Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Priority Problem For Severe Hypertension: Nursing Care Plan
Hochgeladen von
Deanne Munar0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
159 Ansichten3 SeitenThe nursing care plan addresses a priority problem of severe hypertension manifested by activity intolerance, abnormal heart rate and blood pressure responses to activity, and exertional discomfort or dyspnea. The goal is for the patient to be able to independently participate in necessary activities after 8 hours, with measurable but tolerable increases in vital signs and decreases in symptoms. Nursing interventions include instructing the patient in energy-conserving techniques and encouraging progressive activity and self-care as tolerated, providing assistance only as needed. The rationale is that these approaches help equalize oxygen supply and demand to prevent overexertion.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
34759820 Activity Intolerance
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe nursing care plan addresses a priority problem of severe hypertension manifested by activity intolerance, abnormal heart rate and blood pressure responses to activity, and exertional discomfort or dyspnea. The goal is for the patient to be able to independently participate in necessary activities after 8 hours, with measurable but tolerable increases in vital signs and decreases in symptoms. Nursing interventions include instructing the patient in energy-conserving techniques and encouraging progressive activity and self-care as tolerated, providing assistance only as needed. The rationale is that these approaches help equalize oxygen supply and demand to prevent overexertion.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
159 Ansichten3 SeitenPriority Problem For Severe Hypertension: Nursing Care Plan
Hochgeladen von
Deanne MunarThe nursing care plan addresses a priority problem of severe hypertension manifested by activity intolerance, abnormal heart rate and blood pressure responses to activity, and exertional discomfort or dyspnea. The goal is for the patient to be able to independently participate in necessary activities after 8 hours, with measurable but tolerable increases in vital signs and decreases in symptoms. Nursing interventions include instructing the patient in energy-conserving techniques and encouraging progressive activity and self-care as tolerated, providing assistance only as needed. The rationale is that these approaches help equalize oxygen supply and demand to prevent overexertion.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
DE RAMOS, Karen R.
07-12-10
BSN III –A1 / Group CA1
MCP – OR
Ma’am Nenita Orobia
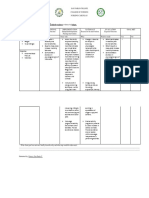
Nursing Care Plan
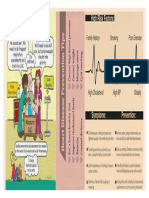
Priority Problem for severe Hypertension
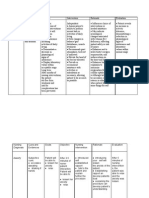
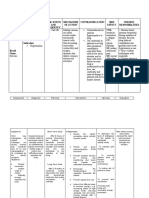
Cues Nursing Rationale Goals and Nursing Rationale Evaluation
Diagnosis Objectives Intervention
Subjective: Activity Insufficient After 8 hours Independent: After 8 hours
… as verbalized intolerance physiological or of nursing Assess the The stated of nursing
by the patient. related to psychological intervention, client’s parameters are intervention,
generalized energy to the patient response to helpful in assessing the patient
Objective: weakness; endure or will be able to activity, responses to the was able to
verbal report imbalance complete participate in noting pulse stress of activity participate in
of fatigue between required or necessary/ rate more and, if present, are necessary/
and oxygen desired daily desired than 20 beats/ indicators of desired
weakness supply and activities. activities; minute faster overexertion. activities;
abnormal demand as report a than resting report a
heart rate or evidenced measurable rate; marked measurable
blood by verbal increase in increase blood increase in
pressure report of activity pressure activity
response to fatigue and intolerance; during or after intolerance;
activity weakness; demonstrate activity; demonstrate
exertional abnormal a decrease in dyspnea or a decrease in
discomfort heart rate Reference: physiologic chest pain; physiologic
or dyspnea or blood page 70 signs of excessive signs of
ECG changes pressure Nurse’s Pocket intolerance. fatigue and intolerance.
reflecting response to Guide weakness;
ischemia activity; Diagnoses, diaphoresis;
exertional prioritized dizziness or Energy-saving
dysrhythmia
discomfort interventions syncope. techniques reduce
s
or dyspnea; and rationale the energy
ECG 11th edition by Instruct client expenditure, thereby
changes Doenges, in energy- assisting in
reflecting Moorhouse and conserving equalization of
ischemia; Murr techniques; oxygen supply and
dysrhythmi eg., using demand.
as chair when
showering,
sitting to
brush teeth or
combing hair,
carrying out
activities in Gradual activity
slower pace. progression prevents
a sudden increase in
cardiac workload.
Encourage Providing assistance
progressive only as needed
activity/ self- encourages
care when independence in
tolerated. performing
Provide activities.
assistance as
needed.
Reference:
Page 41
Nursing Care Plan
Guidelines for
individualizing client
care across the life span
Edition 7 by Doenges,
Moorhouse and Murr
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chapter 35Dokument9 SeitenChapter 35Jyothis James100% (2)
- Cues: Subjective/ Objective Background of The Disease Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenCues: Subjective/ Objective Background of The Disease Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMaria Margaret Macasaet0% (1)
- Tugas Efn II Unit 13Dokument4 SeitenTugas Efn II Unit 13FransiscaapNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For CHFDokument11 SeitenNCP For CHFqingwen100% (5)
- Case Study NCPDokument6 SeitenCase Study NCPEarl Joseph DezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For RS-HF (Cor PulmonaleDokument5 SeitenNCP For RS-HF (Cor PulmonaleMika Saldaña100% (1)
- Prioritized Nursing For Problem For Rheumatic Fever Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention RationaleDokument3 SeitenPrioritized Nursing For Problem For Rheumatic Fever Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention RationaleJoshua VillarbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Volume Excess Related To Decrease Glomerular Filtration Rate and Sodium RetentionDokument6 SeitenFluid Volume Excess Related To Decrease Glomerular Filtration Rate and Sodium RetentionKristel Abe100% (1)
- NCP For Activity in ToleranceDokument5 SeitenNCP For Activity in Tolerancekaycee_periaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Management For Heart Failure: Weigh As NeededDokument1 SeiteNursing Management For Heart Failure: Weigh As NeededPRINCE JOSHUA ANGELESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan HYPERTENSIONDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan HYPERTENSIONJasmin T. RegaspiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabije, Arvie Jayselle PDokument6 SeitenTabije, Arvie Jayselle PJayselle ArvieNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For Activity IntoleranceDokument2 SeitenNCP For Activity IntoleranceMiguel LeybaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For Activity IntoleranceDokument2 SeitenRisk For Activity IntoleranceBlessie FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estoya, Gen Paulo C. - Heart Failure NCP - NCM 112 LecDokument4 SeitenEstoya, Gen Paulo C. - Heart Failure NCP - NCM 112 LecGen Paulo EstoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: HypertensionDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan: HypertensionJasmin T. RegaspiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP HTNDokument2 SeitenNCP HTNLyndon SayongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estoya, Gen Paulo C. - HTN NCP - NCM 112 LecDokument2 SeitenEstoya, Gen Paulo C. - HTN NCP - NCM 112 LecGen Paulo EstoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlansDokument6 SeitenNursing Care PlansJhessa Curie PitaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDokument5 SeitenPregnancy Induced Hypertension Nursing Care Planjohncarlo ramosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Darwin Jay Sang An BSN 1aDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan Darwin Jay Sang An BSN 1aHaroldJohnCabalgadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity#2: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDokument4 SeitenActivity#2: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentCLOYD JHON OBISPONoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentAdhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP 2Dokument2 SeitenNCP 2hsiria100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Subjective: O Short Term: Short TermDokument3 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Subjective: O Short Term: Short TermRaidis PangilinanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Acute Lymphoblastic LeukemiaDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Acute Lymphoblastic LeukemiabluennaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Pathophysiologic Basis/Rationale Desired Outcome Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Pathophysiologic Basis/Rationale Desired Outcome Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationGILIANNE MARIE JIMENEANoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity IntoleranceDokument3 SeitenActivity IntoleranceRaidis PangilinanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationRichmond LacadenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identify Non-Modifiable and Modifiable Risk Factors For HypertensionDokument3 SeitenIdentify Non-Modifiable and Modifiable Risk Factors For HypertensionwokorowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument6 SeitenNursing Care PlanperezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument10 SeitenNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationPantaleon PacisNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP GeriaDokument2 SeitenNCP GeriaEitan LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alzheimers DiseaseDokument2 SeitenAlzheimers Diseasekarl de guzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NURSING CARE PLAN (For Case Study)Dokument2 SeitenNURSING CARE PLAN (For Case Study)Kathleen Martinez100% (1)
- Cues Objective S Interventions Rationale Evaluatio NDokument2 SeitenCues Objective S Interventions Rationale Evaluatio NJoehoney BarreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Intolerance DeliveryDokument3 SeitenActivity Intolerance Deliveryjunex123100% (2)
- Identification DataDokument22 SeitenIdentification DataRUCHI TMU StudentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Family Nursing Care PlanDokument7 SeitenFamily Nursing Care PlanRebecca Caga SarmientoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For Anemia Activity IntoleranceDokument8 SeitenNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For Anemia Activity IntoleranceJinaan MahmudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prioritization of Problems Rank Problem Identified: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDokument5 SeitenPrioritization of Problems Rank Problem Identified: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesTom CuencaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Requirement - Caadlawon, Ariane KateDokument5 SeitenNCP Requirement - Caadlawon, Ariane KateAngel KateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Actual Nursing Care Plan #1: Deficient Fluid VolumeDokument7 SeitenActual Nursing Care Plan #1: Deficient Fluid VolumeAubrey SungaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 8 NCP (Multiple Sclerosis)Dokument2 SeitenCase 8 NCP (Multiple Sclerosis)je-ann catedralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abad, Izhiel C.: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenAbad, Izhiel C.: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationIzhiel AbadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disturbed SleepDokument3 SeitenDisturbed SleepNicole MapiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marjorie ncp8Dokument2 SeitenMarjorie ncp8Jovel CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP: Labor Stage 1 Transition Phase (Deceleration)Dokument7 SeitenNCP: Labor Stage 1 Transition Phase (Deceleration)JavieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7Dokument2 SeitenIneffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7dana100% (4)
- NCP DMDokument6 SeitenNCP DMstara123Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Post OpDokument2 SeitenNCP Post OpEyanah Delos ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypertensionDokument3 SeitenHypertensionkarl de guzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Activity Intolerance (HTN Crisis)Dokument3 SeitenNCP Activity Intolerance (HTN Crisis)Jenny AjocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDokument4 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentMina RacadioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relapse Prevention Counseling Workbook: A Step-by-Step Guide to Sustainable Recovery: Holistic approaches to recovery and relapse preventionVon EverandRelapse Prevention Counseling Workbook: A Step-by-Step Guide to Sustainable Recovery: Holistic approaches to recovery and relapse preventionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polarity Therapy-How RePolarizing Your Body Can Heal YouVon EverandPolarity Therapy-How RePolarizing Your Body Can Heal YouBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Exposure Therapy for Eating Disorders: A Comprehensive Guide to Exposure Therapy and Resilience-Building for Eating DisordersVon EverandExposure Therapy for Eating Disorders: A Comprehensive Guide to Exposure Therapy and Resilience-Building for Eating DisordersNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Simple Guide to Parkinson's Disease and Related Brain ConditionsVon EverandA Simple Guide to Parkinson's Disease and Related Brain ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cerebrovascular Accident Demystified: Doctor’s Secret GuideVon EverandCerebrovascular Accident Demystified: Doctor’s Secret GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetic Neuropathy Demystified: Doctor's Secret GuideVon EverandDiabetic Neuropathy Demystified: Doctor's Secret GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brosure Prosim3Dokument6 SeitenBrosure Prosim3priyanka choudhryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conconi Workbook-2Dokument2 SeitenConconi Workbook-2api-361464531Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH161 Lecture 9-10 - GIKIDokument42 SeitenCH161 Lecture 9-10 - GIKIHabny ShaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNS PDFDokument412 SeitenCNS PDFSami Juggy G100% (1)
- Laporan Kasus Pneumonia Kelompok 2 FixDokument71 SeitenLaporan Kasus Pneumonia Kelompok 2 Fixrivha ramadhantyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bobath For Musculoskeletal Problem Palembang Online 2020Dokument128 SeitenBobath For Musculoskeletal Problem Palembang Online 2020fisioterapi rsph100% (1)
- Anatomy - Physiology (Chapter 12 - Heart)Dokument20 SeitenAnatomy - Physiology (Chapter 12 - Heart)Avi ZychNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pex 05 07Dokument4 SeitenPex 05 07Jila HafiziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body Temperature: Physiology DepartmentDokument17 SeitenBody Temperature: Physiology DepartmentMaab AlrsheedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids and Electrolytes 3Dokument8 SeitenFluids and Electrolytes 3Potchiee Pfizer100% (1)
- Puneet Kumar, Pran Kishore Deb - Frontiers in Pharmacology of Neurotransmitters-Springer Singapore - Springer (2020)Dokument729 SeitenPuneet Kumar, Pran Kishore Deb - Frontiers in Pharmacology of Neurotransmitters-Springer Singapore - Springer (2020)David S. ValverdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 ECG Strips On The NCLEXDokument1 Seite9 ECG Strips On The NCLEXAlther LorenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical ECG RoundsDokument2 SeitenClinical ECG RoundsKai Siang ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NeurotransmittersDokument39 SeitenNeurotransmitterspreetie87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of PainDokument65 SeitenPhysiology of PainatefmoussaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pain and Pain Pathways FinalDokument56 SeitenPain and Pain Pathways FinalAnji SatsangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Project 2Dokument9 SeitenStudent Project 2Santi pridayantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - Scheme - Form - 2 - (1) Schemes 2021Dokument12 SeitenBiology - Scheme - Form - 2 - (1) Schemes 2021Changamkia WorksNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1622-Article Text-10360-3-10-20220705Dokument5 Seiten1622-Article Text-10360-3-10-20220705eka maulinda almanarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lee, Thonylet E. Mabinta, Dianne Melad, Maria FeDokument25 SeitenLee, Thonylet E. Mabinta, Dianne Melad, Maria FeShivaveerakumar S. Chandrikimath100% (1)
- Emergency Medicine - Med RevisionsDokument69 SeitenEmergency Medicine - Med RevisionsswamysamsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing - CS - Take A Manual Blood PressureDokument1 SeiteNursing - CS - Take A Manual Blood PressureJanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Color Atlas of Forensic Pathology by Dinesh Fernando and Sulochana Wijetunge. Vol IDokument199 SeitenColor Atlas of Forensic Pathology by Dinesh Fernando and Sulochana Wijetunge. Vol IGorka AguirreNoch keine Bewertungen
- GangreneDokument44 SeitenGangreneAkshat SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phases of The Cardiac Action PotentialDokument2 SeitenPhases of The Cardiac Action Potentialkowaikowar50% (2)
- Hemodynamic Monitoring in Critically Ill PatientsDokument46 SeitenHemodynamic Monitoring in Critically Ill PatientsDipo Mas SuyudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Globus Electrostimulation User Guide PDFDokument88 SeitenGlobus Electrostimulation User Guide PDFFranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 01 Introduction To PerceptionDokument48 SeitenChapter 01 Introduction To PerceptionSimrat WNoch keine Bewertungen