Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
1K/2K/4K 2.5V Microwire Serial EEPROM: Features: Package Types
Hochgeladen von
João PauloOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1K/2K/4K 2.5V Microwire Serial EEPROM: Features: Package Types
Hochgeladen von
João PauloCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Not recommended for new designs –
Please use 93LC46C, 93LC56C or 93LC66C.
93LC46/56/66
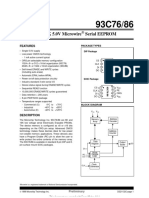
1K/2K/4K 2.5V Microwire Serial EEPROM
Features: Package Types
• Single supply with programming operation down PDIP/SOIC
to 2.5V
• Low-power CMOS technology
CS 1 8 VCC
• 100 µA typical active read current at 2.5V
93LC66
93LC56
93LC46
CLK 2 7 NU
• 3 µA typical standby current at 2.5V
DI 3 6 ORG
• ORG pin selectable memory configuration
DO 4 5 VSS
• 128 x 8- or 64 x 16-bit organization (93LC46)
• 256 x 8- or 128 x 16-bit organization (93LC56) ROTATED SOIC
• 512 x 8 or 256 x 16 bit organization (93LC66)
• Self-timed erase and write cycles NU 1 8 ORG
93LC66X
93LC56X
93LC46X
(including auto-erase) VCC 2 7 VSS
• Automatic ERAL before WRAL CS 3 6 DO
• Power on/off data protection circuitry CLK 4 5 DI
• Industry standard 3-wire serial I/O
• Device status signal during erase/write cycles
• Sequential read function Block Diagram
• 1,000,000 E/W cycles ensured
VCC VSS
• Data retention > 200 years
• 8-pin PDIP/SOIC
Address
(SOIC in JEDEC standards) Memory Decoder
Array
• Temperature ranges supported:
- Industrial (I): -40°C to +85°C
Address
Counter
Description:
DO
Output
The Microchip Technology Inc. 93LC46/56/66 are 1K, Data Register
Buffer
2K and 4K low voltage serial Electrically Erasable DI
PROMs (EEPROM). The device memory is configured Mode
as x8 or x16 bits depending on the external logic of ORG Decode
CS Logic
levels of the ORG pin. Advanced CMOS technology
makes these devices ideal for low power nonvolatile
memory applications. The 93LC Series is available in Clock
CLK
standard 8-pin PDIP and surface mount SOIC Register
packages. The rotated pin-out 93LC46X/56X/66X are
offered in the “SN” package only.
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21712B-page 1
93LC46/56/66
1.0 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Absolute Maximum Ratings(†)
VCC .............................................................................................................................................................................6.5V
All inputs and outputs w.r.t. VSS ........................................................................................................ -0.6V to VCC + 1.0V
Storage temperature ...............................................................................................................................-65°C to +150°C
Ambient temperature with power applied ................................................................................................-40°C to +125°C
ESD protection on all pins ......................................................................................................................................................≥ 4 kV
† NOTICE: Stresses above those listed under “Maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This
is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at those or any other conditions above those indicated in
the operational listings of this specification is not implied. Exposure to maximum rating conditions for extended periods
may affect device reliability.
DC CHARACTERISTICS
VCC = +2.5V to +5.5V
DC CHARACTERISTICS
Industrial (I): TA = -40°C to +85°C
Param.
Sym Characteristic Min Typ Max Units Conditions
No.
D1 VIH1 High-level input voltage 2.0 — VCC +1 V VCC ≥ 2.7V
VIH2 0.7 VCC — VCC +1 V VCC ≥ 2.7V
D2 VIL1 Low-level input voltage -0.3 — 0.8 V VCC ≥ 2.7V
VIL2 -0.3 — 0.2 VCC V VCC ≥ 2.7V
D3 VOL1 Low-level output voltage — — 0.4 V IOL = 2.1 mA, VCC = 4.5V
VOL2 — — 0.3 V IOL = 100 µA, VCC = 2.5V
D4 VOH1 High-level output voltage 2.4 — — V IOL = 400 µA, VCC = 4.5V
VOH2 VCC -0.2 — — V IOL = 100 µA, VCC = 2.5V
D5 ILI Input leakage current — — ±10 µA VIN = 0.1V to VCC
D6 ILO Output leakage current — — ±10 µA VOUT = 0.1V to VCC
D7 CIN, Pin capacitance — — 7 pF VIN/VOUT = 0V (Note 1 & 2)
COUT (all inputs/outputs) TA = 25°C, FCLK = 1 MHz
D8 ICC write Operating current — — 3 mA FCLK = 2 MHz, VCC = 5.5V
(Note 2)
D9 ICC read — — 1 mA FCLK = 2 MHz, VCC = 5.5V
— — 500 µA FCLK = 1 MHz, VCC = 3.0V
— 100 — µA FCLK = 1 MHz, VCC = 2.5V
D10 ICCS Standby current — — 100 µA CLK = CS = 0V; VCC = 5.5V
— — 30 µA CLK = CS = 0V; VCC = 3.0V
— 3 — µA CLK = CS = 0V; VCC = 2.5V
ORG, DI = VSS or VCC
Note 1: This parameter is tested at TA = 25°C and FCLK = 1 MHz.
2: This parameter is periodically sampled and not 100% tested.
DS21712B-page 2 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
93LC46/56/66
AC CHARACTERISTICS
VCC = +2.5V to +5.5V
AC CHARACTERISTICS
Industrial (I): TA = -40°C to +85°C
Param.
Sym Characteristic Min Typ Max Units Conditions
No.
1 FCLK Clock frequency — — 2 MHz VCC ≥ 4.5V
— — 1 MHz VCC < 4.5V
2 TCKH Clock high time 250 — — ns
3 TCKL Clock low time 250 — — ns
4 TCSS Chip select setup time 50 — — ns Relative to CLK
5 TCSH Chip select hold time 0 — — ns Relative to CLK
6 TCSL Chip select low time 250 — — ns
7 TDIS Data input setup time 100 — — ns Relative to CLK
8 TDIH Data input hold time 100 — — ns Relative to CLK
9 TPD Data output delay time — — 400 ns CL = 100 pF
10 TCZ Data output disable time — — 100 ns CL = 100 pf (Note 2)
11 TSV Status valid time — — 500 ns CL = 100 pF
12 TWC Program cycle time — 4 10 ms Erase/Write mode
13 TEC — 8 15 ms ERAL mode (VCC=5V ±10%)
14 TWL — 16 30 ms WRAL mode (VCC=5V ±10%)
15 — Endurance 1M — 1M cycles 25°C, VCC = 5.0V, Block
mode (Note 3)
Note 1: This parameter is tested at TA = 25°C and FCLK = 1 MHz.
2: This parameter is periodically sampled and not 100% tested.
3: This parameter is not tested but ensured by characterization. For endurance estimates in a specific
application, please consult the Total Endurance™ Model which can be obtained from Microchip’s web site
at: www.microchip.com.
FIGURE 1-1: SYNCHRONOUS DATA TIMING
VIH
CS
VIL 4 2 3
5
VIH
CLK
VIL
7 8
VIH
DI
VIL
9 9 10
DO VOH
(Read) 10
VOL 11
DO VOH
(Write) Status Valid
VOL
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21712B-page 3
93LC46/56/66
TABLE 1-1: INSTRUCTION SET FOR 93LC46: ORG = 1 (X 16 ORGANIZATION)
Req. CLK
Instruction SB Opcode Address Data In Data Out
Cycles
READ 1 10 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 — D15 - D0 25
EWEN 1 00 1 1 XXXX — High-Z 9
ERASE 1 11 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 — (RDY/BSY) 9
ERAL 1 00 1 0 XXXX — (RDY/BSY) 9
WRITE 1 01 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 D15 - D0 (RDY/BSY) 25
WRAL 1 00 0 1 XXXX D15 - D0 (RDY/BSY) 25
EWDS 1 00 0 0 XXXX — High-Z 9
TABLE 1-2: INSTRUCTION SET FOR 93LC46: ORG = 0 (X 8 ORGANIZATION)
Req. CLK
Instruction SB Opcode Address Data In Data Out
Cycles
READ 1 10 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 — D7 - D0 18
EWEN 1 00 11XXXXX — High-Z 10
ERASE 1 11 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 — (RDY/BSY) 10
ERAL 1 00 10XXXXX — (RDY/BSY) 10
WRITE 1 01 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 D7 - D0 (RDY/BSY) 18
WRAL 1 00 01XXXXX D7 - D0 (RDY/BSY) 18
EWDS 1 00 00XXXXX — High-Z 10
TABLE 1-3: INSTRUCTION SET FOR 93LC56: ORG = 1 (X 16 ORGANIZATION)
Instruction SB Opcode Address Data In Data Out Req. CLK
Cycles
READ 1 10 X A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 — D15 - D0 27
EWEN 1 00 11XXXXXX — High-Z 11
ERASE 1 11 X A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 — (RDY/BSY) 11
ERAL 1 00 10XXXXXX — (RDY/BSY) 11
WRITE 1 01 X A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 D15 - D0 (RDY/BSY) 27
WRAL 1 00 01XXXXXX D15 - D0 (RDY/BSY) 27
EWDS 1 00 00XXXXXX — High-Z 11
TABLE 1-4: INSTRUCTION SET FOR 93LC56: ORG = 0 (X 8 ORGANIZATION)
Req. CLK
Instruction SB Opcode Address Data In Data Out
Cycles
READ 1 10 X A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 — D7 - D0 20
EWEN 1 00 11XXXXXXX — High-Z 12
ERASE 1 11 X A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 — (RDY/BSY) 12
ERAL 1 00 10XXXXXXX — (RDY/BSY) 12
WRITE 1 01 X A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 D7 - D0 (RDY/BSY) 20
WRAL 1 00 01XXXXXXX D7 - D0 (RDY/BSY) 20
EWDS 1 00 00XXXXXXX — High-Z 12
DS21712B-page 4 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
93LC46/56/66
TABLE 1-5: INSTRUCTION SET FOR 93LC66: ORG = 1 (X 16 ORGANIZATION)
Req. CLK
Instruction SB Opcode Address Data In Data Out
Cycles
READ 1 10 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 — D15 - D0 27
EWEN 1 00 11XXXXXX — High-Z 11
ERASE 1 11 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 — (RDY/BSY) 11
ERAL 1 00 10XXXXXX — (RDY/BSY) 11
WRITE 1 01 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 D15 - D0 (RDY/BSY) 27
WRAL 1 00 01XXXXXX D15 - D0 (RDY/BSY) 27
EWDS 1 00 00XXXXXX — High-Z 11
TABLE 1-6: INSTRUCTION SET FOR 93LC66: ORG = 0 (X 8 ORGANIZATION)
Req. CLK
Instruction SB Opcode Address Data In Data Out
Cycles
READ 1 10 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 — D7 - D0 20
EWEN 1 00 11XXXXXXX — High-Z 12
ERASE 1 11 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 — (RDY/BSY) 12
ERAL 1 00 10XXXXXXX — (RDY/BSY) 12
WRITE 1 01 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 D7 - D0 (RDY/BSY) 20
WRAL 1 00 01XXXXXXX D7 - D0 (RDY/BSY) 20
EWDS 1 00 00XXXXXXX — High-Z 12
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21712B-page 5
93LC46/56/66
2.0 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION After power-up, the device is automatically in the
EWDS mode. Therefore, an EWEN instruction must be
When the ORG pin is connected to VCC, the (x16) performed before any ERASE or WRITE instruction can
organization is selected. When it is connected to be executed.
ground, the (x8) organization is selected. Instruc-
tions, addresses and write data are clocked into the 2.4 Read
DI pin on the rising edge of the clock (CLK). The DO
pin is normally held in a high-Z state except when The READ instruction outputs the serial data of the
reading data from the device, or when checking the addressed memory location on the DO pin. A dummy
Ready/Busy status during a programming operation. zero bit precedes the 16-bit (x16 organization) or 8-bit
The Ready/Busy status can be verified during an (x8 organization) output string. The output data bits will
erase/write operation by polling the DO pin; DO low toggle on the rising edge of the CLK and are stable
indicates that programming is still in progress, while after the specified time delay (TPD). Sequential read is
DO high indicates the device is ready. The DO will possible when CS is held high. The memory data will
enter the high-Z state on the falling edge of the CS. automatically cycle to the next register and output
sequentially.
2.1 Start Condition
2.5 Erase/Write Enable and Disable
The Start bit is detected by the device if CS and DI are
both high with respect to the positive edge of CLK for
(EWEN, EWDS)
the first time. The 93LC46/56/66 power up in the Erase/Write Disable
Before a Start condition is detected, CS, CLK and DI (EWDS) state. All programming modes must be
may change in any combination (except to that of a preceded by an Erase/Write Enable (EWEN) instruction.
Start condition), without resulting in any device opera- Once the EWEN instruction is executed, programming
tion (Read, Write, Erase, EWEN, EWDS, ERAL and remains enabled until an EWDS instruction is executed
WRAL). As soon as CS is high, the device is no longer or VCC is removed from the device. To protect against
in the Standby mode. accidental data disturb, the EWDS instruction can be
used to disable all erase/write functions and should
An instruction following a Start condition will only be
follow all programming operations. Execution of a READ
executed if the required amount of opcode, address
instruction is independent of both the EWEN and EWDS
and data bits for any particular instruction is clocked in.
instructions.
After execution of an instruction (i.e., clock in or out of
the last required address or data bit) CLK and DI 2.6 Erase
become “don't care” bits until a new Start condition is
detected. The ERASE instruction forces all data bits of the speci-
fied address to the logical “1” state. CS is brought low
2.2 Data In/Data Out (DI/DO) following the loading of the last address bit. This falling
edge of the CS pin initiates the self-timed programming
It is possible to connect the Data In and Data Out pins cycle.
together. However, with this configuration it is possible
The DO pin indicates the Ready/Busy status of the
for a “bus conflict” to occur during the “dummy zero”
device if CS is brought high after a minimum of 250 ns
that precedes the read operation, if A0 is a logic high
low (TCSL). DO at logical “0” indicates that program-
level. Under such a condition the voltage level seen at
ming is still in progress. DO at logical “1” indicates that
Data Out is undefined and will depend upon the relative
the register at the specified address has been erased
impedances of Data Out and the signal source driving
and the device is ready for another instruction.
A0. The higher the current sourcing capability of A0,
the higher the voltage at the Data Out pin. The erase cycle takes 4 ms per word typical.
2.3 Data Protection
During power-up, all programming modes of operation
are inhibited until VCC has reached a level greater than
1.4V. During power-down, the source data protection
circuitry acts to inhibit all programming modes when
VCC has fallen below 1.4V at nominal conditions.
The EWEN and EWDS commands give additional
protection against accidentally programming during
normal operation.
DS21712B-page 6 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
93LC46/56/66
2.7 Write The DO pin indicates the Ready/Busy status of the
device if CS is brought high after a minimum of 250 ns
The WRITE instruction is followed by 16 bits (or by 8 low (TCSL) and before the entire write cycle is complete.
bits) of data which are written into the specified
address. After the last data bit is put on the DI pin, The ERAL cycle takes (8 ms typical).
CS must be brought low before the next rising edge
of the CLK clock. This falling edge of CS initiates the 2.9 Write All (WRAL)
self-timed auto-erase and programming cycle.
The WRAL instruction will write the entire memory array
The DO pin indicates the Ready/Busy status of the with the data specified in the command. The WRAL
device if CS is brought high after a minimum of 250 ns cycle is completely self-timed and commences at the
low (TCSL) and before the entire write cycle is complete. falling edge of the CS. Clocking of the CLK pin is not
DO at logical “0” indicates that programming is still in necessary after the device has entered the self clock-
progress. DO at logical “1” indicates that the register at ing mode. The WRAL command does include an auto-
the specified address has been written with the data matic ERAL cycle for the device. Therefore, the WRAL
specified and the device is ready for another instruction does not require an ERAL instruction but the
instruction. chip must be in the EWEN status. The WRAL instruction
The write cycle takes 4 ms per word typical. is ensured at 5V ±10%.
The DO pin indicates the Ready/Busy status of the
2.8 Erase All (ERAL) device if CS is brought high after a minimum of 250 ns
low (Tcsl).
The ERAL instruction will erase the entire memory array
to the logical “1” state. The ERAL cycle is identical to The WRAL cycle takes 16 ms typical.
the ERASE cycle except for the different opcode. The
ERAL cycle is completely self-timed and commences
at the falling edge of the CS. Clocking of the CLK pin is
not necessary after the device has entered the self
clocking mode. The ERAL instruction is ensured at 5V
±10%.
FIGURE 2-1: READ TIMING
CS
CLK
DI 1 1 0 An ••• A0
DO High-Z
0 Dx ••• D0 Dx ••• D0 Dx ••• D0
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21712B-page 7
93LC46/56/66
FIGURE 2-2: EWEN TIMING
CS
1 0 0 1 1 X ••• X
DI
FIGURE 2-3: EWDS TIMING
6
CS
CLK
DI 1 0 0 0 0 X ••• X
FIGURE 2-4: WRITE TIMING
6
CS
CLK
DI 1 0 1 An ••• A0 Dx ••• D0
11
High-Z
DO Busy Ready
12
DS21712B-page 8 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
93LC46/56/66
FIGURE 2-5: WRAL TIMING
6
CS
CLK
DI 1 0 0 0 1 X ••• X Dx ••• D0
11 10
High-Z Busy
DO Ready
High-Z
14
Ensured by Characterization at VCC = 4.5V to +5.5V.
FIGURE 2-6: ERASE TIMING
6
CS
Check Status
CLK
DI 1 1 1 An An-1 An-2 ••• A0
11 10
High-Z Busy
DO Ready
High-Z
12
FIGURE 2-7: ERAL TIMING
6
CS
Check Status
CLK
DI 1 0 0 1 0 X ••• X
11 10
High-Z
DO Busy Ready
High-Z
Ensured by Characterization at Vcc = 4.5V to +5.5V. 13
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21712B-page 9
93LC46/56/66
3.0 PIN DESCRIPTION
The descriptions of the pins are listed in Table 3-1.
TABLE 3-1: PIN FUNCTION TABLE
ROTATED
Name PDIP SOIC Description
TSSOP
CS 1 1 3 Chip Select
CLK 2 2 4 Serial Data Clock
DI 3 3 5 Serial Data Input
DO 4 4 6 Serial Data Output
VSS 5 5 7 Ground
ORG 6 6 8 Memory Configuration
NU 7 7 1 Not Utilized
Vcc 8 8 2 +1.8V to 5.5V Power Supply
3.1 Chip Select (CS) Note: CS must go low between consecutive
A high level selects the device. A low level deselects instructions.
the device and forces it into Standby mode. However, a
programming cycle which is already initiated and/or in 3.3 Data In (DI)
progress will be completed, regardless of the CS input
Data In is used to clock in a Start bit, opcode, address
signal. If CS is brought low during a program cycle, the
and data synchronously with the CLK input.
device will go into Standby mode as soon as the
programming cycle is completed.
3.4 Data Out (DO)
CS must be low for 250 ns minimum (TCSL) between
consecutive instructions. If CS is low, the internal Data Out is used in the Read mode to output data syn-
control logic is held in a Reset status. chronously with the CLK input (TPD after the positive
edge of CLK).
3.2 Serial Clock (CLK) This pin also provides Ready/Busy status information
during erase and write cycles. Ready/Busy status infor-
The serial clock is used to synchronize the communica-
mation is available on the DO pin if CS is brought high
tion between a master device and the 93LC46/56/66.
after being low for minimum chip select low time (TCSL)
Opcode, address and data bits are clocked in on the
and an erase or write operation has been initiated.
positive edge of CLK. Data bits are also clocked out on
the positive edge of CLK. The Status signal is not available on DO, if CS is held
low or high during the entire write or erase cycle. In all
CLK can be stopped anywhere in the transmission
other cases DO is in the High-Z mode. If status is
sequence (at high or low level) and can be continued
checked after the write/erase cycle, a pull-up resistor
anytime with respect to clock high time (TCKH) and
on DO is required to read the Ready signal.
clock low time (TCKL). This gives the controlling master
freedom in preparing opcode, address and data.
3.5 Organization (ORG)
CLK is a “don't care” if CS is low (device deselected). If
CS is high, but Start condition has not been detected, When ORG is connected to VCC, the (x16) memory
any number of clock cycles can be received by the organization is selected. When ORG is tied to VSS, the
device without changing its status (i.e., waiting for Start (x8) memory organization is selected. ORG can only be
condition). floated for clock speeds of 1 MHz or less for the (x16)
CLK cycles are not required during the self-timed write memory organization. For clock speeds greater than
(i.e., auto erase/write) cycle. 1 MHz, ORG must be tied to VCC or VSS.
After detection of a Start condition the specified number
of clock cycles (respectively low-to-high transitions of
CLK) must be provided. These clock cycles are required
to clock in all required opcode, address and data bits
before an instruction is executed (see instruction set
truth table). CLK and DI then become “don't care” inputs
waiting for a new Start condition to be detected.
DS21712B-page 10 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
93LC46/56/66
4.0 PACKAGING INFORMATION
4.1 Package Marking Information
8-Lead PDIP (300 mil) Example:
XXXXXXXX 93LC46
XXXXXNNN I/PNNN
YYWW YYWW
8-Lead SOIC (150 mil) Example:
XXXXXXXX 93LC46
XXXXYYWW I/SNYYWW
NNN NNN
8-Lead Rotated SOIC (150 mil) Example:
XXXXXXXX 93LC46X
XXXXYYWW I/SNYYWW
NNN NNN
Legend: XX...X Customer specific information*
YY Year code (last 2 digits of calendar year)
WW Week code (week of January 1 is week ‘01’)
NNN Alphanumeric traceability code
Note: In the event the full Microchip part number cannot be marked on one line, it will
be carried over to the next line thus limiting the number of available characters
for customer specific information.
* Standard OTP marking consists of Microchip part number, year code, week code, and traceability code.
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21712B-page 11
93LC46/56/66
8-Lead Plastic Dual In-line (P) – 300 mil (PDIP)
E1
n 1
A A2
L
c
A1
β B1
p
eB B
Units INCHES* MILLIMETERS
Dimension Limits MIN NOM MAX MIN NOM MAX
Number of Pins n 8 8
Pitch p .100 2.54
Top to Seating Plane A .140 .155 .170 3.56 3.94 4.32
Molded Package Thickness A2 .115 .130 .145 2.92 3.30 3.68
Base to Seating Plane A1 .015 0.38
Shoulder to Shoulder Width E .300 .313 .325 7.62 7.94 8.26
Molded Package Width E1 .240 .250 .260 6.10 6.35 6.60
Overall Length D .360 .373 .385 9.14 9.46 9.78
Tip to Seating Plane L .125 .130 .135 3.18 3.30 3.43
Lead Thickness c .008 .012 .015 0.20 0.29 0.38
Upper Lead Width B1 .045 .058 .070 1.14 1.46 1.78
Lower Lead Width B .014 .018 .022 0.36 0.46 0.56
Overall Row Spacing § eB .310 .370 .430 7.87 9.40 10.92
Mold Draft Angle Top α 5 10 15 5 10 15
Mold Draft Angle Bottom β 5 10 15 5 10 15
* Controlling Parameter
§ Significant Characteristic
Notes:
Dimensions D and E1 do not include mold flash or protrusions. Mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed
.010” (0.254mm) per side.
JEDEC Equivalent: MS-001
Drawing No. C04-018
DS21712B-page 12 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
93LC46/56/66
8-Lead Plastic Small Outline (SN) – Narrow, 150 mil (SOIC)
E1
D
2
B n 1
h α
45×
c
A A2
f
β L A1
Units INCHES* MILLIMETERS
Dimension Limits MIN NOM MAX MIN NOM MAX
Number of Pins n 8 8
Pitch p .050 1.27
Overall Height A .053 .061 .069 1.35 1.55 1.75
Molded Package Thickness A2 .052 .056 .061 1.32 1.42 1.55
Standoff § A1 .004 .007 .010 0.10 0.18 0.25
Overall Width E .228 .237 .244 5.79 6.02 6.20
Molded Package Width E1 .146 .154 .157 3.71 3.91 3.99
Overall Length D .189 .193 .197 4.80 4.90 5.00
Chamfer Distance h .010 .015 .020 0.25 0.38 0.51
Foot Length L .019 .025 .030 0.48 0.62 0.76
Foot Angle f 0 4 8 0 4 8
Lead Thickness c .008 .009 .010 0.20 0.23 0.25
Lead Width B .013 .017 .020 0.33 0.42 0.51
Mold Draft Angle Top α 0 12 15 0 12 15
Mold Draft Angle Bottom β 0 12 15 0 12 15
* Controlling Parameter
§ Significant Characteristic
Notes:
Dimensions D and E1 do not include mold flash or protrusions. Mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed
.010” (0.254mm) per side.
JEDEC Equivalent: MS-012
Drawing No. C04-057
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21712B-page 13
93LC46/56/66
APPENDIX A: REVISION HISTORY
Revision B
Added note to page 1 header (Not recommended for
new designs).
Updated document format.
DS21712B-page 14 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
93LC46/56/66
ON-LINE SUPPORT SYSTEMS INFORMATION AND
Microchip provides on-line support on the Microchip UPGRADE HOT LINE
World Wide Web site. The Systems Information and Upgrade Line provides
The web site is used by Microchip as a means to make system users a listing of the latest versions of all of
files and information easily available to customers. To Microchip's development systems software products.
view the site, the user must have access to the Internet Plus, this line provides information on how customers
and a web browser, such as Netscape® or Microsoft® can receive the most current upgrade kits. The Hot Line
Internet Explorer. Files are also available for FTP Numbers are:
download from our FTP site. 1-800-755-2345 for U.S. and most of Canada, and
1-480-792-7302 for the rest of the world.
Connecting to the Microchip Internet
Web Site 042003
The Microchip web site is available at the following
URL:
www.microchip.com
The file transfer site is available by using an FTP
service to connect to:
ftp://ftp.microchip.com
The web site and file transfer site provide a variety of
services. Users may download files for the latest
Development Tools, Data Sheets, Application Notes,
User's Guides, Articles and Sample Programs. A vari-
ety of Microchip specific business information is also
available, including listings of Microchip sales offices,
distributors and factory representatives. Other data
available for consideration is:
• Latest Microchip Press Releases
• Technical Support Section with Frequently Asked
Questions
• Design Tips
• Device Errata
• Job Postings
• Microchip Consultant Program Member Listing
• Links to other useful web sites related to
Microchip Products
• Conferences for products, Development Systems,
technical information and more
• Listing of seminars and events
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21712B-page 15
93LC46/56/66
READER RESPONSE
It is our intention to provide you with the best documentation possible to ensure successful use of your Microchip prod-
uct. If you wish to provide your comments on organization, clarity, subject matter, and ways in which our documentation
can better serve you, please FAX your comments to the Technical Publications Manager at (480) 792-4150.
Please list the following information, and use this outline to provide us with your comments about this document.
To: Technical Publications Manager Total Pages Sent ________
RE: Reader Response
From: Name
Company
Address
City / State / ZIP / Country
Telephone: (_______) _________ - _________ FAX: (______) _________ - _________
Application (optional):
Would you like a reply? Y N
Device: 93LC46/56/66 Literature Number: DS21712B
Questions:
1. What are the best features of this document?
2. How does this document meet your hardware and software development needs?
3. Do you find the organization of this document easy to follow? If not, why?
4. What additions to the document do you think would enhance the structure and subject?
5. What deletions from the document could be made without affecting the overall usefulness?
6. Is there any incorrect or misleading information (what and where)?
7. How would you improve this document?
DS21712B-page 16 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
93LC46/56/66
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION SYSTEM
To order or obtain information, e.g., on pricing or delivery, refer to the factory or the listed sales office.
PART NO. X /XX XXX
Examples:
Device Temperature Package Pattern a) 93LC46-I/P: 1K, 128x8 or 64x16 Serial
Range EEPROM, PDIP package
b) 93LC46-I/SN: 1K, 128x8 or 64x16 Serial
EEPROM, SOIC package
Device 93LC46: 1K 2.5V Microwire Serial EEPROM
c) 93LC46T-I/SN: 1K, 128x8 or 64x16
93LC46X: 1K 2.5V Microwire Serial EEPROM in
Serial EEPROM, SOIC package, tape
alternate pinouts (SN package only)
and reel
93LC46T: 1K 2.5V Microwire Serial EEPROM
d) 93LC46X-I/SN: 1K, 128x8 or 64x16
(Tape and Reel)
Serial EEPROM, Rotated SOIC package
93LC46XT: 1K 2.5V Microwire Serial EEPROM
(Tape and Reel) e) 93LC56-I/P: 2K, 256x8 or 128x16 Serial
93LC56: 2K 2.5V Microwire Serial EEPROM EEPROM, PDIP package
93LC56X: 2K 2.5V Microwire Serial EEPROM in f) 93LC56-I/SN: 2K, 256x8 or 128x16
alternate pinouts (SN package only) Serial EEPROM, SOIC package
93LC56T: 2K 2.5V Microwire Serial EEPROM g) 93LC56T-I/SN: 2K, 256x8 or 128x16
(Tape and Reel) Serial EEPROM, SOIC package, tape
93LC56XT:2K 2.5V Microwire Serial EEPROM and reel
(Tape and Reel) h) 93LC56X-I/SN: 2K, 256x8 or 128x16
93LC66: 4K 2.5V Microwire Serial EEPROM Serial EEPROM, Rotated SOIC package
93LC66X: 4K 2.5V Microwire Serial EEPROM in i) 93LC66-I/P: 4K, 512x8 or 256x16 Serial
alternate pinouts (SN package only) EEPROM, PDIP package
93LC66T: 4K 2.5V Microwire Serial EEPROM
j) 93LC66-I/SN: 4K, 512x8 or 256x16
(Tape and Reel)
Serial EEPROM, SOIC package
93LC66XT: 4K 2.5V Microwire Serial EEPROM
(Tape and Reel) k) 93LC66T-I/SN: 4K, 512x8 or 256x16
Serial EEPROM, SOIC package, tape
and reel
Temperature I = -40°C to +85°C l) 93LC66X-I/SN: 4K, 512x8 or 256x16
Range Serial EEPROM, Rotated SOIC package
Package P = Plastic DIP (300 mil body), 8-lead
SN = Plastic SOIC (150 mil body), 8-lead
Sales and Support
Data Sheets
Products supported by a preliminary Data Sheet may have an errata sheet describing minor operational differences and
recommended workarounds. To determine if an errata sheet exists for a particular device, please contact one of the following:
1. Your local Microchip sales office
2. The Microchip Corporate Literature Center U.S. FAX: (480) 792-7277
3. The Microchip Worldwide Site (www.microchip.com)
Please specify which device, revision of silicon and Data Sheet (include Literature #) you are using.
New Customer Notification System
Register on our web site (www.microchip.com/cn) to receive the most current information on our products.
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21712B-page 17
93LC46/56/66
NOTES:
DS21712B-page 18 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
Note the following details of the code protection feature on Microchip devices:
• Microchip products meet the specification contained in their particular Microchip Data Sheet.
• Microchip believes that its family of products is one of the most secure families of its kind on the market today, when used in the
intended manner and under normal conditions.
• There are dishonest and possibly illegal methods used to breach the code protection feature. All of these methods, to our
knowledge, require using the Microchip products in a manner outside the operating specifications contained in Microchip’s Data
Sheets. Most likely, the person doing so is engaged in theft of intellectual property.
• Microchip is willing to work with the customer who is concerned about the integrity of their code.
• Neither Microchip nor any other semiconductor manufacturer can guarantee the security of their code. Code protection does not
mean that we are guaranteeing the product as “unbreakable.”
Code protection is constantly evolving. We at Microchip are committed to continuously improving the code protection features of our
products. Attempts to break Microchip’s code protection feature may be a violation of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act. If such acts
allow unauthorized access to your software or other copyrighted work, you may have a right to sue for relief under that Act.
Information contained in this publication regarding device Trademarks
applications and the like is intended through suggestion only
The Microchip name and logo, the Microchip logo, Accuron,
and may be superseded by updates. It is your responsibility to
dsPIC, KEELOQ, microID, MPLAB, PIC, PICmicro, PICSTART,
ensure that your application meets with your specifications.
PRO MATE, PowerSmart, rfPIC, and SmartShunt are
No representation or warranty is given and no liability is
registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated
assumed by Microchip Technology Incorporated with respect
in the U.S.A. and other countries.
to the accuracy or use of such information, or infringement of
patents or other intellectual property rights arising from such AmpLab, FilterLab, MXDEV, MXLAB, PICMASTER, SEEVAL,
use or otherwise. Use of Microchip’s products as critical SmartSensor and The Embedded Control Solutions Company
components in life support systems is not authorized except are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology
with express written approval by Microchip. No licenses are Incorporated in the U.S.A.
conveyed, implicitly or otherwise, under any intellectual Analog-for-the-Digital Age, Application Maestro, dsPICDEM,
property rights. dsPICDEM.net, dsPICworks, ECAN, ECONOMONITOR,
FanSense, FlexROM, fuzzyLAB, In-Circuit Serial
Programming, ICSP, ICEPIC, Migratable Memory, MPASM,
MPLIB, MPLINK, MPSIM, PICkit, PICDEM, PICDEM.net,
PICLAB, PICtail, PowerCal, PowerInfo, PowerMate,
PowerTool, rfLAB, rfPICDEM, Select Mode, Smart Serial,
SmartTel and Total Endurance are trademarks of Microchip
Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other countries.
SQTP is a service mark of Microchip Technology Incorporated
in the U.S.A.
All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their
respective companies.
© 2004, Microchip Technology Incorporated, Printed in the
U.S.A., All Rights Reserved.
Printed on recycled paper.
Microchip received ISO/TS-16949:2002 quality system certification for
its worldwide headquarters, design and wafer fabrication facilities in
Chandler and Tempe, Arizona and Mountain View, California in
October 2003. The Company’s quality system processes and
procedures are for its PICmicro® 8-bit MCUs, KEELOQ® code hopping
devices, Serial EEPROMs, microperipherals, nonvolatile memory and
analog products. In addition, Microchip’s quality system for the design
and manufacture of development systems is ISO 9001:2000 certified.
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21712B-page 19
WORLDWIDE SALES AND SERVICE
AMERICAS China - Beijing Singapore
Unit 706B 200 Middle Road
Corporate Office
Wan Tai Bei Hai Bldg. #07-02 Prime Centre
2355 West Chandler Blvd.
No. 6 Chaoyangmen Bei Str. Singapore, 188980
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Beijing, 100027, China Tel: 65-6334-8870 Fax: 65-6334-8850
Tel: 480-792-7200
Tel: 86-10-85282100 Taiwan
Fax: 480-792-7277
Fax: 86-10-85282104 Kaohsiung Branch
Technical Support: 480-792-7627
Web Address: www.microchip.com China - Chengdu 30F - 1 No. 8
Rm. 2401-2402, 24th Floor, Min Chuan 2nd Road
Atlanta Ming Xing Financial Tower Kaohsiung 806, Taiwan
3780 Mansell Road, Suite 130 No. 88 TIDU Street Tel: 886-7-536-4816
Alpharetta, GA 30022 Chengdu 610016, China Fax: 886-7-536-4817
Tel: 770-640-0034 Tel: 86-28-86766200 Taiwan
Fax: 770-640-0307 Fax: 86-28-86766599 Taiwan Branch
Boston China - Fuzhou 11F-3, No. 207
2 Lan Drive, Suite 120 Unit 28F, World Trade Plaza Tung Hua North Road
Westford, MA 01886 No. 71 Wusi Road Taipei, 105, Taiwan
Tel: 978-692-3848 Fuzhou 350001, China Tel: 886-2-2717-7175 Fax: 886-2-2545-0139
Fax: 978-692-3821 Tel: 86-591-7503506 Taiwan
Chicago Fax: 86-591-7503521 Taiwan Branch
333 Pierce Road, Suite 180 China - Hong Kong SAR 13F-3, No. 295, Sec. 2, Kung Fu Road
Itasca, IL 60143 Unit 901-6, Tower 2, Metroplaza Hsinchu City 300, Taiwan
Tel: 630-285-0071 223 Hing Fong Road Tel: 886-3-572-9526
Fax: 630-285-0075 Kwai Fong, N.T., Hong Kong Fax: 886-3-572-6459
Dallas Tel: 852-2401-1200
Fax: 852-2401-3431 EUROPE
16200 Addison Road, Suite 255
Addison Plaza China - Shanghai Austria
Addison, TX 75001 Room 701, Bldg. B Durisolstrasse 2
Tel: 972-818-7423 Far East International Plaza A-4600 Wels
Fax: 972-818-2924 No. 317 Xian Xia Road Austria
Shanghai, 200051 Tel: 43-7242-2244-399
Detroit Tel: 86-21-6275-5700 Fax: 43-7242-2244-393
Tri-Atria Office Building Fax: 86-21-6275-5060 Denmark
32255 Northwestern Highway, Suite 190 Regus Business Centre
Farmington Hills, MI 48334 China - Shenzhen
Rm. 1812, 18/F, Building A, United Plaza Lautrup hoj 1-3
Tel: 248-538-2250 Ballerup DK-2750 Denmark
Fax: 248-538-2260 No. 5022 Binhe Road, Futian District
Shenzhen 518033, China Tel: 45-4420-9895 Fax: 45-4420-9910
Kokomo Tel: 86-755-82901380 France
2767 S. Albright Road Fax: 86-755-8295-1393 Parc d’Activite du Moulin de Massy
Kokomo, IN 46902 China - Shunde 43 Rue du Saule Trapu
Tel: 765-864-8360 Batiment A - ler Etage
Room 401, Hongjian Building, No. 2
Fax: 765-864-8387 91300 Massy, France
Fengxiangnan Road, Ronggui Town, Shunde
Los Angeles District, Foshan City, Guangdong 528303, China Tel: 33-1-69-53-63-20
Tel: 86-757-28395507 Fax: 86-757-28395571 Fax: 33-1-69-30-90-79
25950 Acero St., Suite 200
Mission Viejo, CA 92691 China - Qingdao Germany
Tel: 949-462-9523 Steinheilstrasse 10
Rm. B505A, Fullhope Plaza,
Fax: 949-462-9608 D-85737 Ismaning, Germany
No. 12 Hong Kong Central Rd.
Tel: 49-89-627-144-0
San Jose Qingdao 266071, China
Fax: 49-89-627-144-44
1300 Terra Bella Avenue Tel: 86-532-5027355 Fax: 86-532-5027205
Italy
Mountain View, CA 94043 India
Via Salvatore Quasimodo, 12
Tel: 650-215-1444 Divyasree Chambers
20025 Legnano (MI)
Fax: 650-961-0286 1 Floor, Wing A (A3/A4)
Milan, Italy
No. 11, O’Shaugnessey Road
Toronto Tel: 39-0331-742611
Bangalore, 560 025, India
6285 Northam Drive, Suite 108 Fax: 39-0331-466781
Tel: 91-80-22290061 Fax: 91-80-22290062
Mississauga, Ontario L4V 1X5, Canada Netherlands
Japan
Tel: 905-673-0699 Waegenburghtplein 4
Fax: 905-673-6509 Yusen Shin Yokohama Building 10F
NL-5152 JR, Drunen, Netherlands
3-17-2, Shin Yokohama, Kohoku-ku,
Tel: 31-416-690399
Yokohama, Kanagawa, 222-0033, Japan
ASIA/PACIFIC Fax: 31-416-690340
Tel: 81-45-471- 6166 Fax: 81-45-471-6122
United Kingdom
Australia Korea
505 Eskdale Road
Microchip Technology Australia Pty Ltd 168-1, Youngbo Bldg. 3 Floor
Winnersh Triangle
Unit 32 41 Rawson Street Samsung-Dong, Kangnam-Ku
Wokingham
Epping 2121, NSW Seoul, Korea 135-882
Berkshire, England RG41 5TU
Sydney, Australia Tel: 82-2-554-7200 Fax: 82-2-558-5932 or
Tel: 44-118-921-5869
Tel: 61-2-9868-6733 82-2-558-5934
Fax: 44-118-921-5820
Fax: 61-2-9868-6755
07/12/04
DS21712B-page 20 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 93C86Dokument20 Seiten93C86cgmannerheimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8K/16K 5.0V Microwire Serial EEPROM: Features: Package TypesDokument20 Seiten8K/16K 5.0V Microwire Serial EEPROM: Features: Package Typesfarhood ranjbarkhanghahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 93LC66A/B: 4K 2.5V Microwire Serial EEPROMDokument12 Seiten93LC66A/B: 4K 2.5V Microwire Serial EEPROMinsomnium86Noch keine Bewertungen
- 24AA64/24LC64/24FC64: 64K I C Serial EEPROMDokument28 Seiten24AA64/24LC64/24FC64: 64K I C Serial EEPROMJuan Luis Pineda GonzálezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2K 5.0V Automotive Temperature Microwire Serial EEPROM: Features Package TypeDokument12 Seiten2K 5.0V Automotive Temperature Microwire Serial EEPROM: Features Package TypeDanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- AT93CXXDokument15 SeitenAT93CXXcallkalaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data SheetDokument12 SeitenData SheetPrasetyo Muhammad SaktiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 256 Bit/1K 5.0V CMOS Serial EEPROM: Features Package TypeDokument8 Seiten256 Bit/1K 5.0V CMOS Serial EEPROM: Features Package TypeAgustin AndrokaitesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24AA00/24LC00/24C00: 128-Bit I C Bus Serial EEPROMDokument34 Seiten24AA00/24LC00/24C00: 128-Bit I C Bus Serial EEPROMKhalid BenaribaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1K 5.0V Microwire Serial EEPROM: Features Block DiagramDokument12 Seiten1K 5.0V Microwire Serial EEPROM: Features Block Diagraminsomnium86Noch keine Bewertungen
- 93 LC 46 BDokument12 Seiten93 LC 46 Bwabp_23Noch keine Bewertungen
- 24LC21 1K 2.5V Dual Mode I2C Serial EEPROMDokument12 Seiten24LC21 1K 2.5V Dual Mode I2C Serial EEPROMVictor TruccoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24l1026i Memoria EEPROM 1024kDokument28 Seiten24l1026i Memoria EEPROM 1024kMarta_d_eNoch keine Bewertungen
- 93C66Dokument12 Seiten93C66Alex AlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24C32Dokument12 Seiten24C32SilviuCocoloșNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24AA02/24LC02B: 2KI C Serial EEPROMDokument32 Seiten24AA02/24LC02B: 2KI C Serial EEPROMhanifNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24LC04B PDFDokument22 Seiten24LC04B PDFEddy RosarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24AA52/24LCS52: 2K 2.2V I C Serial EEPROM With Software Write-ProtectDokument24 Seiten24AA52/24LCS52: 2K 2.2V I C Serial EEPROM With Software Write-Protecta4rfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24AA16/24LC16B: 16K I C Serial EEPROMDokument25 Seiten24AA16/24LC16B: 16K I C Serial EEPROMDaniel VásquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ic PDFDokument36 SeitenIc PDFdharamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24AA02/24LC02B: 2KI C Serial EEPROMDokument24 Seiten24AA02/24LC02B: 2KI C Serial EEPROMMayk OzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bus Serial EEPROMDokument12 SeitenBus Serial EEPROMMatiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24FC1025 EepromDokument28 Seiten24FC1025 EepromAnirudh ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24aa512 Mic PDFDokument28 Seiten24aa512 Mic PDFkt2018Noch keine Bewertungen
- 24aa515, 24LC515, 24FC515Dokument20 Seiten24aa515, 24LC515, 24FC515dorudNoch keine Bewertungen
- 32K 5.0V I C Smart Serial EEPROM: Features Package TypesDokument12 Seiten32K 5.0V I C Smart Serial EEPROM: Features Package TypesRamon LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24AA1025 24LC1025 24FC1025 1024 Kbit I2C Serial EE-2853738Dokument32 Seiten24AA1025 24LC1025 24FC1025 1024 Kbit I2C Serial EE-2853738İbrahim DemircioğluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet PDFDokument26 SeitenDatasheet PDFNicoli LourençoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8K/16K 5.0V Microwire Serial EEPROM: FeaturesDokument12 Seiten8K/16K 5.0V Microwire Serial EEPROM: FeaturesStephensonNoch keine Bewertungen
- I2c EEPROM 24xx256 DsDokument28 SeitenI2c EEPROM 24xx256 DsRizwan AmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24 LC 256Dokument38 Seiten24 LC 256johnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24AA1025/24LC1025/24FC1025: 1024K I C Serial EEPROMDokument29 Seiten24AA1025/24LC1025/24FC1025: 1024K I C Serial EEPROMSudhagarSubbiyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Three-Wire Serial EEPROM: 1. FeaturesDokument17 SeitenThree-Wire Serial EEPROM: 1. FeatureskppsadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21711c PDFDokument24 Seiten21711c PDFAbdessamad EladakNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22131c PDFDokument24 Seiten22131c PDFAdilsonAmorimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24aa08 - 24lc08 Eeprom PDFDokument40 Seiten24aa08 - 24lc08 Eeprom PDFEdgar DauzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEPROM 24LC256 - Microchip PDFDokument28 SeitenEEPROM 24LC256 - Microchip PDFValdir DerlannNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16K I C Serial EEPROM Extended (M) Operating Temperatures: Number V Range Max. Clock Frequency Temp. RangesDokument22 Seiten16K I C Serial EEPROM Extended (M) Operating Temperatures: Number V Range Max. Clock Frequency Temp. RangeshcarcaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24AA16 24LC16B 24FC16 16K I2C Serial EEPROM 20001703PDokument49 Seiten24AA16 24LC16B 24FC16 16K I2C Serial EEPROM 20001703Pmarko.jojicoo777Noch keine Bewertungen
- Three-Wire Automotive Temperature Serial Eeproms: 1. FeaturesDokument14 SeitenThree-Wire Automotive Temperature Serial Eeproms: 1. FeaturesJose MisselNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 PDFDokument31 Seiten4 PDFAgus OrtizNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCP79410/MCP79411/MCP79412: I C™ Real-Time Clock/Calendar With EEPROM, SRAM, Unique ID and Battery SwitchoverDokument38 SeitenMCP79410/MCP79411/MCP79412: I C™ Real-Time Clock/Calendar With EEPROM, SRAM, Unique ID and Battery SwitchoverDaniel CortelettiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2K Microwire Compatible Serial EEPROM: 93AA56A/B/C, 93LC56A/B/C, 93C56A/B/CDokument30 Seiten2K Microwire Compatible Serial EEPROM: 93AA56A/B/C, 93LC56A/B/C, 93C56A/B/CAndrea MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24Lc08B/16B Modules: 8K/16K I C Serial Eeproms in Iso MicromodulesDokument12 Seiten24Lc08B/16B Modules: 8K/16K I C Serial Eeproms in Iso MicromodulesarminNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24lc512 DatasheetDokument27 Seiten24lc512 DatasheetLeonardo QuevedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22122a.book - 11AA02E48T-I-TT-MicrochipDokument2 Seiten22122a.book - 11AA02E48T-I-TT-MicrochipIori CharaNoch keine Bewertungen
- En25qa64a EonDokument68 SeitenEn25qa64a Eongbjhasd344Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Wire Serial EEPROM Smart Card Module: FeaturesDokument12 Seiten2-Wire Serial EEPROM Smart Card Module: FeaturesMaikol DominguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datashet Etron TechDokument54 SeitenDatashet Etron TechAndres OrjuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24C320-EP MicrochipTechnologyDokument12 Seiten24C320-EP MicrochipTechnologyMateus CorrêaNoch keine Bewertungen
- At25f512a 844895Dokument19 SeitenAt25f512a 844895mirage0706Noch keine Bewertungen
- 11aa02iud 1wire MicrochipDokument32 Seiten11aa02iud 1wire MicrochipManutenção eletrônicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TMC93LC46Dokument15 SeitenTMC93LC46Agustin AndrokaitesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24AA64/24LC64/24FC64: 64K I C™ Serial EEPROMDokument45 Seiten24AA64/24LC64/24FC64: 64K I C™ Serial EEPROMJuan Carlos CrespoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 32K 2.5V I C Serial EEPROM: Features Package TypesDokument12 Seiten32K 2.5V I C Serial EEPROM: Features Package Typesinsomnium86Noch keine Bewertungen
- 24LC08 PDFDokument30 Seiten24LC08 PDFJaime BarrancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 32K 5.0V I C Serial EEPROM: Features Package TypesDokument12 Seiten32K 5.0V I C Serial EEPROM: Features Package Typesinsomnium86Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Digital Electronics for TechniciansVon EverandPractical Digital Electronics for TechniciansBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Vdoc - Pub The Maple Handbook Maple V Release 3Dokument522 SeitenVdoc - Pub The Maple Handbook Maple V Release 3marceloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intelligent Data Analysis (BooksRack - Net) PDFDokument431 SeitenIntelligent Data Analysis (BooksRack - Net) PDFleonor bungaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lista Especial 31-08-2022Dokument36 SeitenLista Especial 31-08-2022Alejandra FerreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- ONEXAM Online Examination System Project SynopsisDokument4 SeitenONEXAM Online Examination System Project Synopsisbahubali king0% (1)
- CSEC Jan 2011 Paper 1Dokument8 SeitenCSEC Jan 2011 Paper 1R.D. KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MHW-N1964 Designing Healthcare Applications With NXPDokument111 SeitenMHW-N1964 Designing Healthcare Applications With NXPfrhuttonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Protocol Analyzer With Wireshark: March 2015Dokument18 SeitenNetwork Protocol Analyzer With Wireshark: March 2015Ziaul HaqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- DT-200 Bluewave2 Operators GuideDokument8 SeitenDT-200 Bluewave2 Operators GuideDragan KocijasevicNoch keine Bewertungen
- TM-3532 AVEVA Diagrams (14.1) Diagrams - PID Designer Rev 2.0Dokument208 SeitenTM-3532 AVEVA Diagrams (14.1) Diagrams - PID Designer Rev 2.0Adeniran Joshua100% (1)
- Mobile Print/Scan Guide For Brother Iprint&ScanDokument100 SeitenMobile Print/Scan Guide For Brother Iprint&ScanozarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimizing Cross-Dock Operations with Tabu SearchDokument7 SeitenOptimizing Cross-Dock Operations with Tabu Searchk5g83jg8hNoch keine Bewertungen
- IliosDokument883 SeitenIlioscolson_tksNoch keine Bewertungen
- d52541 PDFDokument37 Seitend52541 PDFskywalker crazyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uws Threat Hunting 101 White Paper PDFDokument25 SeitenUws Threat Hunting 101 White Paper PDFJacob StamperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Color Iqc / Color Imatch Installation NotesDokument3 SeitenColor Iqc / Color Imatch Installation NotesSohel NomanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robert Bosch Placement Pattern 2 - Freshers ChoiceDokument14 SeitenRobert Bosch Placement Pattern 2 - Freshers ChoicefresherschoiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apollo Roadmap and Test Plan For GTDDokument1 SeiteApollo Roadmap and Test Plan For GTDCristian GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computational GeometryDokument5 SeitenComputational GeometryZvonko TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weird Negative Float SituationsDokument15 SeitenWeird Negative Float SituationsSoham BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abandoned Cart Emails: A Data-Driven Guide To Recovering Lost SalesDokument37 SeitenAbandoned Cart Emails: A Data-Driven Guide To Recovering Lost SalesTochi Krishna AbhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.1 Mux 1Dokument6 Seiten8.1 Mux 1Maddy Trichy50% (2)
- JSE Certification 1 SyllabusDokument4 SeitenJSE Certification 1 SyllabusJohn P. GibsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Timescaledb: SQL Made Scalable For Time-Series Data: 1 BackgroundDokument7 SeitenTimescaledb: SQL Made Scalable For Time-Series Data: 1 BackgroundpokechoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mô Dem Quang TeleneticDokument2 SeitenMô Dem Quang TeleneticHongha ChauNoch keine Bewertungen
- RSA Archer 6.5 Platform User's Guide - 4Dokument182 SeitenRSA Archer 6.5 Platform User's Guide - 4veeshaalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kyle Norris: Office Equipment: Handyman EquipmentDokument1 SeiteKyle Norris: Office Equipment: Handyman EquipmentElizabeth ThorntonNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAPTCHA - Seminar ReportDokument30 SeitenCAPTCHA - Seminar Reportbsbharath198767% (3)
- Syllabus Advanced Systemverilog TrainingDokument12 SeitenSyllabus Advanced Systemverilog TrainingSudhir SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Create your own Sony Xperia FTF firmware files using XperiFirm and FlashToolGuideDokument6 SeitenCreate your own Sony Xperia FTF firmware files using XperiFirm and FlashToolGuidemagexworldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Client-Server Technology, Practices of The Practical LayerDokument4 SeitenClient-Server Technology, Practices of The Practical LayerResearch ParkNoch keine Bewertungen