Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
58
Hochgeladen von
Seyyed Amir MohmmadiCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
58
Hochgeladen von
Seyyed Amir MohmmadiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SCADA AND TELEMETRY IN GAS TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS
Gerry Browne
Honeywell
8440 Westglen Ave., Houston, TX 77063
INTRODUCTION the primary functions such as pipeline modeling, batch
tracking and leak detection are handled by advanced
A common requirement for gas transmission pipeline application software.
systems is to provide a pipeline control system to
remotely monitor and operate the pipeline from a central FIELD INSTRUMENTS, ANALYZERS AND
location. This paper presents an overview of the main ACTUATORS
components of a pipeline control system:
Field instruments and analyzers provide the means to
1. Field Instruments, Analyzers and Actuators measure and convert a measured variable into a signal
2. Controllers that can be understood by a digital controller.
3. Telecommunications
4. SCADA systems Analog instruments typically measure temperature, flow
5. Advanced Pipeline Applications rate and pressure. Digital instruments typically measure
On/Off signals such as a tank high level limit switch, motor
SCADA is an acronym for Supervisory Control and Data running, etc. Pulse signals are generated by electronic
Acquisition. A Supervisory Control system is a system pulses or contact closure signals with frequency
that has the ability and intelligence to perform controls proportional to the measured variable. Pulses are used
with minimal supervision and a Data Acquisition system to represent an incremental measurement such as flow
has the ability to gather data. They are commonly used rate.
in the gas, oil, electric and water transmission and
distribution industries where facilities are spread out over Actuators or output devices can be driven by three types
a large area. of output signal from a controller. Analog actuators use
an analog output signal to control variables such as flow
Telemetry can be defined as the process of where data rate, pressure, etc. Digital outputs are useful for absolute
from a measured device is being transmitted to a distant actions such as opening a valve, launching a pig, etc.
location by any variety of media, e.g., radio, telephone, Pulse outputs are often used as hand-off signals to other
etc. controllers.
PIPELINE CONTROL SYSTEMS Gas and BTU analyzers are complex instruments that
determine gas components.
The primary functions of a complete pipeline control
system include data acquisition, reporting, operator CONTROLLERS (PLC, RTU, FLOW COMPUTER)
control, pump/compressor control, valve control,
nominations, scheduling, custody transfer, imbalance Controllers are devices designed to be placed close to
measurement, billing, pipeline modeling, batch tracking the sensors and actuators. Nearly all modern controllers
(for liquid pipelines only), pump/compressor optimization are microprocessor based with a high level data
and leak detection. Nominations are monthly (or daily) communications interface for connection back to a
bids by customers for available capacity. Imbalances SCADA system and low level connections for field
occur when a customer of the pipeline delivers or devices such as transmitters, switches, actuators, etc.
receives an amount that is different from the nomination. Today most low level connections are either voltage or
current based, but the trend is towards smart sensors
The key physical variables measured at many locations and actuators that communicate using serial data busses.
by field instruments include pressure, temperature, BTU
content, gas composition, flow rate, pump/compressor The function of the controller is to:
status and valve status. Due to the remote location of
many measurement points, transmitters and controllers Periodically read the input signals and convert
can be solar powered with battery back-up if into an internal numeric format
conventional power is not available. Control the output signals to the correct value
Perform calculations and algorithms
Communications can be by leased line, fiber optic line, Send and receive data from an external
radio, microwave, satellite or any combination. Some of computing system
2001 PROCEEDINGS PAGE 275
AMERICAN SCHOOL OF GAS MEASUREMENT TECHNOLOGY
Three types of controllers are used on pipeline systems: New construction vs retrofit It is easy to lay fiber optic
PLCs, RTUs and Flow Computers. PLCs are used at sites lines while laying new pipe.
where conventional power is available (i.e., 24 volt dc or
110 volt ac); RTUs are found in remote locations where Availability of leased lines and public telephone lines.
solar power is used (i.e., 12 volt dc and less than 2 watts);
and Flow Computers are used specifically for flow Availability of radio frequencies for licensing Radio
measurement. communications fall into frequency ranges of 360-512
mHz and 928-960 mHz with bandwiths of 12.5 to 25
PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS (PLC) kHz. Speeds range from 9.6 to 384 kbps. The time
required to obtain a license must also be considered.
Typically PLCs are appropriate in situations where solar
power is not required and difficult communications Availability and cost of satellite space for long distance.
requirements are not an issue. PLCs are widely used in
all control business segments and are a low cost versatile Terrain This governs the height and location of radio
solution. and microwave towers.
RTU CONTROLLERS Requirements for voice and/or video communications in
addition to data.
An RTU is required at remote sites where conventional
power is not available, difficult communications Capital cost vs operating cost.
requirements exist or industry specific algorithms and
processing are required. SCADA SYSTEM
Most RTUs are very small compared with PLCs and are Pipelines require a control system which is very different
designed to handle a small number of I/O, mount in harsh from other types of control systems. A SCADA system
environments and be quick and simple to engineer. is designed for low speed, limited bandwidth
communications over long distances while a typical DCS
A large pipeline SCADA system can communicate with system is designed for high speed, unlimited bandwidth
thousands of RTUs. communications inside a plant. In a SCADA system, data
is transferred in small packets. Constant data such as
FLOW COMPUTERS controller ID data are stored in the central database, not
in the field controller. Operating data is stored in
Flow computers are similar to RTUs, being designed to controllers for intermittent polling and communications
handle a small number of I/O and mount in difficult are minimized by designing controllers to report by
environments. The main differentiation with RTUs is that exception for a change of status. Communication links
flow computers are purpose built for flow measurement must be verified with each report and the sequence of
and control and have a large number of built in algorithms events is often recorded in the controllers so that history
and applications specific to flow measurement and can be re-established if communication links are
control such as AGA flow calculations, custody transfer, interrupted.
meter proving, etc.
The Data Acquisition part of the SCADA system is
TELECOMMUNICATIONS responsible for collecting data from the field and storing
in a database where it is available to other functions on
The telecommunications system is a critical component the system. Each item of data is generally called a point
of pipeline control systems. There are several common or a tag and SCADA systems can be very large, collecting
methods including leased lines, dial-up public service data from hundreds of thousands of points many times
telephone (PSTN) lines, fiber optic lines, satellite, each day. A standard requirement of pipeline control
microwave and radio. For new pipeline construction, fiber systems is the collection of large amounts of historical
optic lines, leased lines and satellite systems are most information about each point.
common. Radios are commonly used for gathering
systems in onshore oil and gas production areas. The Human Machine Interface (HMI) is responsible for
Occasionally, a system involves combinations of two or much of the Supervisory Control part of the SCADA
more telecommunication methods. system. This is where an operator can call up graphic
displays showing the current values of the point database
A number of design considerations go into the selection and send changes to field devices.
of telecommunications methods:
ADVANCED PIPELINE APPLICATIONS
Short haul vs long haul Radios can communicate about
25 miles. Beyond that, repeaters are needed. A large number of applications can be run on a SCADA
system to provide the pipeline owner with higher levels
of optimization, safety and efficiency than possible with
human control.
PAGE 276 2001 PROCEEDINGS
AMERICAN SCHOOL OF GAS MEASUREMENT TECHNOLOGY
Some examples are; Leak Detection, Shut-in Leak Dual/Redundant System, Service Modem, Condensate
Detection, Leak Location, Batch Scheduling, Batch Detection/Location, Multi-Phase Modeling, GIS System
Tracking, Composition Tracking, DRA Tracking (Drag (Geographical Information System).
Reducing Agent), Product Distribution, Inventory
Analysis, Allocation, Nomination, Pig Scheduling & ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Tracking, Training Simulator, Look-Ahead, Survival Time,
Predictive Modeling, Pump Optimization (among Joe L. Martinez
stations), Compressor Optimization (among stations), Williams Gas Pipeline Transco
Scenario Study, Pipeline Efficiency, Forecast of Demand,
2001 PROCEEDINGS PAGE 277
AMERICAN SCHOOL OF GAS MEASUREMENT TECHNOLOGY
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- 04Dokument146 Seiten04shipset100% (1)
- Power Command 3201 Generator SetDokument10 SeitenPower Command 3201 Generator Setoscar eduardo castro yate100% (1)
- Belimo Smoke ControlDokument35 SeitenBelimo Smoke ControlNenad Mutavdzic100% (1)
- Control Strategies For Dynamic Systems - John Lumkes PDFDokument598 SeitenControl Strategies For Dynamic Systems - John Lumkes PDFMScMtepele100% (2)
- Basic Control Theory PDFDokument74 SeitenBasic Control Theory PDFJoshuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masoneilan Positioner SVI II AP Instruc ManDokument180 SeitenMasoneilan Positioner SVI II AP Instruc ManCecep AtmegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCP Corporate BrochureDokument16 SeitenRCP Corporate BrochureBiswadeep Ghosh100% (1)
- Introduction To PID ControlDokument6 SeitenIntroduction To PID ControlIonescu ViorelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dm752 Iv10 62 Access ControlDokument49 SeitenDm752 Iv10 62 Access ControlSeyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Warrick Conductivity Level Controls - Complete - En.esDokument33 SeitenWarrick Conductivity Level Controls - Complete - En.esLuigui Flores Hernandez100% (1)
- SLD For Shuiba LightingDokument1 SeiteSLD For Shuiba LightingSeyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lake Ontario: Vollum Rd. Pike RDDokument2 SeitenLake Ontario: Vollum Rd. Pike RDSeyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1MW - On Grid Plant Tulip1Dokument2 Seiten1MW - On Grid Plant Tulip1Seyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preliminary - Not For Construction: Apex Clean Energy, Inc 310 4th St. NE, Suite 200 Charlottesville, VA 22902Dokument1 SeitePreliminary - Not For Construction: Apex Clean Energy, Inc 310 4th St. NE, Suite 200 Charlottesville, VA 22902Seyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wind Farm InspectionDokument3 SeitenWind Farm InspectionSeyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- L-530-Lighting Layout For PIG Launcher at MAB RefineryDokument3 SeitenL-530-Lighting Layout For PIG Launcher at MAB RefinerySeyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wind Power Geoplanner™ Off-Air TV Analysis: Galloo Island Wind ProjectDokument11 SeitenWind Power Geoplanner™ Off-Air TV Analysis: Galloo Island Wind ProjectSeyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secretary Dps Ny - Go: The Town of Henderson Is An Equal Opportunity Provider and EmployerDokument2 SeitenSecretary Dps Ny - Go: The Town of Henderson Is An Equal Opportunity Provider and EmployerSeyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nor Tri D18089 FD101 - 000Dokument1 SeiteNor Tri D18089 FD101 - 000Seyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- {45B6005D-F748-4A95-9255-B75B9B3A50DC}Dokument1 Seite{45B6005D-F748-4A95-9255-B75B9B3A50DC}Seyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- {E4A2ED9D-5852-477C-8636-019A2FB7822F}Dokument6 Seiten{E4A2ED9D-5852-477C-8636-019A2FB7822F}Seyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
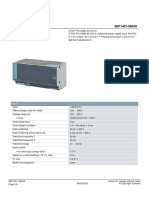
- Data Sheet 6EP1457-3BA00: InputDokument4 SeitenData Sheet 6EP1457-3BA00: InputSeyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wind Power Geoplanner™ Am and FM Radio Report: Galloo Island Wind ProjectDokument6 SeitenWind Power Geoplanner™ Am and FM Radio Report: Galloo Island Wind ProjectSeyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name & Address Requested Copies: Secretary@dps - Ny.govDokument3 SeitenName & Address Requested Copies: Secretary@dps - Ny.govSeyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maharashtra State Electricity Transmission Co - LTD EHV (O&M) Circle, NasikDokument23 SeitenMaharashtra State Electricity Transmission Co - LTD EHV (O&M) Circle, NasikSeyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Galloo Island Wind, LLC: Project Execution PlanDokument25 SeitenGalloo Island Wind, LLC: Project Execution PlanSeyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Galloo Island Wind Energy Facility: Case No. 15-F-0327Dokument8 SeitenGalloo Island Wind Energy Facility: Case No. 15-F-0327Seyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Plan: The Start of The Joint Venture Between Metal Systems Co. & Solar Optimo CoDokument15 SeitenWork Plan: The Start of The Joint Venture Between Metal Systems Co. & Solar Optimo CoSeyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- For Continuity Refer To DWG # E1801-As-00-Ec-00113: El Salam Road El Salam RoadDokument1 SeiteFor Continuity Refer To DWG # E1801-As-00-Ec-00113: El Salam Road El Salam RoadSeyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS vs. Solar Optimo BudgetDokument1 SeiteMS vs. Solar Optimo BudgetSeyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Price List - September - 2013 (E-Copy)Dokument57 SeitenPrice List - September - 2013 (E-Copy)Seyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kidwind WindFarmSitingDokument12 SeitenKidwind WindFarmSitingSeyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asset Tracking in Hazardous Areas: Technical Datasheet Application NoteDokument2 SeitenAsset Tracking in Hazardous Areas: Technical Datasheet Application NoteSeyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Galloo Island Wind Energy Facility: Case No. 15-F-0327Dokument8 SeitenGalloo Island Wind Energy Facility: Case No. 15-F-0327Seyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- External Grid: SenvionDokument6 SeitenExternal Grid: SenvionSeyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AVL Internal Manufacturer 191097Dokument285 SeitenAVL Internal Manufacturer 191097Seyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zenitel - Vingtor-Stentofon Hotline Station - 1007110000 PDFDokument2 SeitenZenitel - Vingtor-Stentofon Hotline Station - 1007110000 PDFSeyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Specifications of Dental Chair & X-Ray Unit Annexure-IIDokument2 SeitenTechnical Specifications of Dental Chair & X-Ray Unit Annexure-IISeyyed Amir MohmmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Access Control Terminal Installation Guide PDFDokument2 SeitenAccess Control Terminal Installation Guide PDFSoporte TecnicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment PressureDokument6 SeitenAssignment PressureNadia RefaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operators Manual For The Control Techniques PLC Iii Cut-to-Length Control SystemDokument79 SeitenOperators Manual For The Control Techniques PLC Iii Cut-to-Length Control Systemdorin serbanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Strategies For Water Level Control of Two Tank System 11 AugDokument7 SeitenControl Strategies For Water Level Control of Two Tank System 11 AugGJESRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1Dokument19 SeitenLecture 1Mahmoud TorkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- FuzzyDokument13 SeitenFuzzySaurabh Rajput33% (3)
- Osmania University B.E. Examinations Time Table 2011-2012 2012Dokument8 SeitenOsmania University B.E. Examinations Time Table 2011-2012 2012MahabubnagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual For D1750 PDFDokument372 SeitenManual For D1750 PDFsatyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robotic ArmDokument38 SeitenRobotic ArmCristina Rhain WinterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hoja Tecnica QJ341Dokument2 SeitenHoja Tecnica QJ341Guillermo PaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Three Term ControlDokument12 SeitenThree Term Controlpop3alyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control System Based On PLC For WindingDokument4 SeitenControl System Based On PLC For WindinghanzrizNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 On - Off Control PDFDokument36 Seiten2.1 On - Off Control PDFOscar Lob GioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mcs BrochuresDokument8 SeitenMcs BrochuresMohsen PeykaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- PID ReportDokument38 SeitenPID ReportNishiya Vijayan100% (1)
- Resolver Vs Encoder PDFDokument2 SeitenResolver Vs Encoder PDFgksamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Introduction MechatronicsDokument77 Seiten1 Introduction MechatronicsJeewan AtwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aircraft Flight Control System ModellingDokument10 SeitenAircraft Flight Control System ModellingMahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Loop 11Dokument17 SeitenControl Loop 11nmulyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PowerWizard 1-0 (GB)Dokument2 SeitenPowerWizard 1-0 (GB)kagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distributed Control System & Scada: Chapter-3Dokument33 SeitenDistributed Control System & Scada: Chapter-3LJIETSEM7ICNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control System - المنهج المقرر PDFDokument122 SeitenControl System - المنهج المقرر PDFTariq ZeyadNoch keine Bewertungen