Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
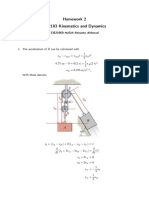
Assignment 2 MEN204 15 11 2017
Hochgeladen von
Amit KapoorOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Assignment 2 MEN204 15 11 2017
Hochgeladen von
Amit KapoorCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Assignmnt-2
MEN502 Strength of Material and Basics of Design
Submission Last date-15/11/2017
1. Derive an expression for shearing stresses in triangular, circular and I-section beam. Also find the shear
stress at Neutral axis and denote the position of maximum stress.
2. A wooden beam 50 mm wide and 150 mm deep is reinforced by gluing steel plate 10 mm thick 50 mm
wide on the top of section. If the beam is simply supported over its ends which is 5 m away from each
other. The beam carries a point load of 500 kN at mid of the beam. Calculate the maximum shear stress
at the junction of wood and steel plate. take m=20.
3. A plate 10 cm wide and 1.25 cm thick is to be welded to another plate by means of single transverse weld
and double parallel fillet weld. Determine the length of the weld run in each case if the joint is subjected
to loads of 100 kN. The recommended design stress in tension is not to exceed 70 N/mm2 and in shear
56 N/mm2
4. A single riveted lap joint is to be made of 10 mm plates. Find the diameter of the rivets, their pitch and
the efficiency of the joint. Take = 64 N/mm2 and t = 80 N/mm2 .
5. Why interchangeability is required in production of elements and parts and their assemblies? Define Fits
and Tolerances and explain their significance in modern mechanical engineering.
6. A solid circular shaft of diameter 40 mm is subjected to axial pull of 150 kN and torsional moment of
2.5 kNm. Determine
(a) Principal stresses induced in shaft
(b) Maximum shear stress
7. Design a solid circular shaft, to find the diameter, transmitting 50 kW power rotating at 120 rpm. Max-
imum torque is likely to exceed by 30%. Maximum permissible shear stress is 60 MPa. Also calculate
angle of twist for a length of 1800 mm. Take G = 80 GPa.
8. Design a typical cotter joint to transmit a load of 50 kN in tension or compression. Consider that the
rod, socket and cotter are all made of a material with the following allowable stresses: Allowable tensile
stress, t = 150 MPa Allowable crushing stress, cr = 110 MPa Allowable shear stress, y = 110 MPa
[ Hint - Assume and calculate using empirical relationships ].
9. Two mild steel rods are connected by a knuckle joint to transmit an axial force of 100 kN. Design the joint
completely assuming the working stresses for both the pin and rod materials to be 100 MPa in tension,
65 MPa in shear and 150 MPa in crushing.
[ Hint - Assume and calculate using empirical relationships ].
10. A forged steel bar 50 mm in diameter, is subjected to a reversed bending stress of 250 N/mm2 . The bar
is made up of steel 40C8 (Sut = 600 N/mm2 ). Calculate the life of bar for a reliability of 90 %. Use
tables and charts from design data handbook.
11. Explain the following
(a) Couplings and types
(b) Keys
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Kawasaki Bayou 300 Service Manual RepairDokument678 SeitenKawasaki Bayou 300 Service Manual RepairMac Thon81% (64)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Wear Resistance of Material Used in Slurry TransportDokument7 SeitenWear Resistance of Material Used in Slurry TransportwoodoobooNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5R55W (Ranger / Explorer) & 5R55S: 5 SPEED 4WD WITH LOCK UP (Full Electronic Control)Dokument4 Seiten5R55W (Ranger / Explorer) & 5R55S: 5 SPEED 4WD WITH LOCK UP (Full Electronic Control)Krzysztof Kjb100% (1)
- Mech3005 0405 Acr-AirsideDokument57 SeitenMech3005 0405 Acr-AirsideAmit KapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- JLG 600a 600aj Illustrated Parts ManualDokument20 SeitenJLG 600a 600aj Illustrated Parts Manualvirgen100% (49)
- General Bearing Requirements and Design CriteriaDokument6 SeitenGeneral Bearing Requirements and Design Criteriaapi-3701567100% (2)
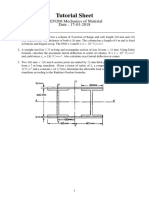
- Tutorial Sheet: MEN208 Mechanics of Material Date: 17-01-2018Dokument1 SeiteTutorial Sheet: MEN208 Mechanics of Material Date: 17-01-2018Amit KapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - 1: Men206 Engineering Analysis and Design Submission Date: 20-02-2018Dokument2 SeitenAssignment - 1: Men206 Engineering Analysis and Design Submission Date: 20-02-2018Amit KapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 28 06 2018Dokument1 SeiteAssignment 1 28 06 2018Amit KapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - 1: MEN303 Design of Mechanical Systems Submission Date: 28-06-2018Dokument2 SeitenAssignment - 1: MEN303 Design of Mechanical Systems Submission Date: 28-06-2018Amit KapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine Perfomance Job Sheet 10Dokument2 SeitenEngine Perfomance Job Sheet 10Christian Villa GuerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No. 5: AIM: To Measure Fluid Flow by (A) ORIFICE METER and (B) V-NOTCHDokument5 SeitenExperiment No. 5: AIM: To Measure Fluid Flow by (A) ORIFICE METER and (B) V-NOTCHVipul SolankiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Saving Hydraulic DriveDokument20 SeitenEnergy Saving Hydraulic DriveJamin SmtpngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear MomentumDokument62 SeitenLinear Momentumblackwhite121201Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tajima CordingDokument45 SeitenTajima CordingWilsonGutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centrifugal BlowerDokument3 SeitenCentrifugal BlowerVicy gostNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wood's Powr-Grip Guide To Maintenance, Troubleshooting, and RepairDokument4 SeitenWood's Powr-Grip Guide To Maintenance, Troubleshooting, and Repairkamikadze7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Punching Shear PDFDokument13 SeitenPunching Shear PDFmohamedadel100Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rule Bki V Rules For Materials 2009Dokument249 SeitenRule Bki V Rules For Materials 2009Saadi AlimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hafizh Renanto Akhmad - PR 2 KindinDokument14 SeitenHafizh Renanto Akhmad - PR 2 KindinHafizh Renanto AkhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rai Rac-18cDokument24 SeitenRai Rac-18cKyaw San OoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estimation of Flow Patterns: NPTEL, IIT Kharagpur, Prof. Gargi Das, Department of Chemical EngineeringDokument4 SeitenEstimation of Flow Patterns: NPTEL, IIT Kharagpur, Prof. Gargi Das, Department of Chemical EngineeringahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report On Robotic WeldingDokument8 SeitenLab Report On Robotic WeldingSanatan ChoudhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Griffith Relation - A Historical Review: by Dietrich Munz and Theo FettDokument28 SeitenThe Griffith Relation - A Historical Review: by Dietrich Munz and Theo FettV.v. TaguisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiat Kobelko Ex255t Shop ManualDokument20 SeitenFiat Kobelko Ex255t Shop Manualrosa100% (56)
- Aci 318 Code Provisions For Deflection Control of Two-Way Concrete SlabDokument81 SeitenAci 318 Code Provisions For Deflection Control of Two-Way Concrete SlabwelwelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Z2000 Modulating Zone Comfort System Control PanelDokument4 SeitenZ2000 Modulating Zone Comfort System Control PanelibrahimsirpiNoch keine Bewertungen
- V20 120kW Product DescriptionDokument4 SeitenV20 120kW Product DescriptiongarmeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ps-1 Unit 3Dokument21 SeitenPs-1 Unit 3Prathap VuyyuruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The Mathematical Nonlinear Wave MotionDokument157 SeitenIntroduction To The Mathematical Nonlinear Wave Motionmehr1384Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9323A270G Parts CatalogDokument9 Seiten9323A270G Parts CatalogOFFICE DANACNoch keine Bewertungen
- K20502en Ed6 Yardy Ev Yardy Duct en NTDokument52 SeitenK20502en Ed6 Yardy Ev Yardy Duct en NTUtzu SandruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimentalmechanics (1) UnlockedDokument127 SeitenExperimentalmechanics (1) UnlockeddivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2022 Chassis Cab: Owner'S ManualDokument420 Seiten2022 Chassis Cab: Owner'S Manualmbadarau1206Noch keine Bewertungen
- Easy-Line 05 EDokument2 SeitenEasy-Line 05 EChuma KhanNoch keine Bewertungen