Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Huawei 3900 Series Base Station Product Description
Hochgeladen von
Lê Hữu ÁiCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Huawei 3900 Series Base Station Product Description
Hochgeladen von
Lê Hữu ÁiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
3900 Series Base Station
Product Description
Issue 08
Date 2015-06-30
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2015. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior
written consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and
the customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be
within the purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specified in the contract, all statements,
information, and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees or
representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address: Huawei Industrial Base
Bantian, Longgang
Shenzhen 518129
People's Republic of China
Website: http://www.huawei.com
Email: support@huawei.com
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential i
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description Contents
Contents
1 Introduction.................................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 Overview ........................................................................................................................................................... 1
1.2 Benefits .............................................................................................................................................................. 3
2 Hardware Architecture ................................................................................................................. 5
2.1 Overview ........................................................................................................................................................... 5
2.2 Basic Modules ................................................................................................................................................... 6
2.2.1 BBU .......................................................................................................................................................... 6
2.2.2 RFU .......................................................................................................................................................... 6
2.2.3 RRU .......................................................................................................................................................... 7
2.2.4 AAU ......................................................................................................................................................... 9
2.3 BTS3900 (Ver.D) Cabinet................................................................................................................................ 12
2.4 BTS3900L (Ver.D) Cabinet ............................................................................................................................. 14
2.5 BTS3900AL (Ver.A) Cabinet .......................................................................................................................... 18
2.6 BTS3900A ....................................................................................................................................................... 20
2.7 BTS3900C ....................................................................................................................................................... 23
2.8 DBS3900 ......................................................................................................................................................... 25
2.8.1 APM30H (Ver.D)/ APM30H (Ver.E) Outdoor Power Cabinet ............................................................... 29
2.8.2 TP48600A Power Cabinet ...................................................................................................................... 31
2.8.3 TMC11H (Ver.D)/ TMC11H (Ver.E) Outdoor Transmission Cabinet .................................................... 32
2.8.4 IBBS20D Battery Cabinet ...................................................................................................................... 33
2.8.5 IBBS200T (Ver.D)/ IBBS200D (Ver.D)/ IBBS200T (Ver.E)/ IBBS200D (Ver.E) Battery Cabinet ....... 34
2.8.6 IBBS300D/IBBS300T Battery Cabinet.................................................................................................. 35
2.8.7 IBBS700D/IBBS700T Battery Cabinet.................................................................................................. 36
2.8.8 OMB (Ver.C) Outdoor Power Cabinet ................................................................................................... 37
2.8.9 IMB03 Power Subrack ........................................................................................................................... 39
2.8.10 Indoor Open Rack ................................................................................................................................ 39
2.8.11 Indoor Centralized Rack, (IFS06+IMB03)........................................................................................... 39
2.8.12 Outdoor Pole Support 06, (OPS06) ...................................................................................................... 40
2.8.13 IBC10 Cabinet (for Cloud BB) ............................................................................................................ 41
2.9 Macro Base Station + Distributed Base Station .............................................................................................. 43
3 Logical Structure ......................................................................................................................... 45
4 Operation and Maintenance ..................................................................................................... 47
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential ii
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description Contents
4.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................................... 47
4.2 O&M System Structure ................................................................................................................................... 47
5 Technical Specifications ............................................................................................................ 50
5.1 Input Power Specifications .............................................................................................................................. 50
5.2 Equipment Specifications ................................................................................................................................ 51
5.3 Environment Specifications ............................................................................................................................. 53
5.4 Standards.......................................................................................................................................................... 54
6 Acronyms and Abbreviations ................................................................................................... 57
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential iii
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 1 Introduction
1 Introduction
1.1 Overview
To keep abreast of rapidly advancing mobile communications technologies, mobile operators
are continually seeking partners who provide cutting-edge technologies to set up high-quality,
multimode-enabled, and future-oriented mobile networks efficiently and cost-effectively.
With this aim in mind, Huawei developed 3900 series base stations, which are designed based
on a high-performance platform and use an optimized hardware and software architecture.
These base stations can work in multiple modes due to their cutting-edge modular design.
They also have broad bandwidth and are eco-friendly and easily upgradeable.
Specifically, 3900 series base stations use the newly developed power amplifiers (PAs),
provide the temperature control function, and employ the innovated power saving technique.
In addition, by adopting the cutting-edge modular design, 3900 series base stations use
multimode modules with different appearances to meet requirements in various conditions.
Thanks to all these merits of 3900 series base stations, mobile operators can set up
high-quality, multimode-enabled, and future-oriented mobile networks and capital
expenditure (CAPEX) on site acquisition, capacity expansion, and environment protection can
be greatly reduced.
Different types of 3900 series base stations can be delivered on request because the newly
designed modules and auxiliary devices can be flexibly combined and configured.
Figure 1-1 shows the different types of 3900 series base stations.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 1
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 1 Introduction
Figure 1-1 3900 series base station types
This document focuses on the BTS3900, BTS3900A, BTS3900L, BTS3900AL, BTS3900C, and
DBS3900 only. For a description of the other types of 3900 series base stations, see the product
description for the base station in question.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 2
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 1 Introduction
1.2 Benefits
Smooth Evolution
Upgrading from Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) to Universal Mobile
Telecommunications System (UMTS) and then to Long Term Evolution (LTE) is easy thanks
to the following factors:
In SRAN7.0 or earlier: A BBU3900 is equipped with different boards, among which
some work in one mode and the others work in another mode. The BBU3900 can process
services for both of these modes. With two BBUs, the triple-mode application can be
achieved.
In SRAN8.0: The GSM, UMTS, and LTE modes share one BBU3900.
Developed with the Software-defined radio (SDR) technique, RF modules can work in
GU, GL, or UL dual-mode. SDR RF modules and single-mode RF modules can be
installed in the same cabinet to achieve multimode and multi-band applications.
Energy-Efficient and Eco-Friendly
Thanks to their small size and modular design, PAs do not take up much space in the
equipment room and power resources are saved with the new power-saving technique.
The following measures also help save energy:
RF channels are blocked and PA voltage is adjusted if the downlink load reaches a preset
threshold.
The power supply unit (PSU) shuts down if the base station is provided with sufficient
power.
The temperature control function controls board temperature, outdoor cabinets use a
direct ventilation system, and RRUs adopt the natural heat dissipation mechanism.
Low CAPEX
In terms of the CAPEX for devices
3900 series base stations use one set of multimode devices to support multimode
applications.
An external reference clock and transmission resources are shared across modes on a
3900 series base station, reducing the CAPEX for transmission resources and external
clock sources.
Various types of radio frequency (RF) modules are introduced, for example,
software-defined radio (SDR) RF modules supporting antenna-sharing, dual-transmitter
RF modules supporting the multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) technology, and
single-transmitter RF modules with high power and large capacity.
The GU or GL refarming feature is introduced to facilitate the evolution from GSM to
UMTS, and LTE and eventually to save the CAPEX for evolution.
In terms of operation and maintenance (O&M), different modes on a single 3900 series base
station share the same auxiliary devices and are managed by the same network management
system, which greatly reduces O&M costs. The O&M manpower required is also reduced,
because 3900 series base stations are easy to install and maintain and it is easy to expand their
capacities.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 3
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 1 Introduction
High Transmission Reliability and High Board Performance
The following features are introduced to ensure high transmission reliability and high board
performance:
Support for the Huawei SingleBTS platform
Support for Co-Radio Resource Management (Co-RRM), Co-Transmission Resource
Management (Co-TRM), Co-Operation and Management (Co-OAM), and Co-Radio
Network Plan&Radio Network Optimization (Co-RNP&RNO)
Support for route backup. Transmission paths can be switched over to protect
high-priority service data.
Support for the backup of important boards and power modules
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 4
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
2 Hardware Architecture
2.1 Overview
3900 series base stations are classified into macro base stations, and LampSite. Each type of
base station is applicable to a specific scenario, which enables operators to efficiently set up a
network with low CAPEX. 3900 series base stations are universal and different types of base
stations can be configured by flexibly combining basic modules and various cabinets.
Classification Scenario Type Module Cabinet
Macro base Indoor BTS3900 BBU+RFU BTS3900 (Ver.D) or
stations IMS06
BTS3900L BBU+RFU BTS3900L (Ver.D) or
IMS06
Outdoor BTS3900A BBU+RFU APM30H (Ver.D)
/APM30H (Ver.E) or
TMC11H (Ver.D)
/TMC11H (Ver.E)
and RFC
BTS3900AL BBU+RFU BTS3900AL (Ver.A)
BTS3900C BBU+RRU OMB (Ver.C)
Distributed DBS3900 BBU+RRU APM30H (Ver.D)
base stations BBU+AAU /APM30H (Ver.E),
TMC11H (Ver.D)
/TMC11H (Ver.E),
OMB (Ver.C), or
TP48600A
(TP48600A-H17B1)
LampSite - DBS3900 BBU+RHUB APM30H (Ver.D)
LampSite +pRRU /APM30H (Ver.E),
TMC11H (Ver.D)
/TMC11H (Ver.E),
OMB (Ver.C), or
TP48600A
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 5
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
NOTE
This document focuses on the BTS3900, BTS3900A, BTS3900L, BTS3900AL, BTS3900C and
DBS3900 only. For details about the other base stations, see the product description of the base station in
question.
2.2 Basic Modules
3900 series base stations have a modular design. The basic modules are the baseband unit
(BBU) and radio frequency module which includes radio frequency unit (RFU), remote radio
unit (RRU), and active antenna unit (AAU). The BBU uses common public radio interfaces
(CPRIs) and electrical or optical cables to communicate with the RFUs or RRUs.
2.2.1 BBU
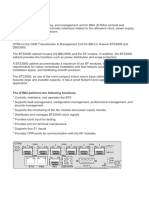
The BBU (BBU3900 and BBU3910) is a baseband control unit and performs the following
functions:
Centrally manages the entire base station, including operation and maintenance,
signaling processing, and the system clock.
Processes uplink and downlink baseband signals.
Provides physical ports, which are used to connect the base station to the transport
network for information exchange; a maintenance channel, which is used to connect the
BBU to the operation and maintenance center (OMC); CPRI ports for communication
with RF modules; and ports for communication with environment monitoring devices.
Figure 2-1 shows the slot layout of a BBU.
Figure 2-1 Slot layout of a BBU
NOTE
For details about the BBU3900 and BBU3910, see the BBU3900 Description and BBU3910
Description, respectively.
2.2.2 RFU
RFUs can be used in a macro base station. The RFU modulates and demodulates baseband
and RF signals, processes data, amplifies power, and conducts VSWR detection.
RFUs fall into the following three types:
Multimode modules: MRFU, MRFUd, MRFUdw, MRFUe
GSM modules: GRFU, DRFU
UMTS modules: WRFU, WRFUa, WRFUd, WRFUe
LTE modules: CRFUd, LRFU, LRFUe
Figure 2-2 shows the appearance of an RFU.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 6
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-2 Appearance of an RFU
The MRFUd, MRFUe, CRFUd, WRFUd, and WRFUe can only be used in a BTS3900
(Ver.C)/BTS3900 (Ver.D), BTS3900L (Ver.C)/BTS3900L (Ver.D), BTS3900A
(Ver.C)/BTS3900A (Ver.D)/BTS3900A (Ver.E), or BTS3900AL (Ver.A) cabinet. The other
types of RFU modules can be used in any cabinet type.
NOTE
For the specifications and parameters of each type of RFU, see the description of the RFU in
question.
GRFU, MRFU, MRFUd, MRFUe, WRFU, WRFUa, WRFUd, WRFUe, CRFUd, and LRFUe
modules have the same appearance but can be identified by different silkscreens.
2.2.3 RRU
As an RF component on a distributed base station, the RRU modulates and demodulates
baseband and RF signals, combines and divides baseband and RF signals, and processes data.
RRUs can be installed on a pole, wall, or stand. They can also be installed close to antennas to
shorten the feeder length, reduce feeder loss, and improve system coverage.
RRUs fall into the following three types:
Multimode modules: RRU3908, RRU3926, RRU3928, RRU3929, RRU3936, RRU3938,
RRU3939, RRU3942, RRU3952, RRU3953, RRU3953w, RRU3959, RRU3959w,
RRU3961, RRU3965, RRU3965d, RRU3952m, RRU3808, RRU3832, pRRU3901,
pRRU3902
GSM modules: RRU3004, RRU3008
UMTS modules: RRU3804, RRU3806, RRU3801E, RRU3824, RRU3826, RRU3828,
RRU3829, RRU3838, RRU3839
LTE modules: RRU3201, RRU3203, RRU3220, RRU3220E, RRU3221, RRU3222,
RRU3229, RRU3240, RRU3260, RRU3262, RRU3268, RRU3269, RRU3642,
RRU3841
RHUB3908
Figure 2-3 shows the appearance of an RRU.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 7
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-3 Appearance of an RRU
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 8
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
The RRU3229, RRU3841, RRU3829, RRU3929, RRU3942, and RRU3961 are recommended
for use in APM30H (Ver.C)/APM30H (Ver.D) or TMC11H (Ver.C)/TMC11H (Ver.D) cabinets.
When the RRU3229, RRU3841, RRU3829, RRU3929, RRU3942, or RRU3961 is used in an
APM30H (Ver.B) or TMC11H (Ver.B) cabinet, some auxiliary devices must be reconstructed.
Other types of RRUs can be used in any cabinet type.
NOTE
The preceding figure shows an RRU3804 of an old version, an RRU3804 of a new version, an
RRU3806 of an old version, and an RRU3806 of a new version.
For the specifications and parameters of each type of RRU, see the description of the RRU in
question.
2.2.4 AAU
The AAU is a new type of RF module. An AAU module connects to baseband signal
processing boards using CPRI ports and incorporates the functions of RF modules and
conventional antennas, which simplifies site deployment.
AAUs fall into the following five types: AAU3902, AAU3910, AAU3911, AAU3920,
AAU3940.
Figure 2-4 shows the exterior of an AAU3902.
Figure 2-4 Exterior of an AAU3902
(1) Front (2)Rear
Figure 2-5 shows the appearance of an AAU3910.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 9
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-5 Appearance of the AAU3910
(1) Front (2) Rear
Figure 2-6 shows the appearance of the AAU3911.
Figure 2-6 Appearance of the AAU3911
(1) Front (2) Rear
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 10
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-7 shows the appearance of the AAU3920.
Figure 2-7 Appearance of the AAU3920
(1)Front (2)Rear
Figure 2-8 shows the appearance of the AAU3940.
Figure 2-8 Appearance of the AAU3940
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 11
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
2.3 BTS3900 (Ver.D) Cabinet
BTS33900 (Ver.D) cabinets house indoor macro base stations because these cabinets have a
large capacity and a small size, and are easy to expand the capacities.
BTS3900 (Ver.D) cabinets support -48 V DC and AC power input.
Figure 2-9 shows the internal structure of a BTS3900 (Ver.D) cabinet supporting -48 V DC
power input.
Figure 2-9 BTS3900 (Ver.D) cabinet supporting –48 V DC power input
BTS33900 (Ver.D) cabinet can be stacked on IMS06 in the AC scenarios that require a large
configuration. Figure 2-10 shows a BTS33900 (Ver.D) cabinet in an AC scenario.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 12
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-10 BTS3900 (Ver.D) cabinet in an AC scenario
Table 2-1 lists typical configurations of a single-mode BTS3900 (Ver.D) cabinet.
Table 2-1 Typical configurations of a single-mode BTS3900 (Ver.D) cabinet
Mode Typical Number of RF Output Power of Each
Configurations Modules Carrier
GSM S4/4/4 6 DRFU 20 W (900 MHz)/18 W
(1800 MHz)
S12/12/12 6 GRFU 12 W
S12/12/12 6 MRFU 12 W
S12/12/12 6 MRFUe 20 W
S8/8/8 + S8/8/8 3 MRFUd + 3 MRFUd 20 W (900 MHz) + 20 W
(1800 MHz)
UMTS 3x4 3 WRFU 20 W
3 x 4 (MIMO) 3 WRFUd 30 W (1 x 15 W)
3x4 3 MRFU 20 W
3 x 4 (MIMO) 3 MRFUd 40 W (2 x 20 W)
LTE 3 x 20 MHz 6 MRFU/3 MRFUd 80 W (2 x 40 W)/120 W (2
(MIMO) x 60 W)
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 13
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
NOTE
The preceding configurations assume that each cell uses one dual-polarized antenna.
Table 2-2 lists typical configurations of a dual-mode BTS3900 (Ver.D) cabinet.
Table 2-2 Typical configurations of a dual-mode BTS3900 (Ver.D) cabinet
Mode Typical Number of RF Output Power of
Configurations Modules Each Carrier
GU GSM S4/4/4 + UMTS 3 3 MRFUd 20 W + 40 W
x2
GL GSM S8/8/8 + LTE 3 x 3 MRFUd (GO) + 3 20 W + 80 W (2 x 40
20 MHz (MIMO) MRFUd (LO) W)
UL UMTS 3 x 2 (MIMO) + 3 MRFUd (UO) + 3 80 W (2 x 40 W) +
LTE 3 x 20 MHz MRFUd (LO) 120 W (2 x 60 W)
(MIMO)
NOTE
The preceding configurations assume that each cell uses one dual-polarized antenna.
In Table 2-2, GU indicates that GSM and UMTS share one BBU, GL indicates that GSM and LTE
share one BBU, and UL indicates that UMTS and LTE share one BBU.
2.4 BTS3900L (Ver.D) Cabinet
BTS3900 (Ver.D) cabinets house BBUs and RFUs and provide the power distribution and
surge protection functions. A single BTS3900L (Ver.B), BTS3900L (Ver.C), or BTS3900L
(Ver.D) cabinet can house a maximum of 12 RFUs and 2 BBUs. This saves installation space
and facilitates smooth evolution.
BTS3900L (Ver.D) cabinets support –48 V DC and AC power input.
Figure 2-11 shows the internal structure of a BTS3900L (Ver.D) cabinet supporting –48 V DC
power input.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 14
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-11 BTS3900L (Ver.D) cabinet supporting –48 V DC power input
BTS33900L (Ver.D) cabinet can be stacked on IMS06 in AC scenarios. Figure 2-12 shows a
BTS33900L (Ver.D) cabinet in an AC scenario.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 15
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-12 BTS3900L (Ver.D) cabinet in an AC scenario
Table 2-3 lists typical configurations of a single-mode BTS3900L (Ver.D) cabinet.
Table 2-3 Typical configurations of a single-mode BTS3900L (Ver.D) cabinet
Mode Configuration Number of Modules Output Power of
Each Carrier
GSM S4/4/4 6 DRFU 20 W (900 MHz)/18
W (1800 MHz)
S12/12/12 6 GRFU 12 W
S12/12/12 6 MRFU 12 W
S12/12/12 6 MRFUe 20 W
S8/8/8 + S8/8/8 3 MRFUd + 3 MRFUd 20 W (900 MHz) +
20 W (1800 MHz)
UMTS 3x4 3 WRFU 20 W
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 16
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Mode Configuration Number of Modules Output Power of
Each Carrier
3 x 4 (MIMO) 3 WRFUd 30 W (2 x 15 W)
3x4 3 MRFU 20 W
3 x 4 (MIMO) 3 MRFUd 40 W (2 x 20 W)
LTE 3 x 20 MHz (MIMO) 6 MRFU/3 MRFUd 80 W (2 x 40 W)/120
W (2 x 60 W)
NOTE
The preceding configurations assume that each cell uses one dual-polarized antenna.
BTS3900L (Ver.D) cabinets are mainly used in scenarios where multiple frequency bands are
applied and multiple modes co-exist. Table 2-4 lists typical configurations of a multimode
BTS3900L (Ver.D) cabinet.
Table 2-4 Typical configurations of a multimode BTS3900L (Ver.D) cabinet
Mode Configuration Number of Modules Output Power of
Each Carrier
GU GSM S8/8/8 + UMTS 3 x 6 GRFU + 6 WRFU 20 W + 80 W (2 x
2 (MIMO) 40 W)
3 MRFUd (GO) + 3
MRFUd (UO)
GL GSM S8/8/8 + LTE 3 x 20 6 GRFU + 6 MRFU 20 W + 80 W (2 x
MHz (MIMO) (LO) 40 W)
3 MRFUd (GO) + 3 20 W + 120 W (2 x
MRFUd (LO) 60 W)
UL UMTS 3 x 2 (MIMO) 6 WRFU+6 MRFU 80 W (2 x 40 W) +
+ LTE 3 x 20 MHz (LO) 80 W (2 x 40 W)
(MIMO) 3 MRFUd (UO) + 3
MRFUd (LO)
GU+L/ GSM S8/8/8 + UMTS 3 x 3 MRFUd+3 MRFUd 20 W + 80 W (2 x
GL+U 2 (MIMO) + LTE 3 x 20 (UO) + 3 MRFUd (LO) 40 W) + 120 W (2
MHz (MIMO) x 60 W)
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 17
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
NOTE
The preceding configurations assume that each cell uses one dual-polarized antenna.
In Table 2-4, GU indicates that GSM and UMTS share one BBU, GL indicates that GSM and LTE
share one BBU, UL indicates that UMTS and LTE share one BBU, GU+L indicates that GSM and
UMTS share one BBU and LTE uses the other BBU, and GL+U indicates that GSM and LTE share
one BBU and UMTS uses the other BBU.
2.5 BTS3900AL (Ver.A) Cabinet
A BTS3900AL (Ver.A) cabinet performs power distribution and surge protection. It consists
of BBUs and RFUs. As a high-integration outdoor site solution, the BTS3900AL (Ver.A)
cabinet houses a maximum of two BBUs and nine RFUs to save installation space and ensure
smooth evolution.
Figure 2-13 shows the internal structure of a BTS3900AL (Ver.A) cabinet.
Figure 2-13 Internal structure of a BTS3900AL (Ver.A) cabinet
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 18
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
BTS3900AL (Ver.A) cabinets mainly apply to large-capacity scenarios where multiple
frequency bands or multiple modes co-exist. They also support single-mode applications.
Table 2-5 lists typical configurations of a multimode BTS3900AL (Ver.A) cabinet.
Table 2-5 Typical configurations of a multimode BTS3900AL (Ver.A) cabinet
Mode Typical Number of RF Output Power
Configurations Modules of Each Carrier
GU GSM S8/8/8 (900 MHz) 3 MRFUd (GO) + 3 20 W + 20 W +
+ GSM S8/8/8 (1800 MRFUd (GO) + 3 40 W
MHz) + UMTS 3 x 2 WRFU (UO)
(2100 MHz)
GSM S6/6/6 (900 MHz) 3 MRFUd (GU) + 3 20 W + 40 W +
+ UMTS 3 x 1 (900 MRFUd (GO) + 3 20 W + 80 W (2
MHz) + GSM S8/8/8 WRFUd (UO) x 40 W)
(1800 MHz) + UMTS 3
x 2 (2100 MHz)
GL GSM S4/4/4 (900 MHz) 3 GRFU (GO) + 3 20 W + 80 W (2
+ GSM S4/4/4 (1800 GRFU (GO) + 3 LRFU x 40 W)
MHz) + LTE 3 x 20 (LO)
MHz (MIMO)
GSM S6/6/6 + LTE 3 x 6 MRFU (GL) + 3 20 W + 2 x 20 W
10 MHz (2T2R) + LTE LRFU (LO) + 80 W (2 x 40
3 x 20 MHz (MIMO) W)
GSM S8/8/8 (900 MHz) 3 MRFUd (GO) + 3 20 W + 120 W (2
+ LTE 3 x 20 MHz LRFU (LO) x 60 W)
(800 MHz, MIMO)
UL UMTS 3 x 2 + LTE 3 x 3 WRFU + 3 MRFU 40 W + 80 W (2
20 MHz (MIMO) (LO) x 40 W)
3 MRFU (UO) + 3
MRFU (LO)
UMTS 3 x 2 (MIMO) + 3 WRFUd + 6 LRFU 80 W (2 x 40 W)
LTE 3 x 20 MHz + 80 W (2 x 40
(4T4R) 3 MRFUd (UO) + 6 W)
MRFUd (LO)
GU+L/GL+U GSM S8/8/8 + UMTS 3 3 MRFUd (UO) + 3 20 W + 80 W (2
(independent x 2 (MIMO) + LTE 3 x WRFUd + 3 MRFUd x 40 W) + 120 W
BBUs) 20 MHz (MIMO) (LO) (2 x 60 W)
GU+L/GL+U GSM S6/6/6 + UMTS 3 3 MRFUd (GU) + 3 20 W + 40 W (2
(interconnecte x 1 (MIMO) +GSM MRFUd (GL) + 3 x 20 W) + 20 W
d BBUs) S6/6/6 + LTE 3 x 10 WRFU + 40 W (2 x 20
MHz (MIMO) + UMTS W) + 80 W (2 x
3 x 2 (MIMO) 40 W)
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 19
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
The preceding configurations assume that each cell uses one dual-polarized antenna.
In Table 2-5, GU indicates that GSM and UMTS share one BBU, GL indicates that GSM and LTE
share one BBU, UL indicates that UMTS and LTE share one BBU, GU+L indicates that GSM and
UMTS share one BBU and LTE uses the other BBU, and GL+U indicates that GSM and LTE share
one BBU and UMTS uses the other BBU.
2.6 BTS3900A
The BTS3900A consists of an RF cabinet and a power cabinet, or of an RF cabinet and a
transmission cabinet.
RF cabinet: The RF cabinet is installed outdoors and uses a direct ventilation system.
Together with the power cabinet or transmission cabinet, the RF cabinet provides the
power distribution and surge protection functions for the BBU and RFUs. An RF cabinet
can house a maximum of six RFUs.
Power cabinet: If a 110 V AC or 220 V AC power supply is applied, an APM30H (Ver.D)
or an APM30H (Ver.E) power cabinet is used and the BBU can be installed inside the
power cabinet.
Transmission cabinet: If a –48 V DC power supply is applied, a TMC11H (Ver.D) or a
TMC11H (Ver.E) transmission cabinet is used and the BBU can be installed inside the
transmission cabinet.
Take the internal structure of the BTS3900A with AC power supply as an example. It differs
from the internal structure of the BTS3900A with –48 V DC power supply only in the
configuration of power modules.
Figure 2-14shows the internal structure of the BTS3900A (Ver.D) cabinet with AC power
supply.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 20
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-14 Internal structure of the BTS3900A (Ver.D) with AC power supply
Figure 2-15 shows the internal structure of the BTS3900A (Ver.E) cabinet with AC power
supply.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 21
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-15 Internal structure of the BTS3900A (Ver.E) with AC power supply
Table 2-6 lists typical configurations of an RF cabinet used by the single-mode BTS3900A
(Ver.D)/BTS3900A (Ver.E).
Table 2-6 Typical configurations of an RF cabinet used by the single-mode BTS3900A (Ver.D)
/BTS3900A (Ver.E)
Typical Number of Output Power of Each
Configurations Modules Carrier
GSM S4/4/4 6 DRFU 20 W (900 MHz)/18 W (1800
MHz)
S12/12/12 6 GRFU 12 W
S12/12/12 6 MRFU 12 W
S12/12/12 6 MRFUe 20 W
S8/8/8 + S8/8/8 3 MRFUd + 3 20 W (900 MHz) + 20 W
MRFUd (1800 MHz)
UMTS 3x4 3 WRFU 20 W
3x4 (MIMO) 3 WRFUd 30 W (2 x 15 W)
3x4 3 MRFU 20 W
3 x 4 (MIMO) 3 MRFUd 40 W (2 x 20 W)
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 22
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Typical Number of Output Power of Each
Configurations Modules Carrier
LTE 3 x 20 MHz (MIMO) 6 MRFU/3 MRFUd 80 W (2 x 40 W)/120 W (2 x
60 W)
NOTE
The preceding configurations assume that each cell uses one dual-polarized antenna.
Table 2-7 lists typical configurations of an RF cabinet used by the dual-mode BTS3900A
(Ver.D) /BTS3900A (Ver.E).
Table 2-7 Typical configurations of an RF cabinet used by the dual-mode BTS3900A (Ver.D)
/BTS3900A (Ver.E)
Mode Typical >Number of Modules Output Power
Configurations of Each Carrier
GU GSM S4/4/4 + UMTS 3 x 3 MRFUd 20 W + 40 W
2
GL GSM S8/8/8 + LTE 3 x 3 MRFUd (GO) + 3 MRFUd 20 W + 80 W (2
20 MHz (MIMO) (LO) x 40 W)
UL UMTS 3 x 2 (MIMO) + 3 MRFUd (UO) + 3 MRFUd 80 W (2 x 40 W)
LTE 3 x 20 MHz (LO) + 120 W (2 x 60
(MIMO) W)
NOTE
The preceding configurations assume that each cell uses one dual-polarized antenna.
In Table 2-7, GU indicates that GSM and UMTS share one BBU, GL indicates that GSM and LTE
share one BBU, and UL indicates that UMTS and LTE share one BBU.
2.7 BTS3900C
The BTS3900C is a mini outdoor base station and applies to hot spots, tunnels, and borders.
The BTS3900C consists of an OMB (Ver.C) and an RRU subrack. The OMB (Ver.C) can
house a BBU. The RRU can house RRU3804, RRU3801E, RRU3806 RRU3805, RRU3808,
RRU3824, RRU3826, RRU3838, RRU3908 V2, RRU3929, RRU3829, RRU3828, RRU3928,
RRU3926, RRU3936, or RRU3942 modules. The BTS3900C can be used in a multimode
base station or a UO single-mode base station.
An RRU subrack only houses a DC RRU.
A BTS3900C supports the DC and AC power input.
If DC power is used, the BTS3900C must be configured with a DC power distribution
box. Figure 2-16 shows the cabinets used by of a BTS3900C (DC).
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 23
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
If AC power is used, the BTS3900C must be configured with an AC surge protection
module, an AC power system, and a DC power distribution box. Figure 2-17 shows the
cabinets used by a BTS3900C (AC).
Figure 2-16 Cabinets used by a BTS3900C (DC)
(1) OMB (Ver.C) (2) RRU cabinet
Figure 2-17 Cabinets used by a BTS3900C (AC)
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 24
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
(1) OMB (Ver.C) (2) RRU cabinet
Table 2-8 lists typical configurations of a BTS3900C.
Table 2-8 Typical configurations of a BTS3900C
Mode Typical RF Modules Output Power of Each
Configurations Carrier
UMTS 1x3 RRU3828 20 W
GU GSM S2 + UMTS RRU3928 20 W + 20 W
1x2
GSM S2 + UMTS RRU3928 20 W + 2 x 20 W
1 x 1 (MIMO)
GL GSM S2 + LTE 1 RRU3928 20 W + 2 x 20 W
x 10 MHz
(MIMO)
2.8 DBS3900
The DBS3900 facilitates site acquisition as well as network planning and optimization, and
reduces network deployment time. It enables operators to efficiently deploy a
high-performance GSM/UMTS/LTE network with a low total cost of ownership (TCO) by
minimizing investment in electricity, space, and manpower.
The DBS3900 consists of BBU and RRUs. The BBU is characterized by its small footprint,
easy installation, and low power consumption. Therefore, the BBU can be easily installed in a
spare space at an existing site. The RRU is also compact and light. It can be installed close to
an antenna to reduce feeder loss and to improve system coverage.
Typical installation scenario 1 for the DBS3900
DBS3900 outdoor site: if the AC power supply is provided, an APM30H (Ver.D) is used;
if –48 V DC power supply is provided, a TMC11H (Ver.D) is used. See Figure 2-18.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 25
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-18 Typical installation scenario 1 for the DBS3900
Typical installation scenario 2 for the DBS3900
DBS3900 outdoor site that has insufficient space: if the AC power supply is provided, an
OMB (Ver.C) AC cabinet is used; if –48 V DC power supply is provided, an OMB
(Ver.C) DC cabinet is used. See Figure 2-19.
Figure 2-19 Typical installation scenario 2 for the DBS3900
Typical installation scenario 3 for the DBS3900
DBS3900 indoor site: if RRUs are installed remotely and the BBU and power
distribution unit are installed indoors on a wall, an IMB03 is used. See Figure 2-20.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 26
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
DBS3900 indoor site: if RRUs must be installed in centralized mode, the L-shaped stand
can be used. See Figure 2-20.
Figure 2-20 Typical installation scenario 3 for the DBS3900
Typical installation scenario 4 for the DBS3900
DBS3900 indoor site: if RRUs are installed remotely, and the BBU and power
distribution unit are installed on a support on the floor of a room, a 19-inch open rack is
used. See Figure 2-21.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 27
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-21 Typical installation scenario 4 for the DBS3900
If RRUs need to be installed on the outdoor ground in centralized mode, an OPS-06 is used.
If the distance between the RRUs and BBU is too long, and no back power is required, AC
RRUs are used.AC RRUs are powered by the AC power equipment supplied by the customer.
When the AC RRUs are installed outdoors, each AC RRU needs to be configured with an
SPD, an AC surge protector.
Table 2-9 lists typical configurations of a single-mode DBS3900.
Table 2-9 Typical configurations of a single-mode DBS3900
Mode Typical Number of RF Output Power of Each Carrier
Configurations Modules
GSM S4/4/4 6 RRU3004 15 W (900 MHz)/10 W (1800
MHz)
S4/4/4 3 RRU3008 20 W
S4/4/4 3 RRU3908 20 W
UMTS 3x4 3 RRU3804 15 W
3x4 3 RRU3806 20 W
3 x 2 (MIMO) 3 RRU3908 40 W (2 x 20 W)
LTE 3 x 20 MHz 3 RRU3908 40 W (2 x 20 W)
(MIMO)
NOTE
The preceding configurations assume that each cell uses one dual-polarized antenna.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 28
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Table 2-10 lists typical configurations of a dual-mode DBS3900.
Table 2-10 Typical configurations of a dual-mode DBS3900
Mode Typical Number of RF Output Power of
Configurations Modules Each Carrier
GU GSM S4/4/4 + UMTS 3 3 RRU3008 + 6 20 W + 60 W (2 x
x 2 (MIMO) RRU3804 30 W)
3 RRU3008 + 3 20 W + 40 W (2 x
RRU3808 20 W)
GL GSM S4/4/4+ LTE 3 x 3 RRU3008 + 3 20 W + 40 W (2 x
20 MHz (MIMO) RRU3908 (LO) 20 W)
UL UMTS 3 x 2 (MIMO) + 6 RRU3804 + 3 60 W (2 x 30 W) +
LTE 3 x 20 MHz RRU3908 (LO) 40 W (2 x 20 W)
(MIMO)
3 RRU3808 +3 RRU3908 40 W (2 x 20 W) +
(LO) 40 W (2 x 20 W)
NOTE
In Table 2-10, GU indicates that GSM and UMTS share one BBU, GL indicates that GSM and LTE
share one BBU, and UL indicates that UMTS and LTE share one BBU.
2.8.1 APM30H (Ver.D)/ APM30H (Ver.E) Outdoor Power Cabinet
The APM30H (Ver.D)/APM30H (Ver.E) power cabinet converts AC input power into DC
power and provides DC power to the DBS3900. It also provides space for installing the BBU
and other equipment. Two 12 Ah battery packs are configured in parallel in the APM30H
(Ver.D) /APM30H (Ver.E) cabinet and supply power to the cabinet for short-term use. The
light and small APM30H (Ver.D) /APM30H (Ver.E) dissipates heat using a heat exchanger
and internal and external circulation fans.
Figure 2-22 shows the internal structure of the APM30H (Ver.D)
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 29
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-22 Internal structure of the APM30H (Ver.D)
(1) Outdoor air circulation (2) Junction box (3) Fan assembly
component
(4) SLPU (5) Door status sensor (6) ELU
(7) EPU subrack (8) BBU (9) EMUA
(10) Air baffle (11) AC HAU (12) SOU
Figure 2-23 shows the internal structure of the APM30H (Ver.E)
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 30
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-23 Internal structure of the APM30H (Ver.E)
(1) Outdoor air circulation
(2) Junction box (3) Fan assembly
component
(4) SLPU (5) ELU (6) Door status sensor
(7) EPU subrack (8) BBU (9) GATM
(10) EMU (11) Air baffle (12) AC HAU
(13) SOU (14) PDU03D-02 (15) PDU01D-01
2.8.2 TP48600A Power Cabinet
The TP48600A provides power to the DBS3900. It also provides space for installing the BBU
and other equipment. Figure 2-24 shows the internal structure of the TP48600A.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 31
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-24 Internal structure of the TP48600A
2.8.3 TMC11H (Ver.D)/ TMC11H (Ver.E) Outdoor Transmission
Cabinet
The TMC11H (Ver.D) /TMC11H (Ver.E) transmission cabinet is used outdoors. It is small and
easy to transport. The TMC11H (Ver.D) /TMC11H (Ver.E) dissipates heat using a heat
exchanger. If –48 V DC input power is available or more space is required for transmission
equipment, the TMC11H (Ver.D) /TMC11H (Ver.E) can be configured to accommodate either
situation.
Figure 2-25 shows the internal structure of the TMC11H (Ver.D) /TMC11H (Ver.E).
If the TMC11H (Ver.D) /TMC11H (Ver.E) is only used to provide space for transmission
equipment, the internal structure is shown in part A of Figure 2-25.
If the TMC11H (Ver.D) /TMC11H (Ver.E) is configured with the BBU in a –48 V DC
power supply scenario, the internal structure is shown in part B of Figure 2-25.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 32
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-25 Internal structure of the TMC11H (Ver.D) /TMC11H (Ver.E)
(1) Fan box (2) SLPU (3) ELU
(4) DCDU-12C (5) BBU (6) Door status sensor
(7) EMUA (8) Filler module (9) AC HAU
(10)Outer air circulation (11)Junction box
component
2.8.4 IBBS20D Battery Cabinet
IBBS20D battery cabinet is used in scenarios where long-term power backup is required. It is
small and easy to transport and can be used outdoors. The IBBS20D uses a direct ventilation
system.
Configured with built-in battery groups, IBBS20D cabinets provide a maximum backup DC
power capacity of 20 Ah.
Figure 2-26 shows the internal structure of an IBBS20D.
Figure 2-26 Internal structure of the IBBS20D
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 33
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
2.8.5 IBBS200T (Ver.D)/ IBBS200D (Ver.D)/ IBBS200T (Ver.E)/
IBBS200D (Ver.E) Battery Cabinet
IBBS200T (Ver.D), IBBS200D (Ver.D), IBBS200T (Ver.E), and IBBS200D (Ver.E) battery
cabinets are used in scenarios where long-term power backup is required. They are small and
easy to transport and can be used outdoors. The IBBS200T (Ver.D) or IBBS200T (Ver.E) can
operate at high temperatures because it has a built-in air conditioner. The IBBS200D (Ver.D)
or IBBS200D (Ver.E) uses a direct ventilation system.
In a battery cabinet, a BAU02D is optionally installed. The BAUA checks whether batteries
are installed. If no, an alarm is reported. This function can protect batteries from being stolen.
With the built-in battery group, each IBBS200T (Ver.D)/IBBS200D (Ver.D)/IBBS200T
(Ver.E)/IBBS200D (Ver.E) supports a maximum of 200 Ah backup power, or two of these
cabinets share 400 Ah DC backup power.
Figure 2-27 shows the internal structure of the IBBS200D (Ver.D)/ IBBS200D (Ver.E).
Figure 2-27 Internal structure of the IBBS200D (Ver.D)/ IBBS200D (Ver.E)
(1) Fan installation module (2) CMUEA (3) ELU
(4) Storage battery (5) PDB (6) Door status sensor
(7) Heating film
Figure 2-28 shows the internal structure of the IBBS200T (Ver.D)/ IBBS200T (Ver.E).
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 34
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-28 Internal structure of the IBBS200T (Ver.D) / IBBS200T (Ver.E)
(1) TEC (2) CMUEA (3) ELU
(4) Storage battery (5) PDB (6) Door status sensor
2.8.6 IBBS300D/IBBS300T Battery Cabinet
IBBS300D and IBBS300T battery cabinets are used in scenarios where long-term power
backup is required. They can be used outdoors.
The IBBS300D uses a direct ventilation system. The IBBS300T can operate at high
temperatures because it has a built-in air conditioner.
Configured with built-in battery groups, one IBBS300D/IBBS300T cabinet provides a
maximum backup DC power capacity of 300 Ah.
Figure 2-29 shows the internal structure of an IBBS300D.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 35
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-29 Internal structure of an IBBS300D
Figure 2-30 shows the internal structure of an IBBS300T.
Figure 2-30 Internal structure of an IBBS300T
2.8.7 IBBS700D/IBBS700T Battery Cabinet
IBBS700D and IBBS700T battery cabinets are used in scenarios where long-term power
backup is required. They can be used outdoors. The IBBS700D uses a direct ventilation
system. The IBBS700T can operate at high temperatures because it has a built-in air
conditioner.
Configured with built-in battery groups, one BBS700D/IBBS700T cabinet provides a
maximum backup DC power capacity of 600 Ah.
Figure 2-31 shows the internal structure of the IBBS700D.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 36
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-31 Internal structure of the IBBS700D
Figure 2-32 shows the internal structure of the IBBS700T.
Figure 2-32 Internal structure of the IBBS700T
2.8.8 OMB (Ver.C) Outdoor Power Cabinet
The OMB (Ver.C) power cabinet supplies power to the DBS3900. It also provides space for
installing the BBU and other equipment.
The OMB (Ver.C) power cabinet can be supplied with either AC or DC power.
Figure 2-33 and Figure 2-34 show the internal structures of the OMB (Ver.C) AC cabinet and
OMB (Ver.C) DC cabinet, respectively.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 37
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-33 OMB (Ver.C) AC cabinet
(1) HEUB (2) BBU (3) DC power distribution box
(4) AC power system (5) AC surge protector
Figure 2-34 OMB (Ver.C) DC cabinet
(1) HEUB (2) BBU (3) DC power distribution box
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 38
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
2.8.9 IMB03 Power Subrack
The IMB03 is equipped with the BBU and customer equipment. It can be supplied with either
AC or DC power. The IMB03 provides a 3 U space, and can be installed on a wall with one of
its sides against a wall, on an indoor floor installation support horizontally, and on an
H-shaped rack with one of its sides against the rack. Figure 2-35 shows the IMB03.
Figure 2-35 IMB03
2.8.10 Indoor Open Rack
An indoor open rack is used for an indoor distributed base station. It can be installed on a
support on the floor of a room and stacked with other racks. It provides a standard 10 U space
for installing the BBU, DCDU-03B or DCDU-11B, EPS4815, and other 19-inch equipment.
Figure 2-36 shows an indoor open rack.
Figure 2-36 Indoor open rack
2.8.11 Indoor Centralized Rack, (IFS06+IMB03)
When RRUs need to be installed in a centralized mode in an indoor DBS3900 site, an indoor
centralized rack (ICR) is used. The ICR is installed on a support on the floor of a room, and
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 39
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
provides a 3U+3U space at the bottom. A maximum of six DC RRUs can be installed on the
upper part of the ICR in side-mounted mode, or a maximum of two RRUs can be installed on
the upper part of the ICR horizontally. Figure 2-37 shows an indoor centralized rack.
Figure 2-37 Indoor centralized rack
2.8.12 Outdoor Pole Support 06, (OPS06)
OPS06 is a solution used for Huawei RRU outdoor applications. The OPS06 pole and base
are used to install RRUs in a centralized manner. The OPS06 supports floor installation and a
maximum of six flag-mounted RRUs or two flat-mounted RRUs.
Figure 2-38 shows an OPS06 with flag-mounted RRUs.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 40
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-38 Outdoor Pole Support 06
2.8.13 IBC10 Cabinet (for Cloud BB)
The IBC10 cabinet is used to accommodate BBU and USU in cloud BB scenarios.
Figure 2-39 shows the internal structure of an IBC10.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 41
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
Figure 2-39 Internal structure of an IBC10
(1) USU (2) Temperature sensor at the (3) ELU
air intake vent of the BBU
(4) BBU (5) DCDU-12C (6) Fan assembly
(FAU03D)
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 42
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
2.9 Macro Base Station + Distributed Base Station
The 3900 series base stations allow a macro base station and a distributed base station to be
deployed at the same site. In this scenario, the RFUs and RRUs are connected to the same
BBU. This deployment provides flexible networking of base stations, enabling further
capacity expansion and evolution in the future.
Table 2-11 lists the maximum configuration when a macro base station and a distributed base
station are deployed at the same site.
Table 2-11 Maximum configuration when a macro base station and a distributed base station are
deployed at the same site
Base Version Mode Number of Number Number of
Station BBUs of RFUs RRUs
BTS3900 SRAN6.0 and single/dual-m 1 12 6
(Ver.D) later versions ode
(Separate-MPT) triple-mode 2 12 9
SRAN8.0 single/dual/tri 1 12 6
SRAN9.0 ple-mode
(Co-MPT)
BTS3900 SRAN6.0 and single/dual-m 1 12 6
L (Ver.D) later versions ode
(Separate-MPT)
triple-mode 2 12 9
SRAN8.0 single/dual/tri 1 12 6
SRAN9.0 ple-mode
(Co-MPT)
BTS3900 SRAN6.0 and single/dual-m 1 6 9
A (Ver.D) later versions ode
(Separate-MPT)
triple-mode 2 6 9
SRAN8.0 single/dual/tri 1 6 9
SRAN9.0 ple-mode
(Co-MPT)
BTS3900 SRAN11.0 single/dual/tri 1 6 9
A (Ver.E) (Co-MPT) ple-mode
BTS3900 SRAN7.0 and single/dual-m 1 9 9
AL later versions ode
(Ver.A) (Separate-MPT)
triple-mode 2 9 12
SRAN8.0 single/dual/tri 1 9 9
SRAN9.0 ple-mode
(Co-MPT)
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 43
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 2 Hardware Architecture
NOTE
*: In this scenario, the APM cabinet connected to RRUs must be separately configured.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 44
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 3 Logical Structure
3 Logical Structure
From the perspective of logical structure, 3900 series base stations consist of control
subsystem, transport subsystem, baseband subsystem, RF subsystem, clock subsystem, and
power and environment monitoring subsystem. Figure 3-1 shows the logical structure of 3900
series base stations.
Figure 3-1 Logical structure of 3900 series base stations
Control subsystem (BTS CTL subsystem): controls and manages resources in a base
station. It provides the management plane interface between the base station and the
OMC, the control plane interface between the base station and other NEs, and the
interface for controlling and negotiating common devices in a multimode base station.
Transport subsystem (BTS TRP subsystem): forwards data between the transport
network and the base station. It provides physical ports between the base station and the
transport network and the user plane interface between the base station and other NEs.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 45
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 3 Logical Structure
Baseband subsystem (BTS BB subsystem): processes uplink and downlink baseband
data.
RF subsystem (BTS RF subsystem): transmits and receives radio signals. It provides
ports for data transmission between the antenna system and the base station.
Clock subsystem (BTS TAS subsystem): synchronizes the base station clock with
external clock sources. It provides ports between the base station and external clock
sources.
Power and environment monitoring subsystem (BTS MPE subsystem): provides power
supply, dissipates heat, and monitors the environment for a base station. It provides ports
between the base station and site devices.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 46
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 4 Operation and Maintenance
4 Operation and Maintenance
4.1 Overview
3900 series base stations are managed by an O&M system using either MML commands or a
graphical user interface (GUI). This system is hardware-independent and provides
comprehensive functions to meet users' various O&M requirements.
4.2 O&M System Structure
O&M systems for 3900 series base stations in SRAN7.0 and earlier manage separate-MPT
base stations locally or remotely using the GBTS SMT, BSC LMT, NodeB LMT, eNodeB
LMT, or U2000, as shown in Figure 4-1.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 47
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 4 Operation and Maintenance
Figure 4-1 O&M system structure for separate-MPT base stations
For such base stations, the O&M system consists of the following:
GBTS SMT: locally manages one GBTS. O&M personnel use network cables to connect
the PC running the GBTS SMT to the O&M port of the GBTS that the GBTS SMT will
manage.
BSC LMT: remotely manages multiple GBTSs. O&M personnel use the BSC LMT to
remotely manage multiple GBTSs in a centralized manner.
NodeB LMT: manages one NodeB. O&M personnel can use network cables to connect
the PC running the NodeB LMT to the O&M port of the NodeB that the NodeB LMT
will manage. Alternatively, O&M personnel can remotely manage a NodeB through
O&M channels by connecting the PC running the NodeB LMT to the NodeB.
eNodeB LMT: manages one eNodeB. O&M personnel can use network cables to connect
the PC running the eNodeB LMT to the O&M port of the eNodeB that the eNodeB LMT
will manage. Alternatively, O&M personnel can remotely manage an eNodeB through
O&M channels by connecting the PC running the eNodeB LMT to the eNodeB.
U2000: Huawei central O&M system. It centrally manages multiple base stations,
provides a data configuration device called Configuration Management Express (CME),
and incorporates the alarm monitoring, performance monitoring, software update, and
inventory device management functions.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 48
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 4 Operation and Maintenance
O&M systems for 3900 series base stations in SRAN8.0 manage co-MPT base stations locally
or remotely using SRAN LMT and U2000, as shown in Figure 4-2.
Figure 4-2 O&M system structure for a co-MPT base station
For such base stations, the O&M system consists of the following:
SRAN LMT: configure and maintain a BTS, NodeB, or eNodeB. O&M personnel can
use an Ethernet cable to connect the PC running the SRAN LMT to the O&M port on a
base station. Alternatively, they can remotely manage the base station by connecting the
PC running the SRAN LMT to the base station through O&M channels.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 49
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 5 Technical Specifications
5 Technical Specifications
5.1 Input Power Specifications
Table 5-1 lists the input power specifications for the different base station types.
Table 5-1 Input power specifications
Item Input Power
BTS3900 –48 V DC; voltage range: –38.4 V DC to –57 V DC
(Ver.D) 200 V AC to 240 V AC single-phase; voltage range: 176 V AC to 290 V
AC
220/346 V AC to 240/415 V AC three-phase; voltage range: 176/304 V
AC to 290/500 V AC
BTS3900A –48 V DC; voltage range: –38.4 V DC to –57 V DC
(Ver.D)/ 120/208 V AC to 127/220 V AC dual-live-wire; voltage range: 105/176
BTS3900A V AC to 150/260 V AC
(Ver.E)
100/200 V AC to 120/240 V AC dual-live-wire; voltage range: 90/180
V AC to 135/270 V AC
200 V AC to 240 V AC single-phase; voltage range: 176 V AC to 290 V
AC
220/346 V AC to 240/415 V AC three-phase; voltage range: 176/304 V
AC to 290/500 V AC
BTS3900L –48 V DC; voltage range: –38.4 V DC to –57 V DC
(Ver.D) 200 V AC to 240 V AC single-phase; voltage range: 176 V AC to 290 V
AC
220/346 V AC to 240/415 V AC three-phase; voltage range: 176/304 V
AC to 290/500 V AC
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 50
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 5 Technical Specifications
Item Input Power
DBS3900 BBU3900 (UPEUc):
(Ver.D) –48 V DC; voltage range: –38.4 V DC to –57 V DC
BBU3910 (UPEUd):
–48 V DC; voltage range: –38.4 V DC to –57 V DC
RRU:
–48 V DC; voltage range: –36 V DC to –57 V DC
BTS3900AL 120/208 V AC to 127/220 V AC dual-live-wire; voltage range: 105/176
(Ver.A) V AC to 150/260 V AC
100/200 V AC to 120/240 V AC dual-live-wire; voltage range: 90/180
V AC to 135/270 V AC
200 V AC to 240 V AC single-phase; voltage range: 176 V AC to 290 V
AC
220/346 V AC to 240/415 V AC three-phase; voltage range: 176/304 V
AC to 290/500 V AC
–48 V DC, voltage range: –38.4 V DC to –57 V DC
BTS3900C –48 V DC; voltage range: –38.4 V DC to –57 V DC
(Ver.C) 200 V AC to 240 V AC single-phase; voltage range: 176 V AC to 290 V
AC
100/200 V AC to 120/240 V AC dual-live-wire; voltage range: 90/180
V AC to 135/270 V AC
5.2 Equipment Specifications
Table 5-2 lists the equipment specifications for the different base station types.
Table 5-2 Equipment specifications
Item Cabinet Specification
Dimensio BTS3900 (Ver.D) cabinet (DC) 900 mm x 600 mm x 450 mm
n (H x W
x D) BTS3900 (Ver.D) cabinet (AC) 1250 mm x 600 mm x 450 mm
(including the IMS06)
Base: 40 mm x 600 mm x 420
mm)
Cabinets used by RFC (Ver.D) 700 mm x 600 mm x 480 mm
the BTS3900A
(Ver.D) or APM30H (Ver.D)/ 700 mm x 600 mm x 480 mm
BTS3900A TMC11H (Ver.D)/
(Ver.E) APM30H (Ver.E)/
TMC11H (Ver.E)
Base 200 mm x 600 mm x 434 mm
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 51
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 5 Technical Specifications
Item Cabinet Specification
BTS3900L (Ver.D) cabinet (DC) 1600 mm x 600 mm x 450 mm
BTS3900L (Ver.D) cabinet (AC) 1950 mm x 600 mm x 450 mm
(including the IMS06)
Base: 40 mm x 600 mm x 420
mm)
BTS3900AL(Ver.A) cabinet 1925 mm x 770 mm x 750 mm
(including the base)
Base: 200 mm x 770 mm x
700 mm
BTS3900C (Ver.C) cabinet 600 mm x 420 mm x 430 mm
OMB (Ver.C): 600 mm x 240
mm x 430 mm
RRU: 600 mm x 180 mm x
430 mm
Weight BTS3900 (Ver.D) cabinet (DC) Full configuration ≤ 135 kg
(including one BBU and six
RFUs, excluding the AC
power module)
BTS3900 (Ver.D) cabinet (AC) Full configuration ≤ 180 kg
(including one BBU, six
RFUs, and AC power module)
Cabinets used by the BTS3900A (Ver.D) or ≤ 194 kg (with boards installed
BTS3900A (Ver.E) in AC cabinets before
delivery)
APM30H ≤ 87 kg (full
configuration, excluding
transmission equipment and
storage batteries)
RFC ≤ 107 kg (full
configuration)
BTS3900L (Ver.D) cabinet (DC) Full configuration ≤ 235 kg
(including two BBUs and
twelve RFUs, excluding
transmission equipment)
BTS3900L (Ver.D) cabinet (AC) Full configuration ≤ 280 kg
(including two BBUs, twelve
RFUs, and AC power module,
excluding transmission
equipment)
BTS3900AL (Ver.A) cabinet Full configuration ≤ 550 kg
(including the base and fully
configured batteries, excluding
transmission equipment)
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 52
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 5 Technical Specifications
Item Cabinet Specification
BTS3900C (Ver.C) cabinet AC cabinet: ≤ 32 kg
(excluding the BBU and RRU)
DC cabinet: ≤ 28 kg
(excluding the BBU and RRU)
Heat Cabinets used by APM30H 50°C@700 W or 50°C@1500
dissipation the BTS3900A (Ver.D)/TMC11H W
capability (Ver.D) (Ver.D)
Cabinets used by APM30H 50°C@700 W or 50°C@1800
the BTS3900A (Ver.E)/TMC11H W
(Ver.E) (Ver.E)
BTS3900AL (Ver.A) cabinet 50°C@2200 W
BTS3900C (Ver.C) cabinet 50°C@650 W
5.3 Environment Specifications
NOTE
For details about the environment specifications of DBS3900, see the BBU3900 Description, BBU3910
Description, and the description documents of the RRUs.
Table 5-3 lists the environment specifications for the different base station types.
Table 5-3 Environment specifications
Item Specification
Operatin BTS3900 –20°C to +55°C
g (Ver.D)/BTS3900 +50°C to +55°C (short-term)
temperat L (Ver.D)
ure
BTS3900A –40°C to +50°C with 1120 W/M² solar radiation
(Ver.D)/ An AC heater assembly unit (HAU) is required if the
BTS3900A operating temperature is below –20°C.
(Ver.E)
BTS3900AL -40°C to +50°C with 1120 W/M² solar radiation (without
(Ver.A) storage batteries); an AC heater assembly unit (HAU) is
required if the operating temperature is below –20°C.
-40°C to +40°C with 1120 W/M² solar radiation (with
storage batteries); an AC heater assembly unit (HAU) is
required if the operating temperature is below –20°C.
BTS3900C –33°C to +50°C
(Ver.C) cabinet
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 53
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 5 Technical Specifications
Item Specification
Relative BTS3900 5% RH to 95% RH
humidity (Ver.D)/BTS3900
L (Ver.D)
BTS3900A 5% RH to 100% RH
(Ver.D)/
BTS3900A
(Ver.E)/BTS3900
AL
(Ver.A)/BTS3900
C (Ver.C)
Atmosph 70 kPa to 106 kPa
eric
pressure
NOTE
In Table 5-3, "short term" means continuous operation for not more than 72 hours or accumulated
operation of no more than 15 days a year.
5.4 Standards
Table 5-4 lists the standards for the different base station types.
Table 5-4 Standards
Item Specification
Security X.509 Supported in
standards GBSS14.0/RAN14.0/eRAN3.0/SRAN7.0 and later
RFC 1825
RFC 1826
RFC 1827
RFC4492 Supported in all versions
RFC5246 Supported from
GBSS15.0/RAN15.0/eRAN6.0/SRAN8.0
SSL (Secure Supported in all versions
Socket Layer)
Protection rating BTS3900 IP20
(Ver.D)/BTS390
0L (Ver.D)
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 54
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 5 Technical Specifications
Item Specification
BTS3900A IP55
(Ver.D)/
BTS3900A
(Ver.E)/
BTS3900AL
(Ver.A)/BTS390
0C (Ver.C)
Storage ETSI EN300019-1-1 V2.1.4 (2003-04) class1.2 "Weatherprotected, not
temperature-controlled storage locations"
Transportation ETSI EN300019-1-2 V2.1.4 (2003-04) class 2.3 "Public transportation"
Anti-seismic IEC 60068-2-57: Environmental testing -Part 2-57: Tests -Test Ff:
performance Vibration -Time-history method
YD5083: Interim Provisions for Test of Anti-seismic Performances of
Telecommunications Equipment (telecom industry standard in People's
Republic of China)
Anti-earthquake DBS3900 ETSI EN 300019-1-4: "Earthquake"
performance (Ver.D)/BTS390
0A (Ver.D)/
BTS3900A
(Ver.E)/BTS390
0AL
(Ver.A)/BTS390
0C (Ver.C)
BTS3900 ETSI EN 300019-1-3: "Earthquake"
(Ver.D)/BTS390
0L (Ver.D)
EMC 3900 series base stations meet the Electromagnetic Compatibility
(EMC) requirements and comply with the following standards:
R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC
R&TTE Directive 89/336/EEC
ETSI EN 301489-1/8/23
3GPP TS 25.113
ETSI EN 301908-1
ITU-T SM 329-10
FCC PART15
The GBTS meets the EMC requirements and complies with the
following standards:
R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC
R&TTE Directive 89/336/EEC
ETSI EN 301489-1/8
ETSI EN 301908-1
ITU-T SM 329-10
FCC PART15
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 55
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 5 Technical Specifications
Item Specification
The NodeB meets the EMC requirements and complies with the
following standards:
CISPR 22 (1997)
EN 55022 (1998)
EN 301 489-23 V1.2.1 (2002-11)
CISPR 24 (1998)
IEC 61000-4-2
IEC 61000-4-3
IEC 61000-4-4
IEC 61000-4-5
IEC 61000-4-6
IEC 61000-4-29
GB 9254-1998
ETSI 301 489-1 V1.3.1 (2001-09)
FCC Part 15
The NodeB has been certified by European standards.
The eNodeB meets the EMC requirements and complies with the
following standards:
R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC
R&TTE Directive 89/336/EEC
3GPP TS 36.113
ETSI EN 301489-1/23
ETSI EN 301908-1 V2.2.1 (2003-10)
ITU-R SM.329-10
The eNodeB has been certified by European standards.
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 56
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 6 Acronyms and Abbreviations
6 Acronyms and Abbreviations
3GPP 3rd Generation Partnership Project
AC Alternating current
APM Advanced power module
AAU Active Antenna Unit
BAU 02D Battery Alarm Unit type 02D
BBU Baseband unit
CPRI Common Public Radio Interface
CME Configuration Management Express
CMUA Central monitoring unit type A
CMUE Central monitoring unit type E
CMUEA Central Monitoring Unit type EA
Co-OAM Co-Operation and Maintenance
Co-RNP&RNO Co-Radio Network Planning & Radio Network Optimization
Co-RRM Co-Radio Resource Management
Co-TRM Co-Transmission Management
DC Direct current
DCDU Direct current distribution unit
EMC Electromagnetic compatibility
EMUA Environment monitoring unit type A
EPS Embedded power system
EPU Embedded power subrack unit
ETSI European Telecommunications Standards Institute
GSM Global System for Mobile Communications
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 57
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3900 Series Base Station Product Description 6 Acronyms and Abbreviations
GUI Graphical user interface
HAU Heater assembly unit
HPMI HERT power monitoring interface unit
IBBS Integrated Backup Battery System
LMT Local maintenance terminal
LTE Long Term Evolution
MIMO Multiple-input multiple-output
O&M Operation and maintenance
OMC Operation and maintenance center
PA Power amplifier
PMU Power monitoring unit
PSU Power supply unit
RF Radio frequency
RFC Radio frequency cabinet
RFU Radio frequency unit
RRU Remote radio unit
SDR Software-defined radio
SLPU Signal Lightning Protection Unit
SMT Site Maintenance Terminal
TCO Total cost of ownership
TEC Thermoelectric cooling unit
TMC Transport Management Cabinet
UMTS Universal Mobile Telecommunications System
Issue 08 (2015-06-30) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 58
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- AIR 6419 B41 Datasheet - PA4Dokument2 SeitenAIR 6419 B41 Datasheet - PA4208.nampa.idNoch keine Bewertungen
- HUAWEI BBU Installation GuideDokument56 SeitenHUAWEI BBU Installation GuideCostin Toma100% (11)
- Radio 4449 B13 B5Dokument45 SeitenRadio 4449 B13 B5Ahmed Timraz100% (1)
- 3900 Series & 5900 Series Base Station V100R015C10SPC080 Node Performance Counter ReferenceDokument845 Seiten3900 Series & 5900 Series Base Station V100R015C10SPC080 Node Performance Counter ReferenceDhananjay Shrivastav100% (3)
- 5G HandbookDokument58 Seiten5G HandbookScribdFgNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTE Workshop v3 PDFDokument135 SeitenLTE Workshop v3 PDFmartdiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- LampSite Solution Product Description 04 (2014!05!20)Dokument33 SeitenLampSite Solution Product Description 04 (2014!05!20)Marco Matteucci100% (1)
- Iru Radio DotDokument66 SeitenIru Radio DotJunaid Jan Muhammad100% (1)
- Vodafone Dispersed Radio Guidelines For Direct Supply and PowershiftDokument13 SeitenVodafone Dispersed Radio Guidelines For Direct Supply and PowershiftMarcelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3900 Macro BTS TroubleshootingDokument92 Seiten3900 Macro BTS Troubleshootingengr_dandayo1Noch keine Bewertungen
- RRU5904w DescriptionDokument31 SeitenRRU5904w DescriptionMauricio100% (1)
- Robust ML Detection Algorithm For Mimo Receivers in Presence of Channel Estimation ErrorDokument5 SeitenRobust ML Detection Algorithm For Mimo Receivers in Presence of Channel Estimation ErrortrNoch keine Bewertungen
- AZQL RRH 8T8R n78 320W DatasheetDokument3 SeitenAZQL RRH 8T8R n78 320W DatasheetThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- FONTE EPW30 48AManual Do ProdutoDokument2 SeitenFONTE EPW30 48AManual Do ProdutoLucas100% (4)
- Power 6302 Product Description Rev T 20190909Dokument26 SeitenPower 6302 Product Description Rev T 20190909fhfgh gjgfhNoch keine Bewertungen
- RRU3829 DescriptionDokument10 SeitenRRU3829 DescriptionMarco MatteucciNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bts3900 & Bts3900l Spare Parts CatalogDokument53 SeitenBts3900 & Bts3900l Spare Parts CatalogleonardomarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Install Radio Radio 2219 InstallationDokument37 SeitenInstall Radio Radio 2219 Installationmarcelo trasse100% (1)
- Ceragon FibeAir IP-20C Technical Description C8.5 ETSI Rev ADokument261 SeitenCeragon FibeAir IP-20C Technical Description C8.5 ETSI Rev ALê Hữu ÁiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5900 Series Base Station Product DescriptionDokument85 Seiten5900 Series Base Station Product DescriptionMauricioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ericsson Lte Bts Rrus 12 b3 1800mhz Rrus12b3 KRC 161 282 2 R1e-102546138Dokument3 SeitenEricsson Lte Bts Rrus 12 b3 1800mhz Rrus12b3 KRC 161 282 2 R1e-102546138Sang Du Minh100% (1)
- Flexi RF Module 3TX 900 (FXDB) : Functional DescriptionDokument5 SeitenFlexi RF Module 3TX 900 (FXDB) : Functional DescriptionnazilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3900 Series Base Station Technical Description (V100R010C10 - 07) (PDF) - enDokument1.101 Seiten3900 Series Base Station Technical Description (V100R010C10 - 07) (PDF) - enSameh SheblNoch keine Bewertungen
- RRU3939 DescriptionDokument13 SeitenRRU3939 Descriptionerginbekar100% (3)
- BBU5900A Installation Guide (01) (PDF) - ENDokument151 SeitenBBU5900A Installation Guide (01) (PDF) - ENArtur Miller Gil romero100% (1)
- BBU Hardware Description (V100R009C00 - 01) (PDF) - enDokument196 SeitenBBU Hardware Description (V100R009C00 - 01) (PDF) - enMyce Elu100% (3)
- Radio 4415 DatasheetDokument2 SeitenRadio 4415 DatasheetJaime FariasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi-Mode Macro RRU HW Roadmap (I) : 2019 2018&before 2020 2021 2022Dokument2 SeitenMulti-Mode Macro RRU HW Roadmap (I) : 2019 2018&before 2020 2021 2022Faran Ul Ghani100% (2)
- BBU3900 Hardware DescriptionDokument81 SeitenBBU3900 Hardware DescriptionJuanzbar Huaman SialerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base Station Cabinets and Subracks (Including The BBU Subrack) Configuration (SRAN12.1 - 02)Dokument81 SeitenBase Station Cabinets and Subracks (Including The BBU Subrack) Configuration (SRAN12.1 - 02)anthony100% (1)
- LTE FDD 3900 Series Base Station Product DescriptionDokument71 SeitenLTE FDD 3900 Series Base Station Product DescriptioncopslockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guideline Replacing WMPT With UMPTDokument5 SeitenGuideline Replacing WMPT With UMPTDani FirmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- UMPT and All Boards Huawei QuipDokument88 SeitenUMPT and All Boards Huawei QuipdragosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Sheet 2217Dokument2 SeitenData Sheet 2217mostafa yehiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HUAWEI GSM DBS3900 Hardware Structure2.0Dokument50 SeitenHUAWEI GSM DBS3900 Hardware Structure2.0JibJib Boonrutai100% (3)
- Downlink Throughput TroubleshootingDokument21 SeitenDownlink Throughput TroubleshootingRajeev Sharma100% (2)
- BTS3900ALDokument337 SeitenBTS3900ALHamza_yakan967100% (1)
- Mobile Terminal Receiver Design: LTE and LTE-AdvancedVon EverandMobile Terminal Receiver Design: LTE and LTE-AdvancedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei BBU3910 DescriptionDokument50 SeitenHuawei BBU3910 DescriptionLê Hữu Ái100% (12)
- Huawei Solution Description of Pts 30mbps Everywhere PDFDokument12 SeitenHuawei Solution Description of Pts 30mbps Everywhere PDFfahmi1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Radio 2217Dokument2 SeitenRadio 2217sammyd2009100% (1)
- Umpt PDFDokument48 SeitenUmpt PDFramos_lisandro67% (3)
- Description For UMPTe and UBBPe BoardDokument16 SeitenDescription For UMPTe and UBBPe BoardHasnain Muhammad100% (4)
- EnodeB LTE Product DescriptionDokument66 SeitenEnodeB LTE Product DescriptionLê Hữu ÁiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zte Zxdu68 b201 Vison CuDokument2 SeitenZte Zxdu68 b201 Vison CuLê Hữu ÁiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3900 Series Base Station Configuration Principles (SRAN9.0 - 13) (PDF) - enDokument236 Seiten3900 Series Base Station Configuration Principles (SRAN9.0 - 13) (PDF) - enMd Ataulla100% (2)
- 1-5 BTS Hardware Quality Standard-20120922-EMTS Project TrainingDokument97 Seiten1-5 BTS Hardware Quality Standard-20120922-EMTS Project Trainingengr_dandayo1Noch keine Bewertungen
- BTS PDFDokument339 SeitenBTS PDFHamza Amellouk100% (1)
- LTEDokument23 SeitenLTEShwetha Ha100% (1)
- RRU5258 Technical Specifications (V100R015C10 - 01) (PDF) - ENDokument42 SeitenRRU5258 Technical Specifications (V100R015C10 - 01) (PDF) - ENROLDAN NORIEGA100% (1)
- 3.2 Installation Alternatives: Radio DescriptionDokument31 Seiten3.2 Installation Alternatives: Radio DescriptionMaximiliano Rodriguez50% (2)
- Mobile Communications Towards 2030Dokument16 SeitenMobile Communications Towards 2030Amol MahoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Backhauling / Fronthauling for Future Wireless SystemsVon EverandBackhauling / Fronthauling for Future Wireless SystemsKazi Mohammed Saidul HuqNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5900 Series Base Station Product Description 03 (20180912)Dokument72 Seiten5900 Series Base Station Product Description 03 (20180912)Haider Al SaadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTE FDD RRU3959&RRU3959w DescriptionDokument31 SeitenLTE FDD RRU3959&RRU3959w DescriptionRegisNoch keine Bewertungen
- BBU3910 Description - 25 (20190330)Dokument89 SeitenBBU3910 Description - 25 (20190330)JosueMancoBarrenechea100% (1)
- HUAWEI DBS3900 Dual Mode Base Station Hardware Structure and PincipleDokument79 SeitenHUAWEI DBS3900 Dual Mode Base Station Hardware Structure and PincipleCarlos CrisostomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Install Radio 2219Dokument39 SeitenInstall Radio 2219turand100100% (1)
- BBU Product Description PDFDokument4 SeitenBBU Product Description PDFArnett Cruz100% (1)
- Huawei Mobily WiMAX LTE (Samar 707649)Dokument78 SeitenHuawei Mobily WiMAX LTE (Samar 707649)Nasir Iqbal100% (1)
- Comba Product Catalog 2012 PDFDokument176 SeitenComba Product Catalog 2012 PDFErsin ADAL100% (1)
- HUAWEI DBS3900 Hardware StructureDokument20 SeitenHUAWEI DBS3900 Hardware Structurealiraza100% (3)
- Huawei BBU PDFDokument4 SeitenHuawei BBU PDFArnett Christopher CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- GTMU Board DescriptionDokument4 SeitenGTMU Board DescriptionJohn EarleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- RRU3668 Hardware Description (05) (PDF) - en PDFDokument42 SeitenRRU3668 Hardware Description (05) (PDF) - en PDFJaime Yarihuaman QuispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- RRU3928 Description V1.2Dokument15 SeitenRRU3928 Description V1.2c2poyraz100% (2)
- RRU3804 Introduction and Hardware InstallationDokument75 SeitenRRU3804 Introduction and Hardware InstallationOsama El MesalawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- LampSite Solution Product Description-20150707Dokument20 SeitenLampSite Solution Product Description-20150707Carlos León PalominoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei Lampsite Solution Overview 01Dokument10 SeitenHuawei Lampsite Solution Overview 01Haitham DaradkehNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3900 Series Base Station Product Description: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDDokument69 Seiten3900 Series Base Station Product Description: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDZaher BarghachounNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dokumen - Tips - 2717 Ipclk1000 Product Descriptionpdf PDFDokument25 SeitenDokumen - Tips - 2717 Ipclk1000 Product Descriptionpdf PDFdan__danNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hauwei MSAN 00332722 UA5000 Product Description V100R017 03 PDFDokument141 SeitenHauwei MSAN 00332722 UA5000 Product Description V100R017 03 PDFsrikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPS Block Plus 200 Ka 1 Phase 230 V: Technical Data Value UnitsDokument5 SeitenCPS Block Plus 200 Ka 1 Phase 230 V: Technical Data Value UnitsLê Hữu ÁiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power System Setting Information - TP48300BDokument2 SeitenPower System Setting Information - TP48300BLê Hữu ÁiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.catalogue PNGB 12200Dokument2 Seiten1.catalogue PNGB 12200Lê Hữu ÁiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.ZXDU68 B301 (V5.0R20M01) Embedded DC Power System DatasheetDokument5 Seiten1.ZXDU68 B301 (V5.0R20M01) Embedded DC Power System DatasheetLê Hữu ÁiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZXD3000 V5.5 (R03) Rectifier Datasheet-UpDokument4 SeitenZXD3000 V5.5 (R03) Rectifier Datasheet-UpLê Hữu ÁiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.catalogue PNGB 121500PDokument2 Seiten1.catalogue PNGB 121500PLê Hữu Ái100% (1)
- Wuhan Intepower 6GFMJ-150Dokument2 SeitenWuhan Intepower 6GFMJ-150Lê Hữu ÁiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSB TPL 121800Dokument2 SeitenCSB TPL 121800Lê Hữu ÁiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coslight GFM-200ZDokument1 SeiteCoslight GFM-200ZLê Hữu Ái100% (1)
- Nguyen Ly Thong Tin SoDokument11 SeitenNguyen Ly Thong Tin SoLê Hữu ÁiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ochure Rev 1 2 0 PDFDokument2 SeitenOchure Rev 1 2 0 PDFGordon BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Millimeter Wave Beamforming For Wireless Backhaul and Access in Small Cell NetworksDokument13 SeitenMillimeter Wave Beamforming For Wireless Backhaul and Access in Small Cell Networkssuperpoop2Noch keine Bewertungen
- (Advanced Techniques For 4G Systems) : Name: Alaa Ashraf Abdelmoneim Elagrody Sec: 1 ID:1Dokument11 Seiten(Advanced Techniques For 4G Systems) : Name: Alaa Ashraf Abdelmoneim Elagrody Sec: 1 ID:1alaa elagrodiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DS AP570SeriesDokument7 SeitenDS AP570SeriesadinNoch keine Bewertungen
- State of The ArtDokument863 SeitenState of The ArtXiuquan ZhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mimo Wifi NabarDokument33 SeitenMimo Wifi NabarAmine BouazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Brief Product Brief: Cmax-Dm30-CpuseiDokument2 SeitenProduct Brief Product Brief: Cmax-Dm30-CpuseiNataša Mihić BoskovićNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIMO Antenna System For LTE (4G) : Suvarna S.phule Prof. A.Y.Kazi Department of Electronics EngineeringDokument6 SeitenMIMO Antenna System For LTE (4G) : Suvarna S.phule Prof. A.Y.Kazi Department of Electronics EngineeringKousal ChakrabortyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZTE ZXSDR B8200 Product DescriptionDokument35 SeitenZTE ZXSDR B8200 Product DescriptionyekoyesewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aau Redefines Site Architecture: Huawei Technologies Co.,Ltd. Singleran Wireless MarketingDokument9 SeitenAau Redefines Site Architecture: Huawei Technologies Co.,Ltd. Singleran Wireless MarketingGeorge KlewkneeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Literature ReviewDokument8 Seiten03 Literature ReviewDonika MarkandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch6 WirelessMobileNetworks 4G5GDokument46 Seitench6 WirelessMobileNetworks 4G5GYohan Ftsadik100% (1)
- Aruba 370 Series Access Points: High Performance 802.11ac Wave 2 For Outdoor EnvironmentsDokument6 SeitenAruba 370 Series Access Points: High Performance 802.11ac Wave 2 For Outdoor EnvironmentsSergio SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIMO PresentationDokument15 SeitenMIMO PresentationAnonymous OPfgsRdpt9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Results 2222Dokument3 SeitenResults 2222Rituvic PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Mutual Coupling, Correlations, and Tarc in Wibro Mimo Array AntennaDokument4 SeitenAnalysis of Mutual Coupling, Correlations, and Tarc in Wibro Mimo Array AntennaKousal ChakrabortyNoch keine Bewertungen
- United States Patent: (10) Patent No.: US 8,793,093 B2Dokument19 SeitenUnited States Patent: (10) Patent No.: US 8,793,093 B2Mary HullNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hexport Multi-Band Antenna: Hpa-33R-Buu-H6 Data SheetDokument10 SeitenHexport Multi-Band Antenna: Hpa-33R-Buu-H6 Data SheetDavid OlayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec6801 PDFDokument101 SeitenEc6801 PDFnandhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Synchronization and Low Complexity Detection For High Speed Wireless Local Area NetworkDokument75 SeitenTime Synchronization and Low Complexity Detection For High Speed Wireless Local Area NetworkarchanadevivemulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cognet: Cognitive Super Resolution Network For Persistent End-To-End Mobility Communication in Mimo SystemsDokument4 SeitenCognet: Cognitive Super Resolution Network For Persistent End-To-End Mobility Communication in Mimo SystemsProjects MNoch keine Bewertungen