Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
11th Advp1
Hochgeladen von
Pranav TejaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
11th Advp1
Hochgeladen von
Pranav TejaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Physics PART – I
SECTION – A
Single Correct Choice Type
This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D)
out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
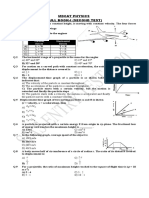
1. Block A and B have masses 40 kg. and 60 kg resp. They are placed on a smooth surface and the
spring connected between them is stretched by 1.5m. If they are released from rest, determine
the speeds of the blocks at the instant the spring became unstrentched
(A) V1 = 3 m/s, V2 = 4.5 m/s (B) V1 = 4.5 m/s, V2 = 3 m/s
(C) V1 = 5 m/s, V2 = 6 m/s (D) V1 = 4 m/s, V2 = 3 m/s
2. The end of a chain of length L and mass per unit length , which is piled up on a horizontal
platform is lifted vertically with a constant velocity u by a variable force F. Find F as a function of
height x of the end above platform.
(A) gx 2u2 (B) 2gx u 2
(C) gx u2 (D) u 2 gx
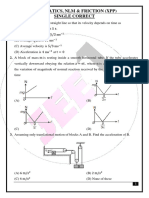
3. In the arrangement of rigid links of equal length l, they can P S
freely rotate about the joined ends as shown in the figure. If
the end U is pulled horizontally with constant speed 20 m/s, R
o
find the approx. speed of end P when the angle SUT is 90 . O U
(A) 5 m/s (B) 10 m/s
(C) 7.1 m/s (D) 14.12 m/s
Q T
4. A disc of radius R is spun to an angular speed 0 about its axis and then
R
imparted a horizontal velocity of magnitude 0 (at t = 0) with its plane v0
4
remaining vertical. The coefficient of friction between the disc and the 0
plane is . The sense of rotation and direction of its linear speed are
shown in the figure. Choose the correct statement. The disc will return to
its initial position
(A) if the value of < 0.5. (B) irrespective of the value of ( > 0).
(C) if the value of 0.5 < < 1. (D) if > 1.
Space for rough work
Multiple Correct Choice Type
This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has 4 choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) for its
answer, out of which ONE OR MORE is/are correct
5. The figures represent two snaps of a travelling wave on a string of mass per unit length, =
1
0.25kg/m. The two snaps are taken at time t = 0 and at t s. Then
24
y(mm) y(mm)
10 10
5 5
–5 x(m) –5 1 x(m)
–10 –10 1
t=0 t=24 s
Figure -1 Figure -2
(A) speed of wave is 4 m/s
(B) the tension in the string is 4 N
(C) the equation of the wave is y = 10 sin (x – 4t )
6
(D) the maximum velocity of the particle m/s
25
1
6. An ideal gas undergoes a process such that P . The molar heat capacity of this process is
T
33.24 J/mol K.
(A) The work done by the gas is 2RT. (B) Degree of freedom of the gas is 4.
C
(C) Degree of freedom of the gas is 3. (D) Y P for the gas is 1.5.
CV
Space for rough work
7. Velocity of a particle of mass 2 kg changes from v1 2iˆ 2ˆj m / s to v 2 (iˆ ˆj)m / s after
colliding with a plane surface
–1 1
(A) the angle made by the plane surface with the positive x–axis is 90º + tan
3
1
(B) the angle made by the plane surface with the positive x–axis is tan1
3
1
(C) the direction of change in momentum makes an angle tan1 with the +ve x–axis
3
1
(D) the direction of change in momentum makes an angle 90 tan1 with the plane surface
3
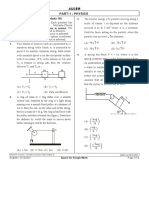
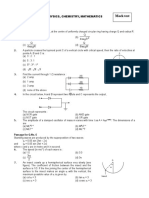
8. A 100 cm long cylindrical flask with inner and outer diameters 2 cm
and 4 cm respectively is completely filled with ice as shown in the
figure. The constant temperature outside the flask is 40ºC. (Thermal
conductivity of the flask is 0.693 W/mºC, Lice = 80 cal/gm).
r1
(A) Rate of heat flow from outside to the flask is 80 J/s. ice
r2
(B) The rate at which ice melts is Kg / s .
4200
(C) The rate at which ice melts is 100 Kg/s.
(D) Rate of heat flow from outside to flask is 40 J/s.
Space for rough work
Comprehension Type
This section contains one group of questions. This group has 3 multiple choice question based on a
paragraph. This question has 4 choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) for its answer, out of which ONLY ONE is
correct
Paragraph for Question Nos. 9 to 11
A bar of cross-section A is subjected to equal and
opposite tensile forces F at its ends. Consider a
plane through the bar making an angle with a F F
plane at right angles to the bar as shown in figure
9. The tensile stress at this plane in terms of F, A and is
F cos2 F
(A) (B)
A A cos 2
F sin2 F
(C) (D)
A A sin2
10. In the above problem, for what value of is the tensile stress a maximum?
(A) Zero (B) 90°
(C) 45° (D) 30°
11. The shearing stress at the plane, in terms of F, A and is
F cos 2 F sin 2
(A) (B)
2A 2A
F sin F cos
(C) (D)
A A
Space for rough work
SECTION – B
(Matching List Type)
This section contains 2 questions. Each question has four statements (A, B, C and D) given in Column I
and five statements (p, q, r, s and t) in Column II. Any given statement in Column I can have correct
matching with ONE or MORE statement(s) given in Column II. For example, if for a given question,
statement B matches with the statements given q and r, then for the particular question, against
statement B, darken the bubbles corresponding to q and r in the ORS.
1. Column-I contains some thermodynamic system and column-II contains its properties. Match the
following columns.
Column – I Column – II
(A) A steel rod is clamped at its two ends and rests (p) 400
on a fixed horizontal base. The longitudinal strain
developed in the rod when temperature rises to
500C is – 3.6 10-4, and the temperature
coefficient of linear expansion of steel is 1.2
10-5 /0C. Find the temperature at which rod is in
relaxed state
(B) Six hundred mole of a gas undergoes a process (q) 27
7 105 N / m2
P=
V
2
4m3
3
where V is volume in m . When volume of the
3
gas is 20 m , its temperature in Kelvin is
approximately equal to
(C) A block of mass 100 gm slides on a rough (r) 20
horizontal surface of zero heat capacity. When
the speed of the block decreases from 10 m/s to
0
5 m/s, its temperature rises by 0.25 C. The heat
capacity of the block in joule/C is
2
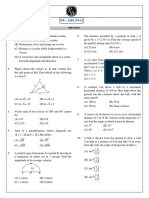
(D) P(N/m ) (s) 15
C
3 105 isochoric
process isothermal
process
A
105 isobaric B
process
T 600 T(Kelvin)
If two moles of a gas consisting of 1
mole of He and 1 mole of H2 undergo a cyclic
process
A B C A as shown in the figure the total
work done in the cycle is 600Rln[9/e] The
temperature T in 0C is
(t) None of these
Space for rough work
2. A standing wave, formed in an organ pipe aligned along the x-axis, is given by
(displacement)y = (5 106 m)sin(4x) cos (1320t) where x is in metre and t is in seconds.
Column – I Column – II
(A) Change in pressure is maximum (p) x = 1/4 m
(B) Change in pressure is minimum (q) x = 1/2 m
(C) Maximum amplitude of vibration (r) x=1m
(D) Minimum amplitude of vibration (s) x = 1/8 m
(t) x = 3/8 m
SECTION – C
Integer Answer Type
This section contains 6 questions. The answer to each of the questions is a single digit integer, ranging
from 0 to 9. The bubble corresponding to the correct is to be darkened in the ORS.
1. The equation of a transverse wave is given by
10 2 sin [30t x 3 y]
where x, y and are in metre, and t in second.
If phase difference between two points
A(2 3m,2m) and B(3 3 m,3m) be n. Find value of n
2. The emissivity of tungsten is approximately 0.35. A tungsten sphere 1 cm in radius is suspended
within a large evacuated enclosure whose walls are at 300 K. What power input is required to
maintain the sphere at a temperature of 3000 K if heat conduction along the supports is
17
neglected? Express your answer in kW after rounding off the nearest integer. Take 108
3
213
S. I. units and .
68
Space for rough work
3. Maximum height reached by a rocket fired with a speed equal to 50% of the escape velocity from
earth's surface is given by R/x. Calculate value of x ? Where R is radius of earth.
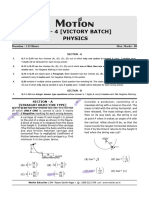
4. A rod AB of length 2 m is hinged at point A and it’s other and B is attached
to a platform on which a block of mass m is kept. Rod rotates about point A
maintaining angle = 30º with the vertical in such a way that platform B
remains horizontal and revolves on the horizontal circular path. If the
coefficient of static friction between the block and platform is = 0.1 then
find the maximum angular velocity in rad/s of rod so that block does not slip
on the platform. [g = 10 m/s2]
A
5. A cylinder of mass M radius R is resting on a horizontal platform (which is parallel to x–y plane)
with its axis fixed along the y–axis and free to rotate about its axis. The platform is given a motion
in X–direction given by X = A cos t. There is sufficient friction present in the surface of contact
that can prevent the slipping between the cylinder and platform. The minimum torque in N-m
acting on the cylinder during its motion is.
[Take M = 4 kg , R = 1m, A = 2m, = 1 rad/s]
6. Oil enters the bend of a pipe in the horizontal plane 4 m/s
with velocity 4 m/s & pressure 280 103 N / m2 A1/4=A2 P
2 A1
as shown. If pressure at Q in (KN/m ) is N 43 . Find
N (specific gravity of oil 0.9 & cos 37 0.8 )
o
37
Q
A1/4 = A2
Space for rough work
Chemistry PART - II
SECTION – A
Single Correct Choice Type
This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D)
out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
1. An inorganic compound (X) on hydrolysis produces a gas which on treatment with sodium
followed by its reaction with ethyl chloride gives another compound (Y). Compound (Y) on heating
with P – 2 catalyst gives (2Z) – pent – 2 – ene as major product. Hence the inorganic compound
(X) is
(A) Tl4C (B) BaC2
(C) SiC (D) Mg2C3
2. Boron trichloride on heating with ammonium chloride at 140C gives a compound (A) which on
reduction with sodium borohydride followed by hydrolysis gives another compound (B). Hence
compound (A) and (B) are respectively.
(A) inorganic graphite & ammonia (B) inorganic benzene & orthoboric acid
(C) trichloroborazine & orthoboric acid (D) diborane & orthoboric acid
3. (S) – 2 – chloropentane on reaction with Cl2 (g) in the presence of U.V. light, gives ‘N’ number of
optically active dichloro derivatives. Hence the value of N is
(A) 5 (B) 6
(C) 7 (D) 4
4. 3 mole of KIO3, 4 mole of KI and 5 mole of HCl are allowed to react according to the equation
given below:
KIO3 2KI 6HCl 3ICl 3KCl 3H2 O
The number of moles of products are
(A) 27 (B) 18
(C) 7.5 (D) 9.5
Space for rough work
Multiple Correct Answers Type
This section contains 4 multiple correct answer(s) type questions. Each question has 4 choices (A), (B),
(C) and (D), out of which ONE OR MORE is/are correct.
5. Which of the following compounds will give same product in hydroboration oxidation and catalytic
hydration?
(A) (B)
(C) (D)
6. Which of the following are aromatic in character?
(A) (B)
(C) (D)
7. Which of the following compounds undergo hydrolysis?
(A) CCl4 (B) SiCl4
(C) BCl3 (D) SiH4
8. Which of the following statement (s) is/are correct regarding photoelectric effect?
(A) No electrons are ejected, regarding of the intensity of the radiation, unless the frequency
exceeds a threshold value characteristic of the metal
(B) The kinetic energy of the ejected electrons increases linearly with the frequency of incident
radiation but is independent of the intensity of the radiation.
(C) Even at low intensities, electrons are ejected immediately if the wavelength is above
threshold value.
(D) It is a direct evidence for the dual nature of light.
Space for rough work
Linked Comprehension Type
This section contains one group of questions. This group has 3 multiple choice question based on a
paragraph. This question has 4 choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) for its answer, out of which ONLY ONE is
correct
Paragraph for question Nos 9 to 11
A more widely used method for locating the double bond of alkene involves the use of ozone. Ozone
reacts with alkene to form unstable compounds called ozonide. Ozonides on reduction with Zn and water
produces carbonyl compound that can be isolated and identified. Ozonolysis can be either of reductive
type or oxidative type.
9. An organic compound A (C5H8) on hydrogenation gives compound B (C5H12). A on ozonolysis
gives methanal and 2 – ketopropanal. The compound (A) is
(A) CH3 (B) CH3
H2C C H2C C
CH CH2 CH2 CH3
(C) CH CH2 (D) H3C CH CH CH2 CH3
H3C HC
CH3
10. O O
i O
C9H14
ii Zn / H O
3
2
(A)
The reactant (A) is
(A) (B)
(C) (D)
Space for rough work
11.
i O3
ii H2O 2B
The product B is
(A) CHO (B) CHO
H2C
CHO
CHO
(C) COOH (D) COOH
H2C
COOH
COOH
SECTION – B
(Matrix-Match Type)
This section contains 2 questions. Each question has four statements (A, B, C and D) given in Column I
and five statements (p, q, r, s and t) in Column II. Any given statement in Column I can have correct
matching with ONE or MORE statement(s) given in Column II. For example, if for a given question,
statement B matches with the statements given q and r, then for the particular question, against
statement B, darken the bubbles corresponding to q and r in the ORS.
1. Match the Column – I with Column – II:
Column – I Column – II
(A) I3 (p) Linear
(B) XeO3 (q) Square planar
(C) Ni(CN)4 (r) Trigonal bipyramidal
(D) OSF4 (s) sp3
2
(t) dsp
2. Match the Column – I with Column – II:
Column – I Column – II
(Compounds) (Ozonolysis products)
(A) (p) Formaldehyde
(B) CH2 = CH – CH = CH – CH3 (q) Glyoxal
(C) (CH3)2C = CH – CH = CH2 (r) Propane – 1, 3 – dial
(D) CH3 – CH = CH2 (s) Acetone
(t) Acetaldehyde
Space for rough work
SECTION – C
(Integer Answer Type)
This section contains 6 questions. The answer to each of the questions is a single digit integer, ranging
from 0 to 9. The bubble corresponding to the correct is to be darkened in the ORS.
SCN
1. One litre of saturated solution contains AgSCN and AgBr. Calculate the ratio of in the
Br
solution. K sp of AgSCN 1.0 10 12 ; K sp of AgBr 5 10 13
2. In the following reaction we start with 2 mol of N2 and 5 mol of H2 exerting a total pressure of
7 atm at a given temperature in a closed vessel when 50% of N2 is converted into NH3, then
N2 3H2 2NH3
What will be the partial pressure of NH3 in atmosphere?
3. If uncertainities in measurement of position and momentum of an electron are equal, then the
6+ x
uncertainity in measurement of its velocity is 7.98 x 10 m/s. then the value of x is.
x+
4. An ion Mn has the magnetic moment 4.9 B.M. The value of x is.
5. A cylinder having internal volume 20 litre contains helium gas at a pressure of 2 atm and 300 K
temperature. The gas is to be used to fill balloons at one atomspheric pressure and 300 K
temperatrue. Number of balloons of capacity 5 litre can be filled is.
6. The maximum number of electrons that can have principal quantum number n = 3 and spin
quantum number s = 1/2 is.
Space for rough work
Mathematics PART – III
SECTION – A
Single Correct Choice Type
This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D)
out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
2 25 2 50
1. If (1 + x + x ) = a0 + a1x + a2 x + … + a50 x then a0 + a2 + a4 + … + a50 is:
(A) even (B) odd and of the form 3n
(C) odd and of the form (3n – 1) (D) odd and of the form (3n + 1).
2. A circle is touching both the coordinate axes and its centre lies o the curve y2 = 4x, then area of
this circle is
(A) 16 (B) 4
(C) 32 (D) none.
3. The number of ordered triplet of positive integers which satisfy the inequality 20 x + y + z 50 is
(A) 50C3 – 19C3 (B) 50C2 – 19C2
51 20
(C) C3 – C3 (D) none.
4. If z1, z2, z3 represent the vertices of an equilateral triangle ABC and
2 2
z2 z1 z3 z1
2 2
sin the is (0 < < )
z2 z3 2z1 z3 z 2
2
(A) (B)
4 3
5
(C) (D) .
6 6
Space for rough work
Multiple Correct Choice Type
This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has 4 choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) for its
answer, out of which ONE OR MORE is/are correct
x2 y2
5. Let 1 be a given ellipse and a bi-focal conic ‘c’ has its foci same as those of the given
9 4
ellipse. If the conic ‘c’ passes through (3, 2), then its equation may be
x2 y2
(A) x2 – y2 = 5 (B) 1
3 2
x2 y2 x2 y2
(C) 1 (D) 1
15 10 18 8
2
6. If the quadratic equation x + 2ax + b(a – 1) = 0 has real roots for all real value of a and b is an
integer, then which of the following is correct?
(A) greatest value of b is 4 (B) no such value of b is possible
(C) least value of b is 0 (D) b can be any integer.
7. In a AEX, T is the mid point of XE, and P is the mid point of ET. If the APE is equilateral of side
length equal to unity then which of the following alternative(s) is/are correct?
(A) AX 13 (B) EAT 90º
1 1
(C) cos XAE (D) AT .
13 3
8. The bisector of internal angles A and ABC meets BC in point D such that BD = 4 and CD = 2. If
altitude AE > 10 and AB and AC are integers, then AC may be
(A) 4 (B) 5
(C) 6 (D) none.
Space for rough work
Comprehension Type
This section contains one group of questions. This group has 3 multiple choice question based on a
paragraph. This question has 4 choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) for its answer, out of which ONLY ONE is
correct
Paragraph for Question Nos. 9 to 11
Read the following write up carefully and answer the following questions:
A line 4 cuts coordinate axes at A(7, 0) and B(0, –5) respectively. A variable line PQ is drawn
perpendicular to AB meeting the coordinate axis at P & Q. The line AQ & BP intersect at R. T is the point
on locus of R, farthest from the origin. A parabola C1 with vertex at T and axis parallel to x-axis is drawn
with lotus rectum 2 units opening towards the right of y-axis. Answer the following questions:
9. Coordinates of T are
(A) (7,5) (B) (7, –5)
(C) (–7, 5) (D) (–7, –5)
10. Equation of parabola C1 is
2 2
(A) y + 10y – 2x + 39 = 0 (B) y + 10y + 2x + 9 = 0
2
(C) y + 10y – 2x + 9 = 0 (D) none.
11. A light ray travelling along the line y = –3, gets reflected from the interior of the parabola, the
equation of the reflected ray is
(A) 4x + 3y = 35 (B) 4x – 3y = – 45
(C) 4x – 3y = 45 (D) none.
Space for rough work
SECTION – B
(Matching List Type)
This section contains 2 questions. Each question has four statements (A, B, C and D) given in Column I
and five statements (p, q, r, s and t) in Column II. Any given statement in Column I can have correct
matching with ONE or MORE statement(s) given in Column II. For example, if for a given question,
statement B matches with the statements given q and r, then for the particular question, against
statement B, darken the bubbles corresponding to q and r in the ORS.
1. There are two Indian couples, 2 American couples and one unmarried person
Column – I Column – II
(A) The total numbers of ways in which they can sit in a row
such that an Indian wife and an American wife are always (p) 5760
on either side of the unmarried person
(B) The total numbers of ways in which they can sit in a row
such that the unmarried man always occupy the middle (q) 24230
position.
(C) The total number of ways in which they can sit around a
circular table such that Indian wife & American wife are on (r) 40320
either side of unmarried person.
(D) If all the nine persons are to be interviewed one by one
then the total number of ways of arranging their interviews (s) 22680
such that no wife gives interview before her husband
(t) 28410
2. Match the following Column-I with Column-II
Column – I Column – II
(A) If 2sinx, sin 2x and 2 cosx are in A.P., then value of |sinx + 5 1
cosx| is (p)
2
(B) If angles of triangle are in A.P. with common difference
1 3
equal to of the greatest angle then, ratio of the greater (q)
3 2
two sides is
(C) Let the sides AB, BC, CD & DA of a cyclic quadrilateral
BD (r) 2 5
ABCD are in G.P. with common ratio 2, then is
AB
2 2 2
(D) Let a, b, c be in A.P. and a , b , c be in H.P. If a c, then a
(s) 3 2
: c is
(t) 1
Space for rough work
SECTION – C
Integer Answer Type
This section contains 6 questions. The answer to each of the questions is a single digit integer, ranging
from 0 to 9. The bubble corresponding to the correct is to be darkened in the ORS.
1. In ABCD, circumradius is 3 and inradius is 1.5 units. If the value of
2 2 3 3 4 mn
acot A + b cot B + c cot C is m n where m and n are prime members, them is
2
2. The value of the product
5 5 5 5 5 5
sin 11 cos 11 cos 10 cos 9 ...cos 3 cos 3
2 2 2 2 2 2
–k
equals to 4 . Then value of k is
x2 y 2
3. From a point P two tangents are drawn to 1 , such that their chord of contact subtends
2 3
x2 y2 6 2
right angle at its centre. If locus of P is the ellipse 2 2 1 , then
a b
13
a b2 is equal to
4. A circle of radius 4 units is inscribed in an equilateral triangle ABC, then an equilateral triangle is
inscribed in the circle, a circle again is inscribed in the later triangle and so on. In this way the
process continues infinitely. If r, x 1, x2, … xn … be the radii of these circles respectively. Then the
sum of radii of all these circles is
5. Consider the complex number z satisfying |z – 3| + |z| + |z + 3| = 12. If the greatest integer less
than or equal to |z| is ‘a’ and the least integer greater than or equal to is ‘b’, then ‘a + b’ is
5 2
6. Let p(x) = x + x + 1 have roots x 1, x2, x3, x4 and x5
g(x) = x2 – 2, then the value of
g(x1) g(x2) g(x3) g(x4) g(x5) – 30g (x1x2x3x4x5) is
Space for rough work
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- IIT JEE - 2012 Paper - 1Dokument15 SeitenIIT JEE - 2012 Paper - 1Sniper ArcheryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics Adv SheetDokument38 SeitenKinematics Adv Sheetvasukushal2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 11 Mid Term Set A QPDokument6 SeitenGrade 11 Mid Term Set A QPgoodboyjatin1981Noch keine Bewertungen
- XI Sample Papers 2023Dokument33 SeitenXI Sample Papers 2023Bhavya JangidNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE Advanced Assign - Physics PDFDokument26 SeitenJEE Advanced Assign - Physics PDFaumoghNoch keine Bewertungen
- PW - AITS - NT-26: PhysicsDokument22 SeitenPW - AITS - NT-26: PhysicsOfficers IasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Physics A1A2 Annual Exam 2023 24 MSDokument14 Seiten11 Physics A1A2 Annual Exam 2023 24 MSharshitsharmasportsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02_NWCM224X1R & CAMP224_Ph-I_CPT-1_Adv_24-08-22_PPKTDokument8 Seiten02_NWCM224X1R & CAMP224_Ph-I_CPT-1_Adv_24-08-22_PPKTjdhmyj2zchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Class 11Dokument9 SeitenPhysics Class 11eagleankush5Noch keine Bewertungen
- NT 21 PaperDokument18 SeitenNT 21 PaperOfficers IasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Marks Zero Marks Negative Marks: SECTION-I: (Maximum Marks: 80) 20 Questions Only One Option Is CorrectDokument6 SeitenFull Marks Zero Marks Negative Marks: SECTION-I: (Maximum Marks: 80) 20 Questions Only One Option Is CorrectTanmay MathurvaishyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instructions for Physics ExamDokument16 SeitenInstructions for Physics ExamPrem TewariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics ARP-4 Questions .PmdDokument6 SeitenPhysics ARP-4 Questions .PmdTaukeer AkbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- LT RPT Jee Phy 18.02.24Dokument4 SeitenLT RPT Jee Phy 18.02.24Deena chemistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jee Main 2024 3Dokument37 SeitenJee Main 2024 3Debayanbasu.juNoch keine Bewertungen
- XI Sample Papers 2023Dokument33 SeitenXI Sample Papers 2023Bhavya JangidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section I: (Multiple Choice Questions) : Physics (Part - A) )Dokument11 SeitenSection I: (Multiple Choice Questions) : Physics (Part - A) )Aisha SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- (WWW - Jeeneetadda.in) NT - 13Dokument17 Seiten(WWW - Jeeneetadda.in) NT - 13Nanjundeswaran shanmugasundaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- 31S2Dokument45 Seiten31S2Mahir KachwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1480059572JEE Main Sample Paper 2Dokument12 Seiten1480059572JEE Main Sample Paper 2Sohini RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xii NM Alpha: Mock Test-9Dokument22 SeitenXii NM Alpha: Mock Test-9sanjaytyagi62445Noch keine Bewertungen
- Phy Sample Paper Xi-2023-24 S 04Dokument17 SeitenPhy Sample Paper Xi-2023-24 S 04ANSUMAN SUVANKARNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE Main 4 2021 Paper PDFDokument12 SeitenJEE Main 4 2021 Paper PDFBiswadeep GiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eamcet '13 PDFDokument44 SeitenEamcet '13 PDFAmaan YousufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beware of Negative Marking Have Control Have Patience Have Confidence 100% SUCCESSDokument12 SeitenBeware of Negative Marking Have Control Have Patience Have Confidence 100% SUCCESSAYUSH DASNoch keine Bewertungen
- SB - NBTS 2.0 Mock Test 01Dokument28 SeitenSB - NBTS 2.0 Mock Test 01iamrakeshmahto2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- IIT JEE Physics TestDokument19 SeitenIIT JEE Physics TestSaumya MundraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics exam with 30 questionsDokument7 SeitenPhysics exam with 30 questionsHarsh ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- P7 Waves On A String, Simple Harmonic Motion (P7)Dokument9 SeitenP7 Waves On A String, Simple Harmonic Motion (P7)Gaurav Kumar JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kcet Model Qp Word Document (2)15!04!2024Dokument9 SeitenKcet Model Qp Word Document (2)15!04!2024mahadevipatil.patil04Noch keine Bewertungen
- 11th Physics-1Dokument4 Seiten11th Physics-1Udharav KesarNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE ADVANCED-Assignment: Presented by Kailash SharmaDokument6 SeitenJEE ADVANCED-Assignment: Presented by Kailash SharmaGulafsha PerweenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11th PhysicsDokument5 Seiten11th PhysicsRaju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Paper 1_advance Paper-1_toughDokument12 SeitenPractice Paper 1_advance Paper-1_toughtiyaagr14Noch keine Bewertungen
- JEE 2023 Full Length Revision Test - 2 - PaperDokument12 SeitenJEE 2023 Full Length Revision Test - 2 - PaperDr. Rambir LohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper V: M MG FDokument4 SeitenPaper V: M MG FAka AkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIT - JEE: TW TEST (ADV) SHMDokument4 SeitenIIT - JEE: TW TEST (ADV) SHMCelestial Ghandat100% (1)
- Duration: 3Hrs: Hale Yearly Examination PhysicsDokument4 SeitenDuration: 3Hrs: Hale Yearly Examination PhysicsVinodd.V 9eNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adv Paper-1 (CTY2022)Dokument7 SeitenAdv Paper-1 (CTY2022)Zain RashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aipmt 2000Dokument49 SeitenAipmt 2000pravinkhartadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Aiims PatternDokument7 SeitenPhysics Aiims PatternMuhammad YudhistiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- CET MODEL PHYSICSDokument5 SeitenCET MODEL PHYSICSVIKHYATHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bitsat Set 3 Bitsat Set 3Dokument36 SeitenBitsat Set 3 Bitsat Set 3anunay.mishra4141Noch keine Bewertungen
- R HH R HH: Reason: in Rolling Down, A Body Acquires BothDokument19 SeitenR HH R HH: Reason: in Rolling Down, A Body Acquires BothdemoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vidyamandir Classes: Innovating For Your SuccessDokument15 SeitenVidyamandir Classes: Innovating For Your SuccessDr. Rambir LohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- KEAM 2017 Phy Che Paper 1 Question Paper Answer Key PDFDokument17 SeitenKEAM 2017 Phy Che Paper 1 Question Paper Answer Key PDFarjun ps100% (1)
- Kota Class Test Physics QuestionsDokument73 SeitenKota Class Test Physics QuestionsSatyam YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotational MotionDokument87 SeitenRotational Motionkushagrajoshi69Noch keine Bewertungen
- Session End Class XiDokument10 SeitenSession End Class Xirubiroy811944Noch keine Bewertungen
- PCM-11-03 (12th & 13th) Paper 1 FINAL TESTDokument24 SeitenPCM-11-03 (12th & 13th) Paper 1 FINAL TESTRaju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 FLP-10 EngineeringDokument8 Seiten10 FLP-10 Engineeringarifareej25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Full Book-I (Second Test)Dokument4 SeitenFull Book-I (Second Test)Syed Shahzad AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xi ND Phy NeetDokument7 SeitenXi ND Phy NeetDeena chemistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code - B: Test - 1 Test Series For NEET - 20Dokument15 SeitenCode - B: Test - 1 Test Series For NEET - 20Naman kkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test02 SolDokument11 SeitenTest02 Solnareshsuja123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics: Total Syllabus CHEMISTRY: Total Syllabus MATHEMATICS: Total SyllabusDokument16 SeitenPhysics: Total Syllabus CHEMISTRY: Total Syllabus MATHEMATICS: Total SyllabusSakshi DadlaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Assignment (Adv Level) - 1Dokument7 SeitenRevision Assignment (Adv Level) - 1Gandharv BhoiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jee Main 2024 1Dokument36 SeitenJee Main 2024 1Debayanbasu.juNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock test physics, chemistry and mathematicsDokument12 SeitenMock test physics, chemistry and mathematicsRanjani VigneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerospace Structural Dynamics - AE31002 Tutorial Sheet - 4: M M X X K K X XDokument1 SeiteAerospace Structural Dynamics - AE31002 Tutorial Sheet - 4: M M X X K K X XPranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clarification Dec2017Dokument3 SeitenClarification Dec2017Brodsky RjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1Dokument1 SeiteTutorial 1Pranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Launch: Brief Description of Your Product Follows The Title HereDokument21 SeitenProduct Launch: Brief Description of Your Product Follows The Title HerePranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DWM Unit-IDokument18 SeitenDWM Unit-IBabuRao GanpatRaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIT KGP Time TableDokument45 SeitenIIT KGP Time TablePujanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TUM Masters in Mechanical Engineering: Proof of German Language AbilityDokument3 SeitenTUM Masters in Mechanical Engineering: Proof of German Language AbilityPranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure distribution over airfoil MH-70Dokument3 SeitenPressure distribution over airfoil MH-70Pranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Distribution Over A Circular Cylinder: 1 Design of ExperimentsDokument3 SeitenPressure Distribution Over A Circular Cylinder: 1 Design of ExperimentsPranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11th Advp2Dokument15 Seiten11th Advp2Pranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Aerospace Structure - AE210041516Dokument2 SeitenIntroduction To Aerospace Structure - AE210041516Pranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plan Ai TS 2017 - 18Dokument3 SeitenPlan Ai TS 2017 - 18Chirag HegdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top German Universities for Engineering by QS 2019 RankingsDokument3 SeitenTop German Universities for Engineering by QS 2019 RankingsPranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HS30047 French1718Dokument2 SeitenHS30047 French1718Pranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11th Advp2Dokument15 Seiten11th Advp2Pranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Notes Chemistry Physical ChemDokument29 SeitenQualitative Notes Chemistry Physical ChemRajeev KaushikNoch keine Bewertungen
- USAPhO SolutionsDokument26 SeitenUSAPhO SolutionsPranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GST Application December 2017Dokument3 SeitenGST Application December 2017Pranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SM GSTDokument12 SeitenSM GSTPranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FileHandler PDFDokument2 SeitenFileHandler PDFPranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CM Batches Common Monthly Test Schedule, Syllabus and PatternDokument3 SeitenCM Batches Common Monthly Test Schedule, Syllabus and PatternPranav Teja50% (2)
- SM GSTDokument12 SeitenSM GSTPranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- P19Dokument13 SeitenP19Pranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upcoming Entrance Exam ScheduleDokument16 SeitenUpcoming Entrance Exam SchedulePranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mca 2Dokument2 SeitenMca 2Pranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEST2017 Keys RevDokument1 SeiteNEST2017 Keys RevPranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017-2018 Conrad Challenge Team HandbookDokument22 Seiten2017-2018 Conrad Challenge Team HandbookPranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To ApplyDokument3 SeitenHow To ApplyKàâjü Kíng KhänNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 15 HYDROCARBONS PDFDokument8 SeitenChapter - 15 HYDROCARBONS PDFPranav TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allen Bradley Power Monitor 3000 Manual PDFDokument356 SeitenAllen Bradley Power Monitor 3000 Manual PDFAndrewcaesar100% (1)
- Abb 60 PVS-TLDokument4 SeitenAbb 60 PVS-TLNelson Jesus Calva HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uji Deteksi Biofilm Dari Isolat Klinik Kateter Urin Bakteri Entercoccus Dibandingkan Dengan Tube MethodDokument27 SeitenUji Deteksi Biofilm Dari Isolat Klinik Kateter Urin Bakteri Entercoccus Dibandingkan Dengan Tube MethodIyannyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Versant ModifiedDokument57 SeitenVersant ModifiedAryan Kharadkar100% (3)
- Specifications Sheet ReddyDokument4 SeitenSpecifications Sheet ReddyHenry CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDE1 V1 G2 H18 L P2 M8 - SpecificationsDokument1 SeiteSDE1 V1 G2 H18 L P2 M8 - SpecificationsCleverson SoaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tipologie Break in OutDokument17 SeitenTipologie Break in OutGiorgio FantauzziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qand ADokument5 SeitenQand AJoshua PascasioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Termites and Microbial Biological Control StrategiesDokument30 SeitenTermites and Microbial Biological Control StrategiesMuhammad QasimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10risk Assessment and ComahDokument25 Seiten10risk Assessment and ComahHansraj RahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- 366 Community Service IdeasDokument5 Seiten366 Community Service IdeasAhmetYılmazVuralNoch keine Bewertungen
- LogiquidsDokument2 SeitenLogiquidsAloma FonsecaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cars Ger Eu PCDokument157 SeitenCars Ger Eu PCsergeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPS120 Rev10 0309 PDFDokument2 SeitenPPS120 Rev10 0309 PDFArfanAliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poultry Disease Prevention and ControlDokument64 SeitenPoultry Disease Prevention and Controlsigra100% (3)
- Deforestation Management System Using Force and SoundDokument4 SeitenDeforestation Management System Using Force and SoundManeesh SvsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forecasting ExercisesDokument2 SeitenForecasting ExercisesAsh VinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LIST Real Estate Contacts ListDokument4 SeitenLIST Real Estate Contacts ListChauhan Harshit100% (1)
- Kuffner Final PresentationDokument16 SeitenKuffner Final PresentationSamaa GamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is Revalida ExamDokument11 SeitenIs Revalida ExamRodriguez, Jhe-ann M.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stories of Prophets - 2Dokument19 SeitenStories of Prophets - 2Hadis MusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hot Tub BrochureDokument124 SeitenHot Tub BrochureMai Tuan AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- PC Poles: DescriptionDokument2 SeitenPC Poles: DescriptionSantoso SantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vincent Hoa's English 101 PortfolioDokument24 SeitenVincent Hoa's English 101 PortfoliovincentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flame Configurations in A Lean Premixed Dump Combustor With An Annular Swirling FlowDokument8 SeitenFlame Configurations in A Lean Premixed Dump Combustor With An Annular Swirling Flowعبدالله عبدالعاطيNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatigue Life Prediction of A320-200 Aileron Lever Structure of A Transport AircraftDokument4 SeitenFatigue Life Prediction of A320-200 Aileron Lever Structure of A Transport AircraftMohamed IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Quill Vol. LVIII Issue 1 1-12Dokument12 SeitenThe Quill Vol. LVIII Issue 1 1-12Yves Lawrence Ivan OardeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pump Course Material Chapter 2Dokument16 SeitenPump Course Material Chapter 2engr victorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cosmic Freedom: David MolineauxDokument2 SeitenCosmic Freedom: David Molineauxsalomon46Noch keine Bewertungen
- Surgical InstrumentsDokument4 SeitenSurgical InstrumentsWafa L. AbdulrahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TEF Canada Expression Écrite : 150 Topics To SucceedVon EverandTEF Canada Expression Écrite : 150 Topics To SucceedBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (17)
- Make It Stick by Peter C. Brown, Henry L. Roediger III, Mark A. McDaniel - Book Summary: The Science of Successful LearningVon EverandMake It Stick by Peter C. Brown, Henry L. Roediger III, Mark A. McDaniel - Book Summary: The Science of Successful LearningBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (55)
- The Everything Guide to Study Skills: Strategies, tips, and tools you need to succeed in school!Von EverandThe Everything Guide to Study Skills: Strategies, tips, and tools you need to succeed in school!Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)
- IELTS Speaking Vocabulary Builder (Band 5-6): Master Phrases and Expressions for the IELTS Speaking ExamVon EverandIELTS Speaking Vocabulary Builder (Band 5-6): Master Phrases and Expressions for the IELTS Speaking ExamBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Math Olympiad Contests Preparation For Grades 4-8: Competition Level Math for Middle School Students to Win MathCON, AMC-8, MATHCOUNTS, and Math LeaguesVon EverandMath Olympiad Contests Preparation For Grades 4-8: Competition Level Math for Middle School Students to Win MathCON, AMC-8, MATHCOUNTS, and Math LeaguesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATI TEAS Study Guide: The Most Comprehensive and Up-to-Date Manual to Ace the Nursing Exam on Your First Try with Key Practice Questions, In-Depth Reviews, and Effective Test-Taking StrategiesVon EverandATI TEAS Study Guide: The Most Comprehensive and Up-to-Date Manual to Ace the Nursing Exam on Your First Try with Key Practice Questions, In-Depth Reviews, and Effective Test-Taking StrategiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCBA Exam Prep A Study Guide to Practice Test Questions With Answers and Master the Board Certified Behavior Analyst ExaminationVon EverandBCBA Exam Prep A Study Guide to Practice Test Questions With Answers and Master the Board Certified Behavior Analyst ExaminationNoch keine Bewertungen
- 700 Driving Theory Test Questions & Answers: Updated Study Guide With Over 700 Official Style Practise Questions For Cars - Based Off the Highway CodeVon Everand700 Driving Theory Test Questions & Answers: Updated Study Guide With Over 700 Official Style Practise Questions For Cars - Based Off the Highway CodeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The LearnCurious Companion to the Digital SAT: VerbalVon EverandThe LearnCurious Companion to the Digital SAT: VerbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideVon Everand1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (7)
- Acing Exams: Study Habits and Skills: Techniques for Keeping Calm and ConfidentVon EverandAcing Exams: Study Habits and Skills: Techniques for Keeping Calm and ConfidentBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- 71 Ways to Practice English Reading: Tips for ESL/EFL LearnersVon Everand71 Ways to Practice English Reading: Tips for ESL/EFL LearnersBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- PSI National Real Estate License Exam Prep 2020-2021: A Study Guide with 550 Test Questions and Answers Explanations (Includes Practice Tests for Brokers and Salespersons)Von EverandPSI National Real Estate License Exam Prep 2020-2021: A Study Guide with 550 Test Questions and Answers Explanations (Includes Practice Tests for Brokers and Salespersons)Bewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- AP® World History: Modern Crash Course, For the New 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeVon EverandAP® World History: Modern Crash Course, For the New 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Movement work according to Elsa Gindler: working with the feetVon EverandMovement work according to Elsa Gindler: working with the feetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning from Lectures: Learning from lectures, listening & notetaking skillsVon EverandLearning from Lectures: Learning from lectures, listening & notetaking skillsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (6)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsVon EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (8)
- Real Stories: The All-Inclusive Textbook for Developmental Writing and ReadingVon EverandReal Stories: The All-Inclusive Textbook for Developmental Writing and ReadingNoch keine Bewertungen