Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
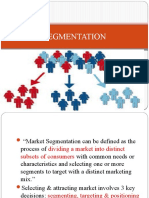
Marketing Session 5 Buying Behaviour and Marketing Strategy-Segmentation
Hochgeladen von
Eman TOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Marketing Session 5 Buying Behaviour and Marketing Strategy-Segmentation
Hochgeladen von
Eman TCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Marketing Session 5
Buying behaviour and Marketing Strategy- Segmentation
A. INTRODUCTION TO SEGMENTATION
B. SEGMENTATION-BASED AND DESCRIPTORS
C. SEGMENTATION-TECHNIQUES
A. INTRODUCTION TO SEGMENTATION
- A market is usually heterogeneous and is segmented into buying
behaviours
- Segmentation is the process of dividing such heterogeneous markets into
smaller segments and these segments are homogeneous within.
1. Analyse buying behaviours and find the variables that define different
buying behaviours
2. Identify the factors that influence buying behaviour and find indicators
3. Define segments
B. SEGMENTATION-BASED AND DESCRIPTORS
1. Geographic: nations, regions, state, neighbourhoods
2. Socio-demographic: age, gender, family size, you compare what happen
within a segment and then relate it to the overall market. These are
known as concentration index. Close to 100 means they are very
representative. Demographic: easy to segment but not necessary accurate
the Prince Charles Osborn example.
3. Lifestyle variables: psychographic segmentation
- Palmolive Target example, as one look at personal for hygiene and
one for beauty lifestyle.
- The Vals Psychographic Inventory:
More resources
Less resources
Primary Motivation: Ideals, Achievement, Self Expression.
First Idea: The size of the segment. Percentage using Internet, in this graph you
should spot out the biggest difference in the segments.
Innovators: lot of resources driven by a different primary motivation
Survivors: narrow focused life, they tend to be cautious consumers, very modest
and loyal to brands especially at discount.
Generations:
Harley Davidson Segments:
- Tour Gliders, Dream Riders, Hard core, the differing types of people to ride each
bike according to life styles. S
Social Techno-graphics by Forrester: Participation in Internet activities.
Types of Gasoline Buyers:
Shopping Segments: time stressed, explorer, trip planner, and bargain hunter.
C. SEGMENTATION-TECHNIQUES
a) Questions for determining segmentation bases or need variable
b) Cluster analysis: DATA REDUCTION technique, simplifying the market by
putting together individuals with a vey similar profile.
- Cluster features: 1,2,3 and 4, in the example, users, us messaging
services, higher propensity to work in remote areas, innovators
who use cell phones a lot.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Consumer Buying Behaviour & Integtrated Marketing CommunicationsVon EverandConsumer Buying Behaviour & Integtrated Marketing CommunicationsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)
- Changing Out The Injector Seals On A 2007 PJ Ford Ranger 3.0 TDCiDokument3 SeitenChanging Out The Injector Seals On A 2007 PJ Ford Ranger 3.0 TDCiAgustinus D100% (3)
- Redbull Report (Consumer Behavior)Dokument7 SeitenRedbull Report (Consumer Behavior)Eman T100% (2)
- CH 3 STP and CBDokument27 SeitenCH 3 STP and CBSimantoPreeom100% (1)
- Assessment Task 1: Knowledge Test: Provide Your Response To Each Question in The Box BelowDokument19 SeitenAssessment Task 1: Knowledge Test: Provide Your Response To Each Question in The Box BelowAlessandro Fonseca100% (1)
- IOT SyllabusDokument3 SeitenIOT Syllabuspoojan thakkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MP 4Dokument8 SeitenMP 4Pei Xin YauNoch keine Bewertungen
- CB Assignment 1Dokument5 SeitenCB Assignment 1Amina RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ParaphraseDokument14 SeitenParaphraseHannah ArohaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Segmentation, Targeting, Positioining: Market Segment-A Group of Customers Who Share A Similar Set of Needs and WantsDokument33 SeitenSegmentation, Targeting, Positioining: Market Segment-A Group of Customers Who Share A Similar Set of Needs and WantsADITYANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8-Identifying Market Segments and Targets-PHILIP OMAR FAMULARCANODokument7 SeitenChapter 8-Identifying Market Segments and Targets-PHILIP OMAR FAMULARCANOPHILIP OMAR FAMULARCANONoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Market SegementationDokument18 SeitenUnit 2 Market Segementationyoledif573Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2) SegmentationDokument46 Seiten2) SegmentationSugandhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 - Identifying-Market-Segments-And-TargetsDokument31 SeitenChapter 9 - Identifying-Market-Segments-And-TargetsChâu Giang TrầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning PART 1Dokument21 SeitenSegmentation, Targeting and Positioning PART 1MartaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Brand "Ayush"Dokument76 SeitenThe Brand "Ayush"AnuragNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer BehaviourDokument8 SeitenConsumer BehaviourLaura NeamtuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outline L4 Tourism Hospitality MarketingDokument7 SeitenOutline L4 Tourism Hospitality MarketingPaul Christian DayandayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Segmentation Targeting Positioning (STP)Dokument20 SeitenSegmentation Targeting Positioning (STP)doreen11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2Dokument29 SeitenModule 2Rabindra DashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument56 SeitenChapter 3krishgvr07Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - Marketing ManagementDokument6 SeitenUnit - Marketing ManagementkapuNoch keine Bewertungen
- C1B022001 - Nabilah Fatimathul Qaidah - Marketing Chapter 9Dokument5 SeitenC1B022001 - Nabilah Fatimathul Qaidah - Marketing Chapter 9Nabilah Fatimathul QaidahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market SegmentsDokument66 SeitenMarket SegmentsAnonymous ibmeej9Noch keine Bewertungen
- SegmentationDokument3 SeitenSegmentationGohil SatyendrasinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 33 Marketing NotesDokument6 Seiten33 Marketing NotesDharmesh BhikadiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 SegementationDokument7 SeitenChapter 4 SegementationJk KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer Buying BehaviorDokument18 SeitenConsumer Buying BehaviorAda Araña DiocenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer Behavour Ch-4Dokument6 SeitenConsumer Behavour Ch-4Ilma GirmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer AnalysisDokument19 SeitenConsumer AnalysisJenine Sipagan0% (1)
- Marketing Market Segmentation PINf20Dokument5 SeitenMarketing Market Segmentation PINf20Kamila RadzvilavičiūtėNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Segmentation: Assignment - 02Dokument7 SeitenMarketing Segmentation: Assignment - 02Swaraj DubalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple PCWareDokument8 SeitenMultiple PCWaredxtrahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auto Indusrty SegmentationDokument9 SeitenAuto Indusrty SegmentationParth PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology: NameDokument9 SeitenJomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology: NameRedemptah Mutheu MutuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 2-Marketing SegmentationDokument23 SeitenTopic 2-Marketing SegmentationTanvir Ahmed RajibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing CHAPTER 5Dokument23 SeitenMarketing CHAPTER 5lim sweetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 MarketingDokument12 SeitenModule 3 MarketingDr. Nijaguna GurumurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Segmentation, Targeting and PositioningDokument11 SeitenMarketing Segmentation, Targeting and PositioningVictor Munene Muchiri100% (2)
- 8.Reading-Benefit SegmentationDokument7 Seiten8.Reading-Benefit Segmentationrajthakre81Noch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer Buying BehaviorDokument18 SeitenConsumer Buying BehaviorAda Araña DiocenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 9 Identifying Market Segments & Targets - Group 1Dokument26 SeitenCH 9 Identifying Market Segments & Targets - Group 1Rizky AlmazeinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trier 5 Segmentation and PositioningDokument75 SeitenTrier 5 Segmentation and Positioninganshuman sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customer ProfilingDokument41 SeitenCustomer ProfilingLea Bianca Quinto100% (1)
- Unit 2 Marketing ManagementDokument34 SeitenUnit 2 Marketing ManagementMuhammed Althaf h sNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 - Principles of Marketing - Market Segmentation, Targeting and PositioningDokument25 Seiten06 - Principles of Marketing - Market Segmentation, Targeting and PositioningZakirya KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MP?.Imp Questions NotesDokument3 SeitenMP?.Imp Questions Notes074 simran panigrahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 9 Identifying Market Segments & Targets - Group 1Dokument26 SeitenCH 9 Identifying Market Segments & Targets - Group 1Rizky AlmazeinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retail Man w3Dokument3 SeitenRetail Man w3Kim ErikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy (WRITTEN REPORT)Dokument9 SeitenCustomer-Driven Marketing Strategy (WRITTEN REPORT)SPOOKY TRIONoch keine Bewertungen
- Market Segmentation and Product PositioningDokument10 SeitenMarket Segmentation and Product Positioningleoneil teNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bases of Market SegmentationDokument23 SeitenBases of Market SegmentationAvik SanyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- STP of Successful BrandDokument7 SeitenSTP of Successful BrandVatsal GadhiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market SegmentationDokument28 SeitenMarket SegmentationElward EL WardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer Behaviour ReviewerDokument37 SeitenConsumer Behaviour ReviewerDonna Chelsea OrdialesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Target Marketing and Marketing SegmentationDokument22 SeitenTarget Marketing and Marketing Segmentationbhavgifee80% (5)
- Market Segmentation: Social Issues Personal Interest ReligionDokument3 SeitenMarket Segmentation: Social Issues Personal Interest ReligionYhom NidoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q1. Discuss The Various Types of Market Segmentation: Submitted By-Rani PujaDokument3 SeitenQ1. Discuss The Various Types of Market Segmentation: Submitted By-Rani PujaRani PoojaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 - Part 1Dokument14 SeitenChapter 9 - Part 1JP ONoch keine Bewertungen
- FASHION MARKETING-Consumer BehaviorDokument26 SeitenFASHION MARKETING-Consumer Behaviorsurbhimo100% (1)
- Benefit Segmentation-A Decision-Oriented Research ToolDokument6 SeitenBenefit Segmentation-A Decision-Oriented Research ToollynusannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retail Fashion Product Storage and LogisticsVon EverandRetail Fashion Product Storage and LogisticsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- A Joosr Guide to... Small Data by Martin Lindstrom: The Tiny Clues That Uncover Huge TrendsVon EverandA Joosr Guide to... Small Data by Martin Lindstrom: The Tiny Clues That Uncover Huge TrendsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Company PMWDokument8 SeitenCompany PMWEman TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 1 Quantitative MethodsDokument2 SeitenProblem Set 1 Quantitative MethodsEman TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Family Budget1Dokument2 SeitenFamily Budget1Mbadilishaji DuniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Redbull ReporDokument6 SeitenRedbull ReporEman TNoch keine Bewertungen
- MarketingDokument4 SeitenMarketingEman TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing: Session 3. The Business Environment (Macro and Micro)Dokument2 SeitenMarketing: Session 3. The Business Environment (Macro and Micro)Eman TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siemens Electric Motor Works Process-Oriented CostingDokument1 SeiteSiemens Electric Motor Works Process-Oriented CostingEman TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation Surfaces (Results Overview) : Philips HRODokument4 SeitenCalculation Surfaces (Results Overview) : Philips HROsanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ford Fiesta Specifications: Exterior DimensionsDokument2 SeitenFord Fiesta Specifications: Exterior DimensionsBuhuntuUhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesDokument18 SeitenGovernment Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Power Electronics & DrivesVK DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adobe Transaction No 0991059129 20190125Dokument2 SeitenAdobe Transaction No 0991059129 20190125Mohamed WinnēriNoch keine Bewertungen
- A-Class Mark II: Print Engines For ApplicatorsDokument25 SeitenA-Class Mark II: Print Engines For ApplicatorsJeffery ReynoldsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erita Astrid - UPBDokument25 SeitenErita Astrid - UPBmas_kinooooNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Daily ConversationDokument27 SeitenEnglish Daily ConversationIrma Chyntia Dewi100% (2)
- Pump Installation Report: 30 Damascus Road, Suite 115 Bedford, Nova Scotia B4A 0C1Dokument1 SeitePump Installation Report: 30 Damascus Road, Suite 115 Bedford, Nova Scotia B4A 0C1Yosif BabekerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algorithmic Versus Human AdviceDokument31 SeitenAlgorithmic Versus Human AdviceDaqiang ChenNoch keine Bewertungen
- HILTI Typical Plumbing ApplicationsDokument140 SeitenHILTI Typical Plumbing ApplicationskuraimundNoch keine Bewertungen
- E TDS ManualDokument30 SeitenE TDS ManualJeetendra ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TM 9-792 M21 AMMUNITION TRAILERDokument128 SeitenTM 9-792 M21 AMMUNITION TRAILERAdvocate100% (1)
- (ENG) C&T Catalog Hydrelio® Technology 2021Dokument24 Seiten(ENG) C&T Catalog Hydrelio® Technology 2021ReenNoch keine Bewertungen
- CFD Analysis of Free Cooling of Modular Data CentersDokument4 SeitenCFD Analysis of Free Cooling of Modular Data CentersEmad AbdelsamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- CASE STUDY - Collapsed Wind Tower - A Root Cause Investigation (Element Materials Technology)Dokument3 SeitenCASE STUDY - Collapsed Wind Tower - A Root Cause Investigation (Element Materials Technology)engrrahman3135Noch keine Bewertungen
- QlikView Sviluppo Progettuale enDokument5 SeitenQlikView Sviluppo Progettuale enEleazar BrionesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConnectorsDokument3 SeitenConnectorsmatrixworld20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Operation Manual: Smart-UPS Uninterruptible Power SupplyDokument18 SeitenOperation Manual: Smart-UPS Uninterruptible Power SupplyHafeez AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Texture Formats Used by CFS3Dokument2 SeitenTexture Formats Used by CFS3Hillmen HussinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix 1: Lesson Plan (Template)Dokument4 SeitenAppendix 1: Lesson Plan (Template)Anonymous X7u8sMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phone Genesys ConfigurationDokument22 SeitenPhone Genesys ConfigurationRodolfo TobiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4wd SystemDokument31 Seiten4wd SystemManuales Transmisiones AutomaticasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Paper On Plate Heat Exchanger PDFDokument8 SeitenResearch Paper On Plate Heat Exchanger PDFc9s9h7r7100% (1)
- Invoice Cod Invoice Cod: Agen Pos Agen PosDokument4 SeitenInvoice Cod Invoice Cod: Agen Pos Agen Poswahids0204Noch keine Bewertungen
- Snare Drum: Some Entries From Various Sources (Loosely Cited)Dokument6 SeitenSnare Drum: Some Entries From Various Sources (Loosely Cited)gljebglejebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mac Puarsa MRL SCHEMATICDokument28 SeitenMac Puarsa MRL SCHEMATICthanggimme.phanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inlet Modules Model Code: ExampleDokument1 SeiteInlet Modules Model Code: ExamplemhasansharifiNoch keine Bewertungen
- After12th FinalDokument114 SeitenAfter12th FinaltransendenceNoch keine Bewertungen