Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
All About Basics
Hochgeladen von
Jumar Divinagracia DimpasCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
All About Basics
Hochgeladen von
Jumar Divinagracia DimpasCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
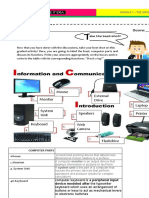
Computer – an electronic/automatic/programmable machine that can
store and delete data, manipulates and process to produce Basic Parts of Computer:
information according to set of instruction called program. 1. System Unit – the core of computer
Computer System – is a step by step process and collaboration of 2. Monitor – other term as vdu (visual display unit) w/c
hardware (peripherals), software components and peopleware. creates a visual display of output.
3. Mouse – navigational tool to control the cursor.
Core Components of Computer System: 4. Keyboard – use to input letters and alphanumeric
Hardware – physical component or medium. characters.
Software – package of program or instruction that tells computer 5. Power Supply – controls the voltage throughout the
what to do. circuitry.
Peopleware refers to anything that has to do with the role of people
in the development or use of computer software and hardware Input – signals or data received by the computer system.
systems. Output – signals or information sent from the computer system.
Input Devices: Types of Port: - uses an infrared light beams to transfer
1. Keyboard 1. PS/2 – Personal System 2 information to the PC .
2. Mouse 2. Serial Port
3. Scanner – provides a softcopy 3. Parallel Port C. Ergonomic Keyboard
4. Mic – receives/record sound 4. USB Port – Universal Serial Bus Port - An ergonomic PC keyboard bears an
5. Joy stick – use to maneuver computer Modem port/RJ-11 Port/Network Port exceptional design that simplifies to place
games 5. Sound Port the hands at a normal position while using
6. Drawing tablet/graphics tablet – similar to 6. Video Port keyboard.
magnetic board that is able to draw 7. Firewire or 1394 Port Types of Ergonomic Keyboard:
graphics and letters. 8. SPDIF Port – Sony/Phillips Digital Interface 1. The Split Keyboard
7. Light pen – use as a control in performing Format 2. The Tented Keyboard
multimedia presentation and electronic 9. S-Video Port
reader 10. RCA Port – Radio Corporation Of America D. Illuminated Keyboards
8. Stylus 11. HDMI Port – High Definition Multimedia - these keyboards have back lights so the
9. Touch pad Interface keys are more viewable even in dim lighted
10. Trackballs circumstances.
11. Barcode Scanners Types of USB Port E. Foldable Keyboard
12. Webcam – use for live conversation
13. Digicam 1. Standard A Types of Printer:
14. Touch Screen 2. Standard B 1. Dot matrix printers
3. Mini A - These printers consist of print head, pins
Output Devices: 4. Mini B and ribbon.
1. Monitor 5. Micro A
2. Speakers – use to provide sound 6. Micro B 2. Characters printer
3. Printers – produce a hardcopy 7. Micro C - it consists of alphabets or characters. Each
4. Projector – provides images through character strikes the ribbon to insert a
light Apple Port: character on the paper.
5. Plotters 3. Ink jet printers
6. Facsimile/Fax machine 1. 30 Pin - It consists of inkjet print cartridges or ink
2. Lightning boxes.
Storage Device: 4. Laser jet printers
1. HDD(hard disk Drive) Types of Monitor - It consists of electrostatic charge, rotating
a. External HDD drum, laser beam and toner.
b. Internal HDD 1. CRT(Cathode Ray Tube)
2. Floppy disk 2. LCD(Liquid crystal display )
3. Zip Disk 3. Plasma 5. Bubble Jet Printers
4. Optical Disc: CD/DVD/BRD 4. SED (Surface-conducted electron-emitted - It uses special heating elements to prepare
5. Flash Drive/Pin Drive/Mobile Disk display) the ink whereas ink-jet printers uses
6. Memory card 5. OLED (organic light-emitting diode piezoelectric crystals.
7. Video Card display)
8. Sound Card Types of Mouse
9. Memory Button Types of Screen 1. Mechanical
10. Cartridge Tapes 1. Glossy screen - This type of personal computer (PC) mouse
11. Reel Tapes 2. Directional screen has a rubber or metal ball on its underside
12. Smart Cards 3. Polarized 3D monitor and it can roll in every direction.
4. Autostereoscopic (3D) screen 2. Optomechanical
Cd – compact disc – saves data in digital 5. Touch screen - This type is the same as the mechanical
format 6. Tablet screens mouse except that it uses optical sensors to
a. 700mb/80minutes the motion of the ball.
b. 900 mb Types of Keyboard: 3. Optical
Dvd– Digital Versatile disc – saves data in -This type uses a laser for detecting the
media format.(4.7 GB and DL - Dual Layer) A. Multimedia Keyboard mouse's movement.
BRD – Blu-ray Disc – a High Definition format - The multimedia PC keyboard has the one a. laser mouse- is a type of computer mouse
hundred and one keys and the keys are that uses a laser beam
Type of Disc: frequently related to shortcuts or hot-keys. b. Cordless or Wireless Mouse
a. Rewritable Cordless or wireless mice transmit data
b. Recordable B. Wireless Keyboards via infrared.
Computer History Inventors/Inventions Description of Event
Year
1936 Konrad Zuse - Z1 Computer First freely programmable computer.
1942 John Atanasoff & Clifford Berry Who was first in the computing biz is not always as easy as ABC.
ABC Computer
1944 Howard Aiken & Grace Hopper The Harvard Mark 1 computer.
Harvard Mark I Computer
1946 John Presper Eckert & John W. Mauchly 20,000 vacuum tubes later...
ENIAC 1 Computer
1948 Frederic Williams & Tom Kilburn Baby and the Williams Tube turn on the memories.
Manchester Baby Computer & The Williams
Tube
1947/48 John Bardeen, Walter Brattain &Wiliam No, a transistor is not a computer, but this invention greatly
Shockley affected the history of computers.
The Transistor
1951 John Presper Eckert & John W. Mauchly First commercial computer & able to pick presidential winners.
UNIVAC Computer
1953 International Business Machines IBM enters into 'The History of Computers'.
IBM 701 EDPM Computer
1954 John Backus & IBM The first successful high level programming language.
FORTRAN Computer Programming Language
1955 Stanford Research Institute, Bank of America, The first bank industry computer - also MICR (magnetic ink
(In Use 1959) and General Electric character recognition) for reading checks.
ERMA and MICR
1958 Jack Kilby & Robert Noyce Otherwise known as 'The Chip'
The Integrated Circuit
1962 Steve Russell & MIT The first computer game invented.
Spacewar Computer Game
1964 Douglas Engelbart Nicknamed the mouse because the tail came out the end.
Computer Mouse & Windows
1969 ARPAnet The original Internet.
1970 Intel 1103 Computer Memory The world's first available dynamic RAM chip.
1971 Faggin, Hoff & Mazor The first microprocessor.
Intel 4004 Computer Microprocessor
1971 Alan Shugart&IBM Nicknamed the "Floppy" for its flexibility.
The "Floppy" Disk
1973 Robert Metcalfe & Xerox Networking.
The Ethernet Computer Networking
1974/75 Scelbi& Mark-8 Altair & IBM 5100 Computers The first consumer computers.
1976/77 Apple I, II & TRS-80 & Commodore Pet More first consumer computers.
Computers
1978 Dan Bricklin& Bob Frankston Any product that pays for itself in two weeks is a surefire winner.
VisiCalc Spreadsheet Software
1979 Seymour Rubenstein & Rob Barnaby Word Processors.
WordStar Software
1981 IBM From an "Acorn" grows a personal computer revolution
The IBM PC - Home Computer
1981 Microsoft From "Quick And Dirty" comes the operating system of the
MS-DOS Computer Operating System century.
1983 Apple Lisa Computer The first home computer with a GUI, graphical user interface.
1984 Apple Macintosh Computer The more affordable home computer with a GUI.
1985 Microsoft Windows Microsoft begins the friendly war with Apple.
ENIAC – Electronics Numerical Integrator and Calculator
UNIVAC – Universal Automatic Computer
IBM – International Business Machine
EDPM – Electronic Data Processing Machine
ERMA – Electronic Recording Method of Accounting
MICR – Magnetic Ink Character Recognition
FORTRAN – Formula Translator
Intel – Integrated Electronics
ARPANet – Advance Research Project Agency Network
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Computer FundamentalDokument20 SeitenComputer FundamentalAman AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Fundamental NotesDokument20 SeitenComputer Fundamental Notesrashii chauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer FundamentalDokument20 SeitenComputer FundamentalAngelo Gabriel LarionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital LiteracyDokument20 SeitenDigital Literacykingslydebruyne17Noch keine Bewertungen
- CC100 Module 3Dokument8 SeitenCC100 Module 3Hassina 05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Com - Science q1 Wk1 2Dokument10 SeitenCom - Science q1 Wk1 2Coren Jane M. TupanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Input Output ProcessDokument9 SeitenInput Output ProcessElixa HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comp 2NDQDokument6 SeitenComp 2NDQsnss.ashleycheyennezoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts of Information Communication TechnologyDokument22 SeitenConcepts of Information Communication Technologyclaire wacukaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comp 2NDQDokument6 SeitenComp 2NDQsnss.ashleycheyennezoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ComputerDokument3 SeitenComputerVince BulayogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Components and SoftwareDokument2 SeitenComputer Components and SoftwareDI NANoch keine Bewertungen
- Four functions of a computer: input, processing, output, storageDokument2 SeitenFour functions of a computer: input, processing, output, storagerahul pardhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CompDokument39 SeitenCompabcdefNoch keine Bewertungen
- GST 214 SummaryDokument6 SeitenGST 214 SummaryniyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMPUTER APPLICATION I - Lesson 4Dokument6 SeitenCOMPUTER APPLICATION I - Lesson 4Hack FinNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASNENewswriting PPDokument28 SeitenASNENewswriting PPJudessaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of The ComputerDokument14 SeitenParts of The ComputerMsLieslNoch keine Bewertungen
- Input and output devices and storage explainedDokument3 SeitenInput and output devices and storage explainedGeh Deng NolealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caballero, Krizah Marie C. Bsma 2e Compap Activity 1Dokument6 SeitenCaballero, Krizah Marie C. Bsma 2e Compap Activity 1KrizahMarieCaballeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tle-Ict Computer Systems Servicing: Quarter 1 - Module 3Dokument10 SeitenTle-Ict Computer Systems Servicing: Quarter 1 - Module 3Jeo MillanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer ComponentsDokument4 SeitenComputer ComponentsMarilyn GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Table of ContentDokument11 SeitenChapter 1 - Table of ContentAngelee BaezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edp101l FinalreviewerDokument7 SeitenEdp101l FinalreviewerJohn Mark MadrazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Hardware 1Dokument23 SeitenComputer Hardware 1AimeeUnidadEsguerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 13: Input, Output, Storage Device: Ailene Sibayan - Bobier Faculty, Computer Studies DepartmentDokument19 SeitenLesson 13: Input, Output, Storage Device: Ailene Sibayan - Bobier Faculty, Computer Studies DepartmentPanes GrenadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Input & Output DevicesDokument2 SeitenInput & Output DevicesOjantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ajad Kumar MauryaDokument9 SeitenAjad Kumar MauryaamarjeetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identification of Parts of The Computer SystemDokument49 SeitenIdentification of Parts of The Computer SystemFretzie Cambiado100% (1)
- Hardware ServicingwdcaDokument14 SeitenHardware ServicingwdcaNeil Joseph AlcalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technologicalconvergence 120404144720 Phpapp02 160622164632Dokument16 SeitenTechnologicalconvergence 120404144720 Phpapp02 160622164632General JoemarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSS ModuleDokument7 SeitenCSS ModuleElixa HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of The ComputerDokument14 SeitenParts of The ComputerMsLieslNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Computers Question Bank: Data Information Knowledge Processed ProcessedDokument12 SeitenIntroduction To Computers Question Bank: Data Information Knowledge Processed ProcessedSyed Muhammad Ijlal HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Computers: Hardware and Software Components ExplainedDokument12 SeitenUnderstanding Computers: Hardware and Software Components ExplainedJavier Salazar AndradeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 Understanding Computer Concepts AlsDokument20 SeitenLesson 1 Understanding Computer Concepts AlsAngelica CarbonquilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Computer?: Input Process OutputDokument2 SeitenWhat Is A Computer?: Input Process OutputRonn RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer HardwareDokument2 SeitenComputer Hardwarereymilyn zuluetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tle Css ReviewerDokument4 SeitenTle Css ReviewerHannah Ataza100% (1)
- Computer Hardware Servicing IiDokument16 SeitenComputer Hardware Servicing IiFacun BalagtasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Input, Output, StorageDokument3 SeitenInput, Output, Storageanjoooy100% (2)
- Page 20Dokument2 SeitenPage 20Deo Aragon LiboonNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Workshop Lab Manual: ObjectiveDokument31 SeitenIT Workshop Lab Manual: ObjectiveSENTHIL RNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Workshop Lab Manual: ObjectiveDokument31 SeitenIT Workshop Lab Manual: ObjectiveNandu GangavaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- PC ConfigurationDokument3 SeitenPC ConfigurationЧухрій СофіяNoch keine Bewertungen
- DF NOTES StudentDokument16 SeitenDF NOTES StudentShrinidhi.k.joisNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSS Module 1Dokument7 SeitenCSS Module 1geronimoalvin400Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tle Module 1 Grade 8Dokument10 SeitenTle Module 1 Grade 8vhernabeth reylaNoch keine Bewertungen
- T L E Module 1 Grade 8Dokument20 SeitenT L E Module 1 Grade 8Jared Floyd Lorezo100% (3)
- ComputerDokument3 SeitenComputerjamalcabdi731Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To ITDokument8 SeitenIntroduction To ITBeriso AbdelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aplikasi Teknologi Informasi Dalam PendidikanDokument52 SeitenAplikasi Teknologi Informasi Dalam PendidikanTri RahayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 6 Page 68-74Dokument7 SeitenModule 6 Page 68-74Junar James Mahinay AbellarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Hardware Worksheet / Quiz: Make Sure That The Worksheet Is Saved Into The Network Drive Folder For CreditDokument2 SeitenComputer Hardware Worksheet / Quiz: Make Sure That The Worksheet Is Saved Into The Network Drive Folder For CreditRaimundo LimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of Computing: Chapters 1-2Dokument53 SeitenBasics of Computing: Chapters 1-2Mohamad AdhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Systems: Jimma University Technology Institute Faculty of Computing and Informatics Muluken Yohannis (MSC)Dokument63 SeitenComputer Systems: Jimma University Technology Institute Faculty of Computing and Informatics Muluken Yohannis (MSC)JOHN CO0% (1)
- Computer System Servicing: Quarter 1 - Module 2Dokument36 SeitenComputer System Servicing: Quarter 1 - Module 2Sitti Sahara CabangcalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raspberry Pi for Arduino Users: Building IoT and Network Applications and DevicesVon EverandRaspberry Pi for Arduino Users: Building IoT and Network Applications and DevicesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entreprenuer Part 2Dokument6 SeitenEntreprenuer Part 2Jumar Divinagracia DimpasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Media and Media EffectsDokument19 SeitenTypes of Media and Media EffectsJumar Divinagracia DimpasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 CSA Part 1Dokument19 SeitenChapter 1 CSA Part 1Jumar Divinagracia DimpasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide For Authors (Research)Dokument3 SeitenGuide For Authors (Research)Jumar Divinagracia DimpasNoch keine Bewertungen
- RubricDokument1 SeiteRubricJumar Divinagracia DimpasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rubrics For InterviewDokument1 SeiteRubrics For InterviewJumar Divinagracia DimpasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade Slip FormDokument1 SeiteGrade Slip FormJumar Divinagracia DimpasNoch keine Bewertungen
- StdsDokument14 SeitenStdsJumar Divinagracia DimpasNoch keine Bewertungen
- StdsDokument14 SeitenStdsJumar Divinagracia DimpasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Ethics IntroDokument4 SeitenEngineering Ethics IntroJumar Divinagracia DimpasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Values and MoralDokument14 SeitenValues and MoralJumar Divinagracia DimpasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moral ValuesDokument8 SeitenMoral ValuesJumar Divinagracia DimpasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Information Extraction Technology: Douglas E. Appelt David J. IsraelDokument41 SeitenIntroduction To Information Extraction Technology: Douglas E. Appelt David J. IsraelJumar Divinagracia DimpasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moral ValuesDokument8 SeitenMoral ValuesJumar Divinagracia DimpasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 63.271: Data Structures Syllabus: Catalog DescriptionDokument3 Seiten63.271: Data Structures Syllabus: Catalog DescriptionWizzman LastNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 17 ElectricityDokument37 SeitenChapter 17 ElectricityFozia MahboobNoch keine Bewertungen
- CASSETTE Inverter YKKJE12 55BZTVMCMORXDokument6 SeitenCASSETTE Inverter YKKJE12 55BZTVMCMORXJuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEE363 (Exp 5) Study of The Different Loading Conditions of AlternatorDokument5 SeitenEEE363 (Exp 5) Study of The Different Loading Conditions of Alternatorsalad.ass420420Noch keine Bewertungen
- Troubleshooting Guide: Manual No: 577014-010 Revision: ADokument13 SeitenTroubleshooting Guide: Manual No: 577014-010 Revision: AVERY SYAYIDINANoch keine Bewertungen
- Generators and Standby Power Systems 2014NEC PDFDokument23 SeitenGenerators and Standby Power Systems 2014NEC PDFmikeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- LCD TV: Owner's InstructionsDokument33 SeitenLCD TV: Owner's Instructionsagrani1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- شركة المهندس لاداره المرافق200Dokument3 Seitenشركة المهندس لاداره المرافق200Fadi HouraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes 03Dokument29 SeitenLecture Notes 03stephen562001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Owner's Manual: Panel DescriptionsDokument1 SeiteOwner's Manual: Panel Descriptionsljputman09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Irf 530 NPBFDokument9 SeitenIrf 530 NPBFGabiBaciuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Op-Amp Imperfections: Autozeroing, Correlated Double Sampling, and Chopper StabilizationDokument31 SeitenOp-Amp Imperfections: Autozeroing, Correlated Double Sampling, and Chopper StabilizationAndres MauricioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rc-5bplus DiagramDokument21 SeitenRc-5bplus Diagramluroguita-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- System Settings Best Practices TerrainMapper V14.02.2020Dokument25 SeitenSystem Settings Best Practices TerrainMapper V14.02.2020イルヴァン シャーロニNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cooling Fans (Radiator Cooling Fan) - ALLDATA RepairDokument1 SeiteCooling Fans (Radiator Cooling Fan) - ALLDATA RepairFran Sanchez0% (1)
- Terasaki Tembreaki20ejDokument109 SeitenTerasaki Tembreaki20ejWijayasekara BuddhikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buc 6w-KuDokument5 SeitenBuc 6w-KukattiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erthing TransformerDokument8 SeitenErthing Transformerbpd21Noch keine Bewertungen
- XPRO Manual Complete PDFDokument2 SeitenXPRO Manual Complete PDFGibran Medina CardosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- JQX 15F (T90)Dokument1 SeiteJQX 15F (T90)Amang GayamNoch keine Bewertungen
- SRT6KXLI Product Data SheetDokument4 SeitenSRT6KXLI Product Data Sheet3maligeNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAN7387 SMDDokument17 SeitenFAN7387 SMDHung KdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ref615 Hafbbabaffe1bbn1xe-B (Feeder)Dokument10 SeitenRef615 Hafbbabaffe1bbn1xe-B (Feeder)Insan AzizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semiconductor BasicsDokument20 SeitenSemiconductor BasicsAngela BrittNoch keine Bewertungen
- Danby Dac5088m User ManualDokument12 SeitenDanby Dac5088m User ManualElla MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Energy Transfer Powered Wireless Sensor Node For Green Iot: Design, Implementation & EvaluationDokument27 SeitenWireless Energy Transfer Powered Wireless Sensor Node For Green Iot: Design, Implementation & EvaluationManjunath RajashekaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iec 62271-111-2012 (Ieee C37.60)Dokument134 SeitenIec 62271-111-2012 (Ieee C37.60)Carlos Porras100% (2)
- Universal Powerline Bus: X-10 To Upb Migration DocumentDokument25 SeitenUniversal Powerline Bus: X-10 To Upb Migration DocumentCristopher PatricioNoch keine Bewertungen
- DVD To Laser EngraverDokument24 SeitenDVD To Laser EngraverTaofik HidayatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Analysis of Mobile Phone Antenna System With Integration of LTE 4G, Sub-6G and Millimeter Wave 5G TechnologiesDokument1 SeiteDesign and Analysis of Mobile Phone Antenna System With Integration of LTE 4G, Sub-6G and Millimeter Wave 5G TechnologiesEnoch HuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5G Air InterfaceDokument8 Seiten5G Air InterfaceRodiNoch keine Bewertungen