 2015: Score ScheduleMDR PRAPHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Quiz Program-2015 Time Schedule: DATE 26.09.2015 Agenda S.I. NO Time Duties Staff In-ChargeDokument1 SeiteSafety Quiz Program-2015 Time Schedule: DATE 26.09.2015 Agenda S.I. NO Time Duties Staff In-ChargeMDR PRAPHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSM Manual NewDokument121 SeitenPSM Manual NewMDR PRAPHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- HiraDokument12 SeitenHiraMDR PRAPHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 5 15 TPI Inspection Properly Maintained Regularly Maintained InspectionDokument5 Seiten3 5 15 TPI Inspection Properly Maintained Regularly Maintained InspectionMDR PRAPHUNoch keine Bewertungen
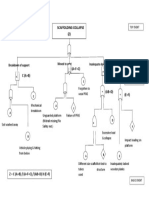
- Scaffolding Collapse (Z) : Moved To Another Location Inadequate Design of Scaffold Breakdown of SupportDokument1 SeiteScaffolding Collapse (Z) : Moved To Another Location Inadequate Design of Scaffold Breakdown of SupportMDR PRAPHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Training, Incentive ProgramsDokument27 SeitenSafety Training, Incentive ProgramsMDR PRAPHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Data Sheet 6ES7231-4HF32-0XB0: General InformationDokument3 SeitenData Sheet 6ES7231-4HF32-0XB0: General InformationRoberto cafeNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Process For Milk - PasteurizationDokument7 SeitenWhat Is The Process For Milk - PasteurizationMichelle OrnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2026 - 1 Specification For Power Trfo - Part 1Dokument46 Seiten2026 - 1 Specification For Power Trfo - Part 1Balamurugan ArumugamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simbologia PDFDokument1 SeiteSimbologia PDFMartin Abraham Perez UriasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Manual PerkinsDokument130 SeitenService Manual Perkinsgelu2003home100% (12)
- Harsh Environment Series Connection Systems 2014-05-05 PDFDokument8 SeitenHarsh Environment Series Connection Systems 2014-05-05 PDFSicein SasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture01 - Introductory ConceptsDokument30 SeitenLecture01 - Introductory ConceptsCarl PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dd311 Specification Sheet EnglishDokument4 SeitenDd311 Specification Sheet EnglishJose Antonio Sanchez SegoviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siemons - Cello Bowing TechniqueDokument15 SeitenSiemons - Cello Bowing TechniqueMassa Awaj100% (2)
- Cummins 4btaDokument5 SeitenCummins 4btaYulius PurnamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ques - 14 55 PDFDokument15 SeitenQues - 14 55 PDFVosuMittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Adjust Rough Idle and Camshaft Timing On VW and Audi TDI Pumpe Duse EngineDokument5 SeitenHow To Adjust Rough Idle and Camshaft Timing On VW and Audi TDI Pumpe Duse EngineALP1981100% (2)
- Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Generators For Pico-HydropowerDokument8 SeitenAxial Flux Permanent Magnet Generators For Pico-HydropowerEngineers Without Borders UKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Area Handing OverDokument6 SeitenArea Handing OveronspsnonsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asic Lectrical Echnology: Parallel Magnetic CircuitsDokument10 SeitenAsic Lectrical Echnology: Parallel Magnetic CircuitsShivangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanizing Philippine Agriculture For Food SufficiencyDokument21 SeitenMechanizing Philippine Agriculture For Food SufficiencyViverly Joy De GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of Purification Methods For Biodiesel. Berrios PDFDokument7 SeitenComparison of Purification Methods For Biodiesel. Berrios PDFMariuxiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 6 Well ControlDokument115 SeitenCH 6 Well ControlFirdaus KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- E&T1350 Electronics Chapter 4 Special Purpose DiodesDokument16 SeitenE&T1350 Electronics Chapter 4 Special Purpose DiodesRMK BrothersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity 02 00033 v2Dokument17 SeitenElectricity 02 00033 v244-Vignesh V BedreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foot MouswitchDokument11 SeitenFoot MouswitchnewbeatleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fabric CuttingDokument13 SeitenFabric CuttingShahjahanBadshaRony100% (1)
- Company ProfileDokument189 SeitenCompany ProfileplanningNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dmart Supply Chain Management 0 Inventory Management ModuleDokument13 SeitenDmart Supply Chain Management 0 Inventory Management Moduleaarushisoral1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Africa's Youth Can Save The WorldDokument21 SeitenAfrica's Youth Can Save The WorldThe Wilson CenterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training Manual Operations: July 1999-Rev.0Dokument110 SeitenTraining Manual Operations: July 1999-Rev.0FharishPutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discussion & Conclusion Dry Fractionation MuzDokument4 SeitenDiscussion & Conclusion Dry Fractionation MuzAhmad MuzammilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theoretical Approaches Regarding The VENTURI EffectDokument4 SeitenTheoretical Approaches Regarding The VENTURI EffectJose A AbrahamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wave Energy Conversion#Dokument3 SeitenWave Energy Conversion#DimSolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Honeywell Mag Meter 4000Dokument28 SeitenHoneywell Mag Meter 4000cgasior1Noch keine Bewertungen