Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Unit 1: Power Plants: For Internal Circulation Only
Hochgeladen von
Rahul muntha0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
18 Ansichten5 SeitenPower plant
Originaltitel
Unit 1 Introduction
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenPower plant
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
18 Ansichten5 SeitenUnit 1: Power Plants: For Internal Circulation Only
Hochgeladen von
Rahul munthaPower plant
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 5
Unit 1: Power Plants
For internal circulation only
IC 452 POWER PLANT INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL
Unit 1 : Brief survey of methods of power generation-hydro,
thermal, nuclear, solar and wind power Introduction to
thermal power plant processes building blocks - ideal steam
cycles Boiler types, Boiler - turbine units and its range
systems, feed water systems, steam circuits, combustion
process, products of combustion process, fuel systems,
treatment of flue gases, steam turbine, condensate systems,
alternator, feed water conditioning, turbine bypass valves.
Importance of instrumentation in power generation details
of boiler processes, P & I diagram of boiler combined cycle
power plant, power generation and distribution.
Power Generating Stations
Type of Generation stations
Thermal Power Plant. Large plants carry constant load (base load plant).
Smaller plants loads are regulated but they operate continuously. Minimum
down time is 20-35 hours.
Nuclear Power Plant. These plants carry constant load and are used as base
loads plants.
Hydroelectric Plants. These plants are loaded to the maximum capacity,
because of the low operating cost. (Water is free)
Combined steam and Gas-Turbine Power Plants. High efficiency plants for
variable load.
Gas-turbine. Peak load plants, high operating and low investment cost.
Solar, Wind. Loaded to the maximum capacity when sun or wind power
available.
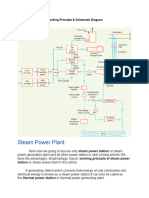
Thermal Power Plant
1. The fuel (pulverized coal, atomized oil or gas) is mixed with
pre-heated air and injected into the boiler, where the high
temperature ignites the fuel.
2. The fuel burning produces ashes and exhaust gases. The
ashes are filtered out from the exhaust and washed away by
water. Powerful exhaust fans drives the smoke out to the
atmosphere through the stack.
3. Pre-heated water is pumped through the tubes covering the
boiler walls. The high heat evaporates the water and
generates steam, which is collected in the steam drum.
Thermal Power Plant
4. The high pressure steam drives the turbine, which has a high
pressure and a low pressure stage. For some turbines the
steam is re-heated between these two stages.
5. The water-cooled condenser condenses the steam into water.
The water is pumped back to the boiler.
6. Both, the air and the water are preheated to increase efficiency.
7. The turbine drives the generator which produces electricity.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Me Lab 3Dokument27 SeitenMe Lab 3Jerome Vega AndesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction and Working of Thermal Power PlantDokument5 SeitenConstruction and Working of Thermal Power PlantdibyenindusNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1) Conventional - Non Renewable Power GenerationDokument49 Seiten1) Conventional - Non Renewable Power GenerationManmit SalunkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Various Plants used for Electric Power Generation: Hydro, Nuclear & ThermalDokument6 SeitenVarious Plants used for Electric Power Generation: Hydro, Nuclear & ThermalWilson FuentesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Power Generation - Lecture 8Dokument51 SeitenElectrical Power Generation - Lecture 8dp05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Thermal Power Plant & Brief DiscussionDokument35 SeitenOverview of Thermal Power Plant & Brief DiscussionSayan HazraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical study of the Steam-Generating UnitDokument12 SeitenPhysical study of the Steam-Generating UnitIsmaeli KielNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17.THERMAL POWER PLANT PPT 1Dokument25 Seiten17.THERMAL POWER PLANT PPT 1Amit kumar Gupta100% (6)
- Report #1: Alternating-Current Project: Steam-Electric Power PlantDokument41 SeitenReport #1: Alternating-Current Project: Steam-Electric Power PlantKian TecsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Captive Power PlantDokument30 SeitenCaptive Power PlantDeepakGawasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power Plant Working & EquipmentDokument53 SeitenThermal Power Plant Working & Equipmentdp05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power Plant: Shubham Thakur 13BME8149 5MEL3 Mechanical EngineeringDokument34 SeitenThermal Power Plant: Shubham Thakur 13BME8149 5MEL3 Mechanical EngineeringMos MohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power PlantDokument35 SeitenThermal Power PlantAngelaa DassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power Plant BasicsDokument5 SeitenThermal Power Plant BasicsAnudeep ChittluriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power System ComponentsDokument17 SeitenPower System ComponentsbobidmrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power Plant Rankine CycleDokument27 SeitenThermal Power Plant Rankine Cyclevenki249100% (1)
- Summer Training Experience at NTPC Dadri Power PlantDokument33 SeitenSummer Training Experience at NTPC Dadri Power PlantSubodh DuhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PP 9th Meeting GENERATING STATIONS Thermal Power PlantDokument5 SeitenPP 9th Meeting GENERATING STATIONS Thermal Power PlantJohn Kenneth LoricoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Site Selection For Thermal Power PlantDokument3 SeitenSite Selection For Thermal Power PlantNehaKashyapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ukai Thermal Power Plant-Eman Refai Abdelkhaliq-Sec 3Dokument13 SeitenUkai Thermal Power Plant-Eman Refai Abdelkhaliq-Sec 3eman.refai13lcsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power PlantDokument42 SeitenThermal Power PlantAravind C.KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal EngineeringDokument10 SeitenThermal Engineeringlokeshdhangar842Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power PlantDokument33 SeitenThermal Power Plantnavdeep kaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eee 202 Lecture NotesDokument46 SeitenEee 202 Lecture Notesotarus497Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 1Dokument7 SeitenExp 1HR HabibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power Plant Project ReportDokument63 SeitenThermal Power Plant Project Reportasutoshjena28174% (23)
- Steam Power PlantDokument7 SeitenSteam Power PlantsuganyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Power Engineering Units and EfficiencyDokument32 SeitenIntroduction to Power Engineering Units and EfficiencyMuhammad abdur rehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction and Thermal Power PlantDokument27 SeitenIntroduction and Thermal Power PlantKshitij AggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generating Electricity from Thermal EnergyDokument63 SeitenGenerating Electricity from Thermal EnergyArif AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power Plant - EeDokument20 SeitenThermal Power Plant - EePrabhat Chandra100% (1)
- Introduction To Power Plants and BoilersDokument47 SeitenIntroduction To Power Plants and Boilersl8o8r8d8s8i8v8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power PlantDokument9 SeitenThermal Power PlantRajeev Ranjan PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power Plant: Gaini Zail Singh Punjab Technical University Campus (Bathinda)Dokument30 SeitenThermal Power Plant: Gaini Zail Singh Punjab Technical University Campus (Bathinda)Sriram ramsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On Thermal Power Station: Presented ByDokument24 SeitenPresentation On Thermal Power Station: Presented Bykritika negiNoch keine Bewertungen
- By: Nidhi Bansal Roll No.-2509071Dokument25 SeitenBy: Nidhi Bansal Roll No.-2509071chintu3242Noch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of Electrical Energy GenerationDokument65 SeitenImportance of Electrical Energy GenerationtawqeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To CFPPDokument34 SeitenIntroduction To CFPPVenkat CherukuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Plant Engineering BasicsDokument21 SeitenPower Plant Engineering BasicsSiman NapstervkkNoch keine Bewertungen
- DVC Mejia ReportDokument37 SeitenDVC Mejia ReportRahul RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dry Cooling Systems1.2Dokument40 SeitenDry Cooling Systems1.2paragmishra1986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power Seminar ReportDokument10 SeitenThermal Power Seminar ReportAram Nasih MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power PlantsDokument24 SeitenThermal Power Plantslakshmigsr6610100% (1)
- Steam Power Plant EssentialsDokument51 SeitenSteam Power Plant EssentialsVishal PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boost Steam Generation EfficiencyDokument22 SeitenBoost Steam Generation EfficiencyKishore KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Power Systems: An OverviewDokument29 SeitenElectric Power Systems: An OverviewSaravanan T YNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXP-1 Steam Power PlantDokument7 SeitenEXP-1 Steam Power PlantsejalNoch keine Bewertungen
- BME-Power Producing Devices - NOTESDokument46 SeitenBME-Power Producing Devices - NOTESAisha JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2 - Steam TurbineDokument32 SeitenLecture 2 - Steam TurbineZulyadain Ishak100% (1)
- PPTDokument20 SeitenPPTSriram ramsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPPDokument3 SeitenCPPabhisai84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Heat GeneratorDokument6 SeitenHeat GeneratorZac Ryan CasteloNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1.power Plant LayoutDokument5 Seiten1.1.power Plant LayoutBALAMBAL R100% (1)
- Physics 4.Dokument5 SeitenPhysics 4.SOLAIMANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power PlantDokument29 SeitenThermal Power PlantSiri VenniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Steam TurbineDokument32 Seiten06 Steam Turbinesakera 88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesVon EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningVon EverandThermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- F0Dokument28 SeitenF0zlajaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- VPHCT 02Dokument33 SeitenVPHCT 02Rahul munthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centum VP 01 ENG Forms NLDokument4 SeitenCentum VP 01 ENG Forms NLNikhilesh MuraleedharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BotonyDokument8 SeitenBotonyRahul munthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemistryDokument9 SeitenChemistryRahul munthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijarcet Vol 5 Issue 2 266 269Dokument4 SeitenIjarcet Vol 5 Issue 2 266 269Rahul munthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhysicsDokument6 SeitenPhysicsRahul munthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control of Common Unit OperationsDokument54 SeitenControl of Common Unit OperationsRahul munthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Towards An Economy Based On Renewable Energy Generation: Is Biogas Part of The Solution?Dokument3 SeitenTowards An Economy Based On Renewable Energy Generation: Is Biogas Part of The Solution?fabianNoch keine Bewertungen
- District Heating and Cooling Systems ExplainedDokument9 SeitenDistrict Heating and Cooling Systems Explainedaldeanz89Noch keine Bewertungen
- Boiler OverviewDokument44 SeitenBoiler OverviewRopafadzo ChihuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hybrid Off-Grid Systems With Sunny Island Battery Inverters: 2017, Innoventum/VillaltaDokument24 SeitenHybrid Off-Grid Systems With Sunny Island Battery Inverters: 2017, Innoventum/VillaltaKamalalogini TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fringe LinksDokument6 SeitenFringe Linksdhana210Noch keine Bewertungen
- Narol, Ahmedabad ,: Air Compressor Air DryerDokument6 SeitenNarol, Ahmedabad ,: Air Compressor Air DryerMahendra ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waste Management - Bhavin Shah - IIM IndoreDokument10 SeitenWaste Management - Bhavin Shah - IIM IndoresudhirnairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bahirdar University Student Designs Off-Grid Home Solar SystemDokument20 SeitenBahirdar University Student Designs Off-Grid Home Solar SystemADEFRIS BELACHEWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Everything You Need to Know About Geothermal EnergyDokument9 SeitenEverything You Need to Know About Geothermal EnergyPoochi DougNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control & Automation Aspects FOR Reliability of Super-Critical UnitsDokument21 SeitenControl & Automation Aspects FOR Reliability of Super-Critical Unitskalyan1492Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biogas: Alix Simnock Brooke Myones Carrie Senft Dan CohnDokument21 SeitenBiogas: Alix Simnock Brooke Myones Carrie Senft Dan CohnNguyênVũXuânNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar-Wind Hybrid System PresentsDokument11 SeitenSolar-Wind Hybrid System Presentsprafulla100% (1)
- Republic Act No 2641Dokument44 SeitenRepublic Act No 2641Mark PascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Effecient Build - Solar KitchenDokument6 SeitenEnergy Effecient Build - Solar KitchenyuvarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air EngineDokument5 SeitenAir EngineVinay MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Car vs. Hydrogen Fuel Cell CarsDokument4 SeitenElectric Car vs. Hydrogen Fuel Cell CarsBen GalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar Water HeatersDokument7 SeitenSolar Water HeatersddroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of Reciprocating Air CompressorDokument4 SeitenStudy of Reciprocating Air Compressor01parth100% (5)
- SolarDokument12 SeitenSolarabdulwadi84Noch keine Bewertungen
- 30KLPD Ethanol Plant ReportDokument18 Seiten30KLPD Ethanol Plant ReportSaanvira Engineering Pvt Lts100% (4)
- Syngas Turbine TechnologyDokument12 SeitenSyngas Turbine TechnologyJunsung KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gist of Energy Audit in The Dairy IndustryDokument3 SeitenGist of Energy Audit in The Dairy Industrykeya2020Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 18 Alternative Energy and The EnvironmentDokument17 SeitenChapter 18 Alternative Energy and The EnvironmentgraceypotterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tesla R32 Heat Pump Air To Water TGTP-12HMDA1 Spec 2023 ENGDokument1 SeiteTesla R32 Heat Pump Air To Water TGTP-12HMDA1 Spec 2023 ENGAnonymous LDJnXeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 Report Liquid HydrogenDokument89 Seiten2016 Report Liquid HydrogenJonas MilerNoch keine Bewertungen
- D-Mart Mysore PPT - (11-02-2020)Dokument11 SeitenD-Mart Mysore PPT - (11-02-2020)Raju KsnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6FA HDGT Product Brochure-GEA17987Dokument8 Seiten6FA HDGT Product Brochure-GEA17987mikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEC 61730 Fire Testing Requirements for PV ModulesDokument6 SeitenIEC 61730 Fire Testing Requirements for PV ModulesJosh ZhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomass Briquettes Made From Areca LeavesDokument7 SeitenBiomass Briquettes Made From Areca Leavesdeepak kbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of temperature and wind on solar PV module performanceDokument10 SeitenEffect of temperature and wind on solar PV module performanceGiacomo GavagninNoch keine Bewertungen