Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Class 12 Physics Derivation From All Lesson
Hochgeladen von
Ansuman Padhi0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
378 Ansichten1 SeiteThis includes all the important derivation that is being included in the CBSE syllabus according to 2018-19.
Originaltitel
Class 12 Physics Derivation from all lesson
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis includes all the important derivation that is being included in the CBSE syllabus according to 2018-19.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
378 Ansichten1 SeiteClass 12 Physics Derivation From All Lesson
Hochgeladen von
Ansuman PadhiThis includes all the important derivation that is being included in the CBSE syllabus according to 2018-19.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
PHYSICS DERIVATIONS
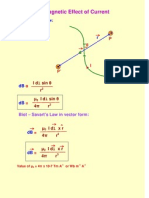
Coulomb’s Law in Vector Form Magnetic field intensity due to
Newton’s Third Law magnetic dipole (bar magnetic) along
Electric Field Intensity on Axial Line & its axis and its perpendicular axis
Equatorial Line of an Electric Dipole Torque on a magnetic dipole (bar
Electric Potential due to a point magnet) in a uniform magnetic field
charge. EMF (i.e. EMF induced in a rod
Electrical Potential on Axial Line & moving in Uniform EMF)
Equatorial Line of Electric Dipole Self and mutual induction
Electric Field Intensity at various point Relation between peak and RMS
due to a uniformly charged spherical value current
shell (thin and thick both) Reactance, impedance and average
Electric Potential due to a thin infinite power in series LCR, LR, CR circuit
plan sheet of charge Resonance in case of series LCR
Capacitance of parallel plate circuit
capacitor (with or without dielectric Displacement Current
medium) Lens-Makers Formula
Application of Gauss Theorem Refraction at convex surfaces
Expression of drift velocity Refraction index at minimum
Relation between drift velocity and deviation in prism
current Young’s double slit experiment
series and parallel connection of Diffraction using single slit
resistors Polarization
Application of Gauss Theorem is Minimum deviation in prism
calculation of electric field intensity Relationship between cut off
due to a thin infinite plane sheet of potential, frequency of the incident
charge and uniformly charged photon and threshold frequency
spherical shell (or conducting sphere) De Broglie relation
The biot-savert law in the calculation Radius of hydrogen-like atoms
of magnetic field due to current Common base transistor amplifier
carrying circular loop Common emitter transistor amplifier
Ampere’s law and its application
Force on a moving charge in uniform
magnetic and electric fields
Cyclotrons
Force on a current carrying in a
uniform magnetic field
Force between two parallel current
carrying conductors
Torque experienced by a current loop
in uniform magnetic fields
Current loop as a magnetic dipole
and its magnetic dipole moment
Magnetic dipole moment of a
revolving electron
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Reduced SyllabusDokument10 SeitenReduced Syllabusharshith0100Noch keine Bewertungen
- Evergreen Class 12th Question BankDokument43 SeitenEvergreen Class 12th Question BankIndrajeet kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Booklet Physics XIIDokument40 SeitenFormula Booklet Physics XIIsreenatpppp84% (127)
- Drug Testing MethodsDokument35 SeitenDrug Testing Methodswilly irawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Imp Derivations + TheoryDokument6 SeitenPhysics Imp Derivations + TheoryAL Surya67% (3)
- Important Derivations Physics Class 12 CBSE - Chapter WiseDokument3 SeitenImportant Derivations Physics Class 12 CBSE - Chapter WisePriyam RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Induction All DerivationsDokument5 SeitenElectromagnetic Induction All DerivationsRonit VaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important Derivation of Physics For Class 12Dokument6 SeitenImportant Derivation of Physics For Class 12Dhruv Tomar100% (2)
- Most Important Derivation For Class 12th PHYSICSDokument6 SeitenMost Important Derivation For Class 12th PHYSICSYash Morjhawal100% (1)
- Derivations IDokument53 SeitenDerivations IGG100% (2)
- All Derivations Term 2 PhysicsDokument14 SeitenAll Derivations Term 2 PhysicsChutzpahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics All Formulas Class 12 DriveDokument40 SeitenPhysics All Formulas Class 12 DriveAryan De100% (1)
- Electric Potential and Capacitance All Derivations: DW Fdxcos180Dokument12 SeitenElectric Potential and Capacitance All Derivations: DW Fdxcos180Amiya Kumar Das100% (1)
- Formulae Magnetic Effect of CurrentDokument14 SeitenFormulae Magnetic Effect of CurrentNathanian81% (16)
- Class 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit NirwanDokument24 SeitenClass 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit Nirwansuyash KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit NirwanDokument6 SeitenClass 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit Nirwanaastha.sawlaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit Nirwan (1) - RemovedDokument31 SeitenClass 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit Nirwan (1) - RemovedAarush Gaming100% (3)
- Chapter-4 - Moving Charges and MagnetismDokument8 SeitenChapter-4 - Moving Charges and MagnetismAdarsh Silkoti100% (1)
- Wave Optics All DerivationsDokument5 SeitenWave Optics All DerivationsSANSKRITI 3928Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Class 12 Revision MaterialDokument52 SeitenChemistry Class 12 Revision Materialkrish dabhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Facts & Formulae ChemistryDokument53 SeitenFacts & Formulae ChemistryTanvir Shafal100% (1)
- Guess Paper Class 12 Physics Important Questions PDFDokument9 SeitenGuess Paper Class 12 Physics Important Questions PDFKaran PratapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 Physics NotesDokument115 SeitenClass 12 Physics NotesAiden Pearce100% (1)
- Class 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit NirwanDokument14 SeitenClass 12 Physics Derivations Shobhit Nirwankjfnk,jg100% (2)
- 12 Physics Notes Ch07 Alternating CurrentDokument7 Seiten12 Physics Notes Ch07 Alternating CurrentCharles GhatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray Optics 2023 New NotesDokument22 SeitenRay Optics 2023 New NotesAman Prajapati100% (2)
- Check List of Physics XIIDokument6 SeitenCheck List of Physics XIIHardik Garg100% (2)
- Ray Optics All DerivationsDokument11 SeitenRay Optics All DerivationsAnuj GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Investigatory On Electromagnetic InductionDokument20 SeitenPhysics Investigatory On Electromagnetic InductionUsha Pachu38% (8)
- 12th Physics Current ElectricityDokument20 Seiten12th Physics Current ElectricityRahul KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wave Optics Notes For Class 12Dokument15 SeitenWave Optics Notes For Class 12Rick Harrison100% (1)
- Practical Viva Questions For Puc 2 - 2022Dokument4 SeitenPractical Viva Questions For Puc 2 - 2022Manu ShreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ohms Law ProjectDokument7 SeitenOhms Law Projectapi-2641987250% (4)
- Physics Activity File Class 12Dokument14 SeitenPhysics Activity File Class 12sanee yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xii Physics FormulaeDokument14 SeitenXii Physics FormulaeKaviya Sankar100% (5)
- D and F Block ElementsDokument51 SeitenD and F Block ElementsSatlip50% (2)
- Class 12 Chapterwise PYQs Shobhit NirwanDokument65 SeitenClass 12 Chapterwise PYQs Shobhit NirwanHimanshu92% (13)
- XII Practicals Viva QDokument8 SeitenXII Practicals Viva QAnshul Sharma100% (1)
- Chemistry Investigatory Project: Study The Change in E.M.F of A Daniel CellDokument20 SeitenChemistry Investigatory Project: Study The Change in E.M.F of A Daniel CellrahuhlNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Coordination Compounds Chapter NotesDokument7 SeitenCBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Coordination Compounds Chapter NotesAbhik Joydhar100% (1)
- Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation Class 12 All DerivationsDokument2 SeitenDual Nature of Matter and Radiation Class 12 All Derivationsmohitjangra9238Noch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Sheet Class 12Dokument3 SeitenFormula Sheet Class 12Siddharth Yaduvanshi86% (7)
- Class 12 Electrostatics Electricity and Magnetism Made Simple NotesDokument68 SeitenClass 12 Electrostatics Electricity and Magnetism Made Simple Noteslplc791Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Project Class XII 2021 22 Investigatory ProjectDokument16 SeitenPhysics Project Class XII 2021 22 Investigatory Projectlakshyajai70100% (1)
- Physics Investigatory Project Abhay Class Xii PDFDokument19 SeitenPhysics Investigatory Project Abhay Class Xii PDFnishra keshavNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Important Derivations/topics of Physics Class XI CBSEDokument2 SeitenList of Important Derivations/topics of Physics Class XI CBSEYoyo75% (4)
- To Study Effect of Intensity of Light (By Varying Distance of He Source) On An LDRDokument3 SeitenTo Study Effect of Intensity of Light (By Varying Distance of He Source) On An LDRAlura100% (1)
- Gravitation All DerivationsDokument9 SeitenGravitation All DerivationsPravesh 10 A80% (5)
- Name Reactions Class 12Dokument12 SeitenName Reactions Class 12Puneet DeshwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 ChemistryDokument16 SeitenClass 12 ChemistrysipherbizNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of DerivationsDokument3 SeitenList of DerivationsGargi PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- DerivationDokument1 SeiteDerivationshreyanshdwivedi15Noch keine Bewertungen
- 12th Imp Topics Chapter WiseDokument4 Seiten12th Imp Topics Chapter WiserampriyachinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important DerivationsDokument3 SeitenImportant Derivationsnewtonfogg123Noch keine Bewertungen
- My ProjectDokument15 SeitenMy Projectbhatr407Noch keine Bewertungen
- JEE Main Syllabus at A Glance Pages PDFDokument10 SeitenJEE Main Syllabus at A Glance Pages PDFSuman DewasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 Physics FormulasDokument16 SeitenClass 12 Physics FormulasPrasanna VijayakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 12 List of DerivationsDokument4 SeitenGrade 12 List of DerivationsHeroicis FolkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adobe Scan 09 Feb 2024Dokument2 SeitenAdobe Scan 09 Feb 2024ANIRUDDHA MONDALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Physics-Department of CS-UOGDokument2 SeitenApplied Physics-Department of CS-UOGRukaiya AkramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Sample PapersDokument8 SeitenBiology Sample PapersAnsuman PadhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Sample PapersDokument5 SeitenBiology Sample PapersAnsuman PadhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Sample PapersDokument5 SeitenBiology Sample PapersAnsuman PadhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Sample PapersDokument9 SeitenBiology Sample PapersAnsuman PadhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Sample PapersDokument7 SeitenBiology Sample PapersAnsuman PadhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Sample PapersDokument9 SeitenBiology Sample PapersAnsuman PadhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Sample PapersDokument3 SeitenBiology Sample PapersAnsuman PadhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Sample PapersDokument7 SeitenBiology Sample PapersAnsuman PadhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Sample PapersDokument8 SeitenBiology Sample PapersAnsuman PadhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exceptions To The Octet Rule: Molecules With Electron-Deficient AtomsDokument22 SeitenExceptions To The Octet Rule: Molecules With Electron-Deficient AtomsJohn RammNoch keine Bewertungen
- Removing Contaminants From Crude Oil - AthlonDokument5 SeitenRemoving Contaminants From Crude Oil - AthlonIrene CarrilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purification of LDH 1Dokument25 SeitenPurification of LDH 1chetanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR FCC PDFDokument7 SeitenDR FCC PDFAle SanzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement of Self Inductance by Maxwell's BridgeDokument7 SeitenMeasurement of Self Inductance by Maxwell's BridgeTI NafisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Soil Science: NRMH 1.1 (2 + 1) First Semester B.Sc. (Hons.) HorticultureDokument38 SeitenFundamentals of Soil Science: NRMH 1.1 (2 + 1) First Semester B.Sc. (Hons.) HorticultureMakarim KhusnulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summative Test #4 Science 6Dokument2 SeitenSummative Test #4 Science 6chona redillasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Units and MeasurementsDokument18 SeitenUnits and MeasurementsLord Siva75% (4)
- EJ 4131 Revised Manuscript FDokument14 SeitenEJ 4131 Revised Manuscript FSantiago GaitanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 3 Energy Summary Grade 3 Learning Standards (From Bced Curriculum)Dokument4 SeitenGrade 3 Energy Summary Grade 3 Learning Standards (From Bced Curriculum)Akbar KurniawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effect of Monosaccharides Versus Disaccharides On The Rate of CO ProductionDokument4 SeitenThe Effect of Monosaccharides Versus Disaccharides On The Rate of CO ProductionRyan LamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atkins & de Paula: Elements of Physical Chemistry 6e: Chapter 7: Chemical Equilibria: The PrinciplesDokument63 SeitenAtkins & de Paula: Elements of Physical Chemistry 6e: Chapter 7: Chemical Equilibria: The Principleskemakoy429Noch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Fotosintesi 2 PDFDokument99 Seiten5 Fotosintesi 2 PDFLuca DelvecchioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epoxi Resins Reactive Diluyents EPOSIR EPONACDokument8 SeitenEpoxi Resins Reactive Diluyents EPOSIR EPONACfatemeh.ahmadkhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensors Evaluation 2019 Oct 19 (19) - DOC#NDL:NDA:DGA:ON:072002 PDFDokument1 SeiteSensors Evaluation 2019 Oct 19 (19) - DOC#NDL:NDA:DGA:ON:072002 PDFDivyansh KohliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masters in Smart Electrical Networks and Systems Intake 2024Dokument36 SeitenMasters in Smart Electrical Networks and Systems Intake 2024Alfonso Franco De ArcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- UhhghghhgjDokument2 SeitenUhhghghhgjDivyansh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Chemistry 0620/52Dokument8 SeitenCambridge IGCSE™: Chemistry 0620/52Sridharan VijayalakshmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System Issues Breakthrough by SlidesgoDokument46 SeitenRespiratory System Issues Breakthrough by SlidesgoPonimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theories On The Origin of The Solar System: By: Cuerpo, L.And Francisco, ADokument21 SeitenTheories On The Origin of The Solar System: By: Cuerpo, L.And Francisco, ARichell G.Noch keine Bewertungen
- VITEEE Chemistry 2014Dokument8 SeitenVITEEE Chemistry 2014SachinNoch keine Bewertungen
- C184 E037bDokument48 SeitenC184 E037bNeyda Flores VasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topworx ValvetopDokument24 SeitenTopworx ValvetopaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acoustics 4Dokument24 SeitenAcoustics 4That GuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shuttlecock DynamicsDokument6 SeitenShuttlecock Dynamicshokl88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hesss Law WorksheetDokument3 SeitenHesss Law WorksheetAtulya BharadwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- CO2+R3N+H2O R3NH+ +HCO3 - : Base Catalyzed MechanismDokument5 SeitenCO2+R3N+H2O R3NH+ +HCO3 - : Base Catalyzed MechanismsammarNoch keine Bewertungen
- API 571 2nd 2011 Unlocked - 051Dokument1 SeiteAPI 571 2nd 2011 Unlocked - 051nguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- GC - 1100Dokument2 SeitenGC - 1100jeyalaljNoch keine Bewertungen