Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
TAX2
Hochgeladen von
DeyCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
TAX2
Hochgeladen von
DeyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
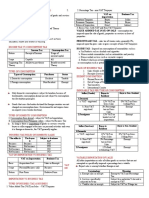
Consumption Tax (Buyer is (Buyer is non-
resident) resident)
occurs when one acquires goods or Non- Taxable No Tax
services by purchase or exchange Resident
upon utilization of goods or services by Resident Taxable Effectively No
consumers or buyers Tax
not on the sale of the seller
Rationale: Types of taxable domestic consumption
1. Promotes savings formation 1. Importation – purchase of residents of goods
from non-residents abroad
2. Helps in wealth redistribution to society
2. Sale – purchase of residents from resident
3. Supports the Benefit Received Theory
sellers
*should not be levied upon basic necessities
Consumption Tax on Importation
Income Consumption
VAT on Importation – importers of
Tax Tax
goods shall pay consumption tax; 12%
Nature Tax upon Tax upon usage
receipt of of income or of the total import cost of the goods
income capital paid prior to the withdrawal of the
Scope Tax to the Tax to all goods from the warehouse of Bureau of
capable Customs
Supporting Ability to Benefit Withholding Tax – purchaser of service
Tax Theory pay theory Received from non-residents shall likewise pay
Theory VAT on importation; 12% of the
contract price of this service
Types of Consumption Consumption Tax on Domestic Consumption
from Resident Sellers
1. Domestic Consumption – consumption of
Philippine Residents Collected from seller; sales of seller or
receipts of services
2. Foreign Consumption – consumption of non-
residents Regularly engaged in business
*only Domestic Consumption can be subjected Sellers – statutory taxpayers
to Philippine Taxation Buyers – economic taxpayers
Destination Principle – for use or consumption Consumption Tax for Resident Buyers Applies to
in the Philippines are subject to consumption Business Only
tax
Seller is not in business
Cross-Border Doctrine – goods which are Business Tax – tax on the privilege to do
destined to foreign territories should not be business; Privilege tax
taxed
Vat on Business Tax
The Seller Domestic Foreign Importation
Consumption Consumption
Basis of Tax Acquisition Sales or 1. Sales – for business which sells goods; total
Cost Receipts amount agreed as consideration for the sale of
Scope of Tax All Consumption goods whether collected or uncollected
Consumption Form
businesses 2. Receipts – for business that sells services
only
Nature of Pure Form Relative
Consumption Form Types of Business taxes:
Tax
Statutory Buyer Seller 1. VAT on Sales
Taxpayer 2. Percentage tax
The Buyer Buyer
economic 3. Excise Tax
Taxpayer
Nature of Direct Indirect Types of Business Taxpayers:
Imposition 1. VAT taxpayers – required to pay VAT
2. Non-VAT taxpayers – who pays percentage
Seller Resident Applicable tax
Buyer Consumption
Tax
Domestic
Sellers VAT on Sales
Business Business Business Tax Tax on added value – added by the
Business Non- Business Tax seller on its purchases in making sales;
Business
based upon the price increases made by
Non- Business None
the producers and distributors
business
Top-up on sales – require to be included
Non- Non- None
business business in the price of goods as a top-up;
Invoice Price (includes both); VAT
INCLUSIVE IF VAT IS NOT SEPARATELY
Seller Resident Applicable INDICATED IN THE SALES DOCUMENT
Buyer Consumption Tax Credit Method – VAT on sales shall
Tax be reduced by the amount of VAT paid
Foreign by the business on its purchases
Sellers
An explicit consumption tax – disclosed
Business Business VAT on
in the invoice or official receipt of the
importation
Business Non- VAT on seller
business importation Quarterly tax – but paid on a monthly
Non- Business VAT on basis
business importation
Methods of Computing VAT:
Non- Non- VAT on
business business importation 1. Direct Method – computed by applying the
VAT rate to the difference of the selling price
Basis of Business tax
and the purchase; not employed in the *percentage tax is computed directly on the
Philippines sales and is reported as an expense
2. Tax Credit Method – imposed upon the sales *percentage tax is presented as part of “taxes
or receipt of the business. and licenses” and a deduction against gross
income under income taxation
Special Features of the Tax Credit Method:
Who pays percentage tax?
1. Invoice-based crediting – entitlement for
input vat is to be substantiated with invoices. 1. Non-VAT Taxpayers
2. Non-observance of the matching of costs or 2. Taxpayers who sells services specifically
expenses and sales – output vat is recorded subject to percentage tax
when a sale is made; input vat is recorded when
*not exceeding the threshold
a purchase is made not when goods are sold
*the concept of sales between VAT taxpayers
VAT Taxpayers
and percentage taxpayers differs (PT – sales is
1. VAT-registered taxpayers equal to the invoice; VAT – sales plus 12%
comprises invoice)
2. VAT-registrable taxpayers
*VAT and percentage tax are mutually exclusive
*1,919,500 ( VAT taxpayers) mandatorily
(VAT taxpayers may pay both)
required to pay
Excise Tax – in addition to Vat or percentage tax
Percentage Tax – sales tax of various rates; 3%
on certain goods imposed in the Philippines for
imposed upon the gross sales or gross receipts
domestic consumption
of non-vat taxpayers
Levied on: tobacco, alcohol, petroleum,
Characteristics of the Percentage Tax
automobiles, jewelry, perfumes, toilet waters,
1. Tax on sales or gross receipts – total amount yacht, sports cars, metallic or non-metallic
due from the buyer is considered sales minerals, quarry resources, coal, coke, gold,
chromite, silver
2. An expensed tax – direct tax or privilege tax
of the sellers Seller of Resident Non-
goods Buyer resident
3. An implicit consumption tax – inclusion in the Buyer
selling price but same is not separately Vat 12% Vat on 0% Vat on
presented in the invoice; not disclosed to the Registered gross sales gross selling
buyer business price
Non-vat 3% Percentage Exempt
4. Monthly or quarterly tax – payable monthly registered tax on gross
*the concept of invoice and selling price to a business sales
percentage taxpayer is the same. The invoice Foreigners 12% Vat on Exempt
price is recorded as sales landed cost of
importation
*percentage tax and input vat paid on
purchases are not separately recognized
Seller of Resident Buyer Non- 1. Vat on Importation – on the import of goods
services resident
Buyer 2. Final Withholding Tax – purchase of services
Vat 12% Vat on gross 0% Vat on from non-residents
Registere receipts gross *payable to Bureau of Customs
d business receipts
Non-vat 3% Percentage Exempt *Withholding tax – 12% of the payment for
registered tax on gross services rendered by non-residents
business receipts
Foreigner 12% Final Exempt *resident purchaser is the one statutory liable
s Withholding Vat for the payment of VAT
VAT % Tax Excise Tax
Exempt Consumptions:
Tax Rate 12% Generall Various
y 3% and *Vat is not applied to goods considered as basic
valorem necessities
tax rates
and 1. agricultural and marine food products in their
specific original state
taxes
*nature objects of human consumption
Basis Mark-up Sales or Sales Value
or value receipts or per unit *In original state – unprocessed or simple
added of process (preparation for the market,
excisable preservation, packaging)
goods or
articles 2. fertilizers, seeds, seedlings and fingerlings,
Timing Upon Upon Upon fish, prawns, livestock and poultry feeds,
of sales or Sales or production including ingredients used in the manufacture
impositi collectio collectio or of feeds
on n n importatio
n 3. personal and household effects
Generall Bigger Smaller Both big or
*belong to Philippine Residents or non-
y paid business business small
by es es businesses residents intending to resettle in the
Export Subject Exempt Exempt ( Philippines; exempt from Customs Duties
Sales to 0% tax is
Vat reimbursa
ble) 4. professional instruments and implements,
wearing apparel, domestic animals, for their
own use and not for sale, barter or exchange
VALUE ADDED TAX ON IMPORTATION
*belong to persons who come to settle in the
Importation – refers to the purchase of gods
Philippines
including services by Philippine residents from
non-residents; domestic consumption and is *must accompany the person upon arrival or
subject to consumption tax within 90 days before or after his/her arrival
Types of Consumption Tax on Importation *must be evidence to show that the change of
residence is bona fide
*not a vehicle, machinery or other equipment 1. importer is engaged or not engaged in trade
used in the manufacturer or merchandise of any or business
kind in commercial quantity
2. importer is a Vat or non-Vat business
5. books and any newspaper, magazine, review
3. importation is for business or personal use
or bulletin which appear at regular intervals
with fixed price for subscription and sale and 4. non-resident seller is engaged or not engaged
which is not devoted principally to the in business
publication of paid ads
Tax basis of Vat on importation
*based upon the necessity of education and
information *computed as 12% of the total landed cost of
the importation
6. fuels, goods and supplies by persons engaged
in international shipping or air transport Composition of landed cost:
operations 1. Dutiable value
*exempt from Vat under the destination 2. Custom duty
principle
3. Excise Tax
7. cooperatives of direct farm inputs,
machineries and equipment, including spare 4. Other in-land cost
parts to be used directly and exclusively in the
production and or processing of their produce
Landed Cost – encompasses all costs of
*must be an agricultural cooperative duly importation incurred prior to the withdrawal of
registered and in good standing with the the goods from the warehouse of BOC except
Cooperative Development Authority unofficial or illegal payments made
8. transactions which are exempt under Dutiable Value – total value used by the BOC in
international agreement to which the determining the tariff and custom duties;
Philippines is signatory encompasses all costs incurred in bringing the
9. exempt under special laws goods up to the Philippine port and prior to any
other in-land costs of import
Presumption of Vatability – generally subject to
Vat unless it can be proven as exempt under 1. cost of the goods
any of those conditions 2. freight
Subsequent Sale by Exempt Person to Non- 3. insurance
exempt Persons – the non-exempt buyer shall
be subject to Vat on importation 4. other charges and costs
Vat on Importation
*since the object of taxation is the Technical Importation
consumption, the importation of goods is
- by consumers in a customs territory
subject to Vat regardless of whether the:
from person located in Special
Economic Zones
- refers to the purchase of non-Ecozone
Philippine residents from Philippine
Ecozone registered enterprise
Customs Territory – the portion of the Republic
of the Philippines outside of designated special
economic zones (foreign territories)
Withholding Vat on Import of Services
- purchase of services from non-residents
is an importation of service which is
subject to Withholding Vat
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 1040 Exam Prep Module X: Small Business Income and ExpensesVon Everand1040 Exam Prep Module X: Small Business Income and ExpensesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumption Taxes: Business Tax Is A Form of Consumption TaxDokument8 SeitenConsumption Taxes: Business Tax Is A Form of Consumption TaxDenvyl MangsatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rationale of Consumption TaxDokument3 SeitenRationale of Consumption Taxmy miNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jpia-Hau: Business and Transfer TaxationDokument12 SeitenJpia-Hau: Business and Transfer Taxationronniel tiglaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bustax Chapter 1Dokument9 SeitenBustax Chapter 1Pineda, Paula MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax 202 - Chapter 1 Consumption TaxDokument4 SeitenTax 202 - Chapter 1 Consumption TaxLizandraArceoBarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 and 2 BUSTAXDokument6 SeitenChapter 1 and 2 BUSTAXCory RitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept of Consumption and Consumption Taxes and Vat On ImportationDokument4 SeitenConcept of Consumption and Consumption Taxes and Vat On ImportationJamaica DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business and Transfer TaxationDokument9 SeitenBusiness and Transfer Taxationcj8kim8maggayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business TaxesDokument20 SeitenBusiness TaxesAnime ScreenshotsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 BustaxDokument10 Seiten01 BustaxJake Raphael Cruz CalaguasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Consumption Taxes NotesDokument2 SeitenIntroduction To Consumption Taxes NotesSelene DimlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importation by Importers) : Income Tax Vs Consumption TaxDokument2 SeitenImportation by Importers) : Income Tax Vs Consumption TaxMark LapidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax 2 NotesDokument2 SeitenTax 2 NotesMark LapidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Tax Chapter 1Dokument3 SeitenBusiness Tax Chapter 1Mamin ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Consumption TaxesDokument6 SeitenChapter 1 Introduction To Consumption TaxesJason MablesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Consumption Tax PDFDokument20 SeitenIntroduction To Consumption Tax PDFShamae Duma-anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 6Dokument6 SeitenLesson 6Iris Lavigne RojoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax 01 Introduction To Consumption TaxesDokument3 SeitenTax 01 Introduction To Consumption TaxesShiela LlenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bustax Chapters 1 4Dokument6 SeitenBustax Chapters 1 4Naruto UzumakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business and Transfer Taxes: An Introduction To Consumption TaxesDokument16 SeitenBusiness and Transfer Taxes: An Introduction To Consumption TaxesAngelo Delos SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSTX Reviewer (Midterm)Dokument7 SeitenBSTX Reviewer (Midterm)alaine daphneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business and Transfer Taxation: TO Consumption TaxesDokument40 SeitenBusiness and Transfer Taxation: TO Consumption TaxesKC GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Value Added TaxDokument5 SeitenIntroduction To Value Added TaxNYSHAN JOFIELYN TABBAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- M7 - Intro To Consumption Tax & VAT On Importation Students'Dokument54 SeitenM7 - Intro To Consumption Tax & VAT On Importation Students'Elaiza RegaladoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch. 1Dokument3 SeitenCh. 1abibiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1 - Business TaxDokument9 SeitenTopic 1 - Business Taxalexissosing.cpaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To Consumption TaxesDokument9 SeitenIntro To Consumption TaxesAnna CynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax 2 - BanggawanDokument175 SeitenTax 2 - BanggawanJessica IslaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Tax 2Dokument5 SeitenChapter 1 Tax 2Hazel Jane EsclamadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TAX 221-AVP (Atillo, Cañete, Dejan, Manlimos, Hortellano)Dokument50 SeitenTAX 221-AVP (Atillo, Cañete, Dejan, Manlimos, Hortellano)reymardicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1 - Consumption and Business TaxDokument4 SeitenTopic 1 - Consumption and Business TaxNicole Daphne FigueroaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 & 2: at The End of This Topic, We Should Be Able To Learn The FollowingDokument33 SeitenModule 1 & 2: at The End of This Topic, We Should Be Able To Learn The FollowingAlicia FelicianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Input VAT ch9 IncompleteDokument3 SeitenInput VAT ch9 IncompleteMarionne GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Taxation Intro To Consumption Taxes: Anie P. Martinez, Cpa, MbaDokument32 SeitenBusiness Taxation Intro To Consumption Taxes: Anie P. Martinez, Cpa, MbaAnie MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Consumption TaxesDokument38 SeitenChapter 1 Introduction To Consumption TaxesGenie Gonzales DimaanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 6. Nature and Concepts of Business TaxesDokument6 SeitenModule 6. Nature and Concepts of Business TaxesYolly DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Consumption Taxes: Prepared By: Mrs. Nelia I. Tomas, CPA, LPTDokument56 SeitenIntroduction To Consumption Taxes: Prepared By: Mrs. Nelia I. Tomas, CPA, LPTTokis SabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CTT Examination Reviewer (Notes) Page A - 30Dokument13 SeitenCTT Examination Reviewer (Notes) Page A - 30Seneca GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax 2 AssignmentDokument6 SeitenTax 2 AssignmentKim EcarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Consumption TaxDokument15 SeitenChapter 1 Introduction To Consumption TaxNesrill Joyce AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Consumption TaxesDokument21 SeitenChapter 1 Introduction To Consumption TaxesNacpil, Alyssa JesseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 - Input VatDokument1 SeiteChapter 9 - Input VatPremium AccountsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 - Input VatDokument1 SeiteChapter 9 - Input VatPremium AccountsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 - Input VatDokument1 SeiteChapter 9 - Input VatPremium AccountsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 - Input VatDokument1 SeiteChapter 9 - Input VatPremium AccountsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 - Input VatDokument1 SeiteChapter 9 - Input VatPremium AccountsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 Input VatDokument2 SeitenChapter 9 Input Vatnewlymade641Noch keine Bewertungen
- Business TaxDokument24 SeitenBusiness TaxKassandra Mari LucesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Value-Added Tax: Who Are Liable To VAT? Formula in Computing Vat PayableDokument15 SeitenValue-Added Tax: Who Are Liable To VAT? Formula in Computing Vat PayablePrimo WilliamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combine PDFDokument198 SeitenCombine PDFliamdrlnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept of Business and Business TaxesDokument3 SeitenConcept of Business and Business TaxesHazel Joy DemaganteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewerrrr Tax 2 PDFDokument11 SeitenReviewerrrr Tax 2 PDFAnthony EboraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business TaxesDokument98 SeitenBusiness TaxesAbigailRefamonteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module Author: Charles C. Onda, MD, CpaDokument9 SeitenModule Author: Charles C. Onda, MD, CpaCSJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Tax Reviewer IDokument5 SeitenBusiness Tax Reviewer IMariefel Irish Jimenez KhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8Dokument6 SeitenChapter 8my miNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIDTERMS Business and Transfer TaxationDokument13 SeitenMIDTERMS Business and Transfer Taxationabrylle opinianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax 301 - Midterm Activity 1Dokument4 SeitenTax 301 - Midterm Activity 1Nicole TeruelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6-8Dokument10 SeitenChapter 6-8DeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- TTP IntroductionDokument8 SeitenTTP IntroductionGlen Joy GanancialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taxation - Defined As A State Power, Legislative: Theory of Taxation - The GovernmentsDokument2 SeitenTaxation - Defined As A State Power, Legislative: Theory of Taxation - The GovernmentsDeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taxation - Defined As A State Power, Legislative: Theory of Taxation - The GovernmentsDokument2 SeitenTaxation - Defined As A State Power, Legislative: Theory of Taxation - The GovernmentsDeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partnership Ad VacDokument4 SeitenPartnership Ad VacDeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partnership Ad VacDokument4 SeitenPartnership Ad VacDeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partnership Ad VacDokument4 SeitenPartnership Ad VacDeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 12 BESR ABM Q2-Week 6Dokument13 SeitenMath 12 BESR ABM Q2-Week 6Victoria Quebral Carumba100% (2)
- NeoLiberalism and The Counter-EnlightenmentDokument26 SeitenNeoLiberalism and The Counter-EnlightenmentvanathelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm ExamDokument3 SeitenMidterm ExamRafael CensonNoch keine Bewertungen
- C.V ZeeshanDokument1 SeiteC.V ZeeshanZeeshan ArshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ermitage Academic Calendar IBP 2022-23Dokument1 SeiteErmitage Academic Calendar IBP 2022-23NADIA ELWARDINoch keine Bewertungen
- Bagabag National High School Instructional Modules in FABM 1Dokument2 SeitenBagabag National High School Instructional Modules in FABM 1marissa casareno almueteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chelsea FC HistoryDokument16 SeitenChelsea FC Historybasir annas sidiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Group 2) Cearts 1 - Philippine Popular CultureDokument3 Seiten(Group 2) Cearts 1 - Philippine Popular Culturerandom aestheticNoch keine Bewertungen
- MII-U2-Actividad 4. Práctica de La GramáticaDokument1 SeiteMII-U2-Actividad 4. Práctica de La GramáticaCESARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managing New VenturesDokument1 SeiteManaging New VenturesPrateek RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- State of Cyber-Security in IndonesiaDokument32 SeitenState of Cyber-Security in IndonesiaharisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intertek India Private LimitedDokument8 SeitenIntertek India Private LimitedAjay RottiNoch keine Bewertungen
- G.R. No. 187512 June 13, 2012 Republic of The Phils Vs Yolanda Cadacio GranadaDokument7 SeitenG.R. No. 187512 June 13, 2012 Republic of The Phils Vs Yolanda Cadacio GranadaDexter Lee GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal AkanDokument96 SeitenAnimal AkanSah Ara SAnkh Sanu-tNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compiled LR PDFDokument13 SeitenCompiled LR PDFFrh RzmnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank OB 221 ch9Dokument42 SeitenTest Bank OB 221 ch9deema twNoch keine Bewertungen
- Affidavit of GC - Reject PlaintDokument9 SeitenAffidavit of GC - Reject PlaintVishnu R. VenkatramanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Luovutuskirja Ajoneuvon Vesikulkuneuvon Omistusoikeuden Siirrosta B124eDokument2 SeitenLuovutuskirja Ajoneuvon Vesikulkuneuvon Omistusoikeuden Siirrosta B124eAirsoftNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module - No. 7 CGP G12. - Name of AuthorsDokument77 SeitenModule - No. 7 CGP G12. - Name of AuthorsJericson San Jose100% (1)
- Ryterna Modul Architectural Challenge 2021Dokument11 SeitenRyterna Modul Architectural Challenge 2021Pham QuangdieuNoch keine Bewertungen
- SweetPond Project Report-2Dokument12 SeitenSweetPond Project Report-2khanak bodraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sherwood (1985) - Engels, Marx, Malthus, and The MachineDokument30 SeitenSherwood (1985) - Engels, Marx, Malthus, and The Machineverdi rossiNoch keine Bewertungen
- United States v. Larry Walton, 552 F.2d 1354, 10th Cir. (1977)Dokument16 SeitenUnited States v. Larry Walton, 552 F.2d 1354, 10th Cir. (1977)Scribd Government DocsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Week 3 - WillDokument4 SeitenTutorial Week 3 - WillArif HaiqalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quotes For Essay and Ethics CompilationDokument5 SeitenQuotes For Essay and Ethics CompilationAnkit Kumar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- NMML Occasional Paper: The Anticolonial Ethics of Lala Har Dayal'sDokument22 SeitenNMML Occasional Paper: The Anticolonial Ethics of Lala Har Dayal'sСаша ПаповићNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Directors - Indian CompaniesDokument209 SeitenList of Directors - Indian CompaniesAditya Sharma100% (1)
- Causes of UnemploymentDokument7 SeitenCauses of UnemploymentBishwaranjan RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stamp Duty (Amendment) Act, 2022Dokument5 SeitenStamp Duty (Amendment) Act, 2022Kirunda ramadhanNoch keine Bewertungen