Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
11 Types of Solids - S ANSWERS
Hochgeladen von
HP400 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
37 Ansichten6 Seitenssr
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenssr
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
37 Ansichten6 Seiten11 Types of Solids - S ANSWERS
Hochgeladen von
HP40ssr
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 6
Sala al aia ie ated et hd
Types of Solids
‘What are some common categories of solids, and their properties?
Why?
Nor al solids are the same, Solid substances have a tremendously wide range of melting point. Helium
salsa 772°C wetland eee,
Some readily dissolve in wates, others do not. In this activity, you'l look at solids, che types
of eubetancer hat ae typically in each category and some of he properties type fr each,
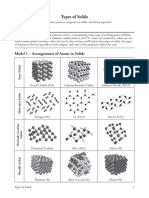
Model 1.— Arrangements of Atoms in Solids
‘
Z
sen
Platinum (Pt) Nickel (Ni)
‘Types of Solids 89
L
2
5.
Lie the four types of solids illustrated in Model 1.
Tonis, molecular, nework covalent and mesa
CCompleee columns A-C in the mble below by referring to the examples in Model 1. Place a
check in the box chat appropriately describes the types of atoms that are usuelly seen in each type
solid.
ry B c D E F
All toms are| All atoms | #9988 85 | Molecalar | Formula ;
Tnoumaals | are meals 22054 arucre | unika | Ate foese
t :
Tonic ,
Tonle x xX | tonic bonds
‘Molecalar [ Covalens bonds
Solids x x Intermolecular fers
| |
‘Network
Covalent x X | Content bonds
Solide
Metalic
Mant x X | Meal bonds
‘Complete columns D and B in the table ebove by referring to the examples in Model 1. Place
an X in the box that appropriately describes the arrangement of atoms ar molecules in the solid
(Cither molecalar—dirtinct molecules, or formula unite—tepeating units in three dimensions
vwith no distinet molecules).
See table in Qustion 2.
‘There are four possible forces of atraction that hold atoms or molecules rogether in a solid:
covalent bonds, ionic bonds, metallic bonds and intermolecular forces. These depend on the type
of asoms in the solid and whether the connections are between ions, ams or molecules, Wichin
‘your group, discuss the type of axractive forces that are moet likely holding the atoms or mol-
‘cules together in each type of solid. List your answers in column F in the table above.
See sable in Question 2.
Read This!
“When a solid substance is eased, che weakest aturaccve force in the solid structure are overcome, and
the solid melts, In some cases, this results in individual atoms or ions, and in othes came, this results in
individual molecules. Regardless, melting is « physical change and does not ater the chemical formula of
POGIL™ Activities for AP* Chemistry
Laaaanaaaanaanaaeecaeererereeeeeaenataeegers
5. For each type of solid in Model 1, indicare the type of attractive forces that are broken upon
rmelting, and describe the individual particles that malee up the etulting liquid.
si
“aaa | SE
Tonic onic bonds Tons
‘Network covalent Covalent bonds Atoms
Metallic Metallic bonds Atoms
6. Match the following descriptions with one of the four types of solids, .
‘Metallic atoms with very loose electrons for & lattice of nuclei held
Mellie _ togpthex by a.20a of electrons, or metallic bonds.
‘with covalent bonds, The molecules
‘intermolecular forces of attraction,
- scion
odes aoe
fenwork covalent
fa pirical oid ba wry song seas fore ould you expec the aking pola of at
__ Belid to be relatively high or relatively low? Explain your reasoning,
Tha els would be higher because the strong bonds would requir y (ig )
Ceara mtn mets
Model 2 ~ Melting Points and Enthalpies of Fusion
aq
‘Type of Solid Substance Rae | Matiog Point ea
Tron(ft) sulfide BS 1195 51.0
Tonic Calcium bromide | CaBr 730 175;
Sodium chloride [NaCl 804 303
‘Nitrogen’ N 210 0.72
Molecular ‘Water 7,0 0.0 6.02
Carbon dioxide CO; 78 8.10
Diamond: c 3550 117.0
‘Network covalent Silica SIO, 1650 "25
Silicon Si 1687 50.0
~|___ Platinum Pe 1770. 24.0
Metallic ‘Brass (Cx and Za ~930 Varies
[7 Nickel Ni 1453 710
o1
8, Notice that the substances lised in Model 2 are the same as those in Model 1.
4 Which type of solid has the lowest melting points?
Moleculer slide have she lowest melting points
4, Is your answer in part « consistent with your answer to Question 7?
Yo.
9. The enthalpy of fusion given in Mode! 2 for each substance ia a measure of the energy (in kJ)
needed to mel a mole of that substance.
‘a. Which type of solid has the lowest enthalpies of fusion?
Molecular solids have she lowest enthalpies of fusion. .
{s Isyour answer in part « consistent with what you know to be the relative strength of the four
types of attractive forces? Explain why or why not.
-Yos when a molecular olid mets, the intermolecelar forces are broken, Thete are the weakest forces
10 very little energy should be needed to melt these substances
10. Using both melcing point data and enthalpy of fusion dara, rank the remaining three types of
solids from weakest artactive forces to strongest attractive forces, Make sure there is consensus in
yout group before moving on.
@ Molecular < Ionic = Metallic < Network covalent
Read This!
‘Js you may have found in answering the previous question, there is lot of overlap in properties
Ae ye acres sadam ec hs ehight racing pin than sore
of the network covalent solids, but the majority of metallic solids heve a much lower melting point than
neewouk covalent solids, The cazegoris for slide are not as clearcut at we would like them to be; never-
theless, chey are useful for predicting relative properties.
R11, Use the concepts you have eared in this acvity to predic the type of eolid for each ofthe fal-
lowing substances. Anyone in your group should be able to juntify your group's answers,
5 Chemical [Meking Point [thal pa ype of Solid
Chlorine cl, 102 641 | Molecular
‘Hydrogen bromide | HBr -87 241 ‘Molecular
Tania Ey 1668 209 Metalic
Sodium bromide | NaBr 747 261 | —_donie
Boron B 2076 50.2 Network covalent
Mercury Hg 7383 229) Mealic
2 POGIL™ Activities for AP* Chemistry
RRAAADALAATATUTATTATATTTLLALATTTTLAGIITT EEE
,
)
j
y
’
,
5
'
'
y
‘
,
)
»
’
,
a
,
y
,
'
,
,
)
'
,
’
’
)
’
)
’
)
'
)
’
)
'
,
'
)
‘
or:
“like dissolves like.”) For a substance to be conductive, in any stare, there must be icles ina
mobile sate 9 that they can complete a circuit. ase pecs
Model 3 ~ Solubility and Conductivity of Solids
T
‘in! netive re Conductive in
simu | Somat | Same |Sicr| crtets| cte
Tron(it) sulfide | FS Insoluble No Yes NIA
Calcium bromide | CaBr, | Very soluble No Yes Yea
Sodium chloride | NaCl | _Vecy soluble No Yes Yes
Nitrogen |. Nz | Slightlysoluble | No No No
‘Warer H,0 NA ‘No ‘Slightly N/A
Carbon dioxide | CO, | Slightiysoluble | No “No No
Diamond c Insoluble No No NA
Silica SiO; Tasoluble No ‘No __ NIA"
Platinum Pe Insoluble ‘Yes Yes N/A
Brass Cuand Zo Insoluble Yes Yes NA
Nickel Ni Tngoluble | Yea Yes NA
. ‘N/A= not applicable
12, Refer to Model 3,
4 Which type(s) of solid is generally very soluble in wares?
Tonic substances are most soluble i wnat,
4 Which type(s) of solid is least soluble in water?
Metallic and network covalent substances are least soluble in water,
13, Refer to Model 3.
4 Which type of solid is most conductive in the solid sate?
Mevallic substances are most conductive as solide,
4, Use the concepts you have learned about the type of solid in part a to explain why itis con-
ductive in the solid stae. :
Metals contain very mobile valence electrons that cam move in the solid to conduct an electric current.
14, Explain why ionic substances would be conductive after they are melted, even though they are
not conductive as solids.
As solids, the ions in an ionic solid are seuch in a crystal lastice—they are not mobile. Once the solid is
melted however, she ions become mobile and can move in she Hguid state +0 conduct an electric current.
“Types of Solids 93
Extension Questions
15, The last column in Model 3 (Condiictive in Aqueous Solutions) has several N/A entries, Give
‘two reasons why conductivity data for thoie substances would not exist.
Fthe substance is insoluble, i would be impossible to measure conductivity data for an aqueous solution.
16, Engineers use marerials to perform different functions based on the properties of the materials,
For centuries we have used metas for tools and more recently for electrical circuits. What proper-
ties of metallic solids make them well suited for this purpose?
Metals are strong, insoluble and conductive as a solid. You would not want our electrical cirewits to
break eaxily, dissolve om a rainy day or be resistant to electrical current,
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Sartre, - Patterns of Bad FaithDokument11 SeitenSartre, - Patterns of Bad FaithHP40Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Curves - ScoreDokument1 SeiteCurves - ScoreHP40Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- A Tribute To QueenDokument2 SeitenA Tribute To QueenHP40Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- I Shall No Lyrics - ScoreDokument1 SeiteI Shall No Lyrics - ScoreHP40Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Charles Mingus: Let My Children Hear MusicDokument2 SeitenCharles Mingus: Let My Children Hear MusicHP40Noch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- 2-25 - Acoustic BassDokument4 Seiten2-25 - Acoustic BassHP40Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- For MZ (1:28) - Baritone SaxDokument1 SeiteFor MZ (1:28) - Baritone SaxHP40Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- "Trade Off": Manjunath BC, Transc. NDFDokument3 Seiten"Trade Off": Manjunath BC, Transc. NDFHP40Noch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Without A Song The Day Would Never EndDokument1 SeiteWithout A Song The Day Would Never EndHP40Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Late Green: (R/h/y/t/h/m/s/ /a/p/p/r/o/x/i/m/a/t/e)Dokument2 SeitenLate Green: (R/h/y/t/h/m/s/ /a/p/p/r/o/x/i/m/a/t/e)HP40Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sick LickebDokument1 SeiteSick LickebHP40Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- 11 Types of Solids - SDokument6 Seiten11 Types of Solids - SHP400% (7)
- Brochure PDFDokument2 SeitenBrochure PDFHP40Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)