Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Aris Express Poster 21 Low 1 PDF
Hochgeladen von
arrivaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Aris Express Poster 21 Low 1 PDF
Hochgeladen von
arrivaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
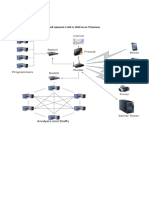
Organizational chart IT Infrastructure
An IT infrastructure diagram is used to model the technical communication
infrastructure of a company. IT systems and belonging hardware systems are
Organizations and companies illustrate their structures with connected by networks using different network devices.
organizational charts. With the ARIS symbolism (organizational unit,
role and person) relationships between individual units like departments An IT infrastructure describes
or employees are demonstrated. The relationships stand for: - which software systems are running on which hardware,
- in which network the hardware is located,
- Who is responsible for whom? - which network devices (switches, routers, firewalls) are used for interlinking
- Who is the supervisor or inferior? existing networks.
- How are the communication channels?
Thus, this model type can be used for planning and documenting network
An organization chart quasi indicates important rules of the infrastructures
organization, visible for all and clearly arranged. The management and
the employees use the chart as a background for internal and external Network components
Network components can be assigned to each network. This enables you to
communication.
immediately identify technological restrictions that arise from the selection of a certain
network for a company.
Network
A network represents a typification of individual network specimens that are based on exactly the same technology. Networks
Organizational unit can be connected to each other and can be arranged hierarchically as logical constructs.
Unit in an organizational hierarchy, e.g., a department or
location. It can be used to show which organizational units
are superior to others. Hardware
The hardware can, on the one hand, be network hardware for implementing the defined network structures or hardware that can
be connected to networks.
Symbol "Person Symbol "Location
release may 2010: ARIS Express 2.1
Individual persons can be assigned to an organizational A location can be a factory, a building, or also an
unit. office or a workplace in a room. Location refers IT system
to a physical place.
Business process IT systems represent logical electronic data processing systems. These systems are not hardware but software systems. ERP
systems and EAI platforms can be named as examples
Groups of persons: "Role A business process is a set of related tasks or activities performed to
Groups of persons can be combined in a role. Here, two produce a product or service. A business process consists of events As is the case with networks, hardware are also not individual hardware specimens that can, e.g., be identified by inventory numbers of the
persons are assigned to one role. triggering activities. Rules control the flow of the process. company, but are typifications that are based on the same technology. Hardware may be arranged in any required hierarchy.
A business process describes
- which activities are performed in the course of a process,
- which organizational units participate in process execution
(persons, groups of persons),
- what input and output data are used,
Data model - what IT systems are involved, and System landscape
- which events and risks occur during process execution.
A data model represents the data view of a company, e.g. which business objects exist. The entity relationship notation
is used for data modeling. Data models are created e.g. to define database structures. System landscapes represent the implementation options of functions and objectives via IT systems.
Events define the state or condition that cause an
activity to start as well as the state that defines the The model shows the modular structure of IT systems and the technological properties (operating systems,
completion of an activity. The start and end elements of user interfaces or database management systems) upon which an IT system is based. IT systems are
Entity Primary key a business process are always events. An event may considered here at type level. IT systems that are based on exactly the same technology are therefore
An entity is an individually identifiable object of The primary key (here: purchase order be the source of several simultaneous activities; on the combined.
reality. In databases, it is represented as a number) is a unique identifier for an object. other hand, an activity may result in several events. To
table. represent these branches and processing loops in a System landscapes describe which IT systems belong to which logical units (domains).
business process, a rule is used.
This assignment information is relevant for budgeting or for defining administrative responsibilities.
Attributes Foreign key Event
Attributes describe properties of a data object The foreign key is a reference to the primary This symbol represents an event that
(entity), i.e. the columns of a table. key of another data object. For example, the triggers activities.
customer ID is a reference to a data object of
the "Customer" type.
Activities Risks Risks are used to annotate activities
The cardinalities of relationships between Activities describe what happens during a
entities illustrate the number of interconnections. that may have very critical effects on the
process, i.e., what exactly is done. They are process and also to define
the core elements of a process. countermeasures. IT system
In the example, a purchase order may include IT systems represent logical electronic data
any number of books (at least one), which is processing systems. These systems are not
shown by the connection end symbol at the Process control via rules hardware but software systems. ERP systems
"Book" object. Input and output data Rules describe process workflow alternatives and and EAI platforms can be named as examples.
A book, in turn, is assigned to any number of Role
A process generates data or requires data thus illustrate possible execution variants. The
purchase orders (or none), which is shown by the The symbol "Role" illustrates who is
to be able to continue. These data are following rule symbols are available:
zero at the "Purchase order" object. performing an activity.
modeled as input or output of activities. Exclusive OR: Domain
Only one of the subsequent (or preceding) options IT systems can be grouped into areas
Cardinalities are set via relationship attributes may occur. (application domains). In doing so, the question of
(main menu: View > Attributes). similarity can be defined according to different
AND rule: classification criteria.
IT systems Process Interface All subsequent/preceding paths are applicable.
Activities can be performed manually or A process is not running isolated. Instead, it
automatically. Automated activities are is embedded in a complex relationship
performed by IT systems. network. Process interfaces are used to OR rule:
illustrate upstream and downstream Any number of paths can be used.
processes
Attributes The following attributes can be maintained:
- Name - Loop type (BPMN diagram only)
BPMN Diagram Objects, models, and relationships may - Description/Definition - Telephone number (Organizational chart only)
Process landscape
have properties. - Author - E-mail address (Organizational chart only)
BPMN is a process notation used to model business and workflow processes alike. BPMN is maintained by OMG. ARIS Express supports modeling These properties are called "attributes" in - Link - Address (Organizational chart only)
of BPMN 2 collaboration diagrams. ARIS and can be maintained in the Attributes - Multi-instance participant (BPMN diagram only) A process landscape is used to structure the process portfolio of a company. Processes in a process
view (main menu: View Attributes). - Compensation activity (BPMN diagram only) landscape can be connected in a sequence to describe an end-to-end scenario or a value chain. Processes
The BPMN collaboration diagram is used to model the interactions between participants, e.g. in a business-2-business (B2B) context. Participants can be arranged hierarchically to further refine certain process areas.
are involved in the process and represented by means of pools. Interactions between these pools are represented by message flows (message
exchanges). The process portfolio is usually structured into the following three process types:
Start events Whiteboard - management processes (e.g. strategy)
- core processes (i.e. value-adding processes)
Start events may use different symbols in BPMN. For example,
"Message event" for processes starting with a message, or "Timer event" A whiteboard model is used to record ideas and tasks and structure them the way you would do on a physical flip chart - support processes (e.g. marketing)
for processes to be started at a specific point in time. using post-it notes. A whiteboard can be created as result of a brainstorming session.
End events
These symbols mark the end of a process. You can also provide The example describes the result of a brainstorming session during which ideas concerning a product - in this case ARIS
information on the process end, for example send a message. Express - are gathered.
Intermediate events Stage
This event type is used within the process flow only; it is not used as a Process
A "Stage" is used to gather activities and
start or end event. This symbol represents a process that can be
objectives for a specific topic. You can also
define KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) described, e.g. by using a "Business process"
Gateways diagram.
They represent decisions within the process flow. Using the and details for a stage.
corresponding symbol, they represent parallel, exclusive, or other Activity
execution modes An "Activity" describes an action that has to
Task be performed within a stage.
In BPMN, tasks are represented by activities. They cover the
This symbol describes the goal that
human ("User task" or "Manual task") or technical execution of
activities have to reach for the
tasks. As "Subprocesses" they represent basic processes.
corresponding stage.
Pools and lanes
These represent organizational units. Details" are used to place additional
Using pools or embedded lanes tasks information concerning the stage and its
can be assigned to persons or groups of activities.
persons. "Key Performance Indicators" (KPI) are
Text annotations
They are used to add comments to
used to specify how goal accomplishment is
measured. http://www.ariscommunity.com/aris-express
model elements An "overall goal" relates to all stages
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Nebosh EcDokument2 SeitenNebosh Ecdaabhi100% (2)
- Chapter1 - Basic Concepts & Computer - EvolutionDokument67 SeitenChapter1 - Basic Concepts & Computer - EvolutionElias HedamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4383 Lambert 530Dokument5 Seiten4383 Lambert 530arriva0% (1)
- Sop Maturity ModelDokument4 SeitenSop Maturity ModelarrivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXSERVS Mariwasa Case 2Dokument2 SeitenEXSERVS Mariwasa Case 2Lui CastañedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MPM344 TemplateDokument15 SeitenMPM344 TemplateGeorge MainaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benelite Process For Upgradation of IllemniteDokument6 SeitenBenelite Process For Upgradation of Illemnitemadangk100% (1)
- Week 1 - Lecture 2 - Computer Organization and Prog LanguagesDokument20 SeitenWeek 1 - Lecture 2 - Computer Organization and Prog LanguagesFaizan AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computers 08 00045 PDFDokument19 SeitenComputers 08 00045 PDFSuphachet PhermphoonwatanasukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Concepts and Computer EvolutionDokument56 SeitenBasic Concepts and Computer EvolutionDaWheng VargasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sia 03LabExer1 InfoSec ManagementDokument2 SeitenSia 03LabExer1 InfoSec ManagementGela SiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 10 EditionDokument52 SeitenWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 10 EditionAdnan Aslam Merchant0% (1)
- CH01-COA10e Intro KPDokument56 SeitenCH01-COA10e Intro KPPhương Nam TrầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineered Systems MapDokument1 SeiteEngineered Systems MapbehejazyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 1Dokument81 SeitenPart 1Kien TrungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Modeling: Prepared by Kevin C. Dittman For Systems Analysis & Design Methods 4ed by J. L. Whitten & L. D. BentleyDokument41 SeitenNetwork Modeling: Prepared by Kevin C. Dittman For Systems Analysis & Design Methods 4ed by J. L. Whitten & L. D. BentleyRheinaldy Dimas PratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSTA K-12 Standards Progression ChartDokument2 SeitenCSTA K-12 Standards Progression ChartBryan TwarekNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSR MIS Lecture 1 - IT InfrastructureDokument30 SeitenCSR MIS Lecture 1 - IT InfrastructureKunal PurohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Embedded Systems DevelopmentDokument5 SeitenSummary of Embedded Systems Developmentmoooo yii trrhjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session-4-5: Manojit ChattopadhyayDokument42 SeitenSession-4-5: Manojit ChattopadhyayUtkarsh GurjarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1-3Dokument134 SeitenChapter 1-3incubusmalique008Noch keine Bewertungen
- CS802A Lec-4 PDFDokument15 SeitenCS802A Lec-4 PDFAnonymous aEBzOzAcX7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Information Systems and Its Components: After Reading This Chapter, You Will Be Able ToDokument104 SeitenInformation Systems and Its Components: After Reading This Chapter, You Will Be Able To417 Rachit SinglaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seco CNDDokument4 SeitenSeco CNDDaisy KhojaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 04: Detail System Analysis CSC 401: Database Management SystemDokument23 SeitenLecture 04: Detail System Analysis CSC 401: Database Management SystemMeraj Mohammed BhuiyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Driven Framework For Networked Application Software GenerationDokument10 SeitenModel Driven Framework For Networked Application Software GenerationJournal of ComputingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer OrganizationDokument159 SeitenComputer Organizationssmukherjee2013Noch keine Bewertungen
- "IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software": Outsourcing Using Cloud ServicesDokument1 Seite"IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software": Outsourcing Using Cloud ServicesalyciafiralinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Document Computer Networks: Sabah Al-Fedaghi and Bader BehbehaniDokument12 SeitenHow To Document Computer Networks: Sabah Al-Fedaghi and Bader Behbehaniakbar zanjanpouriNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Machine Learning Approach For Traffic FlowDokument6 SeitenA Machine Learning Approach For Traffic Flow9967835192Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH01 COA10eDokument57 SeitenCH01 COA10eJohn ANoch keine Bewertungen
- William Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 10 EditionDokument57 SeitenWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and Architecture 10 EditionAbood AbujamousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Components of The Management Information System: Week.5Dokument21 SeitenComponents of The Management Information System: Week.5Tuba MirzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 COADokument35 SeitenLecture 1 COATashinga Ryan ManunureNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ci 7 CH 3 NetworkDokument23 SeitenCi 7 CH 3 NetworkanuveenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TM04 NJ1 MM05Dokument1 SeiteTM04 NJ1 MM05Devina Sulit salmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final ProjectDokument10 SeitenFinal ProjectlheyNoch keine Bewertungen
- City Government of San PabloDokument17 SeitenCity Government of San PabloDinglasan, MeleaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics RequiredDokument8 SeitenMathematics RequiredNihal GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grid IntelligenceDokument10 SeitenGrid IntelligenceManorath PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITEC255 Chapter3 (Part1) With ExplanationsDokument29 SeitenITEC255 Chapter3 (Part1) With ExplanationsyawahabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research On Data Interaction and System Integration of Heterogeneous Systems Based On Web ServicesDokument4 SeitenResearch On Data Interaction and System Integration of Heterogeneous Systems Based On Web ServicesRitam DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 2 ComponentsDokument36 SeitenLec 2 ComponentsHajipur RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Survey of Machine Learning Techniques Applied To Software Defined Networking (SDN) : Research Issues and ChallengesDokument39 SeitenA Survey of Machine Learning Techniques Applied To Software Defined Networking (SDN) : Research Issues and ChallengeszedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Learning Techniques - SDNDokument38 SeitenMachine Learning Techniques - SDNnubnajninNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 01 - Introduction 01Dokument10 SeitenLecture 01 - Introduction 01SadiholicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Defined Networking With Intrusion Detection SystemDokument3 SeitenSoftware Defined Networking With Intrusion Detection SystemerpublicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Netvision: Towards Network Telemetry As A Service: 2018 Ieee 26Th International Conference On Network ProtocolsDokument2 SeitenNetvision: Towards Network Telemetry As A Service: 2018 Ieee 26Th International Conference On Network Protocols军刘Noch keine Bewertungen
- CT Manager: Job Objective: Duties and ResponsibilitiesDokument4 SeitenCT Manager: Job Objective: Duties and Responsibilities71177335Noch keine Bewertungen
- IoT ArchitectureDokument6 SeitenIoT ArchitectureStarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijert Ijert: Structured Network Design and Implementation For A Small Office Home Office - Tutorial/ReportDokument7 SeitenIjert Ijert: Structured Network Design and Implementation For A Small Office Home Office - Tutorial/ReportMd. Nafiz Mahmood ShajibNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are Data Structures?: ? M I S S ? NullDokument5 SeitenWhat Are Data Structures?: ? M I S S ? NullFredNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Effective Network Monitoring Tool For Distributed NetworksDokument5 SeitenAn Effective Network Monitoring Tool For Distributed NetworksEdgar MendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ibmsj 1992Dokument27 SeitenIbmsj 1992Yuri R. BenetskiyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 4 - Distributed RT Embedded SysDokument46 SeitenCH 4 - Distributed RT Embedded SysMelkamu BirlewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapt: Topics Covered in This Tpicsc Ered in This ChapterDokument18 SeitenChapt: Topics Covered in This Tpicsc Ered in This Chapterali amjdNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of Data Structures in Multiple Disciplines of Computer Science A ReviewDokument6 SeitenThe Role of Data Structures in Multiple Disciplines of Computer Science A ReviewDan RonohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Habusadeh, Journal Manager, 854 - 859Dokument6 SeitenHabusadeh, Journal Manager, 854 - 859Mohamed YaCine LaidaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Microprocessor Based Systems ADokument9 SeitenDesign of Microprocessor Based Systems ALutaaya Geoff UGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information System ComponentsDokument1 SeiteInformation System ComponentsAdib AfhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP Networking Comparison Guide For The Transformational EnterpriseDokument6 SeitenIP Networking Comparison Guide For The Transformational Enterpriseshiva1974Noch keine Bewertungen
- CAO Chapter 1Dokument25 SeitenCAO Chapter 1Yogesh ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ict114 Lecture 2Dokument7 SeitenIct114 Lecture 2Shirley LohNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIC10503 Computer Architecture: Chap 1: IntroductionDokument35 SeitenBIC10503 Computer Architecture: Chap 1: IntroductionAfiq DanialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Defined Networking (SDN) - a definitive guideVon EverandSoftware Defined Networking (SDN) - a definitive guideBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (2)
- Linux Essentials for Hackers & Pentesters: Kali Linux Basics for Wireless Hacking, Penetration Testing, VPNs, Proxy Servers and Networking CommandsVon EverandLinux Essentials for Hackers & Pentesters: Kali Linux Basics for Wireless Hacking, Penetration Testing, VPNs, Proxy Servers and Networking CommandsNoch keine Bewertungen
- l4-03 Nov08 Ms FBC GB FVDokument9 Seitenl4-03 Nov08 Ms FBC GB FVarrivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interview: Lowry Computer Products' Mike Lowry Explains The Capabilities of Cutting-Edge Label TechnologyDokument2 SeitenInterview: Lowry Computer Products' Mike Lowry Explains The Capabilities of Cutting-Edge Label TechnologyarrivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Start To RFID: Initiating A Smart Label PilotDokument3 SeitenSmart Start To RFID: Initiating A Smart Label PilotarrivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASC6 WP AndersonDokument2 SeitenASC6 WP AndersonarrivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supply Chain Strategy: Real Options For Doing Business at Internet SpeedDokument4 SeitenSupply Chain Strategy: Real Options For Doing Business at Internet SpeedarrivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lean Management in Hospitals Principles and Key Factors For Successful ImplementationDokument2 SeitenLean Management in Hospitals Principles and Key Factors For Successful ImplementationarrivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1705 04958 PDFDokument24 Seiten1705 04958 PDFarrivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bibak Ispab Sboyson Hrossman April2009Dokument12 SeitenBibak Ispab Sboyson Hrossman April2009arrivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASC2 WP CokinsDokument9 SeitenASC2 WP CokinsarrivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supply-Demand Planning-Asc7 WP JacobyDokument5 SeitenSupply-Demand Planning-Asc7 WP JacobyarrivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supply Chain Management Sample Application ArchitectureDokument40 SeitenSupply Chain Management Sample Application ArchitecturearrivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Review of The Application of The SCOR Model: Supply Chain For Biodiesel Castor - Colombia CaseDokument9 SeitenFinal Review of The Application of The SCOR Model: Supply Chain For Biodiesel Castor - Colombia CasearrivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1705 04958 PDFDokument24 Seiten1705 04958 PDFarrivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Government Rightsizing ProgramDokument30 SeitenNational Government Rightsizing ProgramSharief HangdaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Core PrinciplesDokument26 SeitenThe Core PrinciplesAbed HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 POM 2020Dokument5 SeitenChapter 1 POM 2020Hà MintNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competitor AnalysisDokument4 SeitenCompetitor AnalysisKhadija TahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting EquationnnnDokument9 SeitenAccounting Equationnnnshrestha.aryxnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meena Bhatt - ResumeDokument3 SeitenMeena Bhatt - Resumehemanth vNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report (Rishab)Dokument44 SeitenProject Report (Rishab)Aryan singh The blue gamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRF ProjectDokument98 SeitenMRF ProjectThigilpandi07 YTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Order 111-3369545-5506652Dokument1 SeiteOrder 111-3369545-5506652can kayarNoch keine Bewertungen
- LM Business Math - Q1 W6 - MELC3 Module 8Dokument15 SeitenLM Business Math - Q1 W6 - MELC3 Module 8Cristina C MarianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cryptography and Network Security: UNIT-1Dokument5 SeitenCryptography and Network Security: UNIT-1atmadeep09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atswa Cost AccountingDokument504 SeitenAtswa Cost Accountinggarba shuaibuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Travel Tax SystemDokument28 SeitenThe Travel Tax SystemJay PunongbayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Charge Invoice5506516254Dokument1 SeiteUser Charge Invoice5506516254ganesanbhuvanesh241003Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Requirements For Wire Rods and Coarse Round Wire, Alloy Steel (Metric)Dokument9 SeitenGeneral Requirements For Wire Rods and Coarse Round Wire, Alloy Steel (Metric)Paulo GalvãoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 ALMOST DONEDokument12 SeitenChapter 2 ALMOST DONEayieeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Multimodal TransportDokument39 SeitenOverview of Multimodal TransporthanyimwdmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pratik BBDokument74 SeitenPratik BBPratik PadmanabhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Law and Practice of BankingDokument34 SeitenLaw and Practice of BankingAbdullah Al ShaqureNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method Statement - Fire AlarmDokument9 SeitenMethod Statement - Fire AlarmiamajumalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Invoice 719476113 PDFDokument1 SeiteInvoice 719476113 PDFNisha Avit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part II Brgy. Inarado, Daraga - Findings and RecommendationsDokument11 SeitenPart II Brgy. Inarado, Daraga - Findings and RecommendationsBaby M FoodhubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Branding and Packaging Decisions of The ProductDokument34 SeitenBranding and Packaging Decisions of The ProductPraveen Prasoon100% (1)
- Random Walk Model of ConsumptionDokument22 SeitenRandom Walk Model of Consumptionshahid_hussain_41100% (1)
- Types of Directors and Other Managerial Personnel in A CompanyDokument14 SeitenTypes of Directors and Other Managerial Personnel in A CompanyKamal NaraniyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sap Gui Transaction CdoeDokument32 SeitenSap Gui Transaction Cdoesrkader74Noch keine Bewertungen