Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Regime of Properties I. Acp ACP Governs When
Hochgeladen von
Bea Czarina NavarroOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Regime of Properties I. Acp ACP Governs When
Hochgeladen von
Bea Czarina NavarroCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
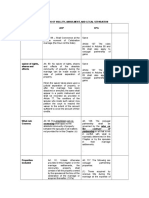
REGIME OF PROPERTIES
I. ACP
ACP governs when:
1) stipulated in the marriage settlement
2) MS is void
3) no MS
*at the precise moment of marriage, no prescription
*No waiver of rights except through judicial separation of property
ACP EXCLUSIONS (Article 92)
1) Property excluded in MS
2) Property acquired through gratuitous title + fruits + income (EXCEPT: if donor
expressly provides otherwise)
3) Property for personal use (EXCEPT: Jewelry/those with substantial amount)
4) Property acquired before marriage by either spouse who has legitimate
descendants + fruits + income
CHARGES AGAINST ACP (Article 94)
1) Support (spouses, common children, legitimate children)
2) Taxes, charges, repairs
3) Expenses for self-improvement
4) Debts/obligations
a. Administrator contracted a debt for the benefit of the family
b. Obtained consent from the other, does not benefit thefamily
c. Without consent: benefit of the family, during marriage
d. Prior to the marriage, benefit of the family
e. Any loss from business/profession
5) Expenses in litigation unless (1) suit is between the husband and wife, (2) suit is
not groundless
Termination of ACP (Article 99)
1) death of either spouse
2) decree of legal separation
3) annulment or nullity of marriage
4) judicial separation of property
a. voluntary
b. involuntary
5) affidavit of reappearance (a reappearing spouse or an interested person files an
affidavit of reappearance to terminate subsequent marriage of the present
spouse validly contracted with another person
Separation-in-fact between husband and wife shall not affect the regime of
absolute community except (Article 100):
1) The spouse who leaves conjugal home shall not be supported (but fault must be
proven/without just cause; EXCEPTION: expenses redounding to the benefit of
the family)
2) Court authorization (for consent)
3) Solidary liability and administration of separate property
LIQUIDATION OF ACP (Article 102)
1) inventory listing ACP and exclusive properties
2) debts and obligations of ACP shall be paid; insufficiency: spouses shall be
solidarily liable
3) remaining exclusive properties shall be delivered
4) remaining ACP (net assets) shall be divided equally unless:
a. a different proportion or division was agreed upon in MS
b. voluntary waiver of share
5) presumptive legitimes delivered unless:
a. void marriage (because there was no marriage in the first place)
i. Art 40 in relation to Article 52 and 52 (subsequent void
marriage for being bigamous) not included!!!
b. legally separated (because marriage is not yet severed)
6) conjugal dwelling and the lot shall be adjudicated to the spouse with whom the
majority of the common children choose to remain unless
*No majority: best interests of the children
II. CPG
CPG governs when:
1) married before Family Code took effect (Aug. 3, 1988)
2) stipulated in the MS
*at the precise moment of marriage, no prescription
*No waiver of rights except through judicial separation of property
CONJUGAL PROPERTIES (Article 117)
*basically anything you acquire using conjugal funds
1) those acquired by onerous title at the expense of common fund
2) labor, industry, work or profession of either spouse
3) fruits received from common and exclusive property
4) share in the hidden treasure
5) acquired through occupation fishing/hunting
6) livestock
7) acquired by chance, gambling, betting
Termination of CPG (Article 126)
6) death of either spouse
7) decree of legal separation
8) annulment or nullity of marriage
9) judicial separation of property
a. voluntary
b. involuntary
10) affidavit of reappearance (a reappearing spouse or an interested person files
an affidavit of reappearance to terminate subsequent marriage of the present
spouse validly contracted with another person
Separation-in-fact between husband and wife shall not affect the regime of
conjugal partnership except (Article 127):
4) The spouse who leaves conjugal home shall not be supported (but fault must be
proven/without just cause; EXCEPTION: expenses redounding to the benefit of
the family)
5) Court authorization (for consent)
6) Solidary liability and administration of separate property
LIQUIDATION OF CPG
1) Inventory
2)
Grounds to impugn legitimacy:
1) physically impossible to have intercourse
a. physical incapacity
b. living separately
c. serious illness
2) biological or scientific reasons
3) artificial insemination wherein consent was obtained through:
a. mistake
b. fraud
c. violence
d. intimidation
e. undue influence
Heirs may only impugn legitimacy when:
1) the husband died before expiration period
2) died after filing complaint
3) died before child was born
PROOF OF FILIATION (primary)
1) birth certificate
2) judicial decision
3) public or private handwritten document
Secondary
1) open and continuous possession of the status
2) other evidence acceptable under the Rules of Court
Rights of legitimate children:
1) Surname
2) Support
3) Successional rights
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Art of Recusing a Judge - With Ultimate Loopholes and a Sample Motion to RecuseVon EverandThe Art of Recusing a Judge - With Ultimate Loopholes and a Sample Motion to RecuseBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- SC Family Law OutlineDokument21 SeitenSC Family Law Outlineaem419100% (2)
- Matrix of Acp CPG and Separation of PropertyDokument7 SeitenMatrix of Acp CPG and Separation of PropertyDenver Dela Cruz PadrigoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Persons Test 2021Dokument10 SeitenPersons Test 2021zane100% (1)
- Supply Agreement-ConcreteDokument10 SeitenSupply Agreement-ConcreteProfessionalNoch keine Bewertungen
- UCC 2 207 Flow ChartDokument2 SeitenUCC 2 207 Flow Chartpac35Noch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Law DLSU Bar CommissionDokument16 SeitenCivil Law DLSU Bar CommissionmaikadjimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Persons Table PDFDokument4 SeitenPersons Table PDFAyra ArcillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wills & Probate DB Ch.4 Intestacy RulesDokument9 SeitenWills & Probate DB Ch.4 Intestacy Rulesmike_theplayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distinction Between Absolute Community Property (Acp) and Conjugal Property of Gains (CPG)Dokument6 SeitenDistinction Between Absolute Community Property (Acp) and Conjugal Property of Gains (CPG)Danielle Gumpad DolipasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rights and Obligations Between The Husband and The Wife (JL-FORM)Dokument23 SeitenRights and Obligations Between The Husband and The Wife (JL-FORM)nulljohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiao V QuiaoDokument3 SeitenQuiao V QuiaoSimon James SemillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Title Iii. Rights AND Obligations Between Husband and WifeDokument12 SeitenTitle Iii. Rights AND Obligations Between Husband and WifeGillian CalpitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Gls Civil Law Review I Family Code PPP 6 Property Relations Part 3 Updated 15 October 2022Dokument33 Seiten6 Gls Civil Law Review I Family Code PPP 6 Property Relations Part 3 Updated 15 October 2022Ralph TiempoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exclusive Grounds (Rp-Pid-Lbsaa) (SD-CD) : Legal SeparationDokument4 SeitenExclusive Grounds (Rp-Pid-Lbsaa) (SD-CD) : Legal SeparationAngel VirayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Property Relations Between SpousesDokument9 SeitenProperty Relations Between SpousesJanzel SantillanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acp CPGDokument4 SeitenAcp CPGRuab PlosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rights and ObligationsDokument2 SeitenRights and ObligationsChaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal Aspect in Real Estate and Taxation Week 3Dokument26 SeitenLegal Aspect in Real Estate and Taxation Week 3kbbalutocNoch keine Bewertungen
- PFR FinalsDokument13 SeitenPFR FinalsYza Cruz0% (1)
- Persons OutlineDokument12 SeitenPersons OutlineMark Anthony ManuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal Separation: Family Code (Title II, Articles 55-67) Introduction To Law by Suarez (2013)Dokument11 SeitenLegal Separation: Family Code (Title II, Articles 55-67) Introduction To Law by Suarez (2013)Jed BentilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acp V CPGDokument3 SeitenAcp V CPGBenitez GheroldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics - Legal Sep Nullity Annulment Divorce PDFDokument2 SeitenEthics - Legal Sep Nullity Annulment Divorce PDFRoane RoblesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Family Law Class NotesDokument35 SeitenFamily Law Class Notessbishara_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- CLR1 - Legal SeparationDokument4 SeitenCLR1 - Legal SeparationisaaabelrfNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACP & CPG Matrix by LardizabalDokument9 SeitenACP & CPG Matrix by LardizabalMel Johannes Lancaon HortalNoch keine Bewertungen
- F Property RelationsDokument83 SeitenF Property RelationsOgami IttoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rights and Obligations in Marriage and Family Under Philippine LawDokument10 SeitenRights and Obligations in Marriage and Family Under Philippine LawDon DxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tables Void, Voidable and Legal SeparationDokument9 SeitenTables Void, Voidable and Legal SeparationFrances Abigail Buban100% (1)
- Property RelationsDokument25 SeitenProperty RelationsNimpa PichayNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Commencement of The Community Regime at Any Other Time Shall Be VoidDokument7 SeitenThe Commencement of The Community Regime at Any Other Time Shall Be VoidChristopher Jimriel RonquilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Commencement of The Community Regime at Any Other Time Shall Be VoidDokument8 SeitenThe Commencement of The Community Regime at Any Other Time Shall Be VoidChiara Grace NalasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- System of Absolute CommunityDokument21 SeitenSystem of Absolute CommunitydeeniboyxaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Property RegimesDokument105 SeitenProperty RegimesJet Ortiz100% (1)
- Persons Table2 For Judge BonifacioDokument4 SeitenPersons Table2 For Judge BonifacioLaurence MillanNoch keine Bewertungen
- System of Absolute CommunityDokument6 SeitenSystem of Absolute CommunityAnonymous C6x95STYyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal SeparationDokument15 SeitenLegal SeparationLASNoch keine Bewertungen
- PFRDokument204 SeitenPFRPrincess Joan InguitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relations Between Husband and WifeDokument23 SeitenRelations Between Husband and WifeMariam BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Title Iii Rights and Obligations Between Husband and WifeDokument4 SeitenTitle Iii Rights and Obligations Between Husband and WifeKim YvesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal SeparationDokument2 SeitenLegal SeparationJm TalatalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (B) Sole AdministrationDokument4 Seiten(B) Sole AdministrationFranch GalanzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characterization of Property in Divorce ProceedingsDokument18 SeitenCharacterization of Property in Divorce ProceedingsAndrea FagundesNoch keine Bewertungen
- System of Absolute CommunityDokument17 SeitenSystem of Absolute CommunitylitoingatanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Persons and Family RelationsDokument7 SeitenPersons and Family RelationsLing EscalanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- PFR FinalsDokument64 SeitenPFR FinalsnashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Persons Table For Judge BonifacioDokument6 SeitenPersons Table For Judge BonifacioLaurence MillanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22 MA - Persons Page22Dokument21 Seiten22 MA - Persons Page22Anonymous syqUJjyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiao v. QuiaoDokument3 SeitenQuiao v. QuiaoAKNoch keine Bewertungen
- TE OutlineDokument113 SeitenTE OutlineJavier RosadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Persons Final ExamDokument28 SeitenPersons Final ExamAnonymous FXhZbcfeGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marriage Settlement (Prenuptial Agreement) - AnDokument3 SeitenMarriage Settlement (Prenuptial Agreement) - AnMichaela NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rights and Obligations Between The Husband and The Wife (JL-FORM)Dokument22 SeitenRights and Obligations Between The Husband and The Wife (JL-FORM)Rose de DiosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rights and Obligations Between SpousesDokument22 SeitenRights and Obligations Between SpousesgleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rights and Obligations Between The Husband and The Wife (JL-FORM)Dokument22 SeitenRights and Obligations Between The Husband and The Wife (JL-FORM)gleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rights and Obligations Between The Husband and The Wife (JL-FORM)Dokument22 SeitenRights and Obligations Between The Husband and The Wife (JL-FORM)Keempen Brian BernadasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Persons Family Relations SY2021 2022 Lecture Notes 6Dokument22 Seiten6 Persons Family Relations SY2021 2022 Lecture Notes 6Mirasol BaykingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Code 10 15Dokument6 SeitenCivil Code 10 15Shiuu IuNoch keine Bewertungen
- California Supreme Court Petition: S173448 – Denied Without OpinionVon EverandCalifornia Supreme Court Petition: S173448 – Denied Without OpinionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Taena Mo Part 2Dokument148 SeitenTaena Mo Part 2Bea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taena Mo HahaDokument290 SeitenTaena Mo HahaBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- KLKLKLDokument3 SeitenKLKLKLBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- KjsndhjaksDokument4 SeitenKjsndhjaksBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- HGJLKLJDokument55 SeitenHGJLKLJBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contingency Measures On Fts and E-DayDokument6 SeitenContingency Measures On Fts and E-DayBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Le Chef Menu Updated 2023Dokument13 SeitenLe Chef Menu Updated 2023Bea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- KJSKDKSDDokument93 SeitenKJSKDKSDBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDKJDKSJDDokument3 SeitenSDKJDKSJDBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- CivRevII DJKJKDokument5 SeitenCivRevII DJKJKBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- HGJLKLJDokument55 SeitenHGJLKLJBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explanation LetterDokument1 SeiteExplanation LetterBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- DO 174-17 Rules Implementing Articles 106 To 109 of The Labor Code, As AmendedDokument13 SeitenDO 174-17 Rules Implementing Articles 106 To 109 of The Labor Code, As AmendedKristiana Montenegro GelingNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBP Makati Flyer (Digital)Dokument2 SeitenIBP Makati Flyer (Digital)Bea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- We Could Leave The Christmas Lights Up 'Til January" and Spin You Around Like We Always Used To. I Just Wanna Dance With YouDokument1 SeiteWe Could Leave The Christmas Lights Up 'Til January" and Spin You Around Like We Always Used To. I Just Wanna Dance With YouBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Garage Sale MechanicsDokument1 SeiteGarage Sale MechanicsBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pol PhiloDokument2 SeitenPol PhiloBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uribe Tips ForwardedDokument1 SeiteUribe Tips ForwardedBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- KsdjhlakjdDokument4 SeitenKsdjhlakjdBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- JshdkaDokument4 SeitenJshdkaBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- JshdkjahsdDokument188 SeitenJshdkjahsdBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- JkshdkajhsdDokument4 SeitenJkshdkajhsdBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- A SHLKSJKLDokument2 SeitenA SHLKSJKLBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- KshdakjsdhkaDokument1 SeiteKshdakjsdhkaBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q1: Should The Marriage Between X and Y Be Recognized in The Philippines? Why or Why Not?Dokument4 SeitenQ1: Should The Marriage Between X and Y Be Recognized in The Philippines? Why or Why Not?Bea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm ExaminationsDokument4 SeitenMidterm ExaminationsBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm ExaminationsDokument4 SeitenMidterm ExaminationsBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rei Sitae or "The Law Where The Property Is Situated" Governs Not Only The Property Subject To SuchDokument8 SeitenRei Sitae or "The Law Where The Property Is Situated" Governs Not Only The Property Subject To SuchBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q1: Should The Marriage Between X and Y Be Recognized in The Philippines? Why or Why Not?Dokument4 SeitenQ1: Should The Marriage Between X and Y Be Recognized in The Philippines? Why or Why Not?Bea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rei Sitae or "The Law Where The Property Is Situated" Governs Not Only The Property Subject To SuchDokument8 SeitenRei Sitae or "The Law Where The Property Is Situated" Governs Not Only The Property Subject To SuchBea Czarina NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proposal Definition EssentialsDokument4 SeitenProposal Definition EssentialsMohit NaithaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Canned Answer ExampleDokument3 SeitenCanned Answer ExampleFaris YoungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retainer Fee ContractDokument2 SeitenRetainer Fee ContractKim Grace PėqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agri Digest 14-16Dokument3 SeitenAgri Digest 14-16Isha SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Club Key Lessee HCM StatusDokument38 SeitenClub Key Lessee HCM StatusMonique RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Government Procurement Act ReportDokument58 SeitenGovernment Procurement Act ReportChris PauloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valencia V CA DigestDokument56 SeitenValencia V CA DigestMartin AlfonsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code 2016Dokument4 SeitenInsolvency and Bankruptcy Code 2016Tanima SoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Limitation Act 1963Dokument21 SeitenThe Limitation Act 1963Swastik SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consulting AgreementDokument4 SeitenConsulting Agreementbudi irawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torts Case DigestDokument3 SeitenTorts Case DigestKaryl Mae Bustamante OtazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Property Notes & Cases 2008Dokument95 SeitenProperty Notes & Cases 2008Dewald Coetzer100% (6)
- No Employer-Employee RelationshipDokument2 SeitenNo Employer-Employee RelationshipJunelyn T. Ella100% (3)
- SOP For Hiring of Houses For Residential AcommodationDokument12 SeitenSOP For Hiring of Houses For Residential AcommodationFaheemAhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Professional Ethics Assignment 3Dokument12 SeitenProfessional Ethics Assignment 3Nikesh ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine National Bank vs. Antonio Bacani, Et AlDokument36 SeitenPhilippine National Bank vs. Antonio Bacani, Et AlDarlyn BangsoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Concept of Bai Bithaman Ajil BBADokument2 SeitenThe Concept of Bai Bithaman Ajil BBANur AthirahNoch keine Bewertungen
- MotumDokument2 SeitenMotumDock AceNoch keine Bewertungen
- BPLODokument8 SeitenBPLOEricka PinedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between Limited Company Vs Partnership Vs Limited Liability PartnershipDokument5 SeitenDifference Between Limited Company Vs Partnership Vs Limited Liability Partnershipsangya01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Request For Quotation (RFQ) : Page 1 of 15Dokument15 SeitenRequest For Quotation (RFQ) : Page 1 of 15Nundeep RakshitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reyes Masugas vs. Reyes GR 174835Dokument1 SeiteReyes Masugas vs. Reyes GR 174835JaylordPataotaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credit Report Shema - NezaDokument2 SeitenCredit Report Shema - NezaSHEMA NezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contract To Sell Rochelle CudiamatDokument4 SeitenContract To Sell Rochelle CudiamatNhel CudiamatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Your Policy DetailsDokument3 SeitenYour Policy DetailsMaddur LavanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Law On Obligations ComprehensiveDokument22 SeitenLaw On Obligations ComprehensiveCruxzelle BajoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belisario Vs IacDokument2 SeitenBelisario Vs IacArvin Guevarra100% (1)
- The Legal Environment of Business - Ch. 9 Flashcards - Quizlet3Dokument12 SeitenThe Legal Environment of Business - Ch. 9 Flashcards - Quizlet3dale huevoNoch keine Bewertungen