Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Antibacterial Drug
Hochgeladen von
Anonymous HH3c17os0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
60 Ansichten4 SeitenDrug guide antibiotic
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenDrug guide antibiotic
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
60 Ansichten4 SeitenAntibacterial Drug
Hochgeladen von
Anonymous HH3c17osDrug guide antibiotic
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
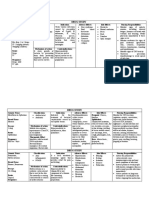
ANTI-BACTERIAL AGENTS
Drug Use MOA Notes PRC PK others
I. -Lactams Cidal, time-dependent antimicrobial all beta-lactams in high conc. cause seizures
A. Penicillin CI: hps coz all Pen have cross-allergenecity,
Limitations: Deactivated by -lactamases, bleeding abn for extended spec pen like
DOC: GPC (S. pyogenes & pen sensitive S. pneumonia, unstable in acid gastric contents, limited antipseudomonal(BT, PT)
staph), GPB (anthracis & diptheria), GNC spectrum,rapid renal excr, hps, poor BBB ADR:
60% pr. binding, Acid labile, low
(menigococcus and gonococcus), GNB (bubonic penetration Frequent: allergy, maculopapular rash (ampicillin
bioav., poor oral, distributed in
plague, Vincents infection by Spirilum minus), Short acting: PenG aqueous(crystalline) Na & amoxicillin), diarrhea (esp w/ ampicillin & co-
PenG (benzylpenicillin) all tx & fluids, penetrate
Spirochetes (treponema like syphilis yaws, leptospira K salt- for severe life threatening infxns amoxiclav), nausea & vomiting w/ co-amoxiclav in
inflamed BBB, kidneys (10% GF,
and bacilli in bubonic plague and spirilum minus), binds with PBP selective Repository Forms: IM: Procaine PenG children
90% TS) Parenteral, t1/2 0.5 h
anaerobes (cocci, fusobac, actino, clostridium in inhibition of transpeptidase (sustain serum levels for 12-24h,high pen R) Occasional: hemolytic anemia, neutropenia,
tetanus and gas gangrene, bacteroides except fragilis) reaction no synthesis of Benzathine PenG (low but sustained levels pseudomembranous colitis, plt dysfxn (high dose
mucopeptide (murein, 1-3wks, 1o & 2o prevention of RF & syphilis) carbenicillin, ticarcillin, azlocillin, piperacillin,
peptidoglycan) Penicillinase susceptible analogue of nafcillin, methilcillin), cholestatic hepatitis (co-
PenV PenG sens bact in respi (strep tonsillitis/pharyngitis), PenG Good oral w/o food, 60% pr amoxiclav)
(Phenoxymethylpenicillin) skin, subQ inactivation of inhibitor of Limitations: poor bioav, qid on empty binding, acid stable Rare: muscle irritability & seizures (in px w/ renal
autolytic enzymes stomach, narrow spectrum impairment), hyperkalemia & arrhythmia (w/ IV
Oxacillin (autolysins, murein B Low oral, 90-94% pr binding penG given rapidly), agranulocytosis & hepatic
Penicillinase Staph infxns, not active vs enterococci, hydrolases cell wall lysis renal damage with semisythetic penicillins,
Penicillinase resistant, isoxazolyl grp Low oral, 95-98% pr binding,
Cloxacillin (oral) anaerobes, gram negative cocci & bacilli (bactericidal) bleeding diathesis, Henoch-Schonlein purpura
acid stable
Retain antibac of Pen and improve against G(-), IV in (ampicillin), disorientation, hallucinations,
Ampicillin inj. enterococci, Listeria, Gonorrhea, H. influenza, E. coli, PBP-1, PBP-3, 6-amino- Low oral, 18-22% pr binding agitation, neurologic rxns like Hoignes syndrome
Proteus, shigella, salmonella penicillanic acid (-lactam + (w/ high dose of procain penicillin G)
5-membered thiazolidine Expanded spectrum (penicillinase sensi), Drug interactions:
same w/ ampicillin but None in Shigella, Tx typhoid
ring) Aminopenicillins High dose cabenicillin/ticarcillin inactivates
fever, anti-H.pylori with PPI and bismuth subcitrate for High oral B, 17% pr binding, acid
Amoxicillin oral aminoglycosides; Ampicillin decrease effects of
ulcers, chemoprophylaxis in bacterial endocarditis in stable
dental surgery oral contraceptives; Amoxicillin after MMR
vaccine cause erythema multiforme; increase
methotrexate toxicity; B lactams +
Ampicillin spectrum plus vs Pseudo, B. fragilis, Kleb., In combi with aminoglycoside/ aminoglycosides = synergism; Probenecid
Piperacillin inj.
more active than ticarcillin fluoroquinolone for pseudo inf. outside Acid labile, 16-48% pr binding increase half life of penicillin; Static agents (ex.
(Antipseudomonal pen.)
Ureidopenicillin acylureido deriv. of ampicillin urinary tract to prevent resistance Tetracycline) reduce effectiveness of B-lactams
Antagonism
Anti--lactamases intrinsic activity, potent irrev inhibitor of
Amox + clavulanic acid oral UTI, otitis media, sinusitis, bite wounds Co-amoxiclav, 7:1 if BID, 4:1 if TID Oral, 20-30% pr binding Ambler Class A B-lactamases (plasma encoded
Ampi + sulbactam IV Complicated intraab/pelvic infxns, polymicrobial RTI inhibitors of -lactamases Sultamicillin- oral, prodrug Oral, 28-38% pr binding TEM B-lactamase), NOT good inhibitor of Class C
Immunocompromised pxs, nosocomial pneumonia w/ Activity vs Pseud&S.fecalis not enhanced by (chrom encoded B-lactamase)
Piperacillin + tazobactam IV 16-48% pr binding
resistance fixed dose combo w/ B-lactamase inhibitor
Same as -lactams 7-aminocephalosporanic acid (betalactam B Renal except cefixime & ADR:
B. Cephalosporins None active against enterococcus, listeria, MRSA
ring fused with 6-membered ceftriaxone (renal and hepatic) Frequent: thrombophlebitis w/ IV use, serum
GPC, penicillinase Staph, strep; alt: for impetigo, dihydrothiazine ring), cephamycins No CSF, Cefalexin & Cefadroxil- sickness like rxn w/ Cefaclor, diarrhea w/
1st Generation cefazolin IV;
osteomyelitis, pharyngitis, skin/soft tx infxn, surgical 90% absorbed orally, low pr Cefoperazone
cefalexin, cefadroxil oral
chemopylaxis (cefazolin), Pen allergic pxs Drug interactions: Disulfiram-like rxn after binding, Cefazolin-80% pr bound Occasional: allergy, GI disturbance,
2nd Gen GPC = 1st, better GN, none w/ Pseudo alcohol ingestion w/ ceph w/ MTT side Poor CSF hypothrombinemia, hemorrhage w/ Ceph w/
chain; toxic renal damage potentiated by NOT for meningitis MTT side chain ex. Cefamandole&
Haemo, enterobacteriaceae, -lactamase Neisseria , concurrent use of aminoglycoside, Cefuroxime axetil (oral)- cefoperazone ,plt dysfxn, coagulopathy, Vit K dep
alt: for chr bronchitis, epiglotitis, otitis media, sinusitis, probenecid, rapid acting diuretic ; drugs for prodrug, 52% absorbed, 50% pr CF def w/ Moxalactam, rash&arthritis w/ Cefaclor
Cefuroxime hemostasis (heparin, anticoags) increase in children, bile sludging & pseudocholelithiasis
pyelonephritis, orbital cellulitis, pneumonia, skin & bound; Cefuroxime IV- the only
soft tx, bone, jt infxns hemorrhage risk w/ Moxalactam & others 2nd gen ceph w/c cross BBB but w/ Ceftriaxone
w/ MTT side chain NOT sufficient for Tx Rare: hemolytic anemia, hepatic dysfxn, blood
Cephamycin (cefoxitin) Enterobacteriaceae, anaerobes, B. Fragilis outside Most active vs. Anaerobes (B. dyscrasias, renal damage, acute interstitial
CNS, mixed infections in peritonitis liver & pelvic inf., fragilis), 65-99% pr bound nephritis & convulsions w/ Cephalotin
surgical chemoprophy in colorectal & appendectomy
Even better GN, resistance to GN-lactamase,
3rd Gen Good CSF
reach bactericidal conc. in CSF except cefoperazone
GN-lactamase producers, penicillin resistant Ceftriaxone-qd, 90% bound,
Cefotaxime, Ceftriaxone (IV)
pneumococci, LIMITED anti-pseudo activity DOC for gonorrhea;MDR S. typhi
single dose Tx of uncomplicated gonorrhea, NOT active 50% absorbed, 65% bound, T1/2
Cefixime (oral)
vs S. aureus & pseudomonas is 3h
Best vs Pseudo (antipseudomonal) & indole (+)
Most active 3rd gen ceph vs P.
Ceftazidime Proteus, empiric treatment of febrile neutropenic pxs
aeruginosa
combi w/ antipseudomonal aminoglycosides
GP, enterobacteriaceae, Pseudo, severe inf. Like Good CSF, more resistant to
4th Gen Cefepime sepsis, pneumonia, meningitis, severe mix g(+) and chromosomal B-lactamase by
g(-), empiric monotherapy in febrile neutropenic pxs. enterobacter
Multiple resistant GN (esp Meropenem), DOC
enterobacters & infxn by ESBL producing GN, mixed betalactam ring attached to 5-membered Not oral, inflamed BBB, renal Dec dose: elderly (renal dysfxn, cerebrovasc dxs)
C. Carbapenem infect of Staph, GNB and anaerobes, monotherapy for ring, sub of carbon for sulfur and unsat. In exc, inactivated by renal (in ADR: Phlebitis, F, uritcaria, pruritus, N, V,
intraabd, febrile neutropenic px & Pseudomonas (in 5-membered ring Prox tubule) dihydropeptidase I pseudomem colitis, seizures w/ imipenem
combo w/ antipseudo aminoglycoside to prevent R)
Same as -lactams,
*10x more neurotox than Admin w/ Cilastatin (renal dehydropeptidase
Broadest spectrum (GP&GN), better vs GP compared PBP-2, 1b Induces -lactamases
benzylpenicillin; R to B- inhibitor) to prevent low urinary conc, IV q 6-8h,
1. Imipenem to Meropene, cidal except to E. faecium, MRSA, C. Not absorbed orally, penetrate all tx & CSF C
lactamases but NOT to metallo- Seizure potential, potent inducer of Class C B-
difficile, Burkhoderia, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia when inflamed, 75% excr unchanged
B-lactamase lactamase (w/c can inactivate other B-lactams)
Better vs GN, CSF levels potentially therapeutic, combo No seizure potential when admin w/ cilastatin
2. Meropenem IV B Hepatobiliary
w/ antipseudomonal aminoglycoside (imipinem higher affinity to GABA)
IM and IV, OD, less active than 2 above vs 95% pr bound, excr renal &
3. Ertapenem not degraded by dehydropeptidase B
Pseudomonas & acinetobacter biliary, IM prep has 1% lidocaine
-lactamase resistant, not induce chrom
GN aerobes (substi for aminoglycosides), allergy to
Same as -lactams, binds mediated B-lactamase (unlike ceph & Not oral, inflamed BBB, renal & Local rxn, rash, D, N, V, aminotransferase,
D. Monobactams Aztreonam pen or cepha, mixed infections, spectrum like AMG, B
PBP-3, cidal imipenem) not crossreact w/ pen&ceph, biliary, penetrates into all thrombocytopenia, pseudomem colitis
combi with clindamycin, vanco, metroni
synergy w/ AMG, levels w/ probenecid
Relative renal toxicity:
neo>kana,amikacin, genta,
w/ edema/ ascitis.obesity base dose on ideal wt
netilmicin>tobra>streptomycin
Dosages for estimated clearance >/=80mL/min
II. Aminoglycosides AMG cidal vs. GN aerobes & S. aureus, conc dep. impaired if w/ hypoxemia and acidemia Relative ototox: neo
Measure peak serum levels 2h after infusion,
(cochlear)>strep (vestibular)>
trough level just before next dose
kana (cochlear)>amika, genta,
tobra, netilmicin
8th (vestibular) nerve damage, paresthesia,
pruritus, renal damage, blood dyscrasias, NMJ
Streptomycin TB, mycobac, Strep viridans w/ PenG (ex. SBE) Bind 30s ribosomes inhibit DI: nephrotox (ceph, AMB, furosemide), IM, not CSF, kidneys
D block (reversed by Neostigmine), SJS, optic
CHON synthesis ototox (ethacrynate/bumetamide), NMJ
neutitis, hepatic necrosis, mocarditis etc.
(curare and MgSO4), inactivated by
UTI with GNB, combo w/ pen or ceph: empiric therapy IM, IV, topical, otic, ophtha, qd Vestibular damage, renal tox ( w/ qd dose),
carbenicillin and ticarcillin
Gentamicin for serious infxn (neonatal sepsis etc), mixed infxn dose, Not w/ heparin lock coz of auditory,NMJ blockade and apnea (reverse w/ Ca
(peritonitis), Pseudo, Prot, Kleb, acute cholangitis ionic bind, excr unchangd by GF or Neostigmine), anaphylaxis, polyneuropathy
Netilmicin Same as gentamicin, but more resistant to inactivation IM, IV, qd dose Less nephrotoxic
Amikacin by enzymes (adenylating) IM, IV, qd, Not w/ heparin
Neither oto/nephrotox, w/ benzylalcohol = fatal
aminocyclitol, Bacteriostatic, alt: Tx gonococci in px
Spectinomycin lithium tox IM gasping syndrome in infants; dec. urine output,
who are allergic to pen
allergy, nausea, chills, fever, insomnia, dizziness
III. Chloramphenicol DOC: severe H. influenza, susceptible S. typhi, Reversibly binds to 50s Prodrugs needs hydrolysis: Succinate ester C Oral (75-100%, >bioav vs *attach polar grp (ester linkage) to inc solubility
Bacteroides (meningitis, brain abscess), alt: for PenG prevent AA transfer inhibit (IV), Palmitate ester (oral) for pediatrics chloramphenicol succinate), 25- CI: Hps, hematotox, preggy, neonates/breastfeed
allergy in pneumococcal and meningococcal peptidyl transferase inh. DI: inhibit drug metab, anticoag w/ 50% pr bound, in CSF, bones, ADR: Anemia, gray baby, GI, allergy, aplastic,
meningitis, rickettsia in pxs w/ tetracycline hps, CHON synthesis dicoumarol, hypoglycemia with inactivated by liver conj, 5-15% leukemia, peripheral neuropathy, pseudomem
pregnant, brucellosis, glanders, plague, intraocular inf sulfonylureas, inc. phenytoin tox, w/ via urine, 4% via bile; can colitis, hemolytic anemia (G6PD def.)
Static except in H. influenza, N, meningitides, phenobarb/toin & rifampicin; disulfiram like antagonize cidal axn of pen and
bacteroides (cidal) syndrome w/ alc. AMG coz static
DOC: Chlamydia--Doxycyclin (urethritis, pelvic inflame CI: hps, preggy, kids under 8, renal failure except
dxs, lymphogranuloma venereum, psittacosis), Inh pr synthesis by binding doxycycline; ADR: freq: GI, bone growth retard,
rickettsia (RMSF, typhus), Lyme, lepto, brucella (in w/ 30s (or 50s) & inh binding permanent pigmentation, teeth hypoplasia;occ:
DI: nephrotox (methoxyflurane), tetra
combo w/ streptomycin), plague, cholera, tularemia of incoming charged malabsoprtion, enterocolitis, photosensitivity
IV. Tetracyclines effects (antacids, iron, ZnSO4, bismuth Oral, variable abs w/ food,
M.fortuitum (only doxycyclin), malaria (doxycycline), aminosyl tRNA into acceptor (demeclocycline), azotemia (except doxy), liver
(tetracycline HCLimpaired by subsalicylate) dec. doxy effects (chelators, divalent cations, antacids; not
Granuloma inguinale site on mRNA-ribosome D damage (IV in preg & px w/ renal dxs), esophageal
food, doxycyclin, nubicycline barbi, CBZ, phenytoin), effects CNS, bound to bones & teeth,
Others: intestinal amebiasis, alt: actinomycosis, rat complex (prevent addition of ulcer, vestibular tox &hyperpigment
both high oral abs, q12hrs) (contraceptives, digoxin), Li tox, lactic liver, spleen; excr in bile & urine
bite, syphilis, tularemia, yersinia, Penicillinase gonocci, aa to peptide), alter (minocycline); rare: allergy, bld dyscrasia, inc
acidosis w/ phenformin, antag with pen
Mycoplasma, acne (long term low dose), leprosy cytoplasmic membrane, intracranial pressure in infants, diabetes insipidus
(minocycline comb w/ rifampicin and ofloxacin); static (demeclocycline), blur vision, Fanconi-like synd
adjuvant in amebiasis (outdated tetras), acute nephritis (minocycline)
DOC: diphtheria inf/carrier state, Mycoplasma CYP1A2 & CYP3A3/4 inhibitors and dec.
pneumo, Legionella, pertussis Tx&prophylaxis, hepatic metabolism of other drugs
chancroid, gastroenteritis Campylo, Chylamidia DI: effect & toxicity of theophyllines, oral
pneumo in preggy/kids anticoags, digoxin, CBZ, cyclosporine, ergot, No BBB, hepatobiliary
V. Macrolides / Azalides (ACE)
Px hps in pen: strep & pneumococcal, syphilis, RF arrhythmia / Torsades de pointes when elimination
prophy, prevent bacty endocarditis after dental macocyclic lactone ring with given w/ astemizole, amiodarone, CI: hepatic impairment, hps to erythromycin
procedure; acne; pre-op chemoprohy in elective 14-16 atoms where haloperidol and terfenadine (Erythro & ADR: occ: Stomtitis,cholestatic jaundice, GI
colorectal surg, alt drug for C trachomatis urethritis deoxysugars are attached; clarithromycin inc. QT interval) irritation, rare: hps, pseudomem colitis,transient
time dep. Base: enteric coated to prevent gastric acid deafness, inc QT interval (torsades de pointes),
MOA: Static, Inhibit RNA- destruction, Stearate: better abs&bioav, ventricular tachy, aggravate M. gravis,
fatty acid R. & better absorbed
dependent CHON syn at Esters: < acid labile vs 2 above, Estolate: Motilin- activates duodenal & jejuna receptors to
Erythromycin (prototype) B (Stearates & ester); Not in brain
chain elongation, bind 50s higher plasma level ut only 20-30% active, initiate peristalsis. Erythromicin & esters (po,IV)
& CSF, excr bile, t1/2=1.5h
block transpeptidation and causes cholestatic jaundice, Ethyl activates motilin receptors and cause
aminoacyl translocation succinate : >rapid hydrolysis vs estolate uncoordinated peristalsis with resultant A, N, V
Added effects vs Haemo, M. avium, M. leprae, T. Not preggy, w/ active metab: 14-
Clarithomycin C T1/2=6h, lesser GI SE
gondii, Anti-H.pylori hydroxyclarithromycin eliminated via urine
15-member lactone ring by addition of T1/2=68h, qd dosing shorter
Azithromycin Broader spectrum but less active vs staph & strep methylated nitrogen into the lactone ring, B duration of therapy, > tx
hence doesnt inhibit CYP450 so no DI penetration, <GI SE
Never a 1st choice, Static vs GN aerobes & non CNS static/cidal (depends on conc, infxn site,
Reversibly binds 50s Oral, CHON bind, No BBB, D, allergy, pseudomem colitis (C. difficile), toxic
VI. Lincosamides anaerobes (ex. Intraab inf, combo w/ AMG or org), time dep
prevent peptidation inh. B conc in bone & bile & urine, elim megacolon, blood dyscrasia, hypotension, impair
Linco/Clindamycin aztreonam), alt: Pen and cephalosporin allergy (esp in DI: NMJ block (w/ curareform drugs),
CHON syn. via hepatic metab liver fxn, esophageal ulcer
osteomyelitis & septic arthritis) lincomycin w/ Kaolin pectin
GPN, but GNB & mycobacty R Binds D-alanine-D-alanine Freq: Thrombophlebitis, fever,chills, Occ: hearing
DOC: MRSA, GP block glycopep polymer, DI: nephrotox (AMG, ceph), ototox IV, not oral, inflamed BBB (need damage (CN8) if cont high dose >10d, allergy,
VII. Glycopeptide IV: Alt: unresponsive or S. viridians & enterococcal Cidal inh. (AMG), digoxin, synergistic with high dose coz low&erratic neuropenia, renal damage; rare: peripheral
C
vancomycin (cidal) endocarditis, pseudomembranous colitis, prosthetic Transglycosylase prevent streptomycin and gentamicin against penetration), 90% urine (beware neuropathy, red neck syndrome (flushing of
device inf. CSF shunt inf., serious nosocomial inf. elong. of peptido and x-link enterococci if w/ renal dysfxn), t1/2= 4-5h upper chest due to histamine release, prevent by
Oral: antibiotic induced pseudomembranous colitis (time dep) x cell wall slow IV over 60-90mins) rash, hypotension
VIII. Fluoroquinolones Synthetic fluorinated conc dep, cidal
analogue of nalidixic acid; all Not for preggy & kids <18 -damage devl cartilage
Ciprofloxacin(prototype 2nd In vitro activity: less active in GPAerobes than GNA Oral, ok pr bound, Vd CSF,
are GABA inhibitors account DI: tox (theophylline), conc (caffeine & ADR: occ:N, V, Abd pain, D, dizzy, HA, tremor,
gen.); DOC anthrax, greatest Not for anaerobes, Alt: Mtb, MAC 40% elim in urine (oral dose)
for CNS tox. warfarin via interfering w/ hepatic metab), macular rash, candida infxn, inc eo, dec neutro,
anti pseudo activity in this grp MSSA, severe UTI (pyelonephritis), GI infxn (ex. MDR 70%(IV), 4 active metabolites
MOT: Inhibit DNA gyrase abs (antacids); prolong QT (inc risk if C inc hepatic enz activity, inc serum crea; rare:
Ofloxacin 2nd gen. Salmonella), STD (gonococcus), -lactam resistant Oral, poor CSF, t1/2=9h
(topoisomera II,IV) inh hypoK, hypoMg, Ia & IIIa antiarrhymic drug, Tendinopathy (Achilles tendinitis), CNS, hepatic
Levofloxacin- 3rd gen, B. fragilis osteomyelitis/septcimea, meningococci carrier respi fluoroquinolone; Oral,
DNA synthesis macrolides, anti hpn, CNS drugs) failure, hyper/hypoglycemia, Torsade de pointes
NOT susceptible eradication & prophylaxis t1/2=7-8h
(least w/ Cipro!)
Gatifloxacin Oral, good CSF
Norfloxacin only for UTI & acute bacty invasive diarrhea shigellosis
IX. Nitromidazoles GN, protozoals, cidal for anaerobes (ex. fragilis & Nitro grp Reduced DI: tox (warfarin, phenytoin, lithium, B Enters abscesses w/ Little pr CI: hypersensitivity, 1st trimester
metronidazole (prototype) clostridia) intracellularly interact w/ cimetidine), disulfiram-like rxn (avoid binding, liver metab, excr in N, HA, dry metallic taste, V, D, weakness,
Anti-protozoal: T. vaginalis, amebiasis, giardiasis DNA loss of helical DNA alcohol on & until 48h after), organic brain urine & feces, NO mutagenic, insomnia, stomatitis,vertigo,paresthesia,phlebitis
Anti-bacty: tetanus, anaerobe infxn, G. vaginalis, H. structure strand breakage syndrome (disulfiram), Metro effect w/ ,rash, dark urine, seizure, CNS, pancreatitis,
tumorigenic, teratogenic effect
pylori, antibiotic induced pseudomem colitis CHON synthesis & cidal phenobarbital ataxia, encephalopathy, leucopenia
DI: effect (sulfonylurease, anticoags, Not for topical or Streptococcal sore throat
TMP:SMX 1:5 useful becomes cidal like cotrimoxazole Oral, all tx& fluids, CSF, metab
phenytoin), antileukemic effect of CI: hps, preggy, lactation, infants <2mos, renal dxs
Systemic (mostly for cotrimoxazole): UTI, Nocardia, Interfere w/ folic acid liver, excretion urine
X. Sulfonamide Sulfas mercaptopurine, megaloblastic anemia (use only soluble sulfas or sulmonamide
Shigella, respi, Pneumocystis carinii, typhoid (alt to synthesis, Compete with Acetylated metabolites insoluble
(methotrexate), dec. effect & inc. mixtures),
chloram), orchitis prostatitis, chlamydia (alt to tetra, PABA DHF static in urine renal damage,
nephrotox (cyclosporines), inc. phenytoin Caution in G6PD def, renal/liver dysfxn
erythro), Toxoplasma (sulfadiazine+pyrimethamine), crystalluria
tox., MetHb (prilocaine/lidocaine cream) Inj vehicle contains benzyl OH & Na metabisulfite
Falciparum (sulfadoxine+pyrimethamine/sulfalene+
Trimethoprim Inhibit DHF reductase w/ metabolites
pyrimethamin), dermatitis herpetiformis (sulfapyridine
Local: ulcerative colitis & ileitis (oral sulfasalazine), eye ADR:Rash, N, V, hemolysis in G6PD, megalo-
infxn (sulfacetamide Na ophthalmic ointment), Sequential inhibition of Concentration attained in blood & tissue Tablet, suspensin, cream, blastic anemia, granulo/thrombocytopenia,
Cotrimoxazole C
prevent colonization in burns (prefer: Ag sulfdiazine) folate pathway Cidal (SMX+TMP) is 20:1 eyedrops pseudomem colitis, kernicterus, SJS, CNS, renal
problems, ataxia, pancreatitis, hepatotox, fever
1. Short/Intermediate Axn --- sulfisoxazole (soluble), sulfadiazine (highly active, low solubility & pr binding, high bld & CSF levels), Sulfamethizole (soluble, rapid elim,
Rapid absorption & excretion
for UTI), Sulfamethoxazole (<sol, >bld levels, slower enteric absorption, liver metab & renal excr, combo w/ trimethoprim co-trimoxazole)
Rapid abs, slow exc, pr binding
2. Long Axn--- sulfadoxine (t1/2=7-9days), sufalenes (sulfametopyrazine), both used in combo w/ pyrimethamine
extensive tubular reabsoprtion
3. Lumina--- sulfsalazine (absorbed in its parent form as sulfapyridine, only for ulcerative colitis & regional enteritis), Sulfguanadine, Sulfasuxidine, Sulfathalidine Poor GI abs
4. Topical--- sulfacetamide Na (optha ointment), Silver sulfadiazine (sulfa acts as vehicle for Ag release that exert antibact effect in burn cases, lesser SE vs mafenide); Metabolic acidosis due to carbonic anhydrase
Mafenide acetate (topical tx for burns but >SE) inhibition (Mafenide acetate)
Irreversible binds 50s
XI. Miscellaneous
complex to form stable
1. Streptogramins
Cidal vs GP expt E. faecium, MRSA, multiple drug quinupristin-ribosome- IV, no CNS nor placenta, taken
macrolactone belong to
resistant GP dalfopristin 3o complx up by macrophages, liver metab, ADR: Infusion pain,arthralgia-myalgia syndrome,
macrolide-linco-streptogramin DI: cyclosporine blood conc.
Prevent resistance reserved for serious, life- CHON syn t1/2 1.5h but prolong PAE (upto rash, jaundice
Quinupristin threatening systemic infection w/ no alt therapy Inhibits chain elongation 10h)
Interfere w/ peptidyl
Dalfopristin
transferase
substrate for chromosomally
encoded multidrug efflux
effective against tetracycline resistant strains pump pf Proteus and Pseudo
poor oral, should be IV, good tx
For skin inf; intraabdominal inf., multidrug resistant intrinsic resistance to all
semisynthetic der. of minocycline; broad & intracellular penetration, wide
2. Glycylcycline - tigecycline nosocomial inf. (MRSA , extended spectrum tetra and tigecycline
spectrum VD, elim via biliary, very low
betalactamase producing GN, acinetobacter, VRSA, Not a substrate for efflux
conc in urine
enterococci, GP and GN anaerobes) pump expressing organisms
(GN, staph) & ribosomal
protection CHONs by GP
Hematologic (thrombocytopenia most common,
Cidal to Strep, static to other GP, vanco-resistant neutropenia) MAO inhibitor, serotonin syndrome
Rapid oral,metab in liver, excr
3. Oxazolidinones - Linezolid E.faecium, multiple drug resistant GP, nosocomial Inhibit early CHON syn DI: HPN (tyramine rich foods) C (fever, agitation, tremor, mental status changes),
urine, tablet, suspensin IV
pneumonia & skin infxn risk of severe hpn if with tyramine rich food,
pseudoephedrine, phenylproplanolamine
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Project ReadingDokument28 SeitenProject ReadingAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetrics Cardiovascular Diseases in PregnanacyDokument3 SeitenObstetrics Cardiovascular Diseases in PregnanacyAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Study of Business and The LikeDokument49 SeitenThe Study of Business and The LikeAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- THYROID GLAND: What Happens When Something Goes Wrong?: PIT UIDokument4 SeitenTHYROID GLAND: What Happens When Something Goes Wrong?: PIT UIAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetrics Pulmonary Diseases During Pregnancy: Clinical StagesDokument2 SeitenObstetrics Pulmonary Diseases During Pregnancy: Clinical StagesAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wheezing SmokeDokument3 SeitenWheezing SmokeAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nitafan v. Cir, 152 Scra 284 (1987)Dokument2 SeitenNitafan v. Cir, 152 Scra 284 (1987)Anonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- 228 B.M. 1625 Uy TimosaDokument2 Seiten228 B.M. 1625 Uy TimosaAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- US V Ah ChongDokument3 SeitenUS V Ah ChongAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 March Public ListedDokument4 Seiten2016 March Public ListedAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Governance and Finance Department: Issuer of Proprietary/Non-Proprietary Shares/CertificatesDokument3 SeitenCorporate Governance and Finance Department: Issuer of Proprietary/Non-Proprietary Shares/CertificatesAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- AngaraDokument4 SeitenAngaraAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instapay Ach Participants: Sender/Receiver Receiver OnlyDokument1 SeiteInstapay Ach Participants: Sender/Receiver Receiver OnlyAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- Persons Notes AgainDokument6 SeitenPersons Notes AgainAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sere Not A DigestDokument4 SeitenSere Not A DigestAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uptodate AppendicitisDokument28 SeitenUptodate AppendicitisAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- When Law Takes Effect: Chapter 6: Official GazetteDokument4 SeitenWhen Law Takes Effect: Chapter 6: Official GazetteAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- Your HEXACO-PI-R Results: Warning: Your Results Are Very Likely Invalid Due To Inattentive RespondingDokument6 SeitenYour HEXACO-PI-R Results: Warning: Your Results Are Very Likely Invalid Due To Inattentive RespondingMichael John BegalmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laz HernandDokument41 SeitenLaz HernandAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self Measures For Self-Esteem Rosenberg Self-EsteemDokument4 SeitenSelf Measures For Self-Esteem Rosenberg Self-Esteemapi-349021587Noch keine Bewertungen
- AngaraDokument4 SeitenAngaraAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Digest of The Com andDokument2 SeitenThe Digest of The Com andAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- Not A Car DigesDokument3 SeitenNot A Car DigesAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- Confidence IDokument4 SeitenConfidence IAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRIM LAW 1 - Reflection Paper On Heroes of Martial LawDokument1 SeiteCRIM LAW 1 - Reflection Paper On Heroes of Martial LawAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- TableDokument7 SeitenTableAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- SummaryDokument3 SeitenSummaryAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIGEST - People V Oanis (GR 4722) PDFDokument2 SeitenDIGEST - People V Oanis (GR 4722) PDFAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIGEST - UCPB v. Uy, G.R. No. 204039 PDFDokument2 SeitenDIGEST - UCPB v. Uy, G.R. No. 204039 PDFAnonymous HH3c17os50% (2)
- DIGEST - People V Oanis (GR 4722) PDFDokument2 SeitenDIGEST - People V Oanis (GR 4722) PDFAnonymous HH3c17osNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Amoxicillin Pir Jul2018Dokument62 SeitenAmoxicillin Pir Jul2018KirubakaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- EpiglotitisDokument12 SeitenEpiglotitisFecky Fihayatul IchsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control of Microbial GrowthDokument15 SeitenControl of Microbial GrowthAreeya SukchereanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peta Kuman 2022Dokument3 SeitenPeta Kuman 2022Musyafa'atun AnitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Pharma Tables) Reviewers Compiled PDFDokument115 Seiten(Pharma Tables) Reviewers Compiled PDFMaverick PascualNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccs InfoDokument13 SeitenCcs Info786ss100% (1)
- Antibacterial ActivityDokument31 SeitenAntibacterial ActivityRatnesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug List FinalsDokument2 SeitenDrug List FinalsMyzhel InumerableNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infective EndocarditisDokument18 SeitenInfective EndocarditisLee Foo WengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brand To Generic Cross ReferenceDokument50 SeitenBrand To Generic Cross Referencengochieu_909Noch keine Bewertungen
- AntibioticsDokument122 SeitenAntibioticsdentistry24100% (1)
- CHM4125 Antibiotics FINAL 2023 UnannotatedDokument106 SeitenCHM4125 Antibiotics FINAL 2023 Unannotatedalec.lafrance88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology MidtermDokument27 SeitenPharmacology Midtermnaomie manaliliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huizhe Wu, MD Mingyan Liu, MD Shuang Wang, MD Wanyu Feng, MD, PHD Weifan Yao, Bs Haishan Zhao, Bs and Minjie Wei, MD, PHDDokument10 SeitenHuizhe Wu, MD Mingyan Liu, MD Shuang Wang, MD Wanyu Feng, MD, PHD Weifan Yao, Bs Haishan Zhao, Bs and Minjie Wei, MD, PHDDyva VanillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioanalyse - Zone Table (Expanded)Dokument16 SeitenBioanalyse - Zone Table (Expanded)Geoemilia180% (5)
- PEDIA - Drug Study & NCPDokument24 SeitenPEDIA - Drug Study & NCPCzarina Mae Lomboy100% (1)
- Penicillins - KatzungDokument6 SeitenPenicillins - KatzungKarl CNoch keine Bewertungen
- AntibioticsDokument9 SeitenAntibiotics7aith22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - AmpicillinDokument2 SeitenDrug Study - Ampicillinliza sianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ampicillin Vs - CarbenicillinDokument2 SeitenAmpicillin Vs - Carbenicillinbeletristicliteratur100% (2)
- Drug AmpicillinDokument2 SeitenDrug AmpicillinRenz Ivan FuntilonNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC Great Lakes SlidesDokument26 SeitenMC Great Lakes Slidesapi-666654042Noch keine Bewertungen
- AntibioticDokument84 SeitenAntibioticDr. Kalavati PrajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transient Tachypnea of The NewbornDokument14 SeitenTransient Tachypnea of The NewbornMarielaTessyGonzalesParedesNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Dental Pharmacology TherapeuticsDokument18 SeitenGeneral Dental Pharmacology Therapeutics74 Soham MajumdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sil GramDokument8 SeitenSil GramJacqueline SweetNoch keine Bewertungen
- PyomeningitisDokument54 SeitenPyomeningitisRiya BagdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paediatric Formulary16 and Final PDFDokument14 SeitenPaediatric Formulary16 and Final PDFJenny WoodruffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary For Antibiotic For USMLE Exam - USMLE MATERIALS - Updated USMLE Study DataDokument5 SeitenSummary For Antibiotic For USMLE Exam - USMLE MATERIALS - Updated USMLE Study Dataomy yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotics That Are Used As ProdrugDokument48 SeitenAntibiotics That Are Used As ProdrugApurba Sarker Apu100% (1)