Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Embedded Systems: Martin Schoeberl Mschoebe@mail - Tuwien.ac - at
Hochgeladen von
DhirenKumarGoleyOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Embedded Systems: Martin Schoeberl Mschoebe@mail - Tuwien.ac - at
Hochgeladen von
DhirenKumarGoleyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Introduction
Our Example System
Summary
Embedded Systems
Martin Schoeberl
mschoebe@mail.tuwien.ac.at
Very Small Information Systems, 2006
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Introduction
Our Example System
Summary
Outline
1 Introduction
Definition and Characteristics
Interface to the World
Resource Constraints
Real-Time Systems
2 Our Example System
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Definition and Characteristics
Introduction
Interface to the World
Our Example System
Resource Constraints
Summary
Real-Time Systems
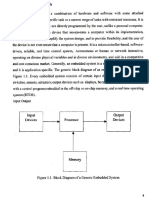
What Are Embedded Systems?
Definition
An embedded system is a computer systems that is part of a
larger system.
Example
Washing machine
Car engine control
Mobile phone
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Definition and Characteristics
Introduction
Interface to the World
Our Example System
Resource Constraints
Summary
Real-Time Systems
What Are Embedded Systems?
Definition
An embedded system is a computer systems that is part of a
larger system.
Example
Washing machine
Car engine control
Mobile phone
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Definition and Characteristics
Introduction
Interface to the World
Our Example System
Resource Constraints
Summary
Real-Time Systems
ES Characteristics
Often mass products
98% of the processors are in ES
Sometimes very specialized systems
No or minimal user interface
Resource constraints
Must usually fulfill strict timing
Usually runs forever (no reboot)
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Definition and Characteristics
Introduction
Interface to the World
Our Example System
Resource Constraints
Summary
Real-Time Systems
ES Characteristics
Often mass products
98% of the processors are in ES
Sometimes very specialized systems
No or minimal user interface
Resource constraints
Must usually fulfill strict timing
Usually runs forever (no reboot)
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Definition and Characteristics
Introduction
Interface to the World
Our Example System
Resource Constraints
Summary
Real-Time Systems
ES Characteristics
Often mass products
98% of the processors are in ES
Sometimes very specialized systems
No or minimal user interface
Resource constraints
Must usually fulfill strict timing
Usually runs forever (no reboot)
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Definition and Characteristics
Introduction
Interface to the World
Our Example System
Resource Constraints
Summary
Real-Time Systems
ES Characteristics
Often mass products
98% of the processors are in ES
Sometimes very specialized systems
No or minimal user interface
Resource constraints
Must usually fulfill strict timing
Usually runs forever (no reboot)
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Definition and Characteristics
Introduction
Interface to the World
Our Example System
Resource Constraints
Summary
Real-Time Systems
ES Characteristics
Often mass products
98% of the processors are in ES
Sometimes very specialized systems
No or minimal user interface
Resource constraints
Must usually fulfill strict timing
Usually runs forever (no reboot)
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Definition and Characteristics
Introduction
Interface to the World
Our Example System
Resource Constraints
Summary
Real-Time Systems
Interface to the World
Minimal user interface
Buttons, lamps (e.g. elevator)
Small display
Sensors
Switch (0/1)
Temperature
Camera
Actuators
Relay (On/Off)
Servo motor
Communication
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Definition and Characteristics
Introduction
Interface to the World
Our Example System
Resource Constraints
Summary
Real-Time Systems
Interface to the World
Minimal user interface
Buttons, lamps (e.g. elevator)
Small display
Sensors
Switch (0/1)
Temperature
Camera
Actuators
Relay (On/Off)
Servo motor
Communication
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Definition and Characteristics
Introduction
Interface to the World
Our Example System
Resource Constraints
Summary
Real-Time Systems
Interface to the World
Minimal user interface
Buttons, lamps (e.g. elevator)
Small display
Sensors
Switch (0/1)
Temperature
Camera
Actuators
Relay (On/Off)
Servo motor
Communication
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Definition and Characteristics
Introduction
Interface to the World
Our Example System
Resource Constraints
Summary
Real-Time Systems
Interface to the World
Minimal user interface
Buttons, lamps (e.g. elevator)
Small display
Sensors
Switch (0/1)
Temperature
Camera
Actuators
Relay (On/Off)
Servo motor
Communication
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Definition and Characteristics
Introduction
Interface to the World
Our Example System
Resource Constraints
Summary
Real-Time Systems
Resource Constraints
Systems have to be cheap
Memory
few 100 Bytes to few MB RAM
few KB to MB ROM
Speed
few MHz up to a few 100MHz
Energy consumption
Communication
Serial line
Special networks (Fieldbus)
A lot of legacy systems
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Definition and Characteristics
Introduction
Interface to the World
Our Example System
Resource Constraints
Summary
Real-Time Systems
Resource Constraints
Systems have to be cheap
Memory
few 100 Bytes to few MB RAM
few KB to MB ROM
Speed
few MHz up to a few 100MHz
Energy consumption
Communication
Serial line
Special networks (Fieldbus)
A lot of legacy systems
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Definition and Characteristics
Introduction
Interface to the World
Our Example System
Resource Constraints
Summary
Real-Time Systems
Resource Constraints
Systems have to be cheap
Memory
few 100 Bytes to few MB RAM
few KB to MB ROM
Speed
few MHz up to a few 100MHz
Energy consumption
Communication
Serial line
Special networks (Fieldbus)
A lot of legacy systems
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Definition and Characteristics
Introduction
Interface to the World
Our Example System
Resource Constraints
Summary
Real-Time Systems
Resource Constraints
Systems have to be cheap
Memory
few 100 Bytes to few MB RAM
few KB to MB ROM
Speed
few MHz up to a few 100MHz
Energy consumption
Communication
Serial line
Special networks (Fieldbus)
A lot of legacy systems
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Definition and Characteristics
Introduction
Interface to the World
Our Example System
Resource Constraints
Summary
Real-Time Systems
Resource Constraints
Systems have to be cheap
Memory
few 100 Bytes to few MB RAM
few KB to MB ROM
Speed
few MHz up to a few 100MHz
Energy consumption
Communication
Serial line
Special networks (Fieldbus)
A lot of legacy systems
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Definition and Characteristics
Introduction
Interface to the World
Our Example System
Resource Constraints
Summary
Real-Time Systems
Real-Time Systems
Imagine a car accident
What happens when the airbag is fired too late?
Even one ms too late is too late!
Timing is an important property
Conservative programming styles
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Definition and Characteristics
Introduction
Interface to the World
Our Example System
Resource Constraints
Summary
Real-Time Systems
Real-Time Systems
Imagine a car accident
What happens when the airbag is fired too late?
Even one ms too late is too late!
Timing is an important property
Conservative programming styles
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Definition and Characteristics
Introduction
Interface to the World
Our Example System
Resource Constraints
Summary
Real-Time Systems
Real-Time Systems
Imagine a car accident
What happens when the airbag is fired too late?
Even one ms too late is too late!
Timing is an important property
Conservative programming styles
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Introduction
Our Example System
Summary
Our Example System
A Java processor board
FPGA based
Processor is software
Can be configured
HW accelerator
Interfaces
Digital IO, Analog input
Serial line
Ethernet
Resources
up to 100MHz CPU
1MB memory
512KB + 32MB Flash
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Introduction
Our Example System
Summary
Our Example System
A Java processor board
FPGA based
Processor is software
Can be configured
HW accelerator
Interfaces
Digital IO, Analog input
Serial line
Ethernet
Resources
up to 100MHz CPU
1MB memory
512KB + 32MB Flash
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Introduction
Our Example System
Summary
Our Example System
A Java processor board
FPGA based
Processor is software
Can be configured
HW accelerator
Interfaces
Digital IO, Analog input
Serial line
Ethernet
Resources
up to 100MHz CPU
1MB memory
512KB + 32MB Flash
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Introduction
Our Example System
Summary
Our Example System
A Java processor board
FPGA based
Processor is software
Can be configured
HW accelerator
Interfaces
Digital IO, Analog input
Serial line
Ethernet
Resources
up to 100MHz CPU
1MB memory
512KB + 32MB Flash
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Introduction
Our Example System
Summary
Summary
Embedded systems are part of a bigger system.
ES systems are small.
ES programming is programming with resource
constraints.
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Appendix For Further Reading
For Further Reading
Wikipedia.
http:
//en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Embedded_system
M. Schoeberl.
JOP: A Java Optimized Processor for Embedded
Real-Time Systems.
PhD thesis, Vienna University of Technology, 2005.
http://www.jopdesign.com/thesis/thesis.pdf
Martin Schoeberl Embedded Systems
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hardware in Loop SimulationDokument18 SeitenHardware in Loop SimulationRahul AshokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automated Database System For Government EstablishmentDokument56 SeitenAutomated Database System For Government EstablishmentAchieverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To RtsDokument4 SeitenIntroduction To RtsKarthik KarthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attributes of Embedded Systems: 3 Characteristics& QualityDokument12 SeitenAttributes of Embedded Systems: 3 Characteristics& QualityPriya NagwekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Outline Overall Structure of RT Systems: A Clock!Dokument4 SeitenCourse Outline Overall Structure of RT Systems: A Clock!Pranava PranuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integracion SI Primera ParteDokument100 SeitenIntegracion SI Primera ParteEduardo Enrique Rojas HinostrozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ARM TutorialDokument25 SeitenARM TutorialThi NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Embedded Systems Date-10/10/2009: Ravi Kumar A.V Lecturer Electronics and CommunicationDokument19 SeitenTo Embedded Systems Date-10/10/2009: Ravi Kumar A.V Lecturer Electronics and CommunicationDr Ravi Kumar A.VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument46 SeitenChapter 1kiramelaku1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2 - 2 - Introduction To Embedded SystemsDokument17 SeitenLecture 2 - 2 - Introduction To Embedded Systemsnarin shirwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topik 1 (A) Automation RelayDokument26 SeitenTopik 1 (A) Automation RelaySayuti SidikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-I Introduction: 1.1 Embedded System (E.S)Dokument4 SeitenUnit-I Introduction: 1.1 Embedded System (E.S)lucky jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Embedded Systems: Using Microcontrollers and The MSP430Dokument34 SeitenIntroduction To Embedded Systems: Using Microcontrollers and The MSP430Đắc Hùng Phú NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 03 10 Debug Embedded Systems Part 1 V 1.01Dokument95 Seiten2021 03 10 Debug Embedded Systems Part 1 V 1.01RakshithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Systems Design, Tuning and Optimization With Matlab and SimulinkDokument19 SeitenControl Systems Design, Tuning and Optimization With Matlab and Simulinkjames83angNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling and SimulationDokument29 SeitenModeling and SimulationMuhammad Hammad Javed IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME451: Control Systems: Dr. Jongeun Choi Department of Mechanical Engineering Michigan State UniversityDokument18 SeitenME451: Control Systems: Dr. Jongeun Choi Department of Mechanical Engineering Michigan State UniversityVu NghiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Embedded Systems: ARM University ProgramDokument25 SeitenIntroduction To Embedded Systems: ARM University Programlola ittaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Embedded SystemsDokument44 SeitenDesign of Embedded SystemssivajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 and Unit 4 (2 Files Merged)Dokument28 SeitenUnit 3 and Unit 4 (2 Files Merged)kalekarmohith02Noch keine Bewertungen
- Embedded System Components Notes 1Dokument12 SeitenEmbedded System Components Notes 1abebawabatuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Systems: Basic Concepts and History: What Is An Operating System?Dokument6 SeitenOperating Systems: Basic Concepts and History: What Is An Operating System?hihi309Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Embedded SystemsDokument84 SeitenIntroduction To Embedded SystemsGodofredo Luayon Jipus Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Embedded Systems: by Jagadeesh.KDokument40 SeitenEmbedded Systems: by Jagadeesh.Kjagadeeshjack100% (1)
- Real-Time Operating System NewDokument18 SeitenReal-Time Operating System NewJonathan JohnsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Embedded SystemsDokument2 SeitenIntroduction To Embedded Systemsvenkata satishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embedded SystemDokument29 SeitenEmbedded SystemSwathi. N.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Tap COntrollerDokument42 SeitenAutomatic Tap COntrollerMukeshpanigrahyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embedded Systems Notes Related To CIE-1Dokument16 SeitenEmbedded Systems Notes Related To CIE-130035ravi KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument67 SeitenUnit 1sophieee19Noch keine Bewertungen
- Real Time Systems: Radek Pel AnekDokument67 SeitenReal Time Systems: Radek Pel AnekVarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embedded System Design IssuesDokument8 SeitenEmbedded System Design Issuesusamadar707Noch keine Bewertungen
- Microprocessor Systems: - A Brief Run DownDokument28 SeitenMicroprocessor Systems: - A Brief Run Downkartika_krazeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embedded Systems Notes MidtermsDokument67 SeitenEmbedded Systems Notes MidtermsCol. Jerome Carlo Magmanlac, ACP100% (1)
- Embedded OS For Real Time ApplicationsDokument13 SeitenEmbedded OS For Real Time ApplicationsAnkit MakolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch01 Intro To Embedded SystemsDokument7 SeitenCh01 Intro To Embedded SystemsJayvee MagnayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Do Users and Processes Interact With The Operating System? Services For ProcessesDokument8 SeitenHow Do Users and Processes Interact With The Operating System? Services For ProcessesAkshay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Course On 8051 MicrocontrollersDokument2 SeitenBasic Course On 8051 Microcontrollerssathish37Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Design Challenges, 05-01-2024Dokument74 Seiten3 Design Challenges, 05-01-2024kx.graphyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SE Chapter2Dokument38 SeitenSE Chapter2JasonDelumenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open OTSDokument2 SeitenOpen OTShoangbkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Embedded SystemDokument42 SeitenIntroduction To Embedded SystemMohd FahmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RE02 Part2Dokument29 SeitenRE02 Part2syed kashifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embedded Systems DesignDokument138 SeitenEmbedded Systems DesignAsante WilliamNoch keine Bewertungen
- C2 NotesDokument15 SeitenC2 NotesBUQRA AN FARDEENA BINTI MOHAMED FAIRUZ STUDENTNoch keine Bewertungen
- C1 NotesDokument7 SeitenC1 NotesBUQRA AN FARDEENA BINTI MOHAMED FAIRUZ STUDENTNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Embedded System": Seminar OnDokument32 Seiten"Embedded System": Seminar Onwarking866Noch keine Bewertungen
- Embedded System DesignDokument163 SeitenEmbedded System DesignSUNIL MP100% (4)
- Es Notes Unit 1Dokument20 SeitenEs Notes Unit 1Sai ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Introduction To Embedded System Design PDFDokument99 SeitenUnit 1 Introduction To Embedded System Design PDFNIDHI. R .SINGH100% (1)
- Discrete-Event Simulation: Introduction To Simulation WS01/02 - L 04 1/40 Graham HortonDokument40 SeitenDiscrete-Event Simulation: Introduction To Simulation WS01/02 - L 04 1/40 Graham HortonPritosh JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECEG4202-Embedded Systems: Welcome To The CourseDokument154 SeitenECEG4202-Embedded Systems: Welcome To The Coursesadam endrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-Overview of Embedded Systems-05!01!2024Dokument107 Seiten3-Overview of Embedded Systems-05!01!2024kx.graphyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NodeB Routine MaintenanceDokument20 SeitenNodeB Routine MaintenanceashrafmetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 1Dokument11 SeitenCH 1Zeeshan FarooqNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLC NotesDokument61 SeitenPLC NotesravipedapudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 (Compatibility Mode)Dokument37 Seiten1 (Compatibility Mode)Kairredin Mahamed HusenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Introduction To Embedded System DesignDokument99 SeitenUnit 1 Introduction To Embedded System Designmahanteshamantu222Noch keine Bewertungen
- Microcontrol EditedDokument87 SeitenMicrocontrol EditedLebron DenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gridsim d115 Nayak RtdsDokument48 SeitenGridsim d115 Nayak Rtds韩鹤远Noch keine Bewertungen
- Input Device Roll No 63Dokument13 SeitenInput Device Roll No 63Jinal ManekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pt6315 en PDFDokument26 SeitenPt6315 en PDFEnéas BaroneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vacon NX OPTC7 DeviceNet Board User Manual DPD0089Dokument52 SeitenVacon NX OPTC7 DeviceNet Board User Manual DPD0089TanuTiganu0% (1)
- 9th - Computer ScienceDokument102 Seiten9th - Computer ScienceAhmad Ali AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- EcCST ManualDokument62 SeitenEcCST Manualmatius.qNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer by Yatendra Sir: MemoryDokument7 SeitenComputer by Yatendra Sir: Memoryparassh knowledgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ServiceManual en E-Series V 1.1.6Dokument201 SeitenServiceManual en E-Series V 1.1.6Nghia PhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch01 Introduction To Information SystemsDokument21 SeitenCh01 Introduction To Information SystemsYataki Lrak AilaludNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBM 1401 RPG Manual PDFDokument115 SeitenIBM 1401 RPG Manual PDFconystanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap11 (Proc Expand)Dokument41 SeitenChap11 (Proc Expand)smhabbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Systems: Read: Chapter 1Dokument18 SeitenOperating Systems: Read: Chapter 1chenwx21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Step7 s7 F FH Systems Operating Manual en-US en-USDokument430 SeitenStep7 s7 F FH Systems Operating Manual en-US en-USabu_kannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Graphics Hardware: StructureDokument10 SeitenUnit 2 Graphics Hardware: StructureAshok PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Secure Dynamic Multi-Keyword Ranked Search Scheme Over Encrypted Cloud DataDokument47 SeitenA Secure Dynamic Multi-Keyword Ranked Search Scheme Over Encrypted Cloud Dataidike chukwuemekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG Schiller AT-10 - Service HandbookDokument164 SeitenECG Schiller AT-10 - Service HandbookFrepa_AL100% (1)
- PN PN Coupler Hardware ManualDokument104 SeitenPN PN Coupler Hardware Manualdjeff71Noch keine Bewertungen
- GooseDokument12 SeitenGoosesteve_osullivanNoch keine Bewertungen
- RoboRIO ManualDokument31 SeitenRoboRIO ManualHectorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8086 - Interfacing Analog To Digital Converters (ADC)Dokument22 Seiten8086 - Interfacing Analog To Digital Converters (ADC)PARIJAAT B MITRANoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - Intro To Problem Solving - Flowchart PseudocodeDokument56 Seiten4 - Intro To Problem Solving - Flowchart PseudocodeImanuel CassidyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PC AppguideDokument8 SeitenPC AppguideEliyanto E BudiartoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Man 018Dokument100 SeitenMan 018belden_21Noch keine Bewertungen
- MSINFODokument122 SeitenMSINFOArturo RojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Model Laptop/desktop BIOS Entering Keys: DEL, F2, F10, F9 Lenovo New Model (fn+F2) Together Sony Assist Key, f2Dokument10 SeitenCommon Model Laptop/desktop BIOS Entering Keys: DEL, F2, F10, F9 Lenovo New Model (fn+F2) Together Sony Assist Key, f2Rajendra ShahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computers in GeneralDokument75 SeitenComputers in GenerallvsaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument30 SeitenUntitledRororo RororoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spray Chapter3Dokument66 SeitenSpray Chapter3Paijo TejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIS - WUA Lecture Notes 1Dokument13 SeitenMIS - WUA Lecture Notes 1Anesu FreddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SIMATIC S7-300: The Universal Controller For System Solutions With Factory Automation As Focal PointDokument81 SeitenSIMATIC S7-300: The Universal Controller For System Solutions With Factory Automation As Focal PointDeath ZoneNoch keine Bewertungen